Type1: JDBC (ODBC) Bridge Drivers
Diunggah oleh
optimistic_harishJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Type1: JDBC (ODBC) Bridge Drivers
Diunggah oleh
optimistic_harishHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
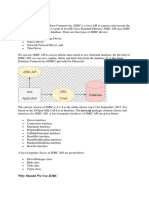
The JDBC API is based mainly on a set of interfaces, not classes.
Its up to the manufacturer of the driver to implement the interfaces with their own set of classes. The above figure is a class diagram that shows the basic JDBC classes and interfaces; these make up the core API. Notice that the only concrete class is DriverManager. The rest of the core API is a set of interfaces. DriverManager is used to load a JDBC Driver. A Driver is a software vendors implementation of the JDBC API. After a driver is loaded, DriverManager is used to get a Connection. In turn, a Connection is used to create a Statement, or to create and prepare a PreparedStatement or CallableStatement. Statement and PreparedStatement objects are used to execute SQL statements. CallableStatement objects are used to execute stored procedures. A Connection can also be used to get a DatabaseMetaData object describing a databases functionality. The results of executing a SQL statement using a Statement or PreparedStatement are returned as a ResultSet. A ResultSet can be used to get the actual returned data or a ResultSetMetaData object that can be queried to identify the types of data returned in the ResultSet. type1 : JDBC (ODBC) Bridge Drivers: This type uses bridge technology to connect a Java Client to a third party API such as ODBC. Sun's JDBC-ODBC bridge is an example of this driver. These drivers are implemented using native code. ex: "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" "jdbc:odbc: dsn" type2 : Native API (Part Java Drivers): These drivers wraps a native API with java classes. The OCI driver is an example of type 2. Because type 2 drivers implemented using local native code, it is expected to have better performance than a pure java drivers. ex: "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" "jdbc:oracle:oci8:@sid" type3 : JDBC-Net Protocol Drivers (Pure Java Drivers):
These drivers communicate using a network protocol to a middle-tier server. The middle tier in turn communicates the Database. Oracle doesn't provide a type3 driver. They do however have a program called "Connection Manager" that, when used in combination with Oracle's type 4 driver, acts as a type 3 drivers in many respects. ex: "ids.sql.IDSDriver" "jdbc.jds://ids.ip:12/con?dsn= dsn" type4 : Native Protocol, (Pure Java Driver) : This type of drivers written early in Java, communicates directly with the Database. No local native code is required. Oracle's thin driver is an example for this. "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" "jdbc:oracle:thin:@ip:1521:sid"
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- JDBC ExcellentDokumen20 halamanJDBC ExcellentNego RemoBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Chapter 1 - Introduction to Java Database ConnectivityDokumen30 halamanJDBC Chapter 1 - Introduction to Java Database ConnectivityFaizan DangeBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity StepsDokumen8 halamanJDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity StepsanuragBelum ada peringkat
- How Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) WorksDokumen29 halamanHow Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) WorksJPBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Advanced JavaDokumen16 halamanUnit-1 Advanced JavaMohit PalveBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Architecture and DriversDokumen82 halamanJDBC Architecture and DriversPallavijoBelum ada peringkat
- Java Database Connectivity (JDBCDokumen29 halamanJava Database Connectivity (JDBCLALITH MOHANBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Questions ExplainedDokumen11 halamanJDBC Questions ExplainedSatish BabuBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Overview What Is JDBC?Dokumen16 halamanJDBC Overview What Is JDBC?jhonBelum ada peringkat
- What Is JDBC DriverDokumen30 halamanWhat Is JDBC Driversneha joshiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5-JDBCmodifiedDokumen8 halamanChapter 5-JDBCmodifiedYohannis DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 JDBC NotesDokumen15 halamanChapter 1 JDBC NotesmariaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - Iii (Working With Database) What Is ODBC?Dokumen25 halamanUnit - Iii (Working With Database) What Is ODBC?Duvva SairamBelum ada peringkat
- JDBCDokumen14 halamanJDBC21r21a3333Belum ada peringkat
- Devjournals - JDBCDokumen13 halamanDevjournals - JDBCPrasanna KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Unit4 Database ConnectivityDokumen12 halamanUnit4 Database ConnectivityPrabesh KarkiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is JDBCDokumen16 halamanWhat Is JDBCbooressaa kachisooBelum ada peringkat
- Database Management System: TechnologyDokumen12 halamanDatabase Management System: Technologyapi-3875928Belum ada peringkat
- UNIT-1.B Java Database Connectivity: What Is JDBC?Dokumen15 halamanUNIT-1.B Java Database Connectivity: What Is JDBC?Ramesh SathriBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 JDBC PrinciplesDokumen4 halaman3.1 JDBC PrinciplesravicsBelum ada peringkat
- What Is JDBC?: Core Java Programming SQL or Mysql DatabaseDokumen11 halamanWhat Is JDBC?: Core Java Programming SQL or Mysql DatabaseKARANAM SANTOSHBelum ada peringkat
- O JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, o Native Driver, o Network Protocol Driver, and o Thin DriverDokumen16 halamanO JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, o Native Driver, o Network Protocol Driver, and o Thin Driverlepeci7607Belum ada peringkat
- Java Database Connectivity: History and ImplementationDokumen20 halamanJava Database Connectivity: History and Implementationatul211988Belum ada peringkat
- Advance Java Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen19 halamanAdvance Java Interview Questions and AnswersDeepak BhagatBelum ada peringkat
- Front End Back End Separation JDBC API Database ConnectivityDokumen63 halamanFront End Back End Separation JDBC API Database ConnectivityAshishBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC (Autosaved)Dokumen45 halamanJDBC (Autosaved)aviaravind753Belum ada peringkat
- Unit3 JDBCDokumen98 halamanUnit3 JDBCMohammed Abdul SalmanBelum ada peringkat
- Creating JDBC ApplicationDokumen23 halamanCreating JDBC Applicationenjoylife_karanBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanJDBC ArchitecturemsukumarbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Dbms - Unit 3 - Notes (Odbc & JDBC)Dokumen29 halamanDbms - Unit 3 - Notes (Odbc & JDBC)ABCBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC MaterialDokumen34 halamanJDBC MaterialLakshmman JsltechBelum ada peringkat
- 1) JDBC-ODBC Bridge DriverDokumen18 halaman1) JDBC-ODBC Bridge DriverVyas AvinashBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-3 AjavaDokumen81 halamanUnit-3 AjavaHarshil VadgamaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBCDokumen8 halamanJDBCPratap Singh RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Sapna Saxena: Presented byDokumen49 halamanSapna Saxena: Presented byRohit SidanaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC 1Dokumen41 halamanJDBC 1Sunny KharbandaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC & OdbcDokumen18 halamanJDBC & OdbcAyush PrinceBelum ada peringkat
- What Is JDBC?: Java Database Connectivity Api Allows Us To Work With RelationalDokumen7 halamanWhat Is JDBC?: Java Database Connectivity Api Allows Us To Work With RelationalSomenath MajhiBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC AssignmentDokumen2 halamanJDBC AssignmentriskBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC NotesDokumen20 halamanJDBC NotesChennamadhavuni SahithiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 5: J2EE and JDBC (Database Access) 1.java Database Connectivity (JDBC)Dokumen29 halamanModule 5: J2EE and JDBC (Database Access) 1.java Database Connectivity (JDBC)sontoshBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Driver Types GuideDokumen9 halamanJDBC Driver Types GuidegitanjalipandaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC NotesDokumen3 halamanJDBC Notesshalakha1992Belum ada peringkat
- JDBC Introduction: Nitin Gupta A-11 Saivatika Devpuri 9302545188 (Web Project Developer)Dokumen8 halamanJDBC Introduction: Nitin Gupta A-11 Saivatika Devpuri 9302545188 (Web Project Developer)nitinguptamca3268Belum ada peringkat
- Java Unit-5 (2B)Dokumen12 halamanJava Unit-5 (2B)Nivas VeeravarapuBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT-III FinalDokumen18 halamanUNIT-III Finalmoaz.sheikh11Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 JDBCDokumen34 halamanChapter 8 JDBCashwini dhageBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC NotesDokumen12 halamanJDBC NotesSeemon BhadoriaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC Chapter 1Dokumen45 halamanJDBC Chapter 1kassahunBelum ada peringkat
- Why Should We Use JDBC: Class - FornameDokumen3 halamanWhy Should We Use JDBC: Class - FornameMaithiliBelum ada peringkat
- Advance JavaDokumen17 halamanAdvance JavaJaimin PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter: 3. Java Data Base Connectivity (JDBC) : 3.1what Is JDBC &Two-Tier Database Design 3.1.1 What Is JDBC?Dokumen13 halamanChapter: 3. Java Data Base Connectivity (JDBC) : 3.1what Is JDBC &Two-Tier Database Design 3.1.1 What Is JDBC?Chetan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC ResultsetDokumen24 halamanJDBC ResultsetNeha NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Java Unit IVDokumen16 halamanJava Unit IVSreejithBelum ada peringkat
- 2484Dokumen44 halaman2484Ankita SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- JDBC DriversDokumen8 halamanJDBC Driversshahidss743886Belum ada peringkat
- Java Database ConnectvityDokumen32 halamanJava Database ConnectvitySHIVAM PANDEYBelum ada peringkat
- JDBCDokumen11 halamanJDBCAnshu PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- BIDM FrameworkDokumen14 halamanBIDM Frameworkoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- OperatorsDokumen34 halamanOperatorsoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Agent-Mediated Trading: Intelligent Agents and E-BusinessDokumen14 halamanAgent-Mediated Trading: Intelligent Agents and E-Businessoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Business Intelligence Using Software Agents: Ana-Ramona BOLOGA Razvan BOLOGADokumen12 halamanBusiness Intelligence Using Software Agents: Ana-Ramona BOLOGA Razvan BOLOGAoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Feedback of FDPDokumen1 halamanFeedback of FDPoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan CollegeDokumen19 halamanFinal Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan Collegeoptimistic_harish67% (3)
- Hide and seek rules for computing elementsDokumen1 halamanHide and seek rules for computing elementsoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Intelligent Agent Based Business Intelligence 1047-1051Dokumen5 halamanIntelligent Agent Based Business Intelligence 1047-1051jayas2k5Belum ada peringkat
- Three Days National Level Online FDP On " Introduction To Machine Learning " From 05th To 07th of JUNE 2020 - QuizDokumen7 halamanThree Days National Level Online FDP On " Introduction To Machine Learning " From 05th To 07th of JUNE 2020 - Quizoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Status - OSDokumen4 halamanSyllabus Status - OSoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Spoken Tutorial, IIT Bombay R Introduction To Basics of R - AssignmentDokumen1 halamanSpoken Tutorial, IIT Bombay R Introduction To Basics of R - Assignmentoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Basics of R Assignment PDFDokumen1 halamanIntroduction To Basics of R Assignment PDFoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- A Survey of Predicting Depression Level Using Social MediaDokumen4 halamanA Survey of Predicting Depression Level Using Social Mediaoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- FDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment SubmissionDokumen12 halamanFDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment Submissionoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Status R1 BCM06102 Application Web Security & SDLCDokumen4 halamanSyllabus Status R1 BCM06102 Application Web Security & SDLCoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- ITIL Syllabus Completion ReportDokumen4 halamanITIL Syllabus Completion Reportoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Multi Threaded ProgrammingDokumen56 halamanMulti Threaded Programmingoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- OperatorsDokumen34 halamanOperatorsoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Java StringBuffer MethodsDokumen22 halamanJava StringBuffer Methodsoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Gui Layout ManagerDokumen23 halamanGui Layout ManagerAnshy SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan CollegeDokumen19 halamanFinal Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan Collegeoptimistic_harish67% (3)
- FDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment SubmissionDokumen12 halamanFDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment Submissionoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Oops With Java: Kirti MathurDokumen40 halamanOops With Java: Kirti Mathuroptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Java GenericsDokumen5 halamanJava Genericsoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Ruby Introduction: A Concise Guide to the Ruby Programming LanguageDokumen74 halamanRuby Introduction: A Concise Guide to the Ruby Programming Languageoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Pyton BookDokumen15 halamanPyton Bookoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- jAVA TTENDENCEDokumen2 halamanjAVA TTENDENCEoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan CollegeDokumen19 halamanFinal Exam - Click Here To Start The Exam - FDPMOOCs01 Courseware - MOOC Platform of Ramanujan Collegeoptimistic_harish67% (3)
- Introduction to R basics - Log, Exp functions and Help tabDokumen1 halamanIntroduction to R basics - Log, Exp functions and Help taboptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- FDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment SubmissionDokumen12 halamanFDP Indoglobal Group of Colleges: 27 April To 1 May R Programming Language Assignment Submissionoptimistic_harishBelum ada peringkat
- Lista Precio Septiembre 0609Dokumen75 halamanLista Precio Septiembre 0609gBelum ada peringkat
- Simplex Addressable Breakglass PDFDokumen12 halamanSimplex Addressable Breakglass PDFNurrul Ahmad Hidayat100% (1)
- CFEExam Prep CourseDokumen28 halamanCFEExam Prep CourseM50% (4)
- Inflatable Packers enDokumen51 halamanInflatable Packers enDavid LuhetoBelum ada peringkat
- Enerflex 381338Dokumen2 halamanEnerflex 381338midoel.ziatyBelum ada peringkat
- MATH2070 Computer Project: Organise Porject FoldDokumen4 halamanMATH2070 Computer Project: Organise Porject FoldAbdul Muqsait KenyeBelum ada peringkat
- Emperger's pioneering composite columnsDokumen11 halamanEmperger's pioneering composite columnsDishant PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Hardened Concrete - Methods of Test: Indian StandardDokumen16 halamanHardened Concrete - Methods of Test: Indian StandardjitendraBelum ada peringkat
- Product Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssembliesDokumen10 halamanProduct Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssemblieslmarcheboutBelum ada peringkat
- NEW CREW Fast Start PlannerDokumen9 halamanNEW CREW Fast Start PlannerAnonymous oTtlhP100% (3)
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1Dokumen7 halamanDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1api-235617848Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical Design of A PLC Panel (Wiring Diagrams) - EEPDokumen6 halamanBasic Electrical Design of A PLC Panel (Wiring Diagrams) - EEPRobert GalarzaBelum ada peringkat
- DSA NotesDokumen87 halamanDSA NotesAtefrachew SeyfuBelum ada peringkat
- Fabric Bursting StrengthDokumen14 halamanFabric Bursting StrengthQaiseriqball100% (5)
- Fundamentals of Marketing NotebookDokumen24 halamanFundamentals of Marketing NotebookMorrisa AlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Department Order No 05-92Dokumen3 halamanDepartment Order No 05-92NinaBelum ada peringkat
- Part I-Final Report On Soil InvestigationDokumen16 halamanPart I-Final Report On Soil InvestigationmangjuhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Growatt SPF3000TL-HVM (2020)Dokumen2 halamanGrowatt SPF3000TL-HVM (2020)RUNARUNBelum ada peringkat
- API MidtermDokumen4 halamanAPI MidtermsimranBelum ada peringkat
- Rencana Pembelajaran Semester Sistem Navigasi ElektronikDokumen16 halamanRencana Pembelajaran Semester Sistem Navigasi ElektronikLastri AniBelum ada peringkat
- Craft's Folder StructureDokumen2 halamanCraft's Folder StructureWowBelum ada peringkat
- Project The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDDokumen7 halamanProject The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDmorraz360Belum ada peringkat
- Empowerment Technologies Learning ActivitiesDokumen7 halamanEmpowerment Technologies Learning ActivitiesedzBelum ada peringkat
- Portable dual-input thermometer with RS232 connectivityDokumen2 halamanPortable dual-input thermometer with RS232 connectivityTaha OpedBelum ada peringkat
- The SAGE Handbook of Digital JournalismDokumen497 halamanThe SAGE Handbook of Digital JournalismK JBelum ada peringkat
- Ju Complete Face Recovery GAN Unsupervised Joint Face Rotation and De-Occlusion WACV 2022 PaperDokumen11 halamanJu Complete Face Recovery GAN Unsupervised Joint Face Rotation and De-Occlusion WACV 2022 PaperBiponjot KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Gates em Ingles 2010Dokumen76 halamanGates em Ingles 2010felipeintegraBelum ada peringkat
- Bob Wright's Declaration of BeingDokumen1 halamanBob Wright's Declaration of BeingBZ Riger100% (2)
- Advance Bio-Photon Analyzer ABPA A2 Home PageDokumen5 halamanAdvance Bio-Photon Analyzer ABPA A2 Home PageStellaEstel100% (1)
- ADSLADSLADSLDokumen83 halamanADSLADSLADSLKrishnan Unni GBelum ada peringkat