Myocardial Infarction
Diunggah oleh
nkosisiphileDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Myocardial Infarction
Diunggah oleh
nkosisiphileHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
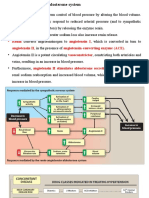
Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the death of heart muscle from the sudden blockage
of a coronary artery by a blood clot. Myocardial infarction most commonly due to occlusion (blockage) of a coronary artery following the rupture of a vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque, which is an unstable collection of lipids (cholesterol and fatty acids) and white blood cells (especially macrophages) in the wall of an artery. The resulting ischemia (restriction in blood supply) and ensuing oxygen shortage, if left untreated for a sufficient period of time, can cause damage or death (infarction) of heart muscle tissue (myocardium).
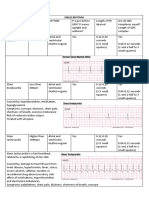
Chest pain or pressure is the most common symptom of a heart attack, Myocardial infarction (MI) or heart attack victims may experience a variety of symptoms including:
Pain, fullness, and/or squeezing sensation of the chest Jaw pain, toothache, headache Shortness of breath Nausea, vomiting, and/or general epigastric (upper middle abdomen) discomfort Sweating Heartburn and/or indigestion Arm pain (more commonly the left arm, but may be either arm) Upper back pain General malaise (vague feeling of illness) No symptoms (Approximately one quarter of all heart attacks are silent, without chest pain or new symptoms. Silent heart attacks are especially common among patients with diabetes mellitus.) An MI requires immediate medical attention. Treatment attempts to salvage as much myocardium as possible and to prevent further complications, hence the phrase "time is muscle". Oxygen, aspirin, and nitroglycerin may be administered. Morphine was classically used if nitroglycerin was not effective; however, it may increase mortality in the setting of NSTEMI. A 2009 and 2010 review of high flow oxygen in myocardial infarction found increased mortality and infarct size, calling into question the recommendation about its routine use. Other analgesics such as nitrous oxide are of unknown benefit. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or fibrinolysis are recommended in those with an STEMI. (wikipedia)
Nursing Care Plan for Myocardial Infarction 12 Nursing Diagnosis for Myocardial Infarction 1. Decreased Cardiac Output related to: changes in the frequency of heart rhythm. 2. Impaired Tissue Perfusion related to: decrease in cardiac output.
3. Ineffective Airway Clearance related to: accumulation of secretions. 4. Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to: lung development is not optimal. 5. Impaired Gas Exchange related to: pulmonary edema. 6. Acute Pain relate to: increase in lactic acid. 7. Fluid Volume Excess related to: retention of sodium and water. 8. Imbalanced Nutrition, Less Than Body Requirements related to: Inadequate intake. 9. Activity Intolerance relate to: imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and needs. 10. Self-Care Deficit related to: physical weakness. 11. Anxiety related to: ncaman death. 12. Knowledge Deficit related to: lack of information.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- IntroductionDokumen13 halamanIntroductionSiyara AntonyBelum ada peringkat
- Propaganda Essay in APA With ReferencesDokumen7 halamanPropaganda Essay in APA With Referencesbmorgan 84Belum ada peringkat
- Oral Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs: Treatment With Blood ThinnersDokumen8 halamanOral Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs: Treatment With Blood Thinnershussain AltaherBelum ada peringkat
- Angiotensin I Angiotensin II, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) - Vasoconstrictor Angiotensin II Stimulates Aldosterone SecretionDokumen11 halamanAngiotensin I Angiotensin II, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) - Vasoconstrictor Angiotensin II Stimulates Aldosterone SecretionAbdullah asadBelum ada peringkat
- Lower Cholesterol with Atorvastatin (LipitorDokumen7 halamanLower Cholesterol with Atorvastatin (LipitorAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Managing corticosteroids and their side effectsDokumen6 halamanManaging corticosteroids and their side effectsKrista Madranca CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Payroll Management in Simhapuri HospitalsDokumen30 halamanPayroll Management in Simhapuri HospitalsbhuvanaBelum ada peringkat
- Common Drug InteractionsDokumen1 halamanCommon Drug InteractionsLuxs23Belum ada peringkat
- Cardio AspirinDokumen3 halamanCardio AspirinBayu PrabowoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac BiomarkersDokumen10 halamanCardiac BiomarkersfelipetheBelum ada peringkat
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Medical Ward RotationDokumen5 halamanIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Medical Ward RotationEiz CabreraBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Acting On Cardio Vascular SystemDokumen16 halamanDrugs Acting On Cardio Vascular SystemANUSHYA B PSGRKCWBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Given During Cardiac Arres For CPRDokumen5 halamanDrugs Given During Cardiac Arres For CPREevyaj MimiBelum ada peringkat
- Legalandethicalissuesincriticalcarenursing 130411224544 Phpapp02Dokumen33 halamanLegalandethicalissuesincriticalcarenursing 130411224544 Phpapp02Guna RamyaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyKobe ManuelBelum ada peringkat
- Verbal or Thelepone OrderDokumen2 halamanVerbal or Thelepone Orderbylaw_12Belum ada peringkat
- Head Injury: Manali H. Solanki F.Y. M.Sc. Nursing J G College of NursingDokumen31 halamanHead Injury: Manali H. Solanki F.Y. M.Sc. Nursing J G College of NursingWaqar AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Ventricular Septal DefectsDokumen7 halamanVentricular Septal DefectsMuhammadAldoGiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- #6 Copd 11 PDFDokumen11 halaman#6 Copd 11 PDFOmar BasimBelum ada peringkat
- United Doctors Hospital Nurses Handover ReportDokumen20 halamanUnited Doctors Hospital Nurses Handover ReportANNETTE GUEVARRABelum ada peringkat
- Career Reflection PaperDokumen7 halamanCareer Reflection Paperapi-4879323160% (1)
- Applying Pharmacology Concepts to Beta Blocker TherapyDokumen269 halamanApplying Pharmacology Concepts to Beta Blocker TherapyTrishaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary EdemaDokumen14 halamanPulmonary EdemaRizzamwah Catague100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Diseases in IndiaDokumen40 halamanGuidelines For The Management of Cardiovascular Diseases in IndiaViky SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Unstable AnginaDokumen10 halamanUnstable AnginaironBelum ada peringkat
- Unstable Angina Diagnosis and Treatment SummaryDokumen28 halamanUnstable Angina Diagnosis and Treatment SummaryLissaberti AmaliahBelum ada peringkat
- Executive Summary:: To Reach The Breakeven Point It Will Take Minimum of 8 Years (Approx.)Dokumen29 halamanExecutive Summary:: To Reach The Breakeven Point It Will Take Minimum of 8 Years (Approx.)sabrina akther eshaBelum ada peringkat
- INOTROPES AND VASOPRESSORS OVERVIEWDokumen62 halamanINOTROPES AND VASOPRESSORS OVERVIEWtwister4Belum ada peringkat
- Nstemi: How To Risk Stratify?Dokumen32 halamanNstemi: How To Risk Stratify?dhannibernadetBelum ada peringkat
- Trends and Issues Affecting Nursing Practice-Newest S-16Dokumen81 halamanTrends and Issues Affecting Nursing Practice-Newest S-16Lorraine CayamandaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Tamponade and ManagementDokumen42 halamanCardiac Tamponade and Managementأم حمدBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge Planning PaperDokumen4 halamanDischarge Planning Paperapi-252001755100% (1)
- Heart Transplantation: Procedure, Recovery, and Long-Term SurvivalDokumen4 halamanHeart Transplantation: Procedure, Recovery, and Long-Term SurvivalAncy AchankunjuBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing-Faculty-Position-Cover-Application LetterDokumen1 halamanNursing-Faculty-Position-Cover-Application LetterJason Lee YapBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselBelum ada peringkat
- AFPMC V. Luna General Hospital: Case StudyDokumen27 halamanAFPMC V. Luna General Hospital: Case StudyLemuel GuevarraBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeAlfred BucabucaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Dokumen28 halamanCardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Sparsh GoelBelum ada peringkat
- Left-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationDokumen64 halamanLeft-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ABelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlanNicolne LorraineBelum ada peringkat
- Tracheostomy Care: PhysiologyDokumen2 halamanTracheostomy Care: PhysiologyrajirajeshBelum ada peringkat
- Life after Tragedy: Essays on Faith and the First World War Evoked by Geoffrey Studdert KennedyDari EverandLife after Tragedy: Essays on Faith and the First World War Evoked by Geoffrey Studdert KennedyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen16 halamanUnit 1reeta yadav0% (1)
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDokumen20 halamanCongestive Cardiac FailureAnand VaghasiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Glycosides 815Dokumen19 halamanCardiac Glycosides 815SanskritiBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Transfusion: Etiology of Blood CellDokumen4 halamanBlood Transfusion: Etiology of Blood Cellbunso padillaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Diseases Symptoms Causes TreatmentsDokumen11 halamanRespiratory Diseases Symptoms Causes TreatmentsMichael Angelo SeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Mews ScoreDokumen13 halamanMews Score2009nicoleta100% (2)
- Heart Failure Guide for NursesDokumen54 halamanHeart Failure Guide for NursesKacelyn QuibanBelum ada peringkat
- START Triage MnemonicDokumen12 halamanSTART Triage Mnemonicwawa3385Belum ada peringkat
- Cryotherapy: in This Fact SheetDokumen8 halamanCryotherapy: in This Fact SheetUdayakrishnan P KanhangadBelum ada peringkat
- Causes, Symptoms, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis-A ReviewDokumen23 halamanCauses, Symptoms, Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis-A ReviewBaharudin WahyuBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Rehab GuidelinesDokumen48 halamanCardiac Rehab GuidelinesCarolina PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Arterial DisordersDokumen40 halamanArterial DisordersSalman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDokumen15 halamanObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18Belum ada peringkat
- Economic Growth: How it works and how it transformed the worldDari EverandEconomic Growth: How it works and how it transformed the worldBelum ada peringkat
- Puppets of Political Propaganda--Time to Pull Our Own StringsDari EverandPuppets of Political Propaganda--Time to Pull Our Own StringsBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction - MIDokumen10 halamanIntroduction - MIkhimiiiBelum ada peringkat
- Coronary Artery DisaeseDokumen48 halamanCoronary Artery DisaeseAzkaZulfiqarBelum ada peringkat
- Myocardial Infarction AssignmentDokumen23 halamanMyocardial Infarction AssignmentPums100% (6)
- Kounis SyndromeDokumen19 halamanKounis SyndromeAnkit Tonger AnkyBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart Disease Surgery TransDokumen9 halamanCongenital Heart Disease Surgery TransPuguinGamingBelum ada peringkat
- Section 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesDokumen28 halamanSection 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesАнђела КостићBelum ada peringkat
- A Simplified ECG GuideDokumen4 halamanA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (25)
- Local Exam 5Dokumen68 halamanLocal Exam 5drnasir31Belum ada peringkat
- Vyvanse Contraindicated in Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen2 halamanVyvanse Contraindicated in Cardiovascular DiseaseBilal NasirBelum ada peringkat
- MORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Dokumen20 halamanMORAES-SILVA Et Al 2017Luiza MartinsBelum ada peringkat
- Imaging Cardiac AmyloidosisDokumen16 halamanImaging Cardiac Amyloidosiskromatin9462Belum ada peringkat
- Hope 053122Dokumen4 halamanHope 053122Audrica HeathcoteBelum ada peringkat
- The New Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease: William P. CastelliDokumen6 halamanThe New Pathophysiology of Coronary Artery Disease: William P. CastelliLeo AramburuBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Hypertension Perioperative ManagementDokumen18 halamanPulmonary Hypertension Perioperative ManagementAdrian AfloroaeiBelum ada peringkat
- Shanghai Score System For Diagnosis of Brugada Syndrome PDFDokumen7 halamanShanghai Score System For Diagnosis of Brugada Syndrome PDFFendy WellenBelum ada peringkat
- DysrythmiasDokumen4 halamanDysrythmiasmgmjlm01_881676250100% (1)
- Cardiogenic Shock in The Setting of Acute Myocardial InfarctionDokumen6 halamanCardiogenic Shock in The Setting of Acute Myocardial InfarctionStijn VermoteBelum ada peringkat
- Heart AnatomyDokumen19 halamanHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Arrhythmia GuideDokumen5 halamanECG Arrhythmia GuideMasarrah AlchiBelum ada peringkat
- ECG ArrhythmiaDokumen27 halamanECG ArrhythmiaSrikitta DanieliaBelum ada peringkat
- InPractice2002 Martin ECGs3 PDFDokumen12 halamanInPractice2002 Martin ECGs3 PDFNag Mallesh RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21 - Blood Vessels and CirculationDokumen13 halamanChapter 21 - Blood Vessels and CirculationSameer AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Monology of StensenDokumen1 halamanMonology of StensenmoonlightsoantaBelum ada peringkat
- TPSVDokumen28 halamanTPSVGeraldine CortesBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDokumen13 halamanNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZBelum ada peringkat
- Invasive and Non Invasive MonitorDokumen22 halamanInvasive and Non Invasive Monitorbagya priyaBelum ada peringkat
- Analisa PicotDokumen3 halamanAnalisa PicotTasya Ramanda EfendiBelum ada peringkat
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDokumen2 halamanDopamine HydrochlorideNasrah N. MusaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation: La Consolacion University Philippines Malolos City, BulacanDokumen6 halamanCase Presentation: La Consolacion University Philippines Malolos City, BulacanElijah MancoBelum ada peringkat
- Restrictive CardiomyopathyDokumen29 halamanRestrictive CardiomyopathyAbnet WondimuBelum ada peringkat
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDokumen3 halamanBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- I Review of Cardiovascular SystemDokumen19 halamanI Review of Cardiovascular SystemJoe TincilBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen16 halamanHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)