EC1301 Mid-Term Exam Questions (09102009 - Make-Up Exam)
Diunggah oleh
Yin HauDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EC1301 Mid-Term Exam Questions (09102009 - Make-Up Exam)
Diunggah oleh
Yin HauHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EC1301
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE
EC1301 PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Semester 1 AY 2009/2010 MID-TERM EXAM (MAKE-UP) 9th October 2009 Time Allowed: 1 Hour
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. This examination paper comprises ELEVEN (11) printed pages, including this page. There are FORTY (40) multiple choice questions. Answer ALL questions. The total mark for this exam is 30 marks. This is a CLOSED book examination. Use the bubble form for your answers. You must submit this examination question and the bubble forms. NAME: ___________________________________________ MATRICULATION NUMBER: ______________________
EC1301
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1.
Ben says that An increase in the tax on beer will raise its price. Susan argues that Taxes should be increased on beer because college students drink too much. We can conclude that A. Bens statement is normative, but Susans is positive. B. Susans statement is normative, but Bens is positive. C. both statements are normative. D. both statements are positive. Taxes can adversely affect the efficiency in allocation of resources in society because A. they do not always fall more heavily on the rich. B. the taxes collected are not enough to finance government. C. they distort prices and thus the decisions of households and firms. D. not everyone pays taxes. Thinking at the margin is sort of like thinking at the edge because A. you risk making small errors. B. you are interested in learning how things would change if circumstances were to vary ever so slightly. C. you are only interested in thinking about the big picture. D. you only consider large changes in variables. In economics we learn that A. sometimes there is such a thing as a free lunch. B. tradeoffs allow us to avoid the problem of opportunity cost. C. opportunity costs are all of the possible alternatives given up when we make a choice. D. None of the above answers are correct. All of the following are examples of voluntary exchanges EXCEPT A. buying flowers. B. purchasing a movie ticket. C. betting in a casino. D. paying a traffic ticket. Diminishing returns can be avoided if A. all factors of production are increased simultaneously. B. the variable factor of production is increased in small amounts. C. the fixed factor of production is reduced by half. 2
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
EC1301 D. 7. None of the above.
If real salaries decrease but nominal salaries do not, this means A. the purchasing power of money has increased. B. prices have not changed. C. prices have risen. D. prices have fallen.
Using the following data to answer questions 8-10
TABLE 1 North Cantina Production Possibilities A Capital goods Consumer goods 5 0 B 4 10 C 3 18 D 2 24 E 1 28 F 0 30
TABLE 2 South Cantina Production Possibilities A Capital goods Consumer goods 5 0 B 4 8 C 3 15 D 2 21 E 1 25 F 0 27
8.
Refer to TABLE 1 and TABLE 2. Suppose that North Cantina is producing 2 units of capital goods and 17 units of consumer goods while South Cantina is producing 2 units of capital goods and 21 units of consumer goods. We can conclude that A. North Cantina is fully and efficiently using its resources, but South Cantina is not. B. South Cantina is fully and efficiently using its resources, but North Cantina is not. C. neither South Cantina nor North Cantina is fully and efficiently using their resources.
EC1301 D. both South Cantina and North Cantina are fully and efficiently using their resources.
9.
Refer to TABLE 1 and TABLE 2. Suppose that resources in North Cantina and South Cantina are identical in quantity and quality. We can conclude that A. South Cantina has better technology than North Cantina in producing both capital and consumer goods. B. North Cantina has better technology than South Cantina in producing both capital and consumer goods. C. North Cantina is growing more rapidly than South Cantina. D. North Cantina has better technology than South Cantina in producing consumer goods, but not capital goods. Refer to TABLE 1 and TABLE 2. The opportunity cost of the fifth unit of capital goods A. is higher in North Cantina than in South Cantina. B. is the same in North Cantina and South Cantina. C. is lower in North Cantina than in South Cantina. D. cannot be determined from the information provided. Suppose Singapore discovers a way to produce clean nuclear fuel. The effect of this discovery would be to A. lead Singapore to produce less nuclear fuel. B. force Singapore to produce at a point inside its Production Possibilities Curve (PPC). C. shift the Singapores Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) outward. D. shift the Singapores Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) inward. You have the choice of going to Hawaii for a week, staying at work for the week, or spending the week skiing. If you decide to go to Hawaii, the opportunity cost is A. the value of working and skiing. B. the value of working or skiing, depending on which you would have done rather than go to Hawaii. C. working, because you would be giving up a weeks pay. D. None of the above if you enjoy the time spent in Hawaii. Suppose that the demand for pizza is given by Q = 40 2P and the supply is given by Q = P 8. If the price of pizza is $18, which of the following is TRUE? A. There will be an excess supply of 6 pizzas. B. There will be an excess demand of 8 pizzas. C. There will be an excess demand of 10 pizzas. D. The market is in equilibrium.
10.
11.
12.
13.
EC1301
14.
Assume product A is an input in the production of product B. In turn product B is a complement to product C. We can expect a decrease in the price of A to A. increase the supply of B and increase the demand for C. B. decrease the supply of B and increase the demand for C. C. decrease the supply of B and decrease the demand for C. D. increase the supply of B and decrease the demand for C. Between 1982 and 2003, the market price of a Personal Computer (PC) fell and the quantity of PCs sold increased. Which of the explanations below is consistent with these facts? A. The demand for PCs increased by more than the supply of PCs increased. B. The supply of PCs increased by more than the demand for PCs increased. C. The demand for PCs decreased by more than the supply of PCs decreased. D. Both the supply of PCs and the demand for PCs decreased. The quantity sold of a product is 200 at the unit price of $10. Suppose the price elasticity of demand for the product by the initial value method is 3.0, and you would like to increase the quantity to 240. Then the new price must be A. $9.70. B. $9.33. C. $9.12. D. $8.82. If the demand curve facing a firm had a price elasticity of demand equal to infinity and the firm raised its price, its total revenue would A. decreased slightly. B. fall to zero. C. not change. D. increase. An antidrug policy which reduces the supply of heroin might A. increase street crime because the addicts demand for heroin is highly inelastic. B. reduce street crime because the addicts demand for heroin is highly elastic. C. reduce street crime because the addicts demand for heroin is highly inelastic. D. increase street crime because the addicts demand for heroin is highly elastic. Suppose that you are in charge of pricing at a local ski rental shop. The business needs to increase revenue. If the supply of skis is elastic A. you should increase the rental price of skis. B. you should decrease the rental price of skis. C. you should not change the rental price of skis.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
EC1301 D. 20. you could not determine what to do with rental price until you determine whether demand is elastic or inelastic.
Which of the following would cause the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of potatoes (an inferior good) to increase? A. An increase in consumer income. B. Greater government restrictions on agricultural chemicals. C. A decrease in consumer income. D. Fewer government restrictions on agricultural chemicals. What is the effect on the price of wooden desks and quantity of wooden desks sold if the price of wood, a resource used to produce wooden desks, rises? A. The equilibrium quantity of wooden desks increases and the equilibrium price falls. B. The equilibrium quantity of wooden desks increases and the equilibrium price rises. C. The equilibrium quantity of wooden desks decreases and the equilibrium price falls. D. The equilibrium quantity of wooden desks decreases and the equilibrium price rises. The production costs of aspirin increase and at the same time, doctors find that one aspirin per day reduces the risk of heart attacks. Supply and demand for aspirin will A. both increase, so that the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity will increase. B. decrease and increase, respectively, so that the equilibrium price will increase, but the equilibrium quantity can decrease, increase, or remain constant. C. increase and decrease, respectively, so that the equilibrium price will decrease, increase, or remain constant, but the equilibrium quantity will increase. D. both decrease so that the equilibrium price falls and the equilibrium quantity will decrease, increase, or remain constant. Suppose that a 10 percent increase in the price of normal good Y causes a 20 percent increase in the quantity demanded of normal good X. The cross elasticity of demand is A. negative and therefore these goods are substitutes. B. negative and therefore these goods are complements. C. positive and therefore these goods are substitutes. D. positive and therefore these goods are complements.
21.
22.
23.
EC1301
24.
The marketing people at Ben and Jerrys Ice Cream Company in Singapore believe that if they lower the price of their Cherry Garcias flavor ice cream by 25 percent, the quantity sold will increase by 5 percent. If they are correct in their belief, then A. the demand for Cherry Garcia flavor ice cream is price elastic. B. their total revenue from Cherry Garcia flavor ice cream will increase if they lower the price. C. the demand for Cherry Garcia flavor ice cream is income elastic. D. their total revenue from Cherry Garcia flavor ice cream will decrease if they lower the price. The price elasticity of demand for gasoline is 0.5 and the price elasticity of supply for gasoline is 1.1. If demand rises by 25 percent, the price of gasoline will A. rise by 15.6 percent. B. fall by 15.6 percent. C. rise by 6.4 percent. D. fall by 6.4 percent. Ceterius paribus (that is, other things being equal), if the average fixed cost curve shifts upward, A. the marginal cost curve shifts upward at all output levels. B. the average variable cost curve shifts upward at all output levels. C. the average total cost remains unchanged at all output levels. D. the vertical distance between the average total cost curve and the average variable cost curve increases at all output levels. In comparing the changes in total costs and total variable costs associated with an additional unit of output, we find that A. the change in total variable costs is equal to marginal cost, while the change in total costs is equal to total fixed costs. B. the change in total costs exceeds the change in total variable costs. C. the change in total variable costs exceeds the change in total costs. D. both are equal to marginal cost. A change in technology that shifts the firms total product curve upward without changing the quantity of capital used A. shifts the average total cost curve upward. B. shifts the average total cost curve downward. C. does not change the cost curves. D. shifts the marginal cost curve upward.
25.
26.
27.
28.
EC1301
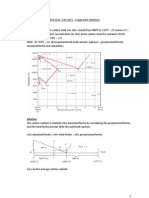
Using the following figure to answer question 29
FIGURE 1
29. maximum profit is A. 0$1,800. B. 0$600. C. 0$1,800. D. 0$600. 30.
Refer to FIGURE 1. The monopolists
Suppose that newspapers companies are now required to use recycled paper, which is more expensive than new paper. Which of the following is more likely to result if the newspaper industry is highly perfect competitive? A. The firms cost will rise, resulting in positive economic profit in the short run and, hence, the industry supply curve will shift rightward in the long run. B. The firms cost will rise, resulting in economic losses in the short run and, hence, the industry supply curve will shift rightward in the long run. C. The firms cost will rise, resulting in economic losses in the short run and, hence, the industry supply curve will shift leftward in the long run.
EC1301 D. The industry supply curve will shift leftward in the short run, causing permanent long-run economic losses.
31.
The irrelevance of sunk costs is best described by which of the following business decisions? A. Airlines continue to sell tickets even though they are reporting losses. B. Airlines exit the market when they report losses. C. New airlines enter the market and earn profits. D. All of the above.
Using the following data to answer questions 32-33
TABLE 3 Quantity (pizzas per hour) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Cost (dollars per hour) 10 18 30 48 70 98 120
32.
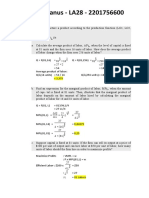
Refer to TABLE 3 above. Peters Pizza is a perfectly competitive firm. The firms costs are shown in the table. If the market price is $15, how much economic profit does the firm make? A. $0 B. $30 C. -$10 D. -$15
EC1301 33. Refer to TABLE 3 above. Peters Pizza is a perfectly competitive firm. The firms costs are shown in the table. If the market price is $15, the firm will A. shut down. B. leave the industry in the long run. C. stay in the industry in the long run. D. incur an economic loss. To maximize profit, the monopolist produces on the _________ portion of the demand curve where _________. A. elastic; price equals marginal cost B. elastic; marginal revenue equals marginal cost C. inelastic; price equals marginal revenue D. inelastic; marginal revenue equals marginal cost Which of the following statements is NOT a characteristic of a monopolist? A. The ability to set its price. B. The fact that producing where MR=MC gives the firm the maximum profit. C. The ability to raise its price without causing total revenue to decrease. D. The ability to set its price above marginal cost. A firm that is a natural monopoly A. is not likely to be concerned about new entrants eroding its monopoly power. B. is not enjoying economies of scale. C. can achieve a lower average total cost if more firms enter the market. D. All of the above. Which of the following would NOT be considered price discrimination? A. Charging more money for long distance telephone calls during business hours than on weekends. B. Charging a lower price for dry cleaning mens shirts than womens shirts. C. Charging higher rates for oil delivery to people who live farther from your business. D. Charging less money to wash a small economy car than a large luxury car. 38. In monopolistically competitive industries, A. non-price competition through product differentiation is vigorous. B. the amount of variety in products is the same as in perfectly competitive industries. C. firms are not sensitive to changes in consumer demand. D. firms produce where marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit to consumers. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm can earn
34.
35.
36.
37.
39.
10
EC1301 A. B. C. D. an economic profit, and so can a monopoly. an economic profit, but a monopoly cannot. no economic profit, but a monopoly might. no economic profit, and neither can a monopoly.
40.
Suppose in the city of SEMBAWANG music stores operate in a monopolistically competitive market. If the price of CDs in SEMBAWANG is currently equal to $20 per CD and the average cost of CDs is $15, in the long run we expect the price of CDs to A. increase. B. stay the same. C. decrease, and the average cost of producing CDs to decrease. D. decrease, and the average cost of producing CDs to increase.
THE END
11
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- LLC Operating AgreementDokumen18 halamanLLC Operating Agreementjwalker6492283% (6)
- Parametric Models For Regression Graded PDFDokumen6 halamanParametric Models For Regression Graded PDFRushi VyasBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Mistakes (FOREX TRADING)Dokumen12 halamanTop 10 Mistakes (FOREX TRADING)Marie Chris Abragan YañezBelum ada peringkat
- A. B. C. D.: EconomicsDokumen57 halamanA. B. C. D.: EconomicsASMARA HABIBBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises – Game Theory and Strategic Behavior SolutionsDokumen10 halamanExercises – Game Theory and Strategic Behavior SolutionsTeyma TouatiBelum ada peringkat
- Josh Magazine NMAT 2007 Quest 4Dokumen43 halamanJosh Magazine NMAT 2007 Quest 4Pristine Charles100% (1)
- Lab #2 Chapter 2 - The Economic ProblemDokumen14 halamanLab #2 Chapter 2 - The Economic ProblemLucasStarkBelum ada peringkat
- ME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetDokumen2 halamanME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetPhyo Wai Aung67% (9)
- Assignment 1 Model AnswerDokumen4 halamanAssignment 1 Model Answergeo_biBelum ada peringkat
- Manegerial EconomicsDokumen97 halamanManegerial EconomicsSanjay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- QUIZ 6A: KEY CONCEPTS OF MONOPOLY, OLIGOPOLY, AND PERFECT COMPETITIONDokumen2 halamanQUIZ 6A: KEY CONCEPTS OF MONOPOLY, OLIGOPOLY, AND PERFECT COMPETITIONAli Shaharyar Shigri100% (1)
- NUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDokumen11 halamanNUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsYin Hau100% (2)
- Market Targeting and Positioning StrategiesDokumen10 halamanMarket Targeting and Positioning StrategiesJacqueline G. BantonBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Choice Indifference CurvesDokumen27 halamanConsumer Choice Indifference CurvesМаксим НовакBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test2Dokumen8 halamanPractice Test2Sarah ZeidatBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 06Dokumen27 halamanChapter 06Merin Lawrance100% (1)
- Perfect CompetitionDokumen3 halamanPerfect CompetitionShreejit MenonBelum ada peringkat
- KarachiDokumen2 halamanKarachiBaran ShafqatBelum ada peringkat
- CH 04Dokumen40 halamanCH 04Mohammed Aljabri100% (1)
- MNO1001X Cheat SheetDokumen8 halamanMNO1001X Cheat SheetYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- D) Indirect Taxes and SubsidiesDokumen7 halamanD) Indirect Taxes and SubsidiesnatlyhBelum ada peringkat
- Inventory Management and Risk PoolingDokumen68 halamanInventory Management and Risk PoolingAbhishek Pratap SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Econ 351 Midterm 1 Questions and AnswersDokumen11 halamanEcon 351 Midterm 1 Questions and Answerstony4dongBelum ada peringkat
- Microeconomics Practice AssignmentDokumen2 halamanMicroeconomics Practice AssignmentAashutosh Rathi100% (1)
- Financial MGMT McqsDokumen64 halamanFinancial MGMT McqsSonuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 09 Segmenting Positioning Forecasting MarketsDokumen67 halamanChapter 09 Segmenting Positioning Forecasting MarketsJames LebronBelum ada peringkat
- 6Dokumen9 halaman6abadi gebru100% (1)
- Microeconomics SPRING 2020 Elasticity: Elastic?Dokumen4 halamanMicroeconomics SPRING 2020 Elasticity: Elastic?Nayeli Ramirez100% (1)
- Final MT 6003 New QBDokumen27 halamanFinal MT 6003 New QBAshokBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet - 2 Demand & SupplyDokumen2 halamanWorksheet - 2 Demand & SupplyPrince SingalBelum ada peringkat
- Why Demand Curve Slopes Downward To The Right?Dokumen3 halamanWhy Demand Curve Slopes Downward To The Right?Aishwarya ThamizharasiBelum ada peringkat
- Plagiarism Rules SzabistDokumen2 halamanPlagiarism Rules Szabistsamey21Belum ada peringkat
- Micro-Economics (Cmi Assign #1)Dokumen6 halamanMicro-Economics (Cmi Assign #1)shakeitoBelum ada peringkat
- Demand and SupplyDokumen16 halamanDemand and SupplyGA ahuja Pujabi aaBelum ada peringkat
- Managerial Economics Ch3Dokumen67 halamanManagerial Economics Ch3Ashe BalchaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 08Dokumen10 halamanChapter 08Fardin Sabahat KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Econ201 Quiz 4Dokumen10 halamanEcon201 Quiz 4arichard88215Belum ada peringkat
- MicroeconomicsDokumen10 halamanMicroeconomicsCarlos Funs0% (1)
- Practice Quiz 2Dokumen4 halamanPractice Quiz 2shivi25040% (1)
- Elesticity of DemandDokumen48 halamanElesticity of DemandDr.Ashok Kumar Panigrahi100% (1)
- ADL 04 Managerial Economics V3Dokumen6 halamanADL 04 Managerial Economics V3solvedcare100% (1)
- Elasticity - Utility ExplainedDokumen16 halamanElasticity - Utility ExplainedreemmajzoubBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Programming Model Formulation and SolutionDokumen38 halamanLinear Programming Model Formulation and SolutionSarmast100% (1)
- MGT603 Sloved MCQsDokumen11 halamanMGT603 Sloved MCQsRASHIDWAHEEDBelum ada peringkat
- Milton M. Pressley: Powerpoint by Creative Assistance by D. Carter and S. KogerDokumen39 halamanMilton M. Pressley: Powerpoint by Creative Assistance by D. Carter and S. Kogerayadav89Belum ada peringkat
- IS LM PresentationDokumen32 halamanIS LM PresentationRajat LoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Essential: AssignmentDokumen21 halamanMarketing Essential: AssignmentlaturtleBelum ada peringkat
- Demand and Supply Concepts ExplainedDokumen4 halamanDemand and Supply Concepts ExplainedRubbanBelum ada peringkat
- QB For Me Unit 2Dokumen4 halamanQB For Me Unit 2archana_anuragiBelum ada peringkat
- RSM311Dokumen7 halamanRSM311sch123321Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen36 halamanChapter 3Md. Samin Salekin100% (1)
- Bilaspur University presentation on managerial economics cost theoryDokumen22 halamanBilaspur University presentation on managerial economics cost theoryVi Pin SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapt 2 MICDokumen13 halamanChapt 2 MICAkkamaBelum ada peringkat
- Discussion ch08Dokumen3 halamanDiscussion ch08SkyeBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome: Sanjida Sayed Barsha Lecturer Bba (Professional) Alhaj Mockbul Hossain University CollegeDokumen63 halamanWelcome: Sanjida Sayed Barsha Lecturer Bba (Professional) Alhaj Mockbul Hossain University Collegeসানজিদা সাঈদ100% (1)
- Questions For ReviewDokumen13 halamanQuestions For Reviewنور عفيفهBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ'S Economics Chapter 4 Elasticity of DemandDokumen7 halamanMCQ'S Economics Chapter 4 Elasticity of DemandPriyank Tiwari100% (1)
- Supply Chain Drivers and Key MetricsDokumen47 halamanSupply Chain Drivers and Key MetricsdurgaBelum ada peringkat
- Key Chap 3Dokumen20 halamanKey Chap 3Đức Đặng0% (1)
- Theory of Production: Chapter-7Dokumen22 halamanTheory of Production: Chapter-7Blue StoneBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation & Assignment Model Problems2007-09Dokumen12 halamanTransportation & Assignment Model Problems2007-09Ketaki SomanBelum ada peringkat
- DocxDokumen16 halamanDocxaksBelum ada peringkat
- SM 2021 MBA Assignment Forecasting InstructionsDokumen3 halamanSM 2021 MBA Assignment Forecasting InstructionsAmit Anand KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Indvi Assignment 2 Investment and Port MGTDokumen3 halamanIndvi Assignment 2 Investment and Port MGTaddisie temesgen100% (1)
- Practice 2 - ECON1010Dokumen6 halamanPractice 2 - ECON1010veres.tankerBelum ada peringkat
- Practice 2_Demand and Supply_HSB1010Dokumen6 halamanPractice 2_Demand and Supply_HSB1010hgiang2308Belum ada peringkat
- Gek 1540 Tut 2 QBDokumen2 halamanGek 1540 Tut 2 QBYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Laplace Transform TableDokumen3 halamanLaplace Transform TableYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Properties and Testing of Materials Chapter 2Dokumen7 halamanMechanical Properties and Testing of Materials Chapter 2Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 7 Suggested AnswersDokumen4 halamanTutorial 7 Suggested AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Entropy 15 01221Dokumen11 halamanEntropy 15 01221Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- LSM1301Dokumen7 halamanLSM1301Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Gek1540 Chapter 6Dokumen4 halamanGek1540 Chapter 6Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics and Its Application in RefrigerationDokumen8 halamanThermodynamics and Its Application in RefrigerationYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Engineers & EnvironmentDokumen8 halamanEngineers & EnvironmentYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Radiation Problem SetDokumen1 halamanHeat Transfer Radiation Problem SetLakshmi BalasubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- CA Lab Manual ScopeDokumen10 halamanCA Lab Manual Scopea2367916100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Radiation Problem SetDokumen1 halamanHeat Transfer Radiation Problem SetLakshmi BalasubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 7 Suggested AnswersDokumen4 halamanTutorial 7 Suggested AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- ME3162 Questions PDFDokumen2 halamanME3162 Questions PDFYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- ME3112-PART 2 Tutorial 2 & 3: ShahrokhDokumen14 halamanME3112-PART 2 Tutorial 2 & 3: ShahrokhYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15Dokumen2 halamanChapter 15Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- TimetableDokumen2 halamanTimetableYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 6 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 6 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 Tutorial 2 - Suggested Solutions for BCC Crystal Structure, Lattice Constant and Element IdentificationDokumen8 halamanMLE1101 Tutorial 2 - Suggested Solutions for BCC Crystal Structure, Lattice Constant and Element IdentificationYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 5 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 5 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- LSM1301Dokumen7 halamanLSM1301Yin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 Tutorial 4 - Suggested Solutions AnalysisDokumen7 halamanMLE1101 Tutorial 4 - Suggested Solutions AnalysisYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 1 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen5 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 1 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- EC1301 - Tutorial 4 (14-18 September 2009) - AnswersDokumen9 halamanEC1301 - Tutorial 4 (14-18 September 2009) - AnswersYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- MLE1101 - Tutorial 3 - Suggested SolutionsDokumen4 halamanMLE1101 - Tutorial 3 - Suggested SolutionsYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- 12 TransientDokumen39 halaman12 TransientYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- L2 - LeadershipDokumen2 halamanL2 - LeadershipYin HauBelum ada peringkat
- Oxylane Supplier Information FormDokumen4 halamanOxylane Supplier Information Formkiss_naaBelum ada peringkat
- CBRMDokumen14 halamanCBRMSurajSinghalBelum ada peringkat
- Amb 336 Case Study AnalysisDokumen10 halamanAmb 336 Case Study Analysisapi-336568710Belum ada peringkat
- G20 Leaders to Agree on Trade, CurrencyDokumen5 halamanG20 Leaders to Agree on Trade, CurrencysunitbagadeBelum ada peringkat
- CRM ProcessDokumen9 halamanCRM ProcesssamridhdhawanBelum ada peringkat
- Eric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost AnalysisDokumen8 halamanEric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost Analysiseric stevanusBelum ada peringkat
- 43-101 Bloom Lake Nov 08Dokumen193 halaman43-101 Bloom Lake Nov 08DougBelum ada peringkat
- Ramos ReportDokumen9 halamanRamos ReportOnaysha YuBelum ada peringkat
- PART I - Multiple Choice (30 Marks)Dokumen13 halamanPART I - Multiple Choice (30 Marks)Siyeong SimBelum ada peringkat
- ACT EAST POLICY & ASEAN by Soumyabrata DharDokumen6 halamanACT EAST POLICY & ASEAN by Soumyabrata DharSoumyabrata DharBelum ada peringkat
- IAS 2 InventoriesDokumen13 halamanIAS 2 InventoriesFritz MainarBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial1 SolutionsDokumen5 halamanTutorial1 Solutionsfgdfdfgd3Belum ada peringkat
- Frame6 UserNetworks p2-30Dokumen29 halamanFrame6 UserNetworks p2-30jasonBelum ada peringkat
- KctochiDokumen5 halamanKctochitradingpithistoryBelum ada peringkat
- Money Market and Its InstrumentsDokumen8 halamanMoney Market and Its InstrumentsKIRANMAI CHENNURUBelum ada peringkat
- EH101 Course InformationDokumen1 halamanEH101 Course InformationCharles Bromley-DavenportBelum ada peringkat
- Liberal View of State: TH THDokumen3 halamanLiberal View of State: TH THAchanger AcherBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 Global DividesDokumen5 halamanLesson 6 Global DividesRachel VillasisBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Consumer's BehaviourDokumen14 halamanChapter 2 Consumer's BehaviourAdnan KanwalBelum ada peringkat
- Proforma LocDokumen3 halamanProforma LocPooja MohiteBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology Telecommunications and Information ExchangeDokumen48 halamanInformation Technology Telecommunications and Information Exchangescribd4tavoBelum ada peringkat
- Business Model Analysis of Wal Mart and SearsDokumen3 halamanBusiness Model Analysis of Wal Mart and SearsAndres IbonBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 2 (Indigo) PDFDokumen3 halamanCase Study 2 (Indigo) PDFDebasish SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 Mutual FundDokumen46 halamanUnit 6 Mutual Fundpadmakar_rajBelum ada peringkat
- Zesco Solar Gyser ProjectDokumen23 halamanZesco Solar Gyser ProjectGulbanu KarimovaBelum ada peringkat