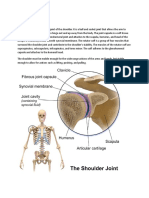
Shoulder
Diunggah oleh
kcxieHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Shoulder
Diunggah oleh
kcxieHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Shoulder: Muscles
Muscle Deltoid Rhomboid major and minor Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Subscapularis Tricep brachii
Innervation Axillary nerve Dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5) Suprascapular nerve Suprascapular nerve Axillary nerve Lower subscapular nerve Upper and lower subscapular nerves Radial n.
Function Clavicular part flexes, medially rotates arm; acromial part abducts arm (from 15-90 degrees), spinal part extends and laterally rotates arm Retract scapula and rotate it to depress glenoid cavity; fix scapula to thoracic wall initiates and assists deltoid in abduction of arm and acts with other rotator cuff muscles laterally rotate arm, help hold humeral head in glenoid cavity of Teres minorb middle part of lateral border scapula laterally rotate arm, help hold humeral head in glenoid cavity adducts, medially rotates arm medially rotates and adducts arm; holds humeral head in glenoid cavity Extends forearm; stabilizes elbow joint, abducts ulna during pronation
Shoulder - Ligaments
Rotator cuff Clinical correlates injury --> instability of glenohumeral joint. Rupture/tear of suprastinatus tendon is most common. Degenerative tendonitis, attrition of supraspinatus tendon --> cannot initiate abduction of upper limb. (if arm is passively abducted 15 degrees or more, then abduction can occur with deltoid) results from direct blow, "shoulder separation": severe when both AC and coracoclavicular ligaments are torn. Shoulder separates from clavicle and falls anterior dislocation occurs most often in young adults. Caused by excessive extension and lateral rotation of the humerus. Can damage axillary nerve calcific supraspinatus tendinitis: inflammation and calcification of subacromial bursa. Painful arc syndrome: pain occurs during 50-130 degrees of abduction adhesive capsulitis: adhesive fibrosis and scarring between inflamed capsule of glenohumeral joint, rotator cuff, subacromial bursa, and deltoid. Cannot abduct arm but can obtain an apparent abduction of up to 45 degrees by elevating and rotating scapula.
rotator cuff
dislocation of acromioclavicular joint dislocation of glenohumeral joint supraspinatus tendon
glenohumeral joint
Shoulder Vasculature
Affected structure nerves axillary nerve
Clinical correlate occurs when surgical neck of humerus is fractured; deltoid atrophies unilaterally, asymmetry of shoulder outlines, loss of sensation over lateral side of proximal part of arm (lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm) to stop profuse bleeding, compress artery by exerting downard pressure in the angle between the clavicle and the attachment of the SCM. dorsal scapular, suprascapular, and subscapular (via circumflex scapular) join on anterior and posterior surfaces of the scapula. Slow occlusion of an artery: allows collateral circulation to develop, ischemia will not result. Abrupt surgical ligation of axillary a. between subscapulart and profunda brachii will lead to ischemia of arm. lymphangitis: inflammation of lymphatic vessels; infections of pectoral region and breast. Most commmon site of metastases of cancer to the breast
axillary artery arteries lymph
arterial anastamoses
axillary lymph nodes
Class notes
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Physical Therapy of The ShoulderDokumen506 halamanPhysical Therapy of The ShoulderArun Tamilvanan100% (2)
- Rockwood and Matsen S The Shoulder 4th EditionDokumen1.616 halamanRockwood and Matsen S The Shoulder 4th EditionCristina Maria80% (5)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointDokumen6 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointSundaraBharathiBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Suppply of Lower LimbDokumen8 halamanBlood Suppply of Lower LimbCamille Magdirila100% (1)
- Shoulder Joint Guide: Rotator Cuff, Movements & Common InjuriesDokumen7 halamanShoulder Joint Guide: Rotator Cuff, Movements & Common InjuriesMary Grace OrozcoBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 1st Semester NotesDokumen60 halamanAnatomy 1st Semester NotesInsaf AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- NERVOUS PhysiologyDokumen85 halamanNERVOUS PhysiologyHenok GirmaBelum ada peringkat
- Osteology of The Upper Limb LectureDokumen40 halamanOsteology of The Upper Limb LectureFavour OnyeaboBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The BackDokumen7 halamanMuscles of The BackDon RaulBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Extremity TraumaDokumen89 halamanUpper Extremity TraumaSiluan Stegărescu VitalieBelum ada peringkat
- Colorectal MalignancyDokumen108 halamanColorectal MalignancySatishht SatishBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics NotesDokumen25 halamanPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEDokumen2 halamanGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Knee JointDokumen17 halamanAnatomy of Knee JointSiti AisyahBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Emryology The BeginningDokumen117 halaman01 Emryology The BeginningOsman Saidu SesayBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckDari EverandEssential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and NeckBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Joint Cartilage PowerpointDokumen81 halamanBone Joint Cartilage PowerpointChevie WisemanBelum ada peringkat
- Rehabilitation After Rotator Cuff RepairDokumen22 halamanRehabilitation After Rotator Cuff Repairgaia_ravasio9277100% (2)
- Tissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationDokumen18 halamanTissues: Types, Functions & ClassificationZainab AliBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of the Pelvis and Hip JointDokumen63 halamanAnatomy of the Pelvis and Hip JointEliud MbuteBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous System: Na ShaoDokumen79 halamanThe Nervous System: Na ShaoArvindhanBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology and BiochemistryDari EverandPhysiology and BiochemistryGeoffrey BourneBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of PelvisDokumen40 halamanAnatomy of PelvisGovGeet100% (1)
- Lab 8 - Joints and Body MovementsDokumen4 halamanLab 8 - Joints and Body Movementssidro123100% (1)
- Ninja Hands of Death - Ashida Kim PDFDokumen49 halamanNinja Hands of Death - Ashida Kim PDFHuzaifa ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The Upper LimbDokumen17 halamanMuscles of The Upper LimbJhanelle S. Dixon-LairdBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular SystemDokumen47 halamanMuscular SystemKrystal Kaye AczonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomia MSKDokumen1.249 halamanAnatomia MSKArthemizio Lopes100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Muscular System: Three Types of Muscle TissuesDokumen73 halamanChapter 9 - Muscular System: Three Types of Muscle TissuesRafie HusniBelum ada peringkat
- Lower Limb Lab SheetDokumen3 halamanLower Limb Lab SheetKelly TrainorBelum ada peringkat
- Overhead Throwing: Biomechanics and PathologyDokumen7 halamanOverhead Throwing: Biomechanics and Pathologyrapannika100% (1)
- ANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbDokumen25 halamanANATOMY I 23.03.20 I The Pectoral Girdle and Upper LimbArianna RomanoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDokumen46 halamanLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Gluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaDokumen4 halamanGluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaSteph SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of the Scapula and ShoulderDokumen6 halamanMuscles of the Scapula and ShoulderAndika Anjani AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Lower LimbDokumen25 halamanLower LimbLalanFernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Laniyati Hamijoyo Sppd-Kr. M.Kes: - Staf Pengajar Divisi Reumatologi Departemen IlmuDokumen71 halamanDr. Laniyati Hamijoyo Sppd-Kr. M.Kes: - Staf Pengajar Divisi Reumatologi Departemen IlmusiputleletBelum ada peringkat
- The Functional Anatomy of The Knee JointDokumen12 halamanThe Functional Anatomy of The Knee JointFadzlee SoujiBelum ada peringkat
- Knee Joint (Anatomy)Dokumen5 halamanKnee Joint (Anatomy)Ojambo FlaviaBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDokumen13 halamanUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Upper Extremities (Joints) FlashcardDokumen317 halamanUpper Extremities (Joints) FlashcardMatet MonjeBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Final ExamDokumen17 halaman2015 Final ExamlBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise on Upper Limb Bones and JointsDokumen2 halamanExercise on Upper Limb Bones and JointsLem A SharBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanatomy - Answers and ExplanationsDokumen6 halamanNeuroanatomy - Answers and ExplanationsshengziyanBelum ada peringkat
- PT Neuro Intro NotesDokumen13 halamanPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- Thoracic Segment KpsDokumen77 halamanThoracic Segment Kpskrishna bptBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology Final ReviewDokumen4 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Final ReviewPaige PattersonBelum ada peringkat
- 7th Week Femoral Sheath, Femoral Triangle and Adductor CanalDokumen17 halaman7th Week Femoral Sheath, Femoral Triangle and Adductor CanalShah NawazBelum ada peringkat
- Arthrokinematics of Body Joints FinalDokumen3 halamanArthrokinematics of Body Joints FinalnmahpbooksBelum ada peringkat
- Joints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanDokumen30 halamanJoints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Functions of the Respiratory SystemDokumen5 halamanEssential Functions of the Respiratory SystemEjie Boy IsagaBelum ada peringkat
- The Human ThoraxDokumen71 halamanThe Human Thoraxbayenn100% (2)
- 11 MusclesDokumen9 halaman11 MusclesElaine Loreen Villanueva100% (1)
- Thoracic Wall.Dokumen48 halamanThoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Lung SurgeriesDokumen43 halamanLung SurgeriesSereinBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Mechanics Lecture NotesDokumen53 halamanBio Mechanics Lecture NotesscdubalBelum ada peringkat
- 11.ascending PathwaysDokumen27 halaman11.ascending PathwaysdenekeBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical Musculature AnatomyDokumen3 halamanCervical Musculature Anatomysimone dumbrellBelum ada peringkat
- A&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Dokumen42 halamanA&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaBelum ada peringkat
- Gross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleDokumen16 halamanGross Anatomy of Fourth VentricleRafique AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Bones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionDokumen15 halamanBones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionChess Nuts100% (1)
- Brachial Plexus Self QuizDokumen2 halamanBrachial Plexus Self Quizsan100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDokumen60 halamanStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeBelum ada peringkat
- Borders: Teachmeseries LTDDokumen3 halamanBorders: Teachmeseries LTDlecturioBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm - Worksheet 1 - PERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION-MANIPULATIONDokumen3 halamanMidterm - Worksheet 1 - PERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION-MANIPULATIONGrace Panuelos Oñate100% (1)
- The Midbrain and Important ConnectionsDokumen118 halamanThe Midbrain and Important ConnectionsBaguma MichaelBelum ada peringkat
- PhysiologyDokumen31 halamanPhysiologyraza20Belum ada peringkat
- Front of Thigh, Femoral Triangle and Femoral VesselsDokumen35 halamanFront of Thigh, Femoral Triangle and Femoral Vesselsgospel munkondya100% (1)
- Threshold and RecruitmentDokumen16 halamanThreshold and RecruitmentShamaine Anne SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Muscle Function: Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Physiological Sciences Budapest 1980, (including the proceedings of the satellite symposium on Membrane Control of Skeletal Muscle Function)Dari EverandMolecular and Cellular Aspects of Muscle Function: Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Physiological Sciences Budapest 1980, (including the proceedings of the satellite symposium on Membrane Control of Skeletal Muscle Function)E. VargaBelum ada peringkat
- Fever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialsDokumen3 halamanFever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialskcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Toxicology TableDokumen20 halamanToxicology TablekcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Pelvic Cavity TableDokumen2 halamanPelvic Cavity TablekcxieBelum ada peringkat
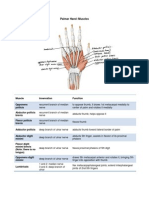
- Palmar HandDokumen3 halamanPalmar HandkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Posterior TriangleDokumen4 halamanPosterior TrianglekcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Cubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmDokumen4 halamanCubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Dorsal Forearm and HandDokumen2 halamanDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Lower LimbDokumen1 halamanLower LimbkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- Ankle and Sole of FootDokumen4 halamanAnkle and Sole of FootkcxieBelum ada peringkat
- NUMS-MBBS Curriculum 1st Year 2020Dokumen108 halamanNUMS-MBBS Curriculum 1st Year 2020nadia100% (1)
- Imaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesDokumen12 halamanImaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesChristian ToalongoBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Pato II N - 1inglesDokumen7 halamanExam Pato II N - 1inglesSergio GarridoBelum ada peringkat
- Articles by Dr. Nata ParnesDokumen19 halamanArticles by Dr. Nata ParnesWatertown Daily TimesBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder ComplexDokumen55 halamanShoulder ComplexKim VillalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Adhesive Capsulitis of The Shoulder: Protocol For The Adhesive Capsulitis Biomarker (Adcab) StudyDokumen6 halamanAdhesive Capsulitis of The Shoulder: Protocol For The Adhesive Capsulitis Biomarker (Adcab) StudyRuben FigueroaBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder Pain EvaluationDokumen8 halamanShoulder Pain EvaluationAnonymous 9lmlWQoDm8Belum ada peringkat
- Kripa. M: Master of Physiotherapy (M.P.T.)Dokumen89 halamanKripa. M: Master of Physiotherapy (M.P.T.)Dr.GK. JeyakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Bones and Joints of the Shoulder: Anatomy and Common InjuriesDokumen4 halamanBones and Joints of the Shoulder: Anatomy and Common InjuriesVanessa Yvonne GurtizaBelum ada peringkat
- The Challenge of The Sporting Shoulder From Injury Prevention Through Sport Specific Rehabilitation Toward Return To PlayDokumen8 halamanThe Challenge of The Sporting Shoulder From Injury Prevention Through Sport Specific Rehabilitation Toward Return To PlayNatalia ReinaBelum ada peringkat
- Joints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Dokumen16 halamanJoints Anatomy (Ashalatha)Abdul KhadirBelum ada peringkat
- Cinahl Rotator Cuff InjuriesDokumen11 halamanCinahl Rotator Cuff InjurieslizardbeeBelum ada peringkat
- The Bankart RepairDokumen8 halamanThe Bankart RepairphantomkatalynBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Quiz#2Dokumen4 halamanLab Quiz#2Kimberly RamocanBelum ada peringkat
- Ravichandran Et Al 2019 Systematic Review On Effectiveness of ShoulderDokumen11 halamanRavichandran Et Al 2019 Systematic Review On Effectiveness of ShoulderCynthia RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder PresentationDokumen22 halamanShoulder Presentationapi-664376361Belum ada peringkat
- Management of Shoulder DislocationsDokumen9 halamanManagement of Shoulder Dislocationsamal.fathullahBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology: Your ExamDokumen10 halamanUnit 1: Anatomy and Physiology: Your Examsarkodie kwameBelum ada peringkat
- 191 Biceps Tenodesis RCR V2Dokumen4 halaman191 Biceps Tenodesis RCR V2mustakBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Rotator Cufftears in The Elderly PopulationDokumen6 halamanManagement of Rotator Cufftears in The Elderly PopulationdrjorgewtorresBelum ada peringkat