ESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4
Diunggah oleh
Surapich ChairgulprasertHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4
Diunggah oleh
Surapich ChairgulprasertHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
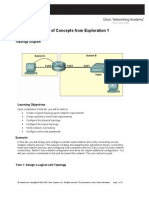
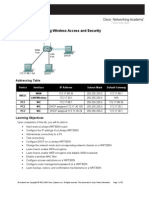
Lab 7.5.
1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Topology Diagram
WAN Port
LAN Port
DHCP
172.17.88.1 /24
DHCP
Addressing Table
Device WRS1 PC1 PC2 PC3 Interface WAN LAN/Wireless NIC NIC NIC IP Address 172.17.88.35 172.17.30.1 172.17.88.1 DHCP assigned 172.17.30.100 DHCP assigned 172.17.30.24 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway 172.17.88.1 N/A 172.17.88.35 172.17.30.1 172.17.30.1
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Hard reset a Linksys WRT300N router Configure the IP settings of a Linksys WRT300N Add wireless connectivity to a PC Test connectivity Configure DHCP on a Linksys WRT300N Change the network mode and corresponding network channel on a WRT300N Learn how to enable WPA encryption Learn how to enable WEP encryption and disable SSID broadcast Enable a wireless MAC filter Configure access restrictions on a WRT300N Configure router management password on a WRT300N Learn backup, restore, and confirmation mechanisms on a WRT300N
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Scenario
In this lab, you will configure a Linksys WRT300N. Make note of the procedures involved in connecting to a wireless network because some changes involve disconnecting clients, which may then have to reconnect after making changes to the configuration.
Task 1: Connect and log into the Wireless Router.
Step 1: Reset the WRS router and establish physically connectivity. Apply power to WRS1, and wait until it the green power LED stops blinking. To clear any previous configurations, do a hard reset. Find the reset button on the back of the router. Using a pen or other thin instrument, hold down the reset button for 5 seconds. When the green power LED stops blinking, the router should now be restored to its factory default settings. Connect a straight through cable from PC1 to the wireless routers WAN port (blue) and connect PC2 to one of the wireless routers LAN ports (yellow). The wireless router will provide an IP address to the PC2 using the default DHCP configuration. PC1 will be acting as the Internet connection, so set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway as listed in the table.
Step 2: Verify connectivity settings for PC2. On PC2, verify the connectivity settings by going to Start > Run and typing cmd. At the command prompt, type the command ipconfig to view your network device information. Notice which IP address is the default gateway. This is the default IP address of a Linksys WRT300N.
Step 3: Open a web browser on PC2 and navigate to the wireless routers Web Utility. Set the URL of the browser to http://192.168.1.1.
Step 4: Log in The default login credentials are a blank username and a password of: admin. Note that this is very
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
insecure since it is the factory default and provided publicly. You will set our own password in a later task. Leave the username blank and set the password to: admin. You should now be viewing the default Setup page of the Linksys WRT300N web utility.
Task 2: Configure the WAN interface.
Normally an Internet Service Provider would use DHCP to give out addresses to the WAN port. For this lab, you will assign the address statically. Step 1: Configure the WAN port to have a static IP address From the Internet Connection Type pull-down menu, select Static IP.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
The screen will change to the view below:
Step 2: Set the IP address settings for Internet Setup. Internet IP Address set to: 172.17.88.35. Subnet Mask set to: 255.255.255.0. Default Gateway set to the ISP address: 172.17.88.1.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Step 3: Save the settings. Scroll down the bottom of the screen and click Save Settings. You are prompted with the following window. Click Continue.
Step 4: Verify connection to PC1. Navigate to the Administration page and then to the Diagnostics tab.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 5 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Enter 172.17.88.1 for the Ping Test, and click Start to Ping. (Note: you might need to allow popups in your browser.) You should see the results below; if not troubleshoot.
Click Close. Note: Due to security settings, at this point, PC1 is not able to ping WRS1. This will be changed in a later task.
Task 3: Configure the LAN IP addressing.
Step 1: Set the Network Setup Address. Navigate back to the Setup page (the Basic Setup is the default tab). Under Network Setup, enter the Router IP of 172.17.30.1
Step 2: Save the settings. Click Save Settings, and then Continue. At this point you will be disconnected from the web page, as you just changed the IP address you are connected to. It will take a minute or two, and you will need to refresh your browser, but you should be redirected to the new URL of the web utility (http://172.17.30.1). If not, you might need to release your IP address and request a new one, before your navigate your browser there. You will be asked to login again. Step 3: Verify IP address changes. Go back to the command prompt and use the command ipconfig. Notice the new IP addresses.
Ping the ISP (172.17.88.1) to verify you can get outside your network. The pings should succeed.
Task 4: Basic Wireless Settings
Step 1: Install drivers for the Linksys USB Wireless NIC on PC3. If your PC already has the Wireless card installed, go to step 2. Depending on the NIC you use, Windows might not have the drivers needed, so you need to install the driver. The other advantage of not using the Windows driver is most manufacturers include configuration utilities that give more options and information then the Windows Wireless Connection Screen. This lab demonstrates using the Linksys
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 6 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
WUSB300N NIC. Ask your instructor for details if your NIC is different. Use the driver CD before you connect the USB NIC in this step. On PC3, insert the driver CD, and auto-install will launch the program (otherwise start the Setup.exe). Follow the on screen prompts, and when it asks you to connect the NIC, plug the cable into the USB port. You will see the Creating a Profile screen (below). Do not connect to the access point yet you will do that in step 3. Make note of any wireless networks and the channels in use. In the example picture below, there are two networks on Channel 1. You will change the channel in the next step. Dont forget to remove the driver CD and put it back in the case. Click on the Linksys wireless network, and hover the mouse over it, and the MAC address of the WRSs Wireless Port will show up. NOTE: This value is 2 more (in hex) than the value listed on the bottom of the case of the Linksys WRS300N. The MAC address listed on the case is used for the wired connections.
Step 2: Basic Wireless Settings. The Linksys WRT300N allows you to choose which network mode to operate in. Currently, the most common network mode for clients is Wireless-G and for routers is BG-Mixed. When a router is operating in BG-Mixed, it can accept both B and G clients. However, if a B client connects, the router must scale down to the slower level of B. For this lab, pick the fastest speed your clients can support. On PC2, navigate to the Wireless page (the Basic Wireless Settings tab is the default). Network Mode If your clients support 802.11n, select Wireless-N Only, otherwise, choose BGMixed.
Network Name (SSID) Change to WRS1_number. Where number is a unique id assigned by your instructor, such as your pod number, to avoid conflicts with other students doing the lab at the same time
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 7 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Wireless-N Only Radio Band Change to Standard 20MHz Channel. Note: setting this to Wide - 40MHz Channel will use 2 radio channels at the same time to boost speeds, but will cause more interference in the 2.4 GHz band. Cisco Aironet products will only allow Wide in the 5.8 GHz band. Standard Channel To avoid interference, change the Standard Channel to a number that is not already in use. Ideally, this would be at least 3 channels away from other wireless networks to reduce interference. For Wireless-N, if you selected Wide for the Radio Band, then this will be your secondary channel, and you can only select one that is 2 channels above or below your Wide Channel. SSID Broadcast Leave Enabled for now. Wireless-BG settings example:
Wireless-N settings example:
Click Save Settings, and then Continue.
Step 3: Verify wireless connection. On PC3, click on Refresh to update your wireless networks. You should see the new network.
Click on the name to highlight it and then click Connect. When it is done, it will congratulate you on creating a profile. Click Finish and you will see the Link Information tab.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 8 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Task 5: Configure DHCP Settings and Router Time Zone Settings
Step 1: Give a static DHCP binding to PC2 and PC3. On PC3, verify connectivity settings by going to Start > Run and typing cmd. At the command prompt, type the command Ipconfig /all to view your network device information. Note the Physical Address (MAC) of the Wireless Connection.
On PC2, navigate back to the Setup page (the Basic Setup is the default tab). In the middle of the Basic Setup Page, under DHCP Server Settings, click the DHCP Reservations button. The window shown below will open.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 9 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
There are two ways to assign DHCP addresses. The first method will always assign the client the same address the client has right now. The second will be in the next step. Find PC2 (your name may be different) in the list of current DHCP clients. (Hint: it should be listed as a LAN connection.) Check the Select box next to your PC. Click Add Clients. Now PC2 will show up under Clients Already Reserved. This gives PC2, (in this example, the computer with a MAC address of 00:13:21:5E:0F:EB), the same IP address it has right now, 172.17.30.100, whenever it requests an address through DHCP.
Step 2: Assign PC3 the 172.17.30.24 address. The second method to assign DHCP addresses is to select the address you want the machine to get. You will assign PC3 the static IP address listed in the Addressing Table, not the one it received initially. Under Manually Adding Client, enter your clients actual name, .24 for the IP address, the actual MAC address of your PCs Wireless Connection, and click Add. Now whenever PC3 connects to the wireless router, it receives the IP address 172.17.30.24 via DHCP.
Click Save Settings and Continue. Click Close to exit the DHCP Reservation window and return to Basic Setup.
Step 3: Verify the static IP address change. On both PC2 and PC3, at the command prompt, type Ipconfig /release and then Ipconfig /renew to verify the IP addresses you assigned are used. On PC3, ping the IP address of PC1 to verify you can reach the internet. Step 4: Configure other DHCP server settings. Right underneath the DHCP Reservation are the other settings for the DHCP server. What is the default maximum number of users the WRS300N will hand out DHCP addresses to? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Start IP Address Change to: 172.17.30.50. Maximum Number of Users Change to: 75 Client Lease Time Change to 120 minutes (2 hours).
These settings give any PC that connects (wired or wirelessly) to this router requesting an IP address through DHCP, an address between 172.17.30.50124. Only 75 clients at a time are able to get an IP
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 10 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
address and they can only have the address for two hours, after which time they must request a new one. Step 5: Configure the router for the appropriate time zone. At the bottom of the Basic Setup page: Time Zone - Change the Time Zone of the router to reflect your location.
Step 6: Save your settings Click Save Settings and Continue.
Task 6: Enable Wireless Security (part 1) using WPA
If your clients will not support WPA, just read this task; the next task will deal with a lower security level. A network is only as secure as its weakest point, and a wireless router is a very convenient place to start if someone wants to damage your network. Unfortunately, there are tools that can discover networks that are not even broadcasting their SSID, and there are even tools that can crack WEP key encryption. A more robust form of wireless security is WPA or WPA2. With WPA or WPA2 encryption enabled it is considered strong enough that you do not need to disable the SSID Broadcast or filter the MAC addresses. In fact, on the Linksys WRS300N, if Wireless MAC Filters are enabled while WPA is active, the wireless clients will connect and will get a DHCP address, but they are not able to reach the network, or even ping their default gateway. Step 1: Wireless Security. On PC2, navigate to the Wireless page, and then select the Wireless Security tab.
Step 2: Select Security Mode. In a corporate environment using WPA2 wireless security, clients will authenticate to the access point. The access point will then contact a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) database server to verify the credentials. Security Mode Using the pull-down menu, select WPA2 Enterprise.
What are the names of the options listed (field names)? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Since you do not have a RADIUS server, you will use WPA2 Personal. Security Mode Using the pull-down menu, select WPA2 Personal.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 11 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Encryption select AES. AES is stronger encryption than TKIP. If your clients support WPA2, but not AES, then leave it at the default of TKIP or AES. Passphrase enter 0123456789 Key Renewal leave at 3600. Click Save Settings and Continue.
Step 3: Configure PC3 to use WPA2. At this point, PC3 will no longer be able to connect until you edit the profile.
On PC3, click the Profiles tab and click to highlight your profile. Click Edit at the bottom. From the Available Wireless Network list, select your wireless network.
Click Connect and a warning will show. Click Continue.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 12 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Leave the Security set to WPA2-Personal and enter the pre-shared key of 0123456789 (as configured before on the router).
Click Connect, and then Finish. The Link Information tab should show you connected. If not, verify the key is entered the same on the WRS and the PC. Step 4: Verify PC3 can connect. On PC3, at the command prompt, ping the IP Address of PC1, to verify you can reach the internet.
Task 7: Enable Wireless Security (part 2) using WEP, Wireless MAC Address Filters, and Disabling SSID Broadcast.
If you have clients that do not support WPA or WPA2, the best option would be to set up a separate access point (on a different VLAN from the more secured wireless). If there is only one access point, enabling WEP with MAC address filtering and disabling SSID broadcast is the best security you can provide. Be aware there are tools that can discover networks that are not broadcasting their SSID, it is not hard to do MAC address spoofing, and there are even tools that can crack WEP key encryption. WPA or WPA2 are the preferred methods to secure wireless. Step 1: Change the Security Mode to WEP. On PC2, select the Wireless Security tab. Security Mode From the pull-down menu, select WEP. Encryption Leave at 40 / 64-bit (10 hex digits) Passphrase Leave blank. Key 1 Enter ABCDEF1234.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 13 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Click Save Settings and Continue. It might take a minute, but PC3 should show it can no longer connect to the access point. Make sure PC3 is no longer connected before you disable the SSID broadcast, or it will still think the connection is active.
Step 2: Disable SSID broadcast. On PC2, navigate to the Basic Wireless Settings tab. SSID Broadcast Click Disabled. Click Save Settings and Continue.
Step 3: Configure PC3 to use WEP. PC3 will no longer be able to connect until you edit the profile. On PC3, click the Profiles tab and click to highlight your profile. Click Edit at the bottom. Since you disabled SSID broadcast, you can no longer select from the Available Wireless Network list. Click Advanced Setup. On the next screen, leave the Network Setting at Obtain a network setting automatically (DHCP) and click Next. Leave the Wireless Mode at Infrastructure Mode, and the Wireless Network Name should match your SSID. Click Next. On the Wireless Security page, from the Security pull-down menu, select WEP, and click Next. Leave WEP set to 64-bit, and Passphrase as blank. For the WEP Key enter ABCDEF1234 and click Next.
Click Save and then on the next screen, Connect to Network. The Link Information tab should show you connected. If not, verify the key is entered the same on the
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 14 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Linksys and the PC. Step 4: Verify PC3 can connect. On PC3, at the command prompt, ping the IP address of PC1, to verify you can reach the internet. Step 5: Add a Wireless MAC Filter. On PC2, click the Wireless MAC Filter tab. Click Enabled.
If you were to select Prevent PCs listed below from accessing the wireless network, any MAC addresses you enter would not be allowed to connect to the wireless network. Obviously denying specific MAC addresses from connecting is not a practical solution for security. A far better solution is to only allow selected MAC addresses to connect. (However, it is not difficult to spoof MAC addresses, so this should not be your only line of defense.) Click Permit PCs listed below to access the wireless network.
Click the Wireless Client List button.
The Wireless Client List shows anyone currently connected to the router via a wireless connection. Also take note of the option Save to MAC filter list. Checking this option automatically adds the MAC address of that client to the list of MAC addresses to prevent or permit access to the wireless network. Check the Save to MAC address filter list box next to your PC.
Click the Add button. The Wireless Client List window will automatically close.
Now you should see the MAC address added to the MAC Address Filter List. Even though you have DHCP set to 75 clients, what is the maximum number of Wireless MAC Addresses you can filter? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Click Save Settings and Continue.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 15 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Step 6: Verify PC3 can still connect. On PC3, click the Profiles tab, highlight your profile, and click Connect. You should reconnect to the network. (If not, attempt to reconnect again.) If you still cannot connect, on PC2, verify in the Wireless MAC Filter page, the Access Restriction is set to Permit, or your client will be blocked! At the command prompt, ping the IP address of PC1, to verify you can still reach the internet.
Task 8: Secure the Linksys Administration
Step 1: Set the router password. Click the Administration page (the Management tab is the default). Router Access Change the router password to cisco123. Re-enter the same password to confirm. Web Utility Access Select both HTTP and HTTPS. Selecting HTTPS access allows a network administrator to manage the router via https://172.17.30.1 with SSL, a more secure form of HTTP. If you choose to use HTTPS in the lab, you may have to accept certificates. Web Utility Access via Wireless Select Disabled. When you disable this option, the Web Utility is not available to clients connected wirelessly. Disabling access is another form of security, because it requires the user to be directly connected to the router before changing settings. (However, in future lab scenarios, if you are configuring the router via wireless access, disabling access would not be a good idea!)
Click Save Settings. You will be prompted for a login. Leave the User Name blank, but use cisco123 for the password, and click OK. Click Continue.
Task 9: Configure Options in the Linksys Security Tab
By default, ping requests to WRS1s WAN interface (172.17.88.35) from sources on its WAN interface (i.e. the internet in this lab represented by PC1) will be blocked for security reasons. For the purpose of verifying connectivity in this lab you would like to allow them. Step 1: Allow anonymous internet requests. Click the Security page (the Firewall tab is the default). Under Internet Filter, uncheck Filter Anonymous Internet Requests.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 16 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Click Save Settings and Continue.
Step 2: Test Connectivity - Ping WRS1s WAN interface. On PC1, open the command prompt and type ping 172.17.88.35. Note: This change only allows you to ping the WAN interface IP address. The Firewall still prevents you from trying to ping PC2, PC3, or the LAN interface of the WRS.
Task 10: Setting Access Restrictions
Configure an access restriction that prevents users with a DHCP address (172.17.30.50 124) access to ping from Monday through Friday. Normally you might want to block other applications, such as HTTP, FTP, or Telnet, but to demonstrate the access control, you will use ping. Step 1: Verify access first. On PC2, at the command prompt, ping the IP address of PC1, to verify you can still reach the internet.
Step 2: Creating an Access Restriction. On PC2, navigate to the Access Restrictions page (there is only one tab). From the Access Policy pull-down menu, how many simultaneous Access Policies can you have active? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Access Policy Leave at 1(). Policy Name Type No_Ping. Status Click on Enabled. Access Restriction Leave at Allow. Schedule: Days Uncheck Everyday, and check Monday through Friday. (If you are completing this lab on a weekend, check that day too.) Scroll down to the Blocked Applications, and in the List, select Ping (0 - 0). Click the >> button to move Ping to the Blocked List.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 17 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Step 3: Set the IP address range. Apply this configuration to anyone that is using an address from the DHCP pool (172.17.30.50 124). Near the top of the window, under the Applied PCs, click the Edit List button. The List of PCs window will open. Under the IP Address Range, enter the IP address range.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 18 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Click Save Settings and then Continue. Click Close on List of PCs window. Back on the Access Restriction window, scroll down and click Save Settings, and then Continue.
Step 4: Verify the restrictions. On both PC2 and PC3, at the command prompt, ping the IP address of PC1. PC3 should ping successfully, as PC3s IP address (172.17.30.24) is outside the range of addresses specified. But PC2 (172.17.30.100) should no longer be able to ping PC1.
Task 11: Backup and Restore the Settings of the Linksys.
Step 1: Backup your configuration. Click the Administration page (the Management tab is the default). Scroll down to the Backup and Restore section. Backup your configuration by clicking the Backup Configurations button. When prompted, save the file to your desktop.
Step 2: Restore your configuration. If your settings are accidentally or intentionally changed or erased, you can restore them from a working configuration using the Restore Configurations option located in the Backup and Restore section. Click the Restore Configuration button. In the Restore Configurations window browse to the previously saved configuration file. Click the Start to Restore button. Your previous settings should be successfully restored. After the restore, the WRS will restart, so you will lose your connection until it is up again (about 20 seconds).
Task 12: Clearing the Linksys Configuration
Step 1: Resetting the router without a hard reset.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 19 of 20
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: Wireless Concepts and Configuration
Lab 7.5.1: Configuring Wireless Access and Security
Navigate to the Administration page and then to the Factory Defaults tab Click the Restore All Settings button.
All contents are Copyright 19922008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 20 of 20
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Dari EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Dari EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Networks CCNADokumen3 halamanIntroduction To Networks CCNAFiorella LeonBelum ada peringkat
- The Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionDari EverandThe Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionBelum ada peringkat
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDari EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA 3 Student Lab ManualDokumen192 halamanCCNA 3 Student Lab ManualNazmul HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless LabsDokumen32 halamanWireless LabsRonald MutendaBelum ada peringkat
- Packet Tracer 1.3.1Dokumen11 halamanPacket Tracer 1.3.13qtrtymBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - SPROUTE 1.0 - Student Guide Vol1 PDFDokumen310 halaman1 - SPROUTE 1.0 - Student Guide Vol1 PDFddungui100% (1)
- Check Point Certified Managed Security Expert Plus VSX NGX Practice Exam QuestionsDokumen24 halamanCheck Point Certified Managed Security Expert Plus VSX NGX Practice Exam QuestionsMCP MarkBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Network Security Threats EvolutionDokumen143 halamanModern Network Security Threats EvolutionNabila Fauzi100% (1)
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 3Dokumen6 halamanESwitching Lab 1 3 3Ninja NuggetBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2Dokumen23 halamanESwitching Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetBelum ada peringkat
- CCNP Route DumpsDokumen239 halamanCCNP Route DumpsJamez STBelum ada peringkat
- 13.1.11 Lab - Configure A Wireless Network - ILMDokumen18 halaman13.1.11 Lab - Configure A Wireless Network - ILMFernando FallaBelum ada peringkat
- 7.5.1 LabDokumen6 halaman7.5.1 LabLHBelum ada peringkat
- 7.5.2 LabDokumen23 halaman7.5.2 LabLHBelum ada peringkat
- PT Activity 7.5.2: Challenge Wireless WRT300N: Topology DiagramDokumen8 halamanPT Activity 7.5.2: Challenge Wireless WRT300N: Topology DiagramFerdie SelgaBelum ada peringkat
- ITE v7 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualDokumen17 halamanITE v7 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualWaldon HendricksBelum ada peringkat
- Ex1 PDFDokumen4 halamanEx1 PDFJinesh AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- ITN 7.02 - Case Study - Part 2 (Modules 4-7)Dokumen2 halamanITN 7.02 - Case Study - Part 2 (Modules 4-7)tssr15.nadjemBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring A Wireless Router and ClientDokumen4 halamanConfiguring A Wireless Router and ClientJomar RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 1.3.1Dokumen12 halamanLab 1.3.1Alondra CarmonaBelum ada peringkat
- So, Here Is My Step-By-Step Guide To Configuring A Wi-FiDokumen3 halamanSo, Here Is My Step-By-Step Guide To Configuring A Wi-FinagapratapBelum ada peringkat
- Medgroup Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: Part 3 - Add Wireless Access To The Urban Clinic Lan PrototypeDokumen2 halamanMedgroup Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge: Part 3 - Add Wireless Access To The Urban Clinic Lan PrototypevilanchBelum ada peringkat
- 1.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Packet Tracer IntroductionDokumen4 halaman1.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Packet Tracer IntroductionCristina ComanBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Dokumen11 halamanESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Surapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- Configuring Linksys Wireless Router: Prof. Yousif at Valencia Community CollegeDokumen29 halamanConfiguring Linksys Wireless Router: Prof. Yousif at Valencia Community CollegeMujeeb AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 1Dokumen12 halamanESwitching Lab 1 3 1Derek Ang Yew PinBelum ada peringkat
- Configure Wireless Network and SettingsDokumen4 halamanConfigure Wireless Network and SettingsDmddldldldlBelum ada peringkat
- Dhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA2014Dokumen5 halamanDhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA2014Landio RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Packet Tracer - Connect To A Wireless NetworkDokumen4 halamanPacket Tracer - Connect To A Wireless NetworkSgr Eka 13Belum ada peringkat
- Airlink101 Access Point - Ap431wDokumen42 halamanAirlink101 Access Point - Ap431wJim ParentBelum ada peringkat
- RouterDokumen18 halamanRoutersaipratapbecBelum ada peringkat
- 6.1.3.9 Packet Tracer - Connect To A Wireless NetworkDokumen4 halaman6.1.3.9 Packet Tracer - Connect To A Wireless NetworkDjazila KortiBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 16Dokumen3 halamanExperiment 16rapraptapayoonBelum ada peringkat
- EW 7209APg ManualDokumen44 halamanEW 7209APg ManualGabriel H. MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Start Guide: Duolinks Sw24 SeriesDokumen4 halamanQuick Start Guide: Duolinks Sw24 Seriesanon-745450Belum ada peringkat
- Dhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBADokumen2 halamanDhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBAHeather SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless LAN USB Adapter: User'S GuideDokumen26 halamanWireless LAN USB Adapter: User'S Guideavoid11Belum ada peringkat
- PT3 FinalsLabExercise#3 Group9Dokumen23 halamanPT3 FinalsLabExercise#3 Group9Chauncey SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Configuracion Del Router: Tarea 1: Cargar Las Configuraciones de Inicio. Paso UnoDokumen23 halamanConfiguracion Del Router: Tarea 1: Cargar Las Configuraciones de Inicio. Paso UnoGiovanni Sanchez HiglerGtsBelum ada peringkat
- CS432 - Cisco Packet Tracer PDFDokumen6 halamanCS432 - Cisco Packet Tracer PDFOburu David KatandiBelum ada peringkat
- Inform 2grupo3Dokumen20 halamanInform 2grupo3daniBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2 - Building A Simple Network: TopologyDokumen12 halamanLab 2 - Building A Simple Network: Topologyjramisch44Belum ada peringkat
- Dec30023 - Computer Networking Fundamentals Lab 4: Configure Wireless Access Point and ClientDokumen10 halamanDec30023 - Computer Networking Fundamentals Lab 4: Configure Wireless Access Point and Clientsaiman suiBelum ada peringkat
- CW 5350 User ManualDokumen23 halamanCW 5350 User ManualJeffrey AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Konigcmp-Wnrout20 40 User GuideDokumen69 halamanKonigcmp-Wnrout20 40 User GuidevoicadanBelum ada peringkat
- EDTECH 552 - Lab 5Dokumen22 halamanEDTECH 552 - Lab 5Brian MatthewBelum ada peringkat
- NL 2611cb3 Plus Manual v1 0Dokumen18 halamanNL 2611cb3 Plus Manual v1 0stankevichijusBelum ada peringkat
- AWAP602 ManualDokumen41 halamanAWAP602 ManualdivxnsBelum ada peringkat
- 300Mbps/150Mbps Wireless LAN Broadband Router: Quick Installation GuideDokumen2 halaman300Mbps/150Mbps Wireless LAN Broadband Router: Quick Installation GuideLuis AngelBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN EnvironmentDokumen16 halamanWireless Configuration: Connect The Router On A Wired LAN Environmentjun arvie100% (1)
- 13.1.10 Packet Tracer Configure A Wireless NetworkDokumen6 halaman13.1.10 Packet Tracer Configure A Wireless NetworkAndrés SarangoBelum ada peringkat
- 13.1.10 Packet Tracer - Configure A Wireless NetworkDokumen5 halaman13.1.10 Packet Tracer - Configure A Wireless NetworkLyes StiviGiBelum ada peringkat
- 657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Dokumen13 halaman657ac38c7eb2clab9 CCN 2023Muhammad Ali RajarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 5 1 13bDokumen4 halamanLab 5 1 13bjoseBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Dari EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Belum ada peringkat
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkDari EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkBelum ada peringkat
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDari EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksBelum ada peringkat
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADokumen4 halamanERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAiAndry50% (2)
- SAD Project ReportDokumen21 halamanSAD Project ReportSurapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADokumen4 halamanERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAiAndry50% (2)
- ERouting OSPF PT Practice SBADokumen4 halamanERouting OSPF PT Practice SBAiAndry50% (2)
- D4 SBA Student SheetDokumen19 halamanD4 SBA Student SheetSurapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4Dokumen20 halamanESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4Surapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Student Laab Skills Based AssessmentDokumen4 halamanESwitching Student Laab Skills Based AssessmentSurapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Dokumen11 halamanESwitching Lab 7 5 2 Brent v2.1Surapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1Dokumen11 halamanENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1LMBvakol2012Belum ada peringkat
- 2013-01-02Dokumen45 halaman2013-01-02Surapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- Course OutlineDokumen4 halamanCourse OutlineSurapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- ENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1Dokumen11 halamanENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1LMBvakol2012Belum ada peringkat
- ENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1Dokumen11 halamanENetwork Basic Configuration PT (Practice SBA) CCNA EX1LMBvakol2012Belum ada peringkat
- DS1307Dokumen13 halamanDS1307Ezaú TalamantesBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 V7.01Dokumen76 halamanChapter 4 V7.01Luciano PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei AR100-AR120-AR150-AR160-AR200 Series Enterprise Routers Data SheetDokumen34 halamanHuawei AR100-AR120-AR150-AR160-AR200 Series Enterprise Routers Data SheettariqrazaBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna R&SDokumen77 halamanCcna R&SarunBelum ada peringkat
- PT FinalDokumen12 halamanPT FinalMartinDalliBelum ada peringkat
- VLan Some Basic Concepts PDFDokumen11 halamanVLan Some Basic Concepts PDFAbhishek gargBelum ada peringkat
- NSX Compendium Vmware NSX For VsphereDokumen20 halamanNSX Compendium Vmware NSX For VsphereninodjukicBelum ada peringkat
- DCC Lab Manual - 2020-2021Dokumen43 halamanDCC Lab Manual - 2020-2021Jay PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco122sx 01Dokumen14 halamanCisco122sx 01barryionBelum ada peringkat
- Experienced Network Engineer Seeks New ChallengesDokumen6 halamanExperienced Network Engineer Seeks New ChallengesShubham BadoniBelum ada peringkat
- I2A - Cognitive CampusDokumen50 halamanI2A - Cognitive CampusmedrekBelum ada peringkat
- B Release Notes Asr9k 692Dokumen19 halamanB Release Notes Asr9k 692rkrao77Belum ada peringkat
- CCNA LabSim MappingDokumen16 halamanCCNA LabSim Mappingشريف فتحي الشرقاويBelum ada peringkat
- Netgear MR814v2 Wireless RouterDokumen7 halamanNetgear MR814v2 Wireless Routerapi-3722962100% (1)
- Linksys OS - Configuring The Linksys WRT610N As An Access PointDokumen5 halamanLinksys OS - Configuring The Linksys WRT610N As An Access Pointasuasu3Belum ada peringkat
- Archer C54 (EU&US) - QIG - V1Dokumen2 halamanArcher C54 (EU&US) - QIG - V1Pranta BarmanBelum ada peringkat
- Google Cloud Professional: Cloud Network Engineer ExamDokumen12 halamanGoogle Cloud Professional: Cloud Network Engineer Exammatt streamBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Instalacion Modulo IP150Dokumen2 halamanManual Instalacion Modulo IP150Miguel Beltran SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Foglight NMS 5.2 Administrator GuideDokumen87 halamanFoglight NMS 5.2 Administrator Guidetredd2Belum ada peringkat
- MPLS - An Introduction (Nortel Networks)Dokumen13 halamanMPLS - An Introduction (Nortel Networks)sandugoguBelum ada peringkat
- Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) GuideDokumen17 halamanIntra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) GuideAhmad YahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Inst Alla Tion Guid E: Wl-EdhowaDokumen155 halamanQuick Inst Alla Tion Guid E: Wl-EdhowaDomenicoBelum ada peringkat
- WISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualDokumen39 halamanWISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualLynn DavisBelum ada peringkat
- Rfx9600 Philips ProntoDokumen48 halamanRfx9600 Philips ProntoCristian Enrique AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Avaya Switch ManualDokumen538 halamanAvaya Switch ManualClay_BerloBelum ada peringkat
- CHAP3QUIZDokumen36 halamanCHAP3QUIZDr NorBelum ada peringkat