Antibacterial Agents
Diunggah oleh
CJ AngelesHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Antibacterial Agents
Diunggah oleh
CJ AngelesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS Are prescribed to combat disease producing microorganisms ( pathogens) Used interchangeably with antimicrobial and antibiotic
ic Examples: Penicillins Cephalosporins Macrolides Tetracyclines Aminoglycosides Fluoroquinolones BACTERIOSTATIC Inhibit the growth of bacteria Tetracycline and sulphonamides BACTERICIDAL Kills bacteria Penicillins and cephalosporins BACTERIA Single cell organisms lacking a true nucleus and nuclear membrane Bacillus rod shape Cocci- spherical Gram positive-retain purple stain Gram negative-not stained MECHANISM OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTION Inhibition of bacterial wall synthesis Alteration of membrane permeability Inhibition of protein synthesis Inhibition of the synthesis of bacterial RNA and DNA Interference with metabolism within the cell ACTION EFFECT DRUGS Inhibition of cell wall synthesis Bactericidal effect Enzyme breakdown of cell wall Inhibition of enzymes in synthesis of cell wall Bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect Membrane permeability increase Interferes with protein synthesis w/o affecting the normal cells Interferes with steps of metabolism within the cell Penicillin Cephalosporins Bacitracin Vancomycin Amphotericin B
Alteration in membrane permeability
Nystatin Polymyxin Colistin
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Erythromycin lincomycin Sulfonamides Trimetoprim Isoniazid Nalidixic acid Rifampin
Interference with cellular metabolism
Pharmacokinetics Must penetrate bacterial cell wall and have an affinity to the binding sites on the bacterial cell Steady state of the antibacterial drug occurs after the fourth to fifth half lives Eliminated through the urine after the 7th half life Pharmacodynamics Attain bactericidal effect if within or above the minimum effective concentration (MEC) General adverse reaction to antibacterial drugs Allergy/hypersensitivity Superinfection Organ toxicity NARROW SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTICS Effective against one type of organism Penicillin and erythromycin against gram positive BROAD SPECTRUM Effective against narrow and broad spectrum antibiotic Used when offending organism is not identified Tetracyclines and cephalosporins Penicillins Natural antibacterial agent obtained from the mold genus Penicillium Miracle drug Pen G was the first to be administered orally and by injection Pen V-next type produced Food interferes with absorption Beta lactam antibiotics Beta lactamases- produced by bacteria and inactivates penicillin BASIC PENICILLINS Penicillin G procaine Penicillin G benzathine Penicillin G sodium Penicillin V potassium Broad spectrum penicillins Ampicillin ( Cloxapen) Amoxicillin ( Amoxil ) Bacampicillin ( Spectrobid) Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) Ampicillin sulbactam (Unasyn) Penicillinase resistant penicillins (Antistaphylococcal penicillins ) Used to treat penicillinase producing S aureus Cloxacillin (Cloxapen) and dicloxacillin ( Dynapen)oral prep Nafcillin (Unipen) and oxacillin ( Prostaphin) IV and IM prep EXTENDED SPECTRUM PENICILLINS Antipseudomonal penicillins Useful against Klebsiella pneumoniae, enterobacter, acinetobacter Carbenicillin indanyl ( Geocillin) Mezlocillin sodium (Mezlin) Beta Lactamase Inhibitors Broad spectrum antibiotic ( amoxicillin) combined with a beta lactamase (enzyme inhibitor/clavulanic acid)= amoxicillin-clavulanic acid ( Augmentin) Examples : Oral use : amoxicillin-clavulanic acid ( Augmentin)
Parenteral use: ampicillin sulbactam ( Unasyn),piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn) and ticarcillinclavulanic acid ( Timentin) Side effects and adverse reactions Hypersensitivity Superinfection Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea Generation Activity
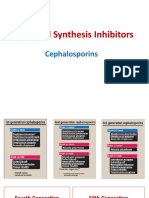
Rash Anaphylactic reaction CEPHALOSPORINS First discovered in seawater-fungus called cephalosporium acremonium Effective against gram positive and gram negative bacteria Have a beta lactam structure Cause bacteria cell lysis Drugs
First
Second
Effective against gram positive ( streptococci, staphylococci) Gram negative ( E.Coli ,Klebsiella, Salmonella and Shigella) Broader spectrum against gram negative ( Haemophilus influenzae,Neisseria Gonorrhea, neisseria meningitidis) Effective against gram negative ( pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter) Less effective boagainst gram positive bacteria Broader gram positive coverage than the third generation
Cephalexin (Keflex) Cefazolin sodium ( Ancef, kefzol)
Cefaclor ( ceclor) Cefuroxime ( Ceftin, Zinacef) Cefoxitin sodium ( Mefoxin) Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) Cefotaxime ( Claforan) Ceftazidime ( vantin ) Cefepime ( Maxipime)
Third
Fourth
Side effects and adverse reactions GI disturbances ( Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) Increased bleeding Nephrotoxicity Drug interactions When taken with alcohol-flushing ,dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting, muscular cramps When taken with uricocosuric drugs, decrease excretion CLIENT TEACHING Keep drugs out of reach of small children Use childproof containers Report signs of superinfection- mouth ulcers, discharge from genital or anal area Ingest buttermilk or yoghurt to prevent superinfection of instestinal flora Take complete course of medication even if infection have ceased Observe for hypersensitivity reaction
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Postoperative Fever - UpToDate PDFDokumen25 halamanPostoperative Fever - UpToDate PDFkatsuiaBelum ada peringkat
- AntibioticDokumen84 halamanAntibioticDr. Kalavati PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology - Chapter 29Dokumen5 halamanPharmacology - Chapter 29Ashley-Michelle LewisBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology AntibioticsDokumen70 halamanPharmacology Antibioticsmaggie100% (1)
- Antimicrobial DrugsDokumen20 halamanAntimicrobial Drugsmaria adventia martinBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Pharmacy Technician Principles and Practice 3rd Edition HopperDokumen24 halamanTest Bank For Pharmacy Technician Principles and Practice 3rd Edition Hopperjenniferhoustonmjcfngpbow100% (42)
- 5) General BacteriologyDokumen86 halaman5) General BacteriologyIanBiagtanBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic Mode of ActionDokumen46 halamanAntibiotic Mode of Actionmkk90Belum ada peringkat
- AntibioticsDokumen54 halamanAntibioticsYvan MercedBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Antibiotics:: Sulfonamides Penicillins Cephalosporins Tetracyclines Aminoglycosides Quinolones MacrolidesDokumen67 halamanAntibiotics:: Sulfonamides Penicillins Cephalosporins Tetracyclines Aminoglycosides Quinolones MacrolidesMarcky_467100% (7)
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryDari EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryBelum ada peringkat
- Antibacterial and Antiinfective AgentsDokumen80 halamanAntibacterial and Antiinfective AgentsAbbeygale GalanBelum ada peringkat
- Amoxicillin Guide: Draw out your antibiotic weapon to defeat bacterial infections like pneumonia, STDs, urinary tract and skin infectionsDari EverandAmoxicillin Guide: Draw out your antibiotic weapon to defeat bacterial infections like pneumonia, STDs, urinary tract and skin infectionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (22)
- Pharmacology of AntibioticDokumen66 halamanPharmacology of AntibioticfgrehBelum ada peringkat
- Antibacterials and AntibioticsDokumen44 halamanAntibacterials and AntibioticsVallejo Taberna HannalieBelum ada peringkat
- AntibioticsDokumen122 halamanAntibioticsdentistry24100% (1)
- NCPDokumen5 halamanNCPCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Bladder Irrigation (Cystoclysis)Dokumen4 halamanBladder Irrigation (Cystoclysis)CJ Angeles100% (2)
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineDari EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèrePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- AntibioticsDokumen70 halamanAntibioticsMunazza QuraishiBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial ChemotherapyDokumen70 halamanAntimicrobial Chemotherapyamanialwerfalli4Belum ada peringkat
- Anti Microbials (Repaired)Dokumen79 halamanAnti Microbials (Repaired)drsidra.mustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Properties and Mechanisms of Common AntibioticsDokumen37 halamanProperties and Mechanisms of Common AntibioticsHa LeemBelum ada peringkat
- 4 AntibiotikDokumen85 halaman4 AntibiotikDion Leonardo SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Infective AgentsDokumen67 halamanAnti-Infective AgentsSHAKTI SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Inhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in VivoDokumen25 halamanInhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in VivoRoshwell RegalaBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic Mechanisms (For Students)Dokumen87 halamanAntibiotic Mechanisms (For Students)Wahab KhaniBelum ada peringkat
- 7a. Antibacterial AgentsDokumen32 halaman7a. Antibacterial AgentsNiala AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- MLAB213 Antibiotics Part 1 Control of GrowthDokumen76 halamanMLAB213 Antibiotics Part 1 Control of GrowthNorman DamaaBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Assignmentt xxx123Dokumen16 halamanMicrobiology Assignmentt xxx123ADITYAROOP PATHAKBelum ada peringkat
- L16 Antibiotics - in - Oral - Maxillofacial - SurgeryDokumen75 halamanL16 Antibiotics - in - Oral - Maxillofacial - SurgeryJu JuBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics 150406092448 Conversion Gate01Dokumen76 halamanAntibiotics 150406092448 Conversion Gate01Dr.Aman SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial DrugsDokumen57 halamanAntimicrobial DrugsFiqri NovianBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Assignmentt TradeDokumen14 halamanMicrobiology Assignmentt TradeADITYAROOP PATHAKBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 7 - AntibioticsDokumen46 halamanLec 7 - AntibioticsAiqa QaziBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobcell Wall InhibitorsDokumen21 halamanAntimicrobcell Wall Inhibitorsymeen9829Belum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial drugs guide to antibiotics and anti-infectivesDokumen16 halamanAntimicrobial drugs guide to antibiotics and anti-infectivesBSN FilesBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial Agents: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-ElteenDokumen133 halamanAntimicrobial Agents: Prof. Khaled H. Abu-ElteenMing GamonganBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology AssignmentDokumen18 halamanMicrobiology AssignmentADITYAROOP PATHAKBelum ada peringkat
- "Clinical Pharmacology of Antibacterial DrugsDokumen44 halaman"Clinical Pharmacology of Antibacterial DrugsLucas Victor AlmeidaBelum ada peringkat
- TNB 11 Antibacterials III Penicillin Beta Lactam and Other Cell Wall InhibitorsDokumen85 halamanTNB 11 Antibacterials III Penicillin Beta Lactam and Other Cell Wall InhibitorsYsabelle DamasoBelum ada peringkat
- Antibacterial Agents Antimicrobial Antibiotic: Leilani O. Estacio, Man RNDokumen44 halamanAntibacterial Agents Antimicrobial Antibiotic: Leilani O. Estacio, Man RNHERLIN HOBAYANBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Infectives AgentsDokumen8 halamanAnti-Infectives AgentsBernardMarkMateoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Wall InhibitorsDokumen36 halamanCell Wall InhibitorsRimsha KhaliqBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporins Others 2Dokumen32 halamanCell Wall Inhibitors - Cephalosporins Others 2Yosra AkashBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of Antibiotics Nurse Licensure Exam ReviewDokumen27 halamanPharmacology of Antibiotics Nurse Licensure Exam ReviewSeth-Thomas TateBelum ada peringkat
- General Aspects of AntimicrobialsDokumen62 halamanGeneral Aspects of AntimicrobialsShree pharmacy 10th batchBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDokumen6 halamanCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsVanessa HermioneBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Infective PPDokumen30 halamanAnti-Infective PPHlaSoe WinBelum ada peringkat
- Biosel-Mikro Mekanisme Antibiotik 2022Dokumen45 halamanBiosel-Mikro Mekanisme Antibiotik 20226. Putu Arbita DivyaBelum ada peringkat
- Β-lactam AntibioticsDokumen37 halamanΒ-lactam AntibioticsMohan Prasad GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitionDokumen33 halamanCell Wall Synthesis InhibitionLoukik TaysheteBelum ada peringkat
- Penicillins and CephalosporinsDokumen30 halamanPenicillins and CephalosporinsSri RamBelum ada peringkat
- AminoglycosidesDokumen41 halamanAminoglycosidesAshish NeupaneBelum ada peringkat
- Infectious DrugsDokumen72 halamanInfectious DrugsArianne Mari BalingitBelum ada peringkat
- 6 AntibioticsDokumen86 halaman6 AntibioticsSalih IntajBelum ada peringkat
- ANTIMICROBIALSDokumen23 halamanANTIMICROBIALSBianca Andrea RagazaBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics Antiviral Antifungal Antimalarial Antiseptic & Disinfectant Agents Antiinflammatory & AntirheumaticDokumen69 halamanAntibiotics Antiviral Antifungal Antimalarial Antiseptic & Disinfectant Agents Antiinflammatory & AntirheumaticNop PiromBelum ada peringkat
- L16 ANTIBIOTICS - IN - ORAL - MAXILLOFACIAL - SURGERY Copy 2Dokumen19 halamanL16 ANTIBIOTICS - IN - ORAL - MAXILLOFACIAL - SURGERY Copy 2Ju JuBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors-Lecture 1Dokumen29 halamanCell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors-Lecture 1Kwanele MvelaseBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs, Microbes, Host - The Elements of Chemotherapy: Antibiotics - Still Miracle DrugsDokumen54 halamanDrugs, Microbes, Host - The Elements of Chemotherapy: Antibiotics - Still Miracle DrugsAngela RoqueBelum ada peringkat
- Amoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsDari EverandAmoxicillin: A Beginner's 20-Minute Quick Guide Overview on its Use Cases to Treat Bacterial Infection and Side EffectsBelum ada peringkat
- The Essential Guide to Ciprofloxacin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.Dari EverandThe Essential Guide to Ciprofloxacin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.Belum ada peringkat
- Ward.. Plan of Activities..Dokumen1 halamanWard.. Plan of Activities..CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- FCL ReflectionDokumen6 halamanFCL ReflectionCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Community Nursing ObjectivesDokumen1 halamanCommunity Nursing ObjectivesCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Private Sub Text1Dokumen1 halamanPrivate Sub Text1CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of RevisionDokumen4 halamanSummary of RevisionCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- LoginDokumen5 halamanLoginCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Consent Form ExampleDokumen1 halamanConsent Form ExampleNader HouellaBelum ada peringkat
- NHPDokumen13 halamanNHPCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- University of Perpetual Help System Dalta Alabang-Zapote Rd. Pamplona, Las Piñas CityDokumen1 halamanUniversity of Perpetual Help System Dalta Alabang-Zapote Rd. Pamplona, Las Piñas CityCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- NCMDokumen9 halamanNCMCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Requirement ERDokumen13 halamanRequirement ERCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Mich DoneDokumen7 halamanChapter 3 Mich DoneCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Certificate of Training: Rolly T. Villones JRDokumen1 halamanCertificate of Training: Rolly T. Villones JRCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- We Are Inviting You To Come To Our Sport Fest5555Dokumen2 halamanWe Are Inviting You To Come To Our Sport Fest5555CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Policies and Procedures on Prevention and Control of Nosocomial InfectionDokumen22 halamanPolicies and Procedures on Prevention and Control of Nosocomial InfectionCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- We Are Inviting You To Come To Our Sport Fest5555Dokumen2 halamanWe Are Inviting You To Come To Our Sport Fest5555CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 104 MusculoskeletalDokumen12 halamanNCM 104 MusculoskeletalCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Colour NameDokumen15 halamanColour NameCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Certificate of Training: Rolly T. Villones JRDokumen1 halamanCertificate of Training: Rolly T. Villones JRCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 104 Common Neurological Health ProblemsDokumen25 halamanNCM 104 Common Neurological Health ProblemsCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 102 - Lecture (Prelims)Dokumen16 halamanNCM 102 - Lecture (Prelims)CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- AnswerDokumen18 halamanAnswerCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Revised Cover PageDokumen6 halamanRevised Cover PageCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Sample QuestionnairesDokumen6 halamanSample QuestionnairesCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen88 halamanChapter 1CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Urine Collection2Dokumen4 halamanUrine Collection2CJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring Intake and OutputDokumen1 halamanMeasuring Intake and OutputCJ AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of Handmade Lemon Soap and Its AntibacterialDokumen11 halamanSynthesis of Handmade Lemon Soap and Its AntibacterialWinarto HaryadiBelum ada peringkat
- The Effectiveness of Ethanolic Extract of Moringa Leaves (Moringa Oleifera Lam.) Gel On The Wound Healing Process of The Rat's PalateDokumen6 halamanThe Effectiveness of Ethanolic Extract of Moringa Leaves (Moringa Oleifera Lam.) Gel On The Wound Healing Process of The Rat's PalateEcha VavataBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Thesis On Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal PlantsDokumen6 halamanMSC Thesis On Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plantsjennawelchhartford100% (1)
- Bovine Mastitis Due To Coliform Bacteria, and Susceptibility To Antibiotics, NigeriaDokumen8 halamanBovine Mastitis Due To Coliform Bacteria, and Susceptibility To Antibiotics, NigeriaPremier PublishersBelum ada peringkat
- Karin Ananditya Fazri 30101407217: Pembimbing: DR, Dian Indah Setyorini, SP - THT-KLDokumen31 halamanKarin Ananditya Fazri 30101407217: Pembimbing: DR, Dian Indah Setyorini, SP - THT-KLVivie Tirany SoediroBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S1684118220300888 MainDokumen7 halaman1 s2.0 S1684118220300888 MainAliefia DamayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Ani Nur RosidahDokumen7 halamanAni Nur RosidahPriawanIndraBelum ada peringkat
- SOP For Kill CurveDokumen2 halamanSOP For Kill CurveRAJENDRA GAJULABelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial Stewardship Integration in EmrsDokumen67 halamanAntimicrobial Stewardship Integration in Emrsapi-668616332Belum ada peringkat
- 2010 SPN BL Rez MALDI TOFDokumen12 halaman2010 SPN BL Rez MALDI TOFSergey SidorenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Sepsis PDFDokumen38 halamanAntimicrobial Therapy in Sepsis PDFTatik HandayaniBelum ada peringkat
- CMI - Speciation, Natural Selection, Migration, Homology EmbryologyDokumen214 halamanCMI - Speciation, Natural Selection, Migration, Homology Embryology7ett_50% (2)
- Ishita MalikDokumen10 halamanIshita MalikIshita malikBelum ada peringkat
- ... Contd Chapter 8 ContaminantsDokumen29 halaman... Contd Chapter 8 ContaminantsGetu AsnakeBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Commonly PrescribedDokumen19 halamanDrugs Commonly PrescribedYounus Shaik100% (2)
- UKMi-Gentamicin InfoDokumen4 halamanUKMi-Gentamicin InfoAmisha VastaniBelum ada peringkat
- Doctor of Veterinary Medicine: Scheme of Study of Five Years Composit Degree ProgrammeDokumen62 halamanDoctor of Veterinary Medicine: Scheme of Study of Five Years Composit Degree ProgrammeAhmed Hassan SamatarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10: Antimicrobial TestDokumen8 halamanChapter 10: Antimicrobial TestMohiuddin HaiderBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal CimetidineDokumen7 halamanJurnal CimetidineAidahBelum ada peringkat
- Tylomix 250 Tylosine Feed PremixDokumen1 halamanTylomix 250 Tylosine Feed PremixLalit ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Muhs Bhalani 2yrDokumen53 halamanMuhs Bhalani 2yrsanjanajaiswal14503100% (1)
- Thành Phần Hóa Học Và Hoạt Động Sinh Học Của Zanthoxylum Limonella (Rutaceae) Đánh GiáDokumen13 halamanThành Phần Hóa Học Và Hoạt Động Sinh Học Của Zanthoxylum Limonella (Rutaceae) Đánh GiáCông PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Risk, Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Cellulitis and ErysipelasDokumen10 halamanRisk, Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Cellulitis and ErysipelasHanunBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial ActivityDokumen13 halamanAntimicrobial ActivityRahul MandalBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Antibiotic Growth Promoter Alternatives On Performance of Broilers - EngormixDokumen3 halamanEffects of Antibiotic Growth Promoter Alternatives On Performance of Broilers - EngormixJamshidBelum ada peringkat
- Cefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassDokumen2 halamanCefadroxil: Antibiotic ClassTariBelum ada peringkat
- Finding A Lead TBDokumen10 halamanFinding A Lead TBAya hBelum ada peringkat
- A Comparative Study of Antibacterial Activity of Leaves and Latex of Jatropha Curcas LDokumen5 halamanA Comparative Study of Antibacterial Activity of Leaves and Latex of Jatropha Curcas Lanna luthfiahBelum ada peringkat