Unit 4 The Respiratory System
Diunggah oleh
Dara MooreJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unit 4 The Respiratory System
Diunggah oleh
Dara MooreHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Science Interactive LTD
Science base multimedia CD-ROM for PC is a collection of 38 units or tools totalling over 1150 PowerPoint slides. Each unit covers a wide range of different delivery and learning styles, offering an exciting way to involve your pupils during lessons or revision sessions. All styles of teaching and learning are supported through use of high quality images, graphics, challenging exercises and questions. Units can be used in the classroom via an interactive whiteboard, data projector or used during individual study via a PC or school network.
Science Interactive LTD. PO BOX 50764 LONDON NW6 9AT email: sales@science-interactive.co.uk
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
web: www:science-interactive.co.uk
Unit 1: The Digestive System Unit 2: The Circulatory System Unit 3: Healthy Body and Immunity Unit 4: The Respiratory System Unit 5: Nervous System and the Senses Unit 6: Human Homeostasis Unit 7: Hormones and the Endocrine System Unit 8: Drugs and Bad Body Maintenance Unit 9: Photosynthesis in Green Plants Unit 10: Water Transport in Plants Unit 11: Flow of Energy and Elements through the Environment Unit 12: Mitosis and Meiosis Unit 13: Inheritance and Selection Unit 14: Evolution and Human Impact Unit 15: Genetic Engineering Unit 16: The Periodic Table and its Elements Unit 17: The Alkali Metals Unit 18: Metals and their Properties Unit 19: The Transitional Metals
Unit 20: Crude Oil and its Products Unit 21: Rock Cycle Unit 22: Elements, Molecules and Compounds Unit 23: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Unit 24: The Halogens, their Uses and Compounds Unit 25: The Noble Gases, their Properties and Uses Unit 26: Rates of Reaction Unit 27: Energy Unit 28: Generating Electricity and its Domestic Use Unit 29: Electricity Unit 30: Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Unit 31: Radioactivity Unit 32: Newton's Forces and the Effects of Forces Unit 33: Earth and Space Unit 34: The Earth and Plate Tectonics Unit 35: The Alkaline Earth Metals Unit 36: Sound and Hearing Unit 37: Natural Forces Unit 38: Cells, Tissue, Organs and Organs systems
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
z z
Unit 4 The Respiratory System
Unit 4: The Respiratory System
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Understand:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Keywords:
Lungs, Diaphragm, Ribs, Alveoli, Intercostal muscles, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Red blood cells, Haemoglobin, Heart, Inhalation, Exhalation, Respiration, Anaerobic, Aerobic, Fitness, Bronchitis, Emphysema, Cancer & Exercise.
6.
7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
The role of the respiratory system and its key organs. The breathing cycle and the role of the each tissue during breathing and gaseous exchange. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and the alveoli tissue. The similarities and differences between expired and inspired air. How haemoglobin in the red blood cell transports oxygen from the alveoli tissue to respiring cells in the body. How smoking affects lung function, whilst increasing the risk of developing lung cancer or emphysema. How asthma affects normal lung function. The role of oxygen in cellular respiration. The differences between anaerobic and aerobic respiration. How the body recovers from oxygen debt. How to maintain bodily fitness for life and the role of the circulatory, respiratory, nervous and digestive system during exercise.
Click mouse to begin
web: www.science-interactive.co.uk email: sales@science-interactive.co.uk
Science Interactive LTD PO BOX 50764 LONDON NW6 9AT
The respiratory system one
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
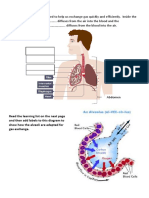
The respiratory system, a collection of cells, t________ and organs works constantly to provide the many billions of cells in the human body with oxygen. The lungs allow gaseous e__________ taking oxygen from the atmosphere into the blood and excreting carbon dioxide from the blood to the atmosphere. A healthy lung consists of many millions of alveoli giving it a huge surface area to help the exchange of these gases. These are highly specialised tissues for exchanging gases. How do villi in the small intestine make use of a large surface area for absorbing nutrients ? The respiratory system:
Thorax
Diagram
Word bank: tissues exchange
Lung volume
Airways
Smoking
Notes
Your chest is home to your lungs. They are both surrounded and protected by your rib cage, a collection of bones and muscles.
Your lungs are constantly inhaling and exhaling air. Left X ray in this picture shows the lungs fully expanded.
The lung tissue is supplied with air by a vast network of tubes called bronchioles. Your windpipe is kept open by rings of cartilage.
Your lungs are in constant contact with the outside. They are also very sensitive to pollutants. Over 100,000 deaths a year are because of lung cancer.
The respiratory system two
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
The lungs are the key organs in the r__________ system. They are located inside your chest or thorax. The lungs delicate tissues are protected by your ribs. Below your lungs is the diaphragm, which aids breathing and separates your lungs from your a__________. The average lung capacity of an adult male is around 5.5 litres. Lance Armstrong, the cyclist, who recently won seven Tour de Frances has a lung capacity in excess of 7 litres. Females have a smaller lung capacity because of their smaller body mass.
The respiratory system:
Tissue
Capillaries
Word bank: respiratory abdomen
Function
Transports air to alveoli tissue. Transports air to bronchioles. Transports air to alveoli tissue. Allow gas exchange. Protects and moves the thorax. Moves the ribs. Changes the volume of the thorax.
Windpipe Bronchus
Bronchioles
Alveoli Alveolus
Bronchiole Lungs Ribs Intercostal muscles Diaphragm
Alveoli
Breathing cycle one
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Your lungs are constantly working to exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide between the alveoli tissue and the pulmonary capillary network. At rest, your lungs e_______ and c_______ about fifteen times every minute. The breathing rate can increase depending on the oxygen demand for your entire body. Your intercostal muscles, ribcage and diaphragm work together to help your lungs inhale and exhale during gaseous exchange. What happens to you breathing rate during periods of exercise and sleep ?
Breathing cycle:
Breathing in (Inhalation) Breathing out (Exhalation)
Word bank: expand contract
Diagram
Notes
Breathing in:
1: Your intercostal muscles contract raising your ribs upwards and outward. 2: Your diaphragm moves downwards. 3: The volume of the thorax increases and the pressure decreases. 4: Air rich in oxygen rushes into the lungs.
Breathing out:
1:Your intercostal muscles relax, lowering your ribs downwards and inwards. 2: Your diaphragm moves upwards. 3: The volume of the thorax decreases and the pressure increases. 4:Air rich in carbon dioxide rushes out of the lungs.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Breathing cycle two
As you complete a full breathing cycle (inhalation & exhalation) you are not only taking in oxygen from the atmosphere, you are also getting rid of waste carbon dioxide. Oxygen moves from an area of high concentration (in the atmosphere) to an area of low concentration (in the blood) by diffusion. In your a_______, you exchange what you need for what you dont need. The air you breathe out is rich in carbon dioxide, moving from an area of high concentration (in the blood) to an area of low concentration (in the atmosphere), also by diffusion.
Breathing cycle:
Model of the human lung Diagram
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Nitrogen Temperature Humidity Inhaled air
Word bank: alveoli
Composition of inhaled and exhaled air
Exhaled air
20% 0.04% 79% 20oC Low
16% 4% 79% 37oC High
Notes
In this model of a lung, the rubber diaphragm moves downwards increasing the volume of the bell jar and decreasing the pressure. Air from outside rushes in. During exhalation, the diaphragm moves upwards, reducing the volume and increasing the pressure. Air rushes out.
The table above shows the composition of gases, humidity and temperature of inhaled and exhaled air. Look at the information and explain the changes in composition of gases, humidity and temperature of inhaled and exhaled air ?
Lung volume
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
During normal breathing, our l_______ take in about half a litre of air during inhalation and exhalation. During heavy exercise, we can take in about 3 litres of air per cycle. The maximum volume of air that we can take in is about 5 litres. We can measure our total lung volume or vital capacity and peak flow of air whilst breathing out. If you compare your vital capacity and peak flow with professional athletes, how might they differ ?
Lung volume:
Measuring peak volume
Word bank: lungs
Lung volumes
Diagram
Notes
Your peak flow rate can be measured using a device as pictured above. It tells us the rate at which air is forced out of your lungs through your wind pipe. Smokers, the elderly and asthmatics can all have a reduced peak flow rate. Why does smoking affect peak air flow ?
Lung volumes: (a) Tidal volume (breathing at rest) (b) Inspiratory reserve volume (c) Expiratory reserve volume (d) Vital lung capacity (Inhalation + Exhalation) (e) Residual volume (always present in lung) (f) Total lung capacity
The alveoli
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
When inhaled air, rich in o__________ reaches the alveoli tissue, oxygen has to transfer to the blood, so it can be transported through the vascular system to the entire body. Oxygen diffuses across the thin alveoli tissue into the b______ where it binds to the red blood cells. The alveoli tissue is highly specialised to help diffusion. They are extremely thin (one cell thick), are kept moist and have a large surface area. If you were able to spread out the lung it would cover a whole tennis court ! The alveoli tissue:
Bronchiole Diagram Alveoli tissue Single alveoli
Word bank: oxygen blood
O2 O2
O2 O2
O2 O2
Notes
The lung tissue is supplied with air by a vast network of tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each bronchiole are many thousands of alveoli which allow gaseous exchange.
Oxygen in the air dissolves in the fluid that coats the alveoli tissue. It then diffuses across to the blood so it can be transported to respiring cells in the human body. Carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction and is excreted in expired air.
The alveolus has a very thin wall and large surface area which is kept moist. These three features help the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across its wall. The alveolus also has a rich blood supply.
Oxygen transport by blood haemoglobin
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Red blood cells contain the protein haemoglobin, which is responsible for binding oxygen at the l______ tissue (alveoli) and delivering it to every r____________ tissue or cell via a huge capillary network. This network can be up to 50,000 km in the human body. Haemoglobin also contains the mineral i_____, to help oxygen transport. Why is iron important in the diet and why do females require greater quantities of this mineral ? Oxygen transport:
At the alveoli Diagram Haemoglobin
Haemoglobin
Word bank: lung respiring iron
In the tissues
O2 O2 CO2 O2 CO2
O2 CO2 O2
O2
O2
Oxyhaemoglobin
Notes
Air contains 21% oxygen which is taken to the alveoli tissue by the bronchioles. Oxygen dissolves across the thin alveoli surface and binds to red blood cells.
Haemoglobin is a protein found in the red blood cell. It contains Iron (Fe2+) and is able to bind oxygen at several sites. Name three foods rich in the mineral iron ?
Oxygen diffuses across the thin capillaries walls to the respiring cells. It travels from an area of high concentration inside the capillary to an area of low concentration inside the cells.
Gaseous exchange in the cells
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Blood capillaries have a very small diameter allowing only one red blood cell through at a time. Blood flows very slowly through your c__________. The capillaries are extremely thin walled which allows oxygen and plasma containing nutrients to diffuse to the cells. Also waste products like u_____ and carbon dioxide can pass from the cells back to the capillary. Why do red blood cells not pass through the capillary walls ? Understanding your capillaries:
Capillaries Diagram Capillary exchange
Net pressure
Word bank: capillaries urea
Carbon dioxide Oxygen Cells Glucose
Urea
Wastes Water
Amino acids
Notes
An electron micrograph of a single capillary. Notice the narrow diameter allowing only one blood cell through.
Oxygen and nutrients including glucose diffuse from blood across the capillary wall to the cells. These are used during cellular respiration. Waste products including carbon dioxide and urea are transported back in the plasma to the lungs and the kidneys.
Blood circulation
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
The circulation of blood through the heart, lungs and other major organs keeps the human body supplied with the o______ and nutrients that it requires for cellular respiration, growth and repair. This transport system also carries the white blood cells, platelets and antibodies around the body defending us against microbial infection. What lifestyle Circulation in the body:
Capillary exchange in detail
factors can prematurely age your cardiovascular system ?
Word bank: oxygen
Red Blood Cell
Red Blood Cell
CO2
Tissue
CO2 O2 O2 O2
O2
Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the tissue surface. Oxygen diffuses across the capillary wall into the cells or tissue. Oxygen is combined with glucose during cellular respiration. Waste products including carbon dioxide and urea are transported in the plasma to the lungs and the kidneys.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Gas exchange using gills
Fish do not have lungs. They are equipped with gills to obtain oxygen for cellular respiration from water. Like lungs, fish gills are highly specialised to allow the d_________ of oxygen from water into the blood. They have a large s________ area, are very thin and have numerous capillaries to transport oxygen away from the gill to the rest of the body. Describe how the shape of gills and alveoli in lungs have common features to help gaseous exchange ?
Gas exchange in fish:
Gas exchange in fish Diagram
Oxygen rich water Gills
Word bank: diffusion surface
Gas exchange in fish gills
Notes
Fish have evolved gills to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between water and the blood supply. The gills have a rich blood supply and have a very large surface area.
Water rich in oxygen flows over the delicate membranes. The oxygen diffuses into the blood supply and travels around the body. Carbon dioxide, the waste product of respiration diffuses from the body, into the water.
Protecting the lungs
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
The lungs are vulnerable to cold air or infection, caused by bacteria or viruses. Cold, dry air is warmed and moistened by the lining found in your n______ and trachea. Bacteria and viruses are trapped by ciliated epithelial cells that line the trachea. Furthermore, these cells also produce m_______ which trap any airborne microbes, which are then moved by the cilia (hairs) to the back of your throat. Here they are swallowed and destroyed by stomach acid. How does smoking damage these cilia hairs ? Protecting the lungs:
Warm and moist air Diagram
Hair cells Bacteria Hair cells and mucus
Word bank: nose mucus
Ciliated epithelia cells Trapping dirt and microbes in the trachea
Notes
Inhaled air is warmed and made moist by the nasal cavity which is richly supplied by warm blood through thousands of capillaries.
The ciliated hair cells trap dust, dirt and bacteria preventing them entering the delicate lung tissue. Smoking damages these specialised cells.
Thousands of hair like protrusions trap dust and bacteria. This is then covered in a sticky mucus which is secreted by the goblet cells. The hairs beat the mucus and bacteria to the back of the throat where it is swallowed. Bacteria are then destroyed by the acid in the stomach.
Damaging your lungs
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
In addition to smoking, your lungs can be damaged by your life style, your place of work or even a traffic jam. Our lungs take in over fifty litres of air every minute of the day. The quality of the a____ we breathe at work, where we live and play affects how our lungs perform over our lives. Remember, our lungs are the most sensitive organs we have and can be quickly damaged by our lifestyles and our own e____________. How might the pollutants from cars and lorries affect our lungs ? Damaging your lungs:
Risk Diagram Smoking Lifestyle Work
Word bank: air environment
Air pollution
Notes
Smoking in the U.K kills over 100,000 adults per year. Despite these figures, the government has yet to ban smoking from public places.
Our lifestyles can also damage our lungs. Smoking and living near busy car jammed roads can damage our delicate lungs for the rest of our lives.
Many work places can expose our lungs to dust and other airborne pollutants. We can protect ourselves by wearing a face mask, which filters out dust.
Traffic pollution can affect the quality of the air we breathe. In our cities, traffic pollution can increase the number of deaths from respiratory failure.
Smoking and its effects on the human body
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Nicotine, the active c__________ in cigarette smoke is highly a__________. Nicotine itself, has an effect on the heart and blood pressure like other stimulants but, it is the t____ and carcinogenic chemicals in cigarette smoke that leads to an increased risk of developing lung, throat and mouth cancer. Smoking over two decades can also lead to the development of emphysema. This disease causes the breakdown of the alveoli tissue. Make a list of the reasons why people start to smoke when they are young ? Smoking and its effects:
Cigarettes (smoke & tar) Diagram Effect on major organs
Word bank: chemical addictive tar
Other effects
Notes
The average UK smoker consumes 20 cigarettes per day until death from heart failure or lung cancer. What is the addictive agent in cigarette smoke ?
Lung cancer kills about 100,000 people in the UK every year with the majority of incidents caused by smoking or passive smoking at work and home. The number of deaths in females is rising...why ?
Increased heart rate and blood pressure may lead to heart disease. This is a major cause of death in smokers. Pictured is a heart valve replacement in a smoker.
Smoking as a cause of lung cancer
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Smoking was first linked as a direct cause of lung cancer by the scientist John Doull. He . studied the main causes of death in many thousands of smokers and non smokers. His research linked s_________ with an increased risk of dying from lung cancer. Smoke irritates the lung causing new cells to grow. Dividing lung cells expose their genes or DNA to the cancer-causing chemicals in cigarette smoke and t_____. A change in the lung cell DNA results in lung c________ in the future. Lung cancer and smoking:
Cancer x-ray Diagram Lung cancer Cancer Deaths in America
Word bank: smoking tar cancer
Giving up
Notes
An X-ray of a cancerous lung tissue (right) Six tumours are growing and increasing in size in both the right and left lung. Untreated this patient will die form the presence of all these tumours. The right picture shows the lung of a dead 56 year old male smoker. Notice how the tissue has changed because of the build up of tar deposits.
Key (Death rates in the US)
70/100,000 50/100,000 35/100,000 20/100,000 From the graph more people smoke in coastal areas or in large cities. Smoking is still seen as a social habit.
Drugs, chewing gum and inhalers all supply the addictive drug nicotine to help smokers give up their habit. Why is will power also important when quitting ?
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Other effects of smoking on the human body
In addition to lung cancer, smoking over a long period can increase the risk of developing emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Again, many of the 300 chemicals that cigarette tar contains causes these respiratory diseases, particularly in the heavy smoker. Emphysema is a fatal lung condition involving the breakdown of the a________ tissue, causing many years of suffering. Coal miners and others whose occupations have exposed them to dust and pollutants can also suffer from these diseases.
Emphysema and bronchitis:
Normal bronchioles
Diagram
Word bank: alveoli
Bronchitis
Normal alveoli
Emphysema
Notes
Normal bronchioles have a large diameter which transports inhaled and exhaled air to and from the alveoli tissue out through the windpipe.
Bronchitis can be fatal in the very old and in smokers. Excessive mucus can damage the delicate lung tissue causing scaring and lead to infection.
The alveolus has a very thin wall, a large surface area which is kept moist and a good blood supply. These four features help the diffusion of O2 and CO2 across its wall.
See how the lung alveoli have been destroyed by the inner walls breaking down. Less oxygen is able to diffuse across the lung into the blood stream.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Aerobic cellular respiration
Aerobic cellular respiration is the release of energy from the breakdown of glucose to water and carbon dioxide. Oxygen from the atmosphere is required to b___________ glucose forming carbon dioxide, water and energy. Respiration occurs in every cell, inside the mitochondria. In animals, 90% of the energy available from ingested food is used for every day activities like muscle contraction, transporting chemicals, absorbing food, building new cells and maintaining a constant body temperature. Why do vegetarians have less impact on the environment ? Energy use of ingested food:
Energy use in animals Diagram
Nutrients 50,000kJ
Word bank: breakdown
Fa e
Re s pi rat i on
ces
Gr
ow th
Process Faeces: Energy contained in 25,000 kJ 1 the faeces and undigested food of the animal. Respiration: Energy used in 20,000 kJ 2 cellular respiration and for body heat. Growth: Energy contained 5,000 kJ 3 in the tissues of the animal (available for the next level.) Half the energy (25,00 kJ) in ingested food passes undigested through the horse's body as waste or faeces.
Notes
The daily nutrient requirement for a horse is around 50,000 kJ with only 5,000 kJ of nutrients ending up as part of the horses body. 20,000 kJ is used for muscle activity, transport, absorbing and digesting food and maintaining a constant body temperature.
Aerobic respiration in the cells
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
If you view animals cells under a microscope, you can see tiny dots in the cytoplasm. These are mitochondria. Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria releasing energy from the breakdown of g________ using oxygen. All living things give out carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration. Muscle cells contain many mitochondria because they require lots of energy. Even plants and simple bacteria contain mitochondria for respiration.
Respiration and mitochondria:
Mitochondria Diagram Notes
Word bank: glucose
C6H12O6
Mitochondria Energy
6H2O
To respire glucose with oxygen providing cell energy. All living cells have these mitochondria. Cellular respiration equation:
6O2
Cells
6CO2
Transport Digestion
C6H12O6 + 6O2
Glucose Oxygen Nerve messages
6H2O + 6CO2
Water Body temp (oC) Carbon dioxide Building cells
Use Diagram
Muscles
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Respiration and combustion
Respiration inside human cells using glucose and oxygen is like the combustion of fossil fuels like p______, which is rich in alkanes like octane. When we combust these fuels with oxygen, energy in the form of h____ and motion is released. New substances are also produced including carbon dioxide and water.
Equation: 2C8H18 Octane
Combustion:
25O2 Oxygen
Octane & Oxygen
CO2 + Carbon dioxide
Engine
18H2O Water
Word bank: petrol heat
Car engine Diagram
Products
Notes
In a modern car, combustion of fuels like petrol provides the energy to move forward. Like cellular respiration waste gases are produced.
In the engine, huge amounts of oxygen are combined with octane. This releases lots of useful forms of energy contained in carbon rich petrol.
The engine is designed to convert the chemical engine contained in octane to kinetic energy. It is highly inefficient releasing only 13% of octanes energy.
The waste products are carbon dioxide and water. However, carbon and carbon monoxide are also released. Compare cellular respiration to combustion in an engine ?
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Anaerobic respiration
During exercise your muscles use oxygen and glucose during cellular respiration. This provides the energy all m_______ cells need to be able to contract and move your body. During vigorous exercise your cardiovascular system cannot supply enough o________ to your muscles. When the demand for oxygen outstrips the supply, your muscle respire glucose without oxygen, producing lactic acid. This is known as anaerobic respiration. When lactic acid builds up in the muscles what does it cause ? Anaerobic respiration:
Anaerobic respiration in muscle cells Diagram
Word bank: muscle oxygen
Lactic acid and exhaustion Lactic acid
C6H12O6
Sugar
6O2
Carbon dioxide
Notes
The skeletal muscles in your legs and arms are able to respire glucose without oxygen forming lactic acid. Although less energy is produced during anaerobic respiration, your muscle can continue to respire without oxygen for several minutes. Athletes train so they can endure the pain associated with lactic acid build up.
The build up of lactic acid can cause exhaustion in trained athletes. When you sprint over 100 metres the burning sensation you can feel in the legs is because of lactic acid build up in your muscles.
Oxygen debt during anaerobic respiration
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
When muscles are working hard, they begin to respire glucose without oxygen. This is called anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid produced during anaerobic respiration builds up and slowly poisons your muscles. Your body cant supply sufficient oxygen to your muscles. This is called oxygen debt. When you stop vigorous exercise, your heart and lungs continue to supply extra oxygen to allow the muscle to breakdown l____ acid. This repays the oxygen debt. Oxygen debt:
Oxygen debt in muscles
Diagram
Oxygen supply (litres)
2.5 2.25 2.0 1.75
Word bank: lactic
Lactic acid production in muscle
Oxygen supply Oxygen demand Oxygen debt
2.5 2.25 2.0 1.75 1.5
Oxygen demand (litres)
C6H12O6
Sugar
Lactic acid
1.5
1.25 1.0 0.75 0.5 0.25 0
B A
C c
1.25 1.0
0.75
0.5 0.25 0
6O2
Carbon dioxide
Time (Minutes)
0 1
4 5
7 8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Notes
During rest (a) the supply of oxygen to the muscles meets demand. During hard vigorous exercise (b), demand increases above supply and the muscle have to continue respiring glucose without oxygen. Anaerobic respiration leads to the oxygen debt and formation of lactic acid. This oxygen debt is repaid when exercise stops (c) by the lungs continuing to oversupply the muscles with the lungs.
During anaerobic respiration, less energy is produced respiring glucose without oxygen. Lactic acid builds up and begins to damage your muscles, giving you the sensation of the burn.
Complete fitness
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Athletes require their key organ systems to work together so that they can exercise and play their sport. Fitness is a measure of how well you body w_____ and exercises. Athletes require total fitness so that they can win and excel at their s______. The cardiovascular, respiratory and skeletal-muscle system all work together to supply the oxygen and nutrients to your muscles. How would you devise a training programme to increase your overall fitness ? Essential organ systems:
Athlete Diagram Cardiovascular Respiratory Muscle
Word bank: works sport
Notes
Professional athletes like runners and footballers work hard to be fit for their sport, but ideas of fitness vary according to their sport.
The cardiovascular system is the human bodys transport system. It moves oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells around a network of tubes.
Your respiratory system is constantly working to exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries in the lung.
The skeletal-muscle system works to move the body during sport. A sprinter requires the fastest contracting muscles during a 100 m race.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Maintaining fitness
Athletes work hard to achieve total fitness, but what does being fit mean ? If you are fit, you will have a low resting heart rate which recovers quickly after e_________. Your lungs efficiently exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide at the alveoli tissue and your skeletal m________ system moves you quickly, without tiring during a race or a game. Exercising (running, weights & gym work) helps us to achieve fitness and improve our ability to compete and win. Fitness and the five S
Strength
Diagram
Word bank: exercise muscle
Stamina
Skill
Suppleness
Speed
Notes
The five s strength, stamina, skill, suppleness and speed are all improved by repetitive training and exercise. Regular exercise also helps prevent people becoming overweight and developing heart disease and diabetes. Nearly 25% of all adults are now considered obese with almost 50% of all pupils of secondary school age not taking enough exercise.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Fermenting grape and grain
Many microbes including yeast can respire successfully without oxygen. Yeast can respire glucose successfully with or without oxygen. When yeast respires glucose without oxygen, it is called fermentation. Fermentation of s_______ from grape or other crops produces alcohol. Wine has been made from grapes using yeast for many centuries. The Romans developed vineyards to supply Rome with w______ from about 400 B.C. onwards. Using the Internet, research into how they make beer from barley, yeast and hops ?
Anaerobic respiration producing alcohol:
Sugar in grapes Diagram Yeast microbes Fermentation
Word bank: sugar wine
Final product
Notes
The sugar in grapes, rice, potato, oats and barley are used to manufacture many different types of alcohol including wine.
Yeast is a naturally occurring bacteria that during fermentation produces alcohol and carbon dioxide as waste products.
Alcohol is produced in huge quantities to supply all drinkers. Weekly, females are allowed 14 units, compared with 21 units for males.
The finished product is taxed by the government raising huge tax revenues. Duty on alcohol raises more than 8 billion per year.
Industrial fermentation using yeast
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Yeast is a very important microbe that supports alcohol manufacture, a multibillion pound industry. Sugar from wheat or grapes is converted to alcohol (beer or wine) in the absence of oxygen by yeast microbes. During f___________, alcohol is produced as a waste product by yeast. Brewing wine or beer are good examples of using biotechnology. Many other useful chemicals can now be made using all types of m________ using fermentation technology. Research into how synthetic insulin for diabetics is manufactured using biotechnology ? Alcohol fermentation:
Fermentation using yeast Diagram
C6H12O6
Sugar Alcohol
Word bank: fermentation microbes
Final products
6O2
Yeast
Carbon dioxide
Notes
Yeast is used in the manufacture of wine, beer and spirits. Sugar contained in grapes or grain is fermented by yeast producing alcohol. The yeast cells multiply rapidly in the sugar until they run out of the food source or high concentrations of alcohol kill them.
After fermentation, the alcohol is separated from the dead yeast cells and allowed to mature over time. Distilling alcohol increases its content in spirits like vodka.
Extension questions and homework
1: 2:
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
Define the following terms: Inhalation, Exhalation, Respiration, Anaerobic, Aerobic, Gas exchange & Fitness. Look at the diagram of the three types of surfaces which exchange substances like oxygen or nutrients by diffusion. Complete the table.
Fatty acids glycerol O2 rich water
Gills
O2 O2
O2 O2
O2 O2
Glucose Amino acids
Tissue
Alveoli Small intestine (villi) Gills
Rich blood supply (Y/N)
Yes
Large surface area (Y/N)
Moist (Y/N)
Yes
Yes
3:
Answer the following questions: a) How does oxygen in the atmosphere move into your bloodstream. b) How is carbon dioxide removed from your respiring cells as a waste product by the lungs. c) The common features of surfaces that allow gas exchange. Name three of them. d) The key elements of the breathing cycle (inhalation and exhalation) e) How are gills in fish similar to lungs found in all mammals. f) Describe the journey of an oxygen molecule from the air sac to muscle tissue in your lower leg.
Science Interactive LTD Copyright 2005
4:
Look at the information in the table below. It shows the results of an investigation designed to investigate how breathing changes during exercise: Activity
Resting Press ups (25 min-1) Press ups (40 min-1)
Volume of each inhalation (cm3)
600 800 1250
Number of inhalations per minute taken
19 26 35
a) How many breaths did the volunteer take during (i) Rest (ii) When doing 25 press ups per minute. b) Calculate the amount of oxygen (cm3) breathed in at (i) Rest (ii) When doing 50 press ups per minute. c) What would the persons breathing be like shortly after exercise was finished. 5: Answer the following questions: a) Describe the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. b) Describe the role of the mitochondria in cells. Which types of tissue contain the most mitochondria and why c) Explain why the build up of lactic acid in your leg muscle begins to slow your speed during a sprint race. d) Explain why the heart can never respire anaerobically. e) Explain how red blood cells are adapted to carry oxygen. How does haemoglobin transport oxygen. 6: Complete the following: During a 200 metre race, the lungs supply ___________ to the respiring muscles. Waste carbon dioxide is taken via the blood stream and excreted by the ________. All athletes begin to become tired, because of the build up of _______________ in the muscles. This is called _______________ respiration. Internet: Go to google.co.uk and find about how athletes use the illegal drug EPO which stimulates the production of red blood cells. How might this give them an advantage over other athletes. Whys is this dangerous for the athlete.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dr. Sebi Lung Diseases Alkaline Diets & Herbs : Stop Lung Diseases or Inflammation, Coughs, Tuberculosis, Bronchitis, Asthma, Pneumonia & Clear Infected Mucus from the Alimentary Canal: Dr. Sebi, #1Dari EverandDr. Sebi Lung Diseases Alkaline Diets & Herbs : Stop Lung Diseases or Inflammation, Coughs, Tuberculosis, Bronchitis, Asthma, Pneumonia & Clear Infected Mucus from the Alimentary Canal: Dr. Sebi, #1Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersDokumen30 halamanEdexcel IGCSE Human Biology AnswersAvrinox88% (48)
- Breathing and Gas Exchange PowerpointDokumen53 halamanBreathing and Gas Exchange Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDokumen26 halamanBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Science Grade 9 Learning Activity Sheets on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDokumen18 halamanScience Grade 9 Learning Activity Sheets on Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsAngel88% (8)
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDokumen24 halamanRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- EMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd Edition Airway ManagementDokumen51 halamanEMT-Basic Textbook - Revised Reprint, 2nd Edition Airway ManagementKathrina Alfonso100% (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDari EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 7 Respiratory System LessonsDokumen19 halamanGrade 7 Respiratory System LessonsclaireBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Dokumen24 halamanBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Utm Proposal TemplateDokumen18 halamanUtm Proposal TemplateKaito Shiro Ichi100% (1)
- Study Plan For PHD StudentsDokumen3 halamanStudy Plan For PHD StudentsDara Moore100% (4)
- Respiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Dokumen12 halamanRespiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Wria AbdulrahmanBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokumen8 halamanCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Notes on Breathing and Exchange of Gasesfast-track for n2021Belum ada peringkat
- Mad 41869 CH 08 PG 141158Dokumen18 halamanMad 41869 CH 08 PG 141158Carolina Lagos LiebigBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokumen4 halamanCBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 30 AnswersDokumen8 halamanChapter 30 AnswersJuan SandovalBelum ada peringkat
- 6.4 QuestionsDokumen18 halaman6.4 QuestionsAurelija GardžiulytėBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper Respiratory SystemDokumen7 halamanResearch Paper Respiratory Systemafnkhujzxbfnls100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasDokumen7 halamanBreathing and Exchange of GasParasBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration NotesDokumen7 halamanRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsBelum ada peringkat
- Week 8 Respiratory System Weekly Workbook 2022Dokumen22 halamanWeek 8 Respiratory System Weekly Workbook 2022rishabhvasisht03Belum ada peringkat
- Gas Exchange and BloodDokumen5 halamanGas Exchange and Bloodsemirah anthonyBelum ada peringkat
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Dokumen8 halamanPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Exercise On Lung VolumeDokumen32 halamanThe Effect of Exercise On Lung VolumemuhadhBelum ada peringkat
- E Book Bio English 03Dokumen42 halamanE Book Bio English 03sanjBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Dokumen6 halamanChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925Belum ada peringkat
- PDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17FDokumen15 halamanPDBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 17Fgandhitirth147Belum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory SystemDokumen5 halamanThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavBelum ada peringkat
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Dokumen17 halamanStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Saraswati PBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Homework Dwi Oktavianto Makdasari X-ADokumen15 halamanBiology Homework Dwi Oktavianto Makdasari X-ADwiBelum ada peringkat
- I.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationDokumen48 halamanI.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationjeetudongreBelum ada peringkat
- Eighth Grade Biology Lesson on Respiratory SystemDokumen5 halamanEighth Grade Biology Lesson on Respiratory SystemTonyan MurrayBelum ada peringkat
- Airway CopdDokumen16 halamanAirway Copdfaisal alharbiBelum ada peringkat
- Human Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsDokumen21 halamanHuman Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and the LungsEnmuskBelum ada peringkat
- RespirationDokumen9 halamanRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557Belum ada peringkat
- Respiratory SystemDokumen25 halamanRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkIBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy and Physiology KNR 182: Lecture Packet For Unit V Respiratory SystemDokumen19 halamanHuman Anatomy and Physiology KNR 182: Lecture Packet For Unit V Respiratory SystemgilissaBelum ada peringkat
- Test 1 Respiratory SysDokumen3 halamanTest 1 Respiratory SysJaskirat SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Physiology LecturesDokumen37 halamanRespiratory Physiology LectureswiasonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDokumen4 halamanChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanBelum ada peringkat
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesDokumen4 halamanBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Class X-Subject: Biology Chapter: Life ProcessesSUHANEERIYABelum ada peringkat
- Gr9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory-And-circulatory-systemDokumen5 halamanGr9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory-And-circulatory-systemCristinekate VinasBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDokumen12 halamanThe Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentDokumen65 halamanRespiration Grade 10 Biology - StudentAsawni McDowellBelum ada peringkat
- Oxygen Insufficiency.Dokumen54 halamanOxygen Insufficiency.Josephine George JojoBelum ada peringkat
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDokumen51 halamanGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasBelum ada peringkat
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokumen8 halamanBreathing and Exchange of GasesgoswamiuwuBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Capacity Study of Teens and AdultsDokumen23 halamanLung Capacity Study of Teens and AdultsjyotiBelum ada peringkat
- Science 9 Slem Week 1 RTP FinalDokumen10 halamanScience 9 Slem Week 1 RTP FinalFrances ApolistaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen138 halamanChapter 7Bëar MëBelum ada peringkat
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases BIOLOGY CLASS 11Dokumen6 halamanBreathing and Exchange of Gases BIOLOGY CLASS 11AvinashBelum ada peringkat
- Grade7 - Text - Respiratory SystemDokumen14 halamanGrade7 - Text - Respiratory SystemNamrata MaheshwariBelum ada peringkat
- Biology G - 9 Notes &practice Questions 2012Dokumen41 halamanBiology G - 9 Notes &practice Questions 2012elroe wubshetBelum ada peringkat
- Biology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemDokumen2 halamanBiology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemMegan TaylorBelum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Science (Bio) Term 1 CH 6 Life Process CWDokumen6 halamanClass 10 Science (Bio) Term 1 CH 6 Life Process CWDivyanshi MalavBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Dokumen10 halamanBiology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Âåřøhī MāhåjáňBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration and BreathingDokumen57 halamanRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDokumen4 halamanReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- BreathingDokumen5 halamanBreathingvictory IsaacBelum ada peringkat
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Movement of Substances Across Cell MembranesDokumen4 halamanMovement of Substances Across Cell MembranesDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- UTM Thesis Template Ver ADIL 1.0Dokumen40 halamanUTM Thesis Template Ver ADIL 1.0Dara Moore100% (1)
- 21st CenturyDokumen17 halaman21st CenturyDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- UTM Template 2007 2010 2013Dokumen19 halamanUTM Template 2007 2010 2013Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Pha100005 ThesisDokumen393 halamanPha100005 ThesisDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- UTM Thesis Manual 2007Dokumen70 halamanUTM Thesis Manual 2007Muhammad Bin KamarulaziziBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1functions: ElationsDokumen3 halamanChapter 1functions: ElationsDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Arpaci-2015-British Journal of Educational TechnologyDokumen14 halamanArpaci-2015-British Journal of Educational TechnologyDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Management Administration & Leadership 2010 Murakami Ramalho 625 43Dokumen19 halamanEducational Management Administration & Leadership 2010 Murakami Ramalho 625 43Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- When To Use What Test PDFDokumen8 halamanWhen To Use What Test PDFnetradeepBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Number Exam Cal RevisionDokumen14 halaman9th Number Exam Cal RevisionDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Human Relations 2009 Reid 1073 112Dokumen40 halamanHuman Relations 2009 Reid 1073 112Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Vanwelsenaers Marc MPDokumen27 halamanVanwelsenaers Marc MPDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Bio Test Mac 2015Dokumen3 halamanSkema Bio Test Mac 2015Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Coor-Geometry Exam Cal RevisionDokumen5 halaman9th Coor-Geometry Exam Cal RevisionDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- 9th AlgebraDokumen8 halaman9th AlgebraDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Motioninair PDFDokumen1 halamanMotioninair PDFDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- 9th Algebra HardDokumen14 halaman9th Algebra HardDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies-2014-Yagil-59-70Dokumen12 halamanJournal of Leadership & Organizational Studies-2014-Yagil-59-70Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Pisa and TimssDokumen2 halamanPisa and TimssDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Wembley Cambridge Gcse Biology Y10Dokumen7 halamanWembley Cambridge Gcse Biology Y10Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Guide MendeleyDokumen6 halamanGuide MendeleyDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- ACADEMIC CALENDAR RESEARCH STUDENTS 2014/15Dokumen2 halamanACADEMIC CALENDAR RESEARCH STUDENTS 2014/15Dara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission PDFDokumen1 halamanTransmission PDFDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan AnekdotDokumen1 halamanLaporan AnekdotDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Classificationmicro PDFDokumen1 halamanClassificationmicro PDFDara MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Classificationmicro PDFDokumen1 halamanClassificationmicro PDFDara MooreBelum ada peringkat