Nursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetes
Diunggah oleh
Gimcy Dela FuenteDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nursing care plan for hypertension, renal calculi, diabetes
Diunggah oleh
Gimcy Dela FuenteHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
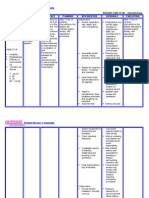
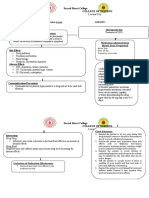
Assessment
SUBJECTIVE: Dati nga nangato ti blood pressure ko, as verbalized by the patient The patient reported dizziness, blurred vision and chest pain The patient complained bearable lower abdominal pain OBJECTIVE: conscious and coherent UTZ revealed staghorn calculi on left kidney V/S taken as follows T: 36.0 C P: 78 bpm R: 15 cpm BP: 130/100 mmHg Patient has a history of: Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, and Renal calculi The patient
Diagnosis
Decreased cardiac output related to increased peripheral vascular resistance secondary to hypertension as evidence by BP of 130/100, patient complaining of dizziness, blurred vision, and chest pain
Inference
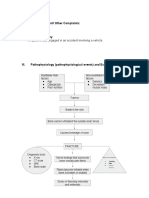
Hypertension occurs when there is a change in arteriolar bed which increases peripheral vascular resistance thus, decreasing blood flow to organs.
Planning
After 8 hours of nursing interventions , the patient will be able to verbalize an absent of dizziness, blurred vision and chest pain and BP will be stabilized to 120/80
Intervention
Independent The nurse will assess the patients blood pressure and cardiac rhythm every hour until stable. The nurse will assess the patients chest pain level and blurred vision every 4 hours until absent. The nurse will educate the patient on how to consult with his doctor before stopping a medication. Promote adequate rest by decreasing stimuli and providing quiet environment. Provide for restrictive diet: low salt, low fat diet Collaborative: Administer antihypertensive medications (e.g. Clonidine), as prescribed.
Rationale
To monitor if medications and the dose is having a favorable effect. To ensure patients safety.
Evaluation
Goal Met: The patient was able to stabiliz e her blood pressure to 120/80 and dizzines s, blurred vision and chest pain were relieved .
To prevent rebound hypertension.
For the patient to be comfortable during the therapy. Salt retains water thus increasing blood volume and blood pressure. May be given to treat hypertension.
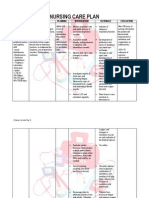
Anxiety related to threat to or change in health status secondary to renal calculi as manifested by verbalization of feelings of inadequacy, fear of unspecific
Anxiety is a feeling of nervousness or worry. This occurs when there is a sudden and unexpected incident that happens to a person.
After 8 hours of nursing interventions , the patient will appear relaxed and report anxiety is reduced to a manageable level and identifies healthy ways to deal with
Independent: Establish a therapeutic relationship, conveying empathy and unconditional positive regard. Encourage patient to express feelings. Acknowledge fear/anxiety. Do not reassure the patient that everything will be all right.
To build rapport and to calm the patient.
To be able for her to free her emotions. Re-assurance is not therapeutic because we are not in control over the situation.
Goal partiall y met: after 8 hours of nursing interven tions, the patient was able to appear relaxed
is anxious due to the operation needed for her renal calculi
consequence and tearfulness.
anxiety.
Provide comfort measures (e.g., calm environment, back rub, soft music). Assist patient to learn precipitating factors and new methods of coping with anxiety. Collaborative: Refer to physician for drug management program/alteration of prescription regimen. Independent: Observe for signs of infection and inflammation. Promote good hand washing by nurse and patient. Provide catheter or perineal care. Teach the female patient to clean from front to back after elimination. Keep the skin dry, linens dry and wrinkle free. Collaborative: Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivities as indicated.
To relax the patient and reduce anxiety. For the patient to easily cope up on the situation. Drugs may be used to reduce anxiety and calm the patient.
but still reported fear about her conditio n.
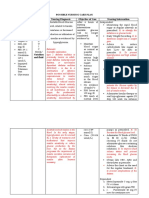
Risk for infection related to high glucose levels, decreased leukocyte function secondary to Type II Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus occurs when the pancreas produces insufficient amounts of the hormone insulin and/or the body's tissues become resistant to normal or even high levels of insulin. This causes high blood glucose (sugar) levels, which can lead to a number of complications if untreated.
After 8 hours of nursing interventions , the patient will identify interventions to prevent or reduce risk of infection.
Patient may be admitted with infection or may develop nosocomial infection. Reduces the risk of cross-contamina-tion. Minimizes the risk for infection.
Peripheral circulation may be impaired, placing patient at increased risk for infection. Identifies organisms so that most appropriate drug therapy can be instituted.
Goal met: after 8 hours of nursing interven tions, the patient was able to identify interven tions to prevent or reduce risk of infectio n.
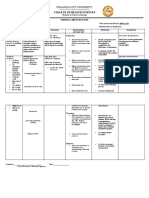
Republic of the Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City College of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan
In Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements in NCM 103A
Submitted to: Ms. Zielene Myrus Alzo, R.N., MAN Clinical Instructor
Submitted by: Alyssa Marie A. Aludino BSN III-Chamomile June 22, 2012
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome AssessmentDokumen3 halamanNCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome Assessmentsarahtot67% (3)
- NCP HypertensionDokumen1 halamanNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For HypertensionDokumen4 halamanNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- Hypertension NCPDokumen1 halamanHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Dokumen8 halamanNursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Mayls Sevilla Calizo100% (1)
- Managing Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen5 halamanManaging Hypertension and Decreased Cardiac Outputanon_9189425950% (2)
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDokumen3 halamanBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessDokumen3 halamanAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation EffectivenessYnah Sayoc75% (4)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen4 halamanDecreased Cardiac OutputChristine MatasBelum ada peringkat
- Tachycardia NCPDokumen2 halamanTachycardia NCPRemita Hutagalung50% (4)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokumen2 halamanImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokumen2 halamanNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- NCP Risk Infection Papillary Thyroid CADokumen2 halamanNCP Risk Infection Papillary Thyroid CAjazvBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDokumen1 halamanHypertension Nursing Care PlanSheila Mae Cabahug100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale ResponseDokumen4 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implimentation Rationale Responsekhate fonteBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For StrokeDokumen4 halamanNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHKrizha Angela Nicolas0% (1)
- Assessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver DiseaseDokumen1 halamanAssessing Ascites in a Patient with Liver Diseasehaniehaehae100% (1)
- NCP HemoDokumen2 halamanNCP HemoJigs HechBelum ada peringkat
- ThyroidectomyDokumen2 halamanThyroidectomyzdahb4444Belum ada peringkat
- NCP For HypertensionDokumen1 halamanNCP For Hypertensionrhizalyn1367% (6)
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFDokumen5 halamanImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolBelum ada peringkat
- NCP DMDokumen6 halamanNCP DMstara123Belum ada peringkat
- NoncomplianceDokumen3 halamanNoncomplianceChristy BerryBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Hypertension and DizzinessDokumen5 halamanManaging Hypertension and DizzinessCee Sanchez100% (1)
- Acute Pain NCPDokumen2 halamanAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (1)
- Nur81 NCP GastroDokumen4 halamanNur81 NCP GastroJordan Gonzales100% (1)
- Grand Case NP 2 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDokumen10 halamanGrand Case NP 2 Laparoscopic CholecystectomyFarida Paula R. SevillaBelum ada peringkat
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDokumen2 halamanCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDokumen1 halamanNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyBelum ada peringkat
- NCP 2Dokumen2 halamanNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDokumen3 halamanASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDokumen2 halamanNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaBelum ada peringkat
- Orif NCPDokumen1 halamanOrif NCPLighto Ryusaki100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Mr. Ying to Prevent FallsDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan for Mr. Ying to Prevent Fallsjanna mae patriarca100% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDokumen4 halamanNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension NCPDokumen4 halamanHypertension NCPChristian Karl B. Llanes0% (2)
- NCPDokumen3 halamanNCPranee diane0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Enhanced NutritionDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan for Enhanced NutritionHippocrates Impressionist CostalesBelum ada peringkat
- ANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanANDAYA, Kristine Alexis L. BSN218 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlexis TineBelum ada peringkat
- Spiritual NCPDokumen12 halamanSpiritual NCPGayzel Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen9 halamanNCPTracy Camille EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For COLON Cancer PatientDokumen4 halamanNCP For COLON Cancer PatientCarolina Tardecilla100% (1)
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionDokumen12 halamanPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorBelum ada peringkat
- Delayed Surgical Recovery Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanDelayed Surgical Recovery Nursing Care PlanMichala100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen3 halamanNursing Care PlanJayalakshmi David50% (2)
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDokumen25 halamanNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- NCP DMDokumen4 halamanNCP DMAarav (мя Ρєяfєт)Belum ada peringkat
- NCP For Ears Nose ThroatDokumen1 halamanNCP For Ears Nose ThroatMcmac YangoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Dokumen7 halamanNursing Care pLAN (Hypertension)Rosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (3)
- Nclex Exam PrepDokumen26 halamanNclex Exam PrepPascal St Peter Nwaorgu100% (1)
- Nursing Management of Upper GI BleedingDokumen10 halamanNursing Management of Upper GI BleedingVia Katherine PanganibanBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Chest PainDokumen2 halamanNCP Chest PainDOni Corleone87% (38)
- Promoting Adequate Gas ExchangeDokumen5 halamanPromoting Adequate Gas Exchangeali sarjunipadangBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen17 halamanNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesDari EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Case Study On CVADokumen34 halamanCase Study On CVAGimcy Dela Fuente50% (2)
- Drug Study For CVADokumen5 halamanDrug Study For CVAGimcy Dela FuenteBelum ada peringkat
- TriviaDokumen2 halamanTriviaGimcy Dela FuenteBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Hand ScrubDokumen7 halamanSurgical Hand ScrubGimcy Dela FuenteBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Hand ScrubDokumen7 halamanSurgical Hand ScrubGimcy Dela FuenteBelum ada peringkat
- Final Year Follow UpDokumen31 halamanFinal Year Follow Upprostho deptBelum ada peringkat
- HSS International PDI Form - February 2023Dokumen2 halamanHSS International PDI Form - February 2023wyzxy2793Belum ada peringkat
- Notes For NCM 109Dokumen13 halamanNotes For NCM 109Mae Arra Lecobu-anBelum ada peringkat
- Salmonella in The CaribbeanDokumen3 halamanSalmonella in The CaribbeanAlvin KiruiBelum ada peringkat
- Left Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDokumen9 halamanLeft Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDominic BristolBelum ada peringkat
- Vit DDokumen36 halamanVit DConstantin MarioaraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDokumen2 halamanDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- TB Diagnosis, Treatment & ControlDokumen16 halamanTB Diagnosis, Treatment & ControlwiwonBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation (Tomato)Dokumen33 halamanPresentation (Tomato)Sukhbir kaurBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Airway ObstructionDokumen17 halamanUpper Airway ObstructionRai Hana100% (1)
- Tingling and NumbnessDokumen67 halamanTingling and NumbnessAradhanaRamchandaniBelum ada peringkat
- Prop Ae771263af039nwpDokumen4 halamanProp Ae771263af039nwpPenielle SaguindanBelum ada peringkat
- Peppermint Oil as an Effective Mosquito RepellentDokumen4 halamanPeppermint Oil as an Effective Mosquito RepellentKester PlaydaBelum ada peringkat
- Urology MCQ Prometric 3Dokumen138 halamanUrology MCQ Prometric 3Sara Badr57% (7)
- International Journal of Women's DermatologyDokumen5 halamanInternational Journal of Women's DermatologySbomBelum ada peringkat
- PART I: Vocabulary (20 Items - 4,0 Pts - 0,2 PTS/ Item) Questions 1-5Dokumen5 halamanPART I: Vocabulary (20 Items - 4,0 Pts - 0,2 PTS/ Item) Questions 1-5Nguyễn TavirelBelum ada peringkat
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Dokumen70 halamanIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Deborah AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Ice MassageDokumen2 halamanIce Massagevenkata ramakrishnaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Telaah Kritis Artikel Terapi PZ 2020Dokumen7 halamanTelaah Kritis Artikel Terapi PZ 2020dewi arifahniBelum ada peringkat
- Calculi in Dog: A Case Report: Komal, Sweety, Vaishali, Tushar Jain and Man SinghDokumen2 halamanCalculi in Dog: A Case Report: Komal, Sweety, Vaishali, Tushar Jain and Man SinghPandu AWUBelum ada peringkat
- LocalizationDokumen38 halamanLocalizationWilson HannahBelum ada peringkat
- Transfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDokumen3 halamanTransfusion - March April 1966 - Allen - Choice of Blood For Exchange TransfusionDR. KHANBelum ada peringkat
- Patient-Nurse DialogueDokumen3 halamanPatient-Nurse Dialogueristy dian puspitaBelum ada peringkat
- Screening Script and Procedure For Reception and SchedulingDokumen3 halamanScreening Script and Procedure For Reception and SchedulingJobert NarvaezBelum ada peringkat
- GOCABR ProtocolDokumen5 halamanGOCABR Protocolnunuk wijayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Immune Disorders..Ppt FairDokumen79 halamanImmune Disorders..Ppt FairSumi SebastianBelum ada peringkat
- Tog 12091Dokumen4 halamanTog 12091princessmeleana6499Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing PracticeDokumen1 halamanNursing PracticeKateBelum ada peringkat
- Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS)Dokumen2 halamanAthens Insomnia Scale (AIS)Asnairah Cati-an RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Sample RequirementsDokumen7 halamanCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Sample RequirementsDr.Nouf alhasawiBelum ada peringkat