Informational Text Qualitative Measures Rubric
Diunggah oleh
Edison FyeHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Informational Text Qualitative Measures Rubric
Diunggah oleh
Edison FyeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
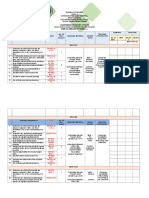
Text Complexity: Qualitative Measures Rubric
INFORMATIONAL TEXT
Text Title___________________________________________ Text Author_____________________________________ Slightly Complex
QUALITATIVE
PURPOSE
Very Complex
o Purpose:
Subtle, implied, difficult to determine; intricate, theoretical elements
o Purpose:
Implied, but fairly easy to infer; more theoretical than concrete
Purpose: Implied, but easy to identify based upon context or source
o Purpose:
Explicitly stated; clear, concrete with a narrow focus
o Organization of Main Ideas: Connections o Organization of Main Ideas: Connections o Organization of Main Ideas: Connections o Organization of Main Ideas: Connections
TEXT STRUCTURE
between an extensive range of ideas or events are deep, intricate and often implicit or subtle; organization of the text is intricate or specialized for a particular discipline between an expanded range ideas, processes or events are deeper and often implicit or subtle; organization may contain multiple pathways and may exhibit traits common to a specific discipline between some ideas or events are implicit or subtle; organization is evident and generally sequential between ideas, processes or events are explicit and clear; organization of text is clear or chronological or easy to predict
o Text Features: If used, are essential in
understanding content
o Text Features: If used, greatly enhance the o Text Features: If used, enhance the
readers understanding of content readers understanding of content
o Text Features: If used, help the reader
navigate and understand content but are not essential
o Use of Graphics: If used, extensive,
intricate, essential integrated graphics, tables, charts, etc., necessary to make meaning of text; also may provide information not otherwise conveyed in the text
o Use of Graphics: If used, essential
integrated graphics, tables, charts, etc.; may occasionally be essential to understanding the text
o Use of Graphics: If used, graphics mostly o Use of Graphics: If used, simple graphics,
supplementary to understanding of the text, such as indexes, glossaries; graphs, pictures, tables, and charts directly support the text unnecessary to understanding the text but directly support and assist in interpreting the written text
o Conventionality: Dense and complex;
LANGUAGE FEATURES
contains abstract, ironic, and/or figurative language
o Conventionality: Complex; contains o Vocabulary: Somewhat complex
some abstract, ironic, and/or figurative language
o Conventionality: Largely explicit and o Vocabulary: Mostly contemporary,
familiar, conversational; rarely unfamiliar or overly academic
easy to understand with some occasions for more complex meaning
o Conventionality: Explicit, literal,
straightforward, easy to understand
o Vocabulary: Generally unfamiliar,
archaic, subject-specific, or overly academic language; may be ambiguous or purposefully misleading
language that is sometimes unfamiliar, archaic, subject-specific, or overly academic
o Vocabulary: Contemporary, familiar,
conversational language
o Sentence Structure: Mainly complex
sentences often containing multiple concepts
o Sentence Structure: Many complex
sentences with several subordinate phrases or clauses and transition words
o Sentence Structure: Simple and
compound sentences, with some more complex constructions
o Sentence Structure: Mainly simple
sentences
o Subject Matter Knowledge: Extensive,
KNOWLEDGE DEMANDS
perhaps specialized or even theoretical discipline-specific content knowledge; range of challenging abstract and theoretical concepts
o Subject Matter Knowledge: Moderate
levels of discipline-specific content knowledge; some theoretical knowledge may enhance understanding; range of recognizable ideas and challenging abstract concepts
o Subject Matter Knowledge: Everyday
practical knowledge and some disciplinespecific content knowledge; both simple and more complicated, abstract ideas
o Subject Matter Knowledge: Everyday,
practical knowledge; simple, concrete ideas
o Intertextuality: Many references or
allusions to other texts or outside ideas, theories, etc.
o Intertextuality: Some references or
allusions to other texts or outside ideas, theories, etc.
o Intertextuality: A few references or
allusions to other texts or outside ideas, theories, etc.
o Intertextuality: No references or allusions
to other texts, or outside ideas, theories, etc.
Questions to Consider in Planning for Instructional Scaffolding of Informational Text: Purpose: Would spending time helping students to establish a purpose for reading this text be appropriate? Will students know in advance what they are expected to do with the information they gain from reading this text?
Text Structure: Would graphic organizers or other aids be appropriate in making the structure of the text visible to students? Would a partial outline or some other text-based aid be appropriate in deciphering the structure of the text? Would previewing and discussing the graphics included with the text prior to reading be appropriate?
Language Features: Would a review of figurative, abstract, or ironic language and a modeling of how that type of language might be interpreted be appropriate? Would glossing certain vocabulary (particularly multiple meaning words that extend across other subject matter content areas, i.e. Tier 2 words) prior to reading be appropriate?
Knowledge Demands: What background knowledge needs to be introduced (or re-introduced) to facilitate reading success that will not supplant the actual information gained from the reading experience? What explicit references and/or allusions to other texts might require additional resources/opportunities for students to explore?
General: In what ways might collaborative groupings of students during the reading process be appropriate?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Edison CCSS Mathematics PresentationDokumen37 halamanEdison CCSS Mathematics PresentationEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- ENC 1101 Composition IDokumen3 halamanENC 1101 Composition IEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Rhyne MAN2021Syllabus SummerB FinalDokumen4 halamanRhyne MAN2021Syllabus SummerB FinalEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- 2013 College Readiness Conference Web LinksDokumen2 halaman2013 College Readiness Conference Web LinksEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- ENC 0015 Developmental WritingDokumen4 halamanENC 0015 Developmental WritingEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- REA 0007 Developmental Reading IDokumen4 halamanREA 0007 Developmental Reading IEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Common Core ELA Overview AngstromDokumen17 halamanCommon Core ELA Overview AngstromEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- CCSS & Partnership For Assessment of Readiness For College and Careers An OverviewDokumen73 halamanCCSS & Partnership For Assessment of Readiness For College and Careers An OverviewEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Noun / - Teks-Chə - Wa-Lə-Tē/ Plural in Ter Tex Tu Al I TiesDokumen12 halamanNoun / - Teks-Chə - Wa-Lə-Tē/ Plural in Ter Tex Tu Al I TiesEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- MGF 1106 SyllabusDokumen9 halamanMGF 1106 SyllabusEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- STA 2023 SyllabusDokumen8 halamanSTA 2023 SyllabusEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- College Readiness Pert Prep Reading WritingDokumen18 halamanCollege Readiness Pert Prep Reading WritingEdison Fye100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Flow Chart For Math CoursesDokumen1 halamanFlow Chart For Math CoursesEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- REA 0017 Developmental Reading IIDokumen4 halamanREA 0017 Developmental Reading IIEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- MAT 1033 SyllabusDokumen8 halamanMAT 1033 SyllabusEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- MAC 1105 SyllabusDokumen10 halamanMAC 1105 SyllabusEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Session 1 - Handout 1 Too Dumb For Complex TextsDokumen5 halamanSession 1 - Handout 1 Too Dumb For Complex TextsEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Too Dumb Article 321 FormDokumen1 halamanToo Dumb Article 321 FormEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Key Evidence:: Collaborative Answers Q. 4Dokumen1 halamanSummary of Key Evidence:: Collaborative Answers Q. 4Edison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Too Dumb For Complex Texts - QuestionsDokumen1 halamanToo Dumb For Complex Texts - QuestionsEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- ENC 0025 Developmental Writing IIDokumen4 halamanENC 0025 Developmental Writing IIEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Key Evidence:: Collaborative Answers Q. 7Dokumen1 halamanSummary of Key Evidence:: Collaborative Answers Q. 7Edison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Measures of Text Difficulty:: Testing Their Predictive Value For Grade Levels and Student PerformanceDokumen58 halamanMeasures of Text Difficulty:: Testing Their Predictive Value For Grade Levels and Student PerformanceMichael MiloneBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Literary Text Qualitative Measures RubricDokumen2 halamanLiterary Text Qualitative Measures RubricEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Ira GuidlinesDokumen4 halamanIra Guidlinesapi-259179075Belum ada peringkat
- Publishers Criteria For K-2Dokumen9 halamanPublishers Criteria For K-2Edison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- Publishers Criteria For 3-12Dokumen19 halamanPublishers Criteria For 3-12Edison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- CC Higher Education ELA LiteracyDokumen50 halamanCC Higher Education ELA LiteracyEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- ELA SBS K5ColorDokumen23 halamanELA SBS K5ColorEdison FyeBelum ada peringkat
- CS571 Lecture4 Scheduling PDFDokumen39 halamanCS571 Lecture4 Scheduling PDFHadcjj ManBelum ada peringkat
- CS402 Automata Theory Assignment SolutionsDokumen5 halamanCS402 Automata Theory Assignment SolutionsMUHAMMAD UMERBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Educ 5312-Research Paper Aydin TargilDokumen3 halamanEduc 5312-Research Paper Aydin Targilapi-361516924Belum ada peringkat
- M.B.Parkes - Scribes, Scripts and Readers (Chap.3 Ordinatio and Compilatio)Dokumen22 halamanM.B.Parkes - Scribes, Scripts and Readers (Chap.3 Ordinatio and Compilatio)Rale RatkoBelum ada peringkat
- Stochastic Calculus For Discontinuous ProcessesDokumen20 halamanStochastic Calculus For Discontinuous Processesjulianli0220Belum ada peringkat
- Skemer, Don - Binding Words - Textual Amulets in The Middle AgesDokumen336 halamanSkemer, Don - Binding Words - Textual Amulets in The Middle AgesImmortalYawn100% (37)
- Anika RajTEA-2-Math-RWS 3-Fractions-2021-22Dokumen3 halamanAnika RajTEA-2-Math-RWS 3-Fractions-2021-22Adharva Raj 7 A Anika Raj 3 FBelum ada peringkat
- TornadoDokumen25 halamanTornadoMuni Sankar MatamBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual MemoryDokumen18 halamanVirtual Memorydasrobles9410@yahoo.com100% (2)
- Grammar EvaluationDokumen7 halamanGrammar Evaluationmaharani robiatulBelum ada peringkat
- Ko 8 Grun Orders Ett CollectDokumen12 halamanKo 8 Grun Orders Ett CollectreibeltorresBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- SCTP vs TCP - Key Differences and Performance AnalysisDokumen25 halamanSCTP vs TCP - Key Differences and Performance AnalysisCatán PatánBelum ada peringkat
- WM LT01 Manual TransferDokumen9 halamanWM LT01 Manual TransferswaroopcharmiBelum ada peringkat
- Sunniyo Ki Aapasi Ladai Ka Ilaaj (Urdu)Dokumen28 halamanSunniyo Ki Aapasi Ladai Ka Ilaaj (Urdu)Mustafawi PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- Liber LucisDokumen172 halamanLiber Luciscruz.ketellyBelum ada peringkat
- Sta. Ana National High School English Learning Competencies ChecklistDokumen6 halamanSta. Ana National High School English Learning Competencies Checklistshirney naelga escabarte50% (2)
- Advanced Excel Formulas and Functions GuideDokumen12 halamanAdvanced Excel Formulas and Functions GuideVasanthKumar BudarpuBelum ada peringkat
- Greek and Latin Roots Vol 1Dokumen144 halamanGreek and Latin Roots Vol 1sstonebennett85% (13)
- 6c Fundamentals of Rietveld Refinement Additional Examples HSP v3 Revised July2012Dokumen41 halaman6c Fundamentals of Rietveld Refinement Additional Examples HSP v3 Revised July2012Yiinjian LowBelum ada peringkat
- Embedded Interview Questions PDFDokumen13 halamanEmbedded Interview Questions PDFViswanath NatarajBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Plan 7th GradeDokumen21 halamanUnit Plan 7th Gradeapi-328252734Belum ada peringkat
- Lampiran 1 Daftar Nama Perusahaan Perkebunan dan Data PenelitianDokumen21 halamanLampiran 1 Daftar Nama Perusahaan Perkebunan dan Data PenelitianJojo Well WellBelum ada peringkat
- JavaScript Unit Testing Tools Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanJavaScript Unit Testing Tools Cheat SheetHéla Ben KhalfallahBelum ada peringkat
- Algorithms and Data Structures-Searching AlgorithmsDokumen15 halamanAlgorithms and Data Structures-Searching AlgorithmsTadiwanashe GanyaBelum ada peringkat
- FilesystemsDokumen59 halamanFilesystemsswastiBelum ada peringkat
- Notas para Interfase Del Sensor DHT11 Al PICDokumen66 halamanNotas para Interfase Del Sensor DHT11 Al PICJaime BarraganBelum ada peringkat
- Solar energy key to futureDokumen4 halamanSolar energy key to futureChona Tahil ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Using The Entity Classes: Adapter - Fetchentity (Customer)Dokumen7 halamanUsing The Entity Classes: Adapter - Fetchentity (Customer)Maja KrstovskaBelum ada peringkat
- Progress Test-Clasa A IV-ADokumen2 halamanProgress Test-Clasa A IV-Alupumihaela27Belum ada peringkat