8th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013
Diunggah oleh
api-70433300Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
8th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013
Diunggah oleh
api-70433300Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
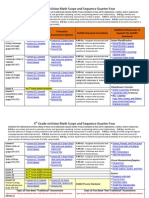
8th Grade Math Connects Planning Guide Quarter Four 2012-2013
UNIT 3: Geometry and Measurement
Chapter 10: Algebra: Nonlinear Functions and Polynomials
Personal Tutor Examples
Formative Assessment: Lesson Quiz Online
DoDEA Standard Correlation
Additional Resources Related to the DoDEA Standards
Chapter Resources: Chapter 10 Readiness Quiz, Chapter 10 Family Letter Ex 1: Identify Functions Lesson 10-1 Lesson 10-1: Using Tables Quiz Linear and Ex 2: Identify Functions Nonlinear Using Tables functions Ex 3: Identify Functions (pg. 528) Using Graphs Ex 4: Identify Functions Using Graphs Ex 5: Identify Functions Using Equations Ex 6: Identify Functions Using Equations Ex 7: Real World Example Lesson 10-2: Ex 1: Graph Quadratic Lesson 10-2 Graphing Functions Quiz Quadratic Ex 2: Graph Quadratic Functions Functions (pg. 534) Ex 3: Graph Quadratic Functions Ex 4: Graph Quadratic Functions Ex 5: Real World Example
Problem Solving Journals by Lesson:Chapter 10 Journals
8.M.2.b: identify functions as linear or nonlinear and contrast their properties using tables, graphs, or equations; 8.M.2.c: analyze relationships between linear equations and their graphs by connecting the meaning of intercepts and slope to the context of the situation; 8.M.2.d: use symbolic algebra to represent situations and to solve problems involving linear and nonlinear relationships;
Lesson Plans/Practice: Smart Board-Linear Functions Using Tables SmartBoard-Linear/Nonlinear using tables, graphs, and equations Standard Deviants School The Basics Exponents and Multiplication
(Manipulative)
Exponents and Division
(Manipulative)
Lesson 10-3: Problem Solving Investigation: Make a Mode (pg. 538) Lesson 10-4: Graphing Cubic Functions (pg. 540)
Ex 1: Make a Model
Lesson 10-3 Quiz
8.M.2.b: identify functions as linear or nonlinear and contrast their properties using tables, graphs, or equations; 8.M.2.d: use symbolic algebra to represent situations and to solve problems involving linear and nonlinear relationships; 8.M.2.h: represent and solve problems using various representations, e.g., graphs, tables, and equations; DoDEA Process Standards 8.M.3.f: use geometric models to represent and explain numerical and algebraic relationships; 8.M.2.d: use symbolic algebra to represent situations and to solve problems involving linear and nonlinear relationships;
Algebra I Recipe: Division Properties of Exponents Algebra I Recipe: Exponents and Order of Operations Algebra I Recipe: Multiplication and Division of Real Numbers Algebra I Recipe: Multiplication Properties of Exponents, Negative, and Zero Exponents Notes: Multiplying Monomials (ppt) Video/Lesson Tutorials: TEAMS: Algebraic Concepts for Middle School: Patterns and Functions (discovery education) Functions: Inputs and OutputsCalories Burned Running ((discovery education)
Ex 1: Graph a Cubic Function Ex 2: Real World Example
Lesson 10-4 Quiz
Extend 10-4: Graphing Calculator Lab: Families of Nonlinear Functions (pg. 544) Lesson 10-5: Multiplying Monomials (pg. 545)
See Lesson 10-4
8.M.2.h: represent and solve problems using various representations, e.g., graphs, tables, and equations; 8.M.2.b: identify functions as linear or nonlinear and contrast their properties using tables, graphs, or equations;
Functions: Inputs and OutputsBBQ Party Planning (discovery Math Factor: General Quadratic Relation: An Introductions
(discovery education) education)
Ex 1: Multiply Powers Ex 2: Multiply Powers Ex 3: Real World Example Ex 4: Multiply Negative Powers
Lesson 10-5 Quiz
Lesson 10-6: Dividing Monomials (pg. 550)
Ex 1: Divide Powers Ex 2: Divide Powers Ex 3: Use Negative Exponents Ex 4: Use Negative Exponents Ex 5: Test Example Ex 6: Real World Example Ex 1: Find the Power of a Power Ex 2: Find the Power of a Power Ex 3: Power of a Product Ex 4: Power of a Product Ex 5: Real World Example
Lesson 10-6 Quiz
Lesson 10-7: Powers of Monomials (pg. 555)
Lesson 10-7 Quiz
8.M.1.a: use the law of exponents for integer exponents; 8.M.1.b: explain the meaning of exponents that are negative and zero; 8.M.1.c: use scientific, exponential, and calculator notation to express very large or small numbers; 8.M.1.f: apply order of operations to simplify expressions and perform operations involving numbers written in exponential notation or radical form; 8.M.2.e: recognize, generate, and justify equivalent forms of algebraic expressions; 8.M.1.a: use the law of exponents for integer exponents; 8.M.1.b: explain the meaning of exponents that are negative and zero; 8.M.1.f: apply order of operations to simplify expressions and perform operations involving numbers written in exponential notation or radical form; 8.M.2.e: recognize, generate, and justify equivalent forms of algebraic expressions; 8.M.1.a: use the law of exponents for integer exponents; 8.M.1.b: explain the meaning of exponents that are negative and zero; 8.M.1.c: use scientific, exponential, and calculator notation to express very large or small numbers; 8.M.1.f: apply order of operations to simplify expressions and perform operations involving numbers written in exponential notation or radical form;
Discovering Algebra With Graphing Calculators: Exploring Quadratics (discovery education) Math Factor: General Quadratic Relation: An Introductions
(discovery education)
Introduction to the quadratic equation Quadratic Equation part 2 Completing the square Quadratic Formula (proof) Applying Quadratic Functions 1 Quadratic Functions 1 Rules for Simplifying Exponents with Similar Bases (discovery
education)
Algebra: Exponents (discovery
education)
Exponent Properties 1 (Khan) Exponent Properties 2 (Khan) Exponent Properties 3 (Khan) Exponent Properties 4 (Khan) Exponent Properties 5 (Khan) Exponent Properties 6 (Khan) Exponent Properties 7 (Khan) Multiplying Monomials PH Multiplying Powers with the Same Base PH Multiplying Powers in an Algebraic Expression PH Simplifying a Power Raised to a Power PH Raising a Product to a Power
Lesson 10-8: Roots of Monomials (pg. 559)
Ex 1: Simplify Square Roots Ex 2: Simplify Square Roots Ex 3: Simplify Cube Roots Ex 4: Simplify Cube Roots Ex 5: Real World Example
Lesson 10-8 Quiz
8.M.2.e: recognize, generate, and justify equivalent forms of algebraic expressions; 8.M.1.f: apply order of operations to simplify expressions and perform operations involving numbers written in exponential notation or radical form; 8.M.2.e: recognize, generate, and justify equivalent forms of algebraic expressions;
Interactive Notes: Rules for Exponents Manipulatives/Applets: LAB-Linear and Nonlinear Functions LAB-Graphing Quadratic Functions LAB-Powers of Monomials Function Flyer Function Machine Linear Function Machine
Chapter 11: Statistics
Personal Tutor Examples
UNIT 5: Statistics, Data Analysis, and Probability Formative Assessment: DoDEA Standard Correlation Lesson Quiz Online
Additional Resources Related to the DoDEA Standards
Chapter Resources: Chapter 11 Readiness Quiz, Chapter 11 Family Letter Problem Solving Journals by Lesson: Chapter 11 Journals Lesson 11-1: Ex 1: Make a Table Lesson 11-1 Quiz DoDEA Process Standards Lesson Plans/Practice: 8.M.2.h: represent and solve problems Problem Solving Play Ball! Activity Pack using various representations, e.g., Investigation: Math Activity 1: Football (pg. 11-12) graphs, tables, and equations; Make a Table Math Activity 2: Soccer (pg. 13-14) Math Activity 3 Basketball(pg.15-17) (pg. 574) Math Activity 4: Baseball (pg.18-21) 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct Ex 1: Construct a Histogram Lesson 11-2 Quiz Lesson 11-2: graphical representations for discrete and Learning about Histograms Ex 2: Analyze and Interpret Histograms continuous data; Data Histogram Application/Practice (pg. 576) 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and Ex 3: Analyze and Interpret Exploring Histograms appropriate arguments for a conclusion Data Bitesize math-histograms based on analysis of data presented Practice with Circle Graphs 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or Constructing Circle Graph Activity common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct SmartBoard-Measures of See Lesson 11-2 Extend 11-2: graphical representations for discrete and Dispersion Graphing continuous data; Calculator Lab: That Quiz-Averages 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and Histograms Human Box and Whisker plot appropriate arguments for a conclusion (pg. 581) Project based on analysis of data presented SmartBoard-Box-and-Whisker Plot 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or Stem and Leaf Examples common errors in data analysis; SKUNK-a stem and leaf plot Ex 1: Construct a Circle Lesson 11-3 Quiz 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct Lesson 11-3: Graph From Percents activity graphical representations for discrete and Circle Graphs continuous data; Ex 2: Construct a Circle Box and Whisker Plot (pg. 582) 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and Graph from Data
Ex 3: Analyze and Interpret Data
Extend 11-3: Spreadsheet Lab: Line, Bar, and Circle Graphs (pg. 589)
See Lesson 11-3
Lesson 11-4: Measures of Central Tendency and Range (pg. 591)
Ex 1: Find Measures of Central Tendency and Range Ex 2: Real World Example Ex 3: Test Example
Lesson 11-4 Quiz
Extend 11-4: Spreadsheet Lab: Mean, Median, and Mode (pg. 597) Lesson 11-5: Measures of Variation (pg. 599)
Ex 1: Find Measures of Variation Ex 2: Find Outliers Ex 3: Use Measures of Variation to Describe Data Lesson 11-5 Quiz
Lesson 11-6: Box and Whisker Plots (pg. 611)
Ex 1: Construct a Box and Whisker Plot Ex 2: Interpret Data Ex 3: Compare Data
Lesson 11-6 Quiz
appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct graphical representations for discrete and continuous data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.b: find, interpret, and use measures of center, quartile, and interquartile range to compare two sets of data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.b: find, interpret, and use measures of center, quartile, and interquartile range to compare two sets of data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.b: find, interpret, and use measures of center, quartile, and interquartile range to compare two sets of data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct graphical representations for discrete and continuous data; 8.M.5.b: find, interpret, and use measures of center, quartile, and interquartile range to compare two sets of data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis;
Line Graph and Central Tendency Unit Video/Lesson Tutorials: Exploring Data Displays and Graphs Difference Between Continuous and Discrete Data (discovery education) Study Jams-Histograms Study Jams-Circle Graph Study Jams-Stem-and-Leaf Plots Babe Ruth-Mean, Median, Mode (brainpop account) Study Jam-Mean Study Jams-Median Study Jams-Mode Box-and-whisker plots (khan) Constructing a box-and-whisker plot Box-and-Whisker Plots (khan) Creating box and whisker plots Example: Range and mid-range Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots ( Manipulatives/Applets: Cool Graphing-six displays LAB-Making Circle Graphs Interactive Circle Graph Box and Whiskers Applet Interactive Histogram Review Mean, Median, Mode, Range Review Bar Graphs Review Pictographs Interpret Circle Graphs Box and Whisker Plots II Review Line Graphs Review Circle Graphs Review Stem and Leaf Plots
Extend 11-6: Graphing Calculator Lab: Box and Whisker Plots (pg. 612)
See Lesson 11-6
Lesson 11-7: Stem and Leaf Plots (pg. 612)
Ex 1: Real World Example Ex 2: Real World Example Ex 3: Real World Example
Lesson 11-7 Quiz
Lesson 11-8: Select an Appropriate Display (pg. 617)
Ex 1: Select an Appropriate Graph Ex 2: Construct an Appropriate Display
Lesson 11-8 Quiz
8.M.5.a: know and use the correct graphical representations for discrete and continuous data; 8.M.5.b: find, interpret, and use measures of center, quartile, and interquartile range to compare two sets of data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct graphical representations for discrete and continuous data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis; 8.M.5.a: know and use the correct graphical representations for discrete and continuous data; 8.M.5.e: construct convincing and appropriate arguments for a conclusion based on analysis of data presented 8.M.5.f: identify faulty arguments or common errors in data analysis;
Mean, Median, Mode and Range of Bar Graphs, Line Graphs Histograms Interactive Bar Graph Interactive Line Graph Interactive Stem and Leaf Interactive Circle Graph Games: Mean, Median, and Mode Game Mean, Median, Mode, and RangeJeopardy The Mean Machine Mean Runners That Quiz-Averages Shark Game Train Race Mean Runners Bar Chart Making Double Bar Graphs Line Graphs Exploring Circle Craphs Making Circle Graphs Great Graphs Box and Whisker Graph Box Plot
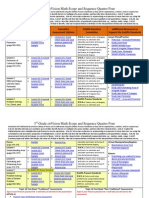
Chapter 12: Probability
Personal Tutor Examples
Formative Assessment: Lesson Quiz Online
DoDEA Standard Correlation
Additional Resources Related to the DoDEA Standards
Chapter Resources: Chapter 12 Readiness Quiz, Chapter 12 Family Letter Lesson 12-1: Ex 1: Use Tree Diagrams Lesson 12-1 Counting Ex 2: Real World Example Quiz Outcomes Ex 3: Real World Example (pg. 632) Lesson 12-2: Ex 1: Independent Events Lesson 12-2 Probability of Ex 2: Test Example Quiz Compound Events Ex 3: Real World Example (pg. 637)
Problem Solving Journals by Lesson: Chapter 12 Journals 8.M.5.g: compute the probability of the occurrence of independent and simple dependent events; 8.M.5.g: compute the probability of the occurrence of independent and simple dependent events;
Lesson Plans/Practice:
Are you Game? Activity pack
Math Activity 1: Race to the Top (pg. 7-9) Math Activity 2: Fair Spinners (pg. 10-11) Math Activity 3: Its In the Bag (pg. 12-14) Math Activity 4: Odd Man Out (pg. 15-17) Math Activity 5: Tossing Coins (pg. 18-20)
Practice Quiz page 21
Lesson 12-3: Experimental and Theoretical probability (pg. 643)
Ex 1: Theoretical and Experimental Probability Ex 2: Theoretical and Experimental Probability Ex 3: Real World Example Ex 4: Use Probability to Predict See Lesson 12-3
Lesson 12-3 Quiz
8.M.5.g: compute the probability of the occurrence of independent and simple dependent events;
Interactive Probability and Experimental Probability Activity Probability Question Set Independent and Dependent Events Probability Notes Exploring probability Video/Lesson Tutorials: Spy Guys Probability Basic Probability (your school must have a brainpop account) Study Jam-Finding Probability Study Jam-Identifying Outcomes and Making Predictions Compound Events (discovery) Basic Probability (brainpop) Independent and Dependent Events (brainpop account) Dependent Events Manipulatives/Applets: Spinner Applet Spinner Applet 2 Dice Applet LAB-Theoretical and Experimental Probability Games: Stick or Switch Probability Pond Basic Probability Practice Catching Critters Probability Fair Pulling Objects form a Bag Probability Circus
Extend 12-3: Probability Lab: Fair Games (pg. 648) Lesson 12-4: Problem Solving Investigation: Act it Out (pg. 650) Lesson 12-5: Using Sampling to Predict (pg. 653)
8.M.5.g: compute the probability of the occurrence of independent and simple dependent events;
Lesson 12-4 Quiz Ex 1: Act it Out
DoDEA Process Standards
Ex 1: Determine Validity of Conclusions Ex 2: Determine Validity of Conclusions Ex 3: Real World Example
Lesson 12-5 Quiz
8.M.5.d: compare sampling methods and analyze effects of random versus biased sampling and justify conclusions;
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Math 8 Commom Core SyllabusDokumen6 halamanMath 8 Commom Core Syllabusapi-261815606Belum ada peringkat
- Syllabus S. E. CSE SUKDokumen35 halamanSyllabus S. E. CSE SUKMohan KalawateBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Unit CoverDokumen3 halamanLesson Unit Coverapi-243105694Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Algebra/Trigonometry SemesterDokumen5 halamanAdvanced Algebra/Trigonometry SemesterAustin ChiversBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Project Educ 5312 WeeblyDokumen6 halamanLesson Plan Project Educ 5312 Weeblyapi-290266366Belum ada peringkat
- Algebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen3 halamanAlgebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Schemes of Work Year 8 (3) - 07-07-2011Dokumen8 halamanSchemes of Work Year 8 (3) - 07-07-2011DeanoTempBelum ada peringkat
- Diana Curriculum AnalysisDokumen14 halamanDiana Curriculum Analysisapi-245618390Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 10 10 13Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 10 10 13api-242219136Belum ada peringkat
- Rational, and Exponential FunctionsDokumen19 halamanRational, and Exponential Functionsapi-494459090Belum ada peringkat
- Graph Functions and Inverses with Geometer's SketchpadDokumen8 halamanGraph Functions and Inverses with Geometer's SketchpadsaikeungBelum ada peringkat
- AP Calculus AB BC MapDokumen10 halamanAP Calculus AB BC Mapsapabapjava2012Belum ada peringkat
- Course Syllabus in Mathematics IIDokumen9 halamanCourse Syllabus in Mathematics IIGena ClarishBelum ada peringkat
- MathDokumen15 halamanMathapi-253418585Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra 1-2 Curriculum Map All UnitsDokumen31 halamanAlgebra 1-2 Curriculum Map All Unitsapi-281539956Belum ada peringkat
- CHSD230 Math 1 Module 4 SEDokumen80 halamanCHSD230 Math 1 Module 4 SETravis EubanksBelum ada peringkat
- CHSD230 Math 1 Honors Module 4H SEDokumen82 halamanCHSD230 Math 1 Honors Module 4H SEAngela LynnBelum ada peringkat
- Growing Growing Growing Unit PlanDokumen22 halamanGrowing Growing Growing Unit Planapi-250461623100% (1)
- Curriculum Plan Due Jan 24Dokumen7 halamanCurriculum Plan Due Jan 24api-253074922Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd Observation Lesson PlanDokumen4 halaman3rd Observation Lesson Planapi-701564760Belum ada peringkat
- NUMERICAL ANALYSIS SUBJECTDokumen3 halamanNUMERICAL ANALYSIS SUBJECTFlorin MatisBelum ada peringkat
- Technology Website - Math Link Write Up by UnitsDokumen12 halamanTechnology Website - Math Link Write Up by UnitsJose Luis MaldonadoBelum ada peringkat
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDokumen6 halaman8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022Dokumen12 halamanYear 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022sumBelum ada peringkat
- HS PreAlgebraDokumen12 halamanHS PreAlgebranixdorfjBelum ada peringkat
- M8u2 Parent LetterDokumen2 halamanM8u2 Parent Letterapi-328200095Belum ada peringkat
- CHSD230 Math 1 Honors Module 4H TEDokumen110 halamanCHSD230 Math 1 Honors Module 4H TEAngela LynnBelum ada peringkat
- Adv Algebra Unit 3Dokumen7 halamanAdv Algebra Unit 3api-264152935Belum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17Dokumen1 halamanCurriculum Map Math 7+ 16-17st72136Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - Ratios and PercentsDokumen4 halamanChapter 7 - Ratios and Percentsmsbakermath100% (1)
- sm1 WK 17 Functions and RelationsDokumen2 halamansm1 WK 17 Functions and Relationsapi-138117317Belum ada peringkat
- Math 2411Dokumen8 halamanMath 2411YktashBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Notes 8 Asal ItDokumen10 halamanTeaching Notes 8 Asal ItJesu Savarimuthu ArockiamBelum ada peringkat
- S3 Ma Sow (2013)Dokumen13 halamanS3 Ma Sow (2013)Francis Ho HoBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra 1aDokumen8 halamanAlgebra 1aapi-310256368Belum ada peringkat
- Syllabus 3 AP Calculus BC Course OutlineDokumen5 halamanSyllabus 3 AP Calculus BC Course OutlineEbuka EfobiBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDokumen3 halamanDigital Unit Plan Templateapi-239653134Belum ada peringkat
- University of The East - Caloocan College of Arts and SciencesDokumen8 halamanUniversity of The East - Caloocan College of Arts and SciencesRafe Alexis MiravillaBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Mathematics Scheme of Work Form 4 (2012)Dokumen24 halamanAdditional Mathematics Scheme of Work Form 4 (2012)Zabidah Awang100% (3)
- School Ytd by Strand and SkillDokumen70 halamanSchool Ytd by Strand and Skillapi-236897542Belum ada peringkat
- Barbara Adams: Judy B. Basara Sylva CohnDokumen19 halamanBarbara Adams: Judy B. Basara Sylva Cohnnickmlee1Belum ada peringkat
- 8th Math Curriculum MapDokumen7 halaman8th Math Curriculum Mapapi-261608473Belum ada peringkat
- Polynomial Functions Unit PlanDokumen10 halamanPolynomial Functions Unit Planapi-255851513Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra Khan Academy Correlation To Spring BoardDokumen18 halamanAlgebra Khan Academy Correlation To Spring Boardapi-293229664Belum ada peringkat
- AP Calculus BC SyllabusDokumen7 halamanAP Calculus BC SyllabusengrroyBelum ada peringkat
- 0580 Y05 SW 1 2Dokumen3 halaman0580 Y05 SW 1 2zurichasBelum ada peringkat
- MathPower 10 Practise MastersDokumen126 halamanMathPower 10 Practise MastersUjwal Boppana83% (6)
- Gwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics: Grade 4 - Instructional Calendar 2020-2021Dokumen3 halamanGwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics: Grade 4 - Instructional Calendar 2020-2021api-519622916Belum ada peringkat
- Pa TextbookDokumen338 halamanPa TextbooksunethraBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating Means and PercentagesDokumen7 halamanCalculating Means and PercentagesRida SnobBelum ada peringkat
- Math 10c Long Range PlanDokumen6 halamanMath 10c Long Range Planapi-266460789Belum ada peringkat
- Math 7 Scope and Sequence 2014-15 v2Dokumen28 halamanMath 7 Scope and Sequence 2014-15 v2api-281653314Belum ada peringkat
- Algebra 2 Curriculum Map One DocumentDokumen38 halamanAlgebra 2 Curriculum Map One DocumentrapnycBelum ada peringkat
- Sway 1Dokumen14 halamanSway 1api-405242909Belum ada peringkat
- Math g5 m1 Full ModuleDokumen249 halamanMath g5 m1 Full ModulepeppylepepperBelum ada peringkat
- Quadratic Equations & FunctionsDokumen5 halamanQuadratic Equations & FunctionsAlex WellmanBelum ada peringkat
- Additional Maths Form 4 Yearly Plan 2012Dokumen17 halamanAdditional Maths Form 4 Yearly Plan 2012丽娜钱霙Belum ada peringkat
- A First Course in Scientific Computing: Symbolic, Graphic, and Numeric Modeling Using Maple, Java, Mathematica, and Fortran90Dari EverandA First Course in Scientific Computing: Symbolic, Graphic, and Numeric Modeling Using Maple, Java, Mathematica, and Fortran90Penilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (2)
- Digital SAT Math Prep For Dummies, 3rd Edition: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatDari EverandDigital SAT Math Prep For Dummies, 3rd Edition: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatBelum ada peringkat
- 7th Grade Math Connects Planning Guide Quarter Four 2012-2013Dokumen4 halaman7th Grade Math Connects Planning Guide Quarter Four 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- 6th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013Dokumen8 halaman6th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- 4th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Dokumen9 halaman4th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Discrete Math Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen3 halamanDiscrete Math Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Dokumen10 halaman3rd Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- 5th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Dokumen8 halaman5th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Analysis Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen5 halamanAnalysis Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Alg 2 Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen7 halamanAlg 2 Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Absolute ValueDokumen19 halamanAbsolute Valueapi-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Alg I Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen7 halamanAlg I Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Geometry Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen6 halamanGeometry Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Grad Credit Course Guidelines-Nspire TechnologyDokumen3 halamanGrad Credit Course Guidelines-Nspire Technologyapi-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Algebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Dokumen3 halamanAlgebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- TI-Nspire CX ManualDokumen118 halamanTI-Nspire CX Manualjsmith96Belum ada peringkat
- Ap Job-Alike Facilitator Summary 2012Dokumen1 halamanAp Job-Alike Facilitator Summary 2012api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- Ap Job-Alike Agenda 2012Dokumen1 halamanAp Job-Alike Agenda 2012api-70433300Belum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 12 Relations and Functions NotesDokumen3 halamanCBSE Class 12 Relations and Functions NotesJeffrish raidnBelum ada peringkat
- Fuzzy Sets and LogicDokumen12 halamanFuzzy Sets and LogicSelvakumariBelum ada peringkat
- Lord Immanuel Institute Foundation, Inc.: First Periodical Test in Mathematics 9Dokumen5 halamanLord Immanuel Institute Foundation, Inc.: First Periodical Test in Mathematics 9Cee Jay AbanillaBelum ada peringkat
- JC1 Math - H2 - 2019Dokumen347 halamanJC1 Math - H2 - 2019GQGrace TohBelum ada peringkat
- Rancangan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Semester: LAM-PT-05-01Dokumen3 halamanRancangan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Semester: LAM-PT-05-01Arul VelanBelum ada peringkat
- Function Approximation Using Polynomials and ProjectionsDokumen23 halamanFunction Approximation Using Polynomials and ProjectionsSean HsuBelum ada peringkat
- MEI A Level Maths Year 1 (As) 4th EditionDokumen562 halamanMEI A Level Maths Year 1 (As) 4th EditionBruh Moment100% (3)
- Calculus For Beginners and Artists: AppletsDokumen44 halamanCalculus For Beginners and Artists: AppletsShyamgBelum ada peringkat
- General Mathematics Week 1-Quarter 1Dokumen57 halamanGeneral Mathematics Week 1-Quarter 1Kay Si100% (1)
- GE3151Dokumen251 halamanGE3151dropoutsree07Belum ada peringkat
- 2007 Metro bank MTAP - DepEd Math ChallengeDokumen2 halaman2007 Metro bank MTAP - DepEd Math ChallengeJoe Titular100% (4)
- Elementary Real Analysis: Second Edition (2008)Dokumen16 halamanElementary Real Analysis: Second Edition (2008)Erfan Ipank Epang'sBelum ada peringkat
- Various Fuzzy Numbers and Their Various Ranking ApproachesDokumen10 halamanVarious Fuzzy Numbers and Their Various Ranking ApproachesIAEME PublicationBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Delhi Govt. Schools PTS-23 Math ExamDokumen6 halamanCBSE Delhi Govt. Schools PTS-23 Math ExamShweta ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Laws of Indices and LogarithmsDokumen50 halamanLaws of Indices and LogarithmsAnimeBelum ada peringkat
- Fish Beginner'S Guide: Fish in 3dec Contents - 1Dokumen8 halamanFish Beginner'S Guide: Fish in 3dec Contents - 1Cristian Eduardo Caceres HuespeBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Excel XP/2003,: Level 100Dokumen10 halamanMicrosoft Excel XP/2003,: Level 100nishaXDBelum ada peringkat
- Rumus ExcelDokumen83 halamanRumus ExcelAndri BagusBelum ada peringkat
- Definite IntegrationDokumen73 halamanDefinite IntegrationAdiAyush SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Differences CalculationDokumen13 halamanFinite Differences Calculationrichie2885Belum ada peringkat
- Graphing Piecewise and Step FunctionsDokumen23 halamanGraphing Piecewise and Step FunctionsAhmed Abdel-RahimBelum ada peringkat
- Calculated Fields in WorkdayDokumen203 halamanCalculated Fields in Workdaysudeep chowdary100% (3)
- Mathematics Quiz 1 Prelims Kuya MeccsDokumen13 halamanMathematics Quiz 1 Prelims Kuya MeccsBeng BebangBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Examination in General Mathematics 11 2022-2023Dokumen6 halamanMidterm Examination in General Mathematics 11 2022-2023Benjie PogoyBelum ada peringkat
- Denotational SemanticsDokumen304 halamanDenotational SemanticsAnuj MoreBelum ada peringkat
- DLL General MathematicsDokumen3 halamanDLL General MathematicsTrisTan Dolojan97% (31)
- SAP S/4HANA Margin Analysis GuideDokumen85 halamanSAP S/4HANA Margin Analysis GuideSunil GBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 10: Introduction To VB Built-In Functions: 10.1 Msgbox FunctionDokumen17 halamanLesson 10: Introduction To VB Built-In Functions: 10.1 Msgbox Functionalokkumar_9365Belum ada peringkat
- Calculus I CompleteDokumen578 halamanCalculus I Completexenocid3r83% (6)
- Syllabus MATDIP301 MATDIP401 PDFDokumen1 halamanSyllabus MATDIP301 MATDIP401 PDFManjunath M100% (1)