6 Phases Nursing Process
Diunggah oleh
Jan Jamison ZuluetaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
6 Phases Nursing Process
Diunggah oleh
Jan Jamison ZuluetaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
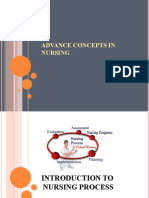
SIX PHASES OF THE NURSING PROCESS 1.
ASSESSMENT - Is collecting, validating, organizing and recording data about the clients health. Purposes: - To establish a data base Activities: A. COLLECTION OF DATA Gathering information about the client, considering the physical, psychological, emotional, socio-cultural, and spiritual factors that may affect his health status. TYPES OF DATA a. Subjective data those that can be described only by the person experiencing it. b. Objective data those that can be observed and measured. METHODS OF COLLECTING DATA a. Interview Planned purposeful conversation b. Observation Use of senses Use of units of measure Physical examination techniques Interpretation of laboratory results SOURCES OF DATA a. Primary Patient/client b. Secondary Family members Significant others Patients record/chart Health team members Related literature B. VERIFYING/VALIDATING DATA C. ORGANIZING DATA 2. DIAGNOSING - It is the process which results to a diagnostic statement or nursing diagnosis. - It is the clinical act of identifying problems. - To diagnose in nursing, it means to analyze assessment information and derive meaning from this analysis. PURPOSES: To identify the clients health care needs and to prepare diagnostic statements.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS - Is a statement of clients potential or actual alteration of health status - It uses the critical-thinking skills of analysis & synthesis - Uses PRS/PES format: P problem R related to factors S signs and symptoms P problem E etiology S signs and symptoms
Activities: - Organize cluster or group data - Compare data against standards - Analyze data after comparing with standards - Identify gaps and inconsistencies in data - Determine the clients health problems, health risks and strengths - Formulate nursing diagnosis statements Comparison of Correct and Incorrect Nursing Diagnosis Correct high risk for ineffective airway clearance related to thick, copious mucus secretions Incorrect high risk for ineffective airway clearance related to pneumonia Correct Incorrect Correct Incorrect high risk for injury related disorientation high risk for injury related to absence of side rails high risk for self-concept disturbance related to the effects of mastectomy mastectomy related to cancer
3. OUTCOME IDENTIFICATION - Refers to formulating and documenting measurable, realistic, client-focused goals. - It provides the basis for evaluating nursing diagnosis. Purposes: - To provide individualized care - To promote client participation - To plan care that is realistic and measurable - To allow involvement of support people Activities: - Establish priorities Priority is something that takes precedence in position, deemed the most important among several items. Priority setting is a decision-making process that ranks the order of nursing diagnosis in terms of importance to the client. - Establishing priorities involves the following: Life threatening situations should be given highest priority. Use the principle of ABCs airway should always be given the highest priority Use Maslows hierarchy of needs Consider something that is very important to the client Clients with unstable condition should be given priority over those with stable condition. Consider the amount of time, materials, equipment required to care for clients Actual problems take precedence over potential concerns Attend to the client before equipment - Nursing diagnoses are classified as high-priority, medium priority, and low priority. High priority are those that are potentially life threatening and require immediate action. Medium priority are those that could result in unhealthy consequences but are not life threatening. Low priority involves problems that usually can be resolved easily with minimal interventions and are unlikely to cause significant dysfunction. - Establish clients goals and outcome criteria Client goal is an educated guess, made as a broad statement about what the clients state will be after the nursing intervention is carried out. Behavioral goal are written to indicate a desired state. They may contain an action verb and a qualifier that indicate the level of performance that needs to be achieved. Qualifier is a description of the parameter for achieving the goal.
Goal may be short term or long term. Short term goal (STG) can be met in a relatively short period. Long term goal (LTG) requires more time Characteristics of well-stated outcome criteria: S specific M measurable A attainable R realistic T time-framed Examples: Goal - The client will report a decreased anxiety level regarding surgery Possible Outcome Criteria During client teaching, the client discusses fears and concerns regarding surgical procedure. After client teaching, the client verbalizes decreased anxiety. The client identifies a support system and strategies to use to reduce stress and anxiety related to the surgical experience.
4. PLANNING - Involves determining beforehand the strategies or course of actions to be taken before implementation of nursing care. PURPOSES: To identify the clients goals and appropriate nursing interventions To direct client care activities To promote continuity of care To focus charting requirements To allow for delegation of specific activities Plan Nursing Intervention To direct activities to be carried out in the implementation phase
Nursing Intervention - Any treatment, based upon clinical judgment and knowledge that a nurse performs to enhance client outcomes. - Used to monitor health status - Prevent, resolve or control a problem - Assist with activities of daily living - Promote optimum health and independence - Nursing intervention are also called nursing orders Nursing Orders are independent, dependent and interdependent activities that nurses carry out to provide client care. PLAN OF CARE - Is a written summary of the care that a client is to receive It is the blueprint of the nursing process. - Is nursing centered. This is essential to identify the scope & depth of the nursing practice. - Focusing on the treatment of human responses to actual or potential health problems - The nurse remains in the nursing practice domain
A step by step process Sufficient data are collected to substantiate nursing diagnosis At least one goal must be stated for each nursing diagnosis Outcome criteria must be identified for each goal Nursing interventions must be specifically designed to meet the identified goal Each intervention should be supported by a specific rationale. The scientific rationale is the justification or reason for carrying out the intervention. Evaluation must address whether each goal was completely met, partially met or completely unmet.
SAMPLE OF NURSING PLAN OF CARE - Nursing diagnosis Risk for injury related to sensory and integrative dysfunction manifested by altered mobility and faulty judgment. - Client goal Client will demonstrate safety habits when performing ADLs and injury prevention. - Client outcome criteria Client uses nurse call light system for assistance for each need to use bathroom immediately after instruction by the nurse. Client demonstrates safety practices in dressing and hygiene. Client uses over the-bed lights, nonskid slippers each time when transferring to chair or out of bed. Client identifies modification for home safety, 12 hours after nurses instruction about home safety.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Family Therapy Treatment Planner With DSM 5 Updates 2nd Edition Practiceplanners Ebook PDF VersionDokumen62 halamanThe Family Therapy Treatment Planner With DSM 5 Updates 2nd Edition Practiceplanners Ebook PDF Versionthomas.corscadden30398% (40)
- Add and Adhd ResearchDokumen25 halamanAdd and Adhd Researchapi-520142437100% (1)
- Nursing ProcessDokumen68 halamanNursing ProcessRaquel M. Mendoza86% (7)
- HT 43 Jan PDFDokumen36 halamanHT 43 Jan PDFSohail LatifBelum ada peringkat
- Group CBT Delusions Reality TestingDokumen23 halamanGroup CBT Delusions Reality TestingIoana DarjanBelum ada peringkat
- ArthritisDokumen25 halamanArthritisJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ProcessDokumen12 halamanNursing Processczhuena100% (14)
- History of nursing development and rolesDokumen29 halamanHistory of nursing development and rolesMitchee ZialcitaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Lab Manual Reviews Health Assessment SkillsDokumen5 halamanNursing Lab Manual Reviews Health Assessment SkillsShelanie Oliquino40% (5)
- Personal Nursing PhilosophyDokumen5 halamanPersonal Nursing PhilosophyLaura Sotomayor100% (2)
- Health As A Multifactorial PhenomenonDokumen2 halamanHealth As A Multifactorial PhenomenonJan Jamison Zulueta100% (9)
- Evolution of Nursing Theories (First Semester 2019)Dokumen93 halamanEvolution of Nursing Theories (First Semester 2019)Lliryc Sotnas OleusnocBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ProcessDokumen8 halamanNursing ProcessGhadeer Hijazeen100% (1)
- How To Handle ComplaintDokumen20 halamanHow To Handle ComplaintmackybhoyamoresBelum ada peringkat
- TCM ReferencesDokumen24 halamanTCM ReferencespelizBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Psychopathology PDFDokumen5 halamanClinical Psychopathology PDFelvinegunawan50% (2)
- Nursing Process 1Dokumen19 halamanNursing Process 1Anonymous zBblKD8gvBelum ada peringkat
- Bed Bath & Bed ShampooDokumen42 halamanBed Bath & Bed ShampooRusjen Claire Villamero100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Part 5Dokumen36 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Part 5Honeylie Patricio100% (1)
- Nursing Process and Documentation GuideDokumen52 halamanNursing Process and Documentation Guidegeorgeloto12100% (2)
- Health Assessment 2Dokumen12 halamanHealth Assessment 2shannon c. lewisBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals-Of-Nursing-Module-PrelimDokumen18 halamanFundamentals-Of-Nursing-Module-PrelimLalajim100% (1)
- Nursing Theorists and Their ModelsDokumen11 halamanNursing Theorists and Their ModelsPaul Rivera100% (1)
- Module 5 Nursing ProcessDokumen34 halamanModule 5 Nursing Processscrewdriver100% (5)
- Unit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessDokumen43 halamanUnit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessSumaira NoreenBelum ada peringkat
- Community Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCommunity Focused Nursing: Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing CareDokumen206 halamanFundamentals of Nursing CarePrincess Faye Tiongson ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- Funda ExamDokumen18 halamanFunda Examronnax100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Nursing PracticeDokumen18 halamanFundamentals of Nursing PracticeCarminaAllado100% (1)
- Nanda Nursing Diagnosis For DepressionDokumen2 halamanNanda Nursing Diagnosis For Depressionsrinivasana50% (4)
- Nursing Process GuideDokumen101 halamanNursing Process GuideTerry SegnabenBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of NursingDokumen48 halamanFundamentals of Nursinganon-429003100% (31)
- ABWM Handbook 2012 2Dokumen45 halamanABWM Handbook 2012 2Wawan Febri RamdaniBelum ada peringkat
- Madeleine Leininger: Founder of Transcultural NursingDokumen20 halamanMadeleine Leininger: Founder of Transcultural NursingTin LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Case Studies on Psychological DisordersDokumen5 halamanCase Studies on Psychological DisordersAshwin Hemant LawanghareBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring Body TemperatureDokumen5 halamanMeasuring Body TemperatureJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing Post Test - Set B Nursing ProceduresDokumen8 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Post Test - Set B Nursing ProceduresVin Lorenzo CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- ENTERAL TUBE FEEDING GUIDEDokumen4 halamanENTERAL TUBE FEEDING GUIDEJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing LectureDokumen18 halamanFundamentals of Nursing LectureChristianArvinMañego100% (3)
- Nursing ProcessDokumen10 halamanNursing ProcessCarylVanetteAcla100% (1)
- Nightingale's 13 CanonsDokumen20 halamanNightingale's 13 CanonsRuo Zhi50% (2)
- NUR 2115 Final Exam Fundamentals of Professional Nursing Final Exam Concept Review Fall 2020 Rasmussen College - RemovedDokumen5 halamanNUR 2115 Final Exam Fundamentals of Professional Nursing Final Exam Concept Review Fall 2020 Rasmussen College - RemovedJudy DurkinBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing The Newborn and Infant-NewDokumen11 halamanAssessing The Newborn and Infant-NewJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 004 Health AssessmentDokumen10 halamanChapter - 004 Health AssessmentTrixie AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Process and Care PlanDokumen14 halamanNursing Process and Care Planapi-328324207100% (2)
- Transfer TechniquesDokumen5 halamanTransfer TechniquesJan Jamison Zulueta100% (1)
- Theories and Changes of AgingDokumen8 halamanTheories and Changes of AgingJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Core Values of Nursing in Conducting HADokumen18 halamanCore Values of Nursing in Conducting HAReann Lee100% (2)
- Different Fields of NursingDokumen29 halamanDifferent Fields of NursingRichmond Tan67% (9)
- Nursing TheoriesDokumen7 halamanNursing TheoriesemsdaxxBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of NursingDokumen485 halamanFundamentals of Nursingshenric16100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Powerpoint CH 3Dokumen43 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Powerpoint CH 3MelissaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing - Basic ConceptsDokumen83 halamanFundamentals of Nursing - Basic ConceptsDarell M. Book100% (7)
- Tidal ModelDokumen3 halamanTidal Modelgopscharan100% (1)
- NLE Test Taking StrategiesDokumen31 halamanNLE Test Taking StrategiesAr-jay JubaneBelum ada peringkat
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsDokumen4 halamanGordon's 11 Functional Health Patternsnina angelaBelum ada peringkat
- TFN Nursing Theories 2011-2012Dokumen376 halamanTFN Nursing Theories 2011-2012katlina80% (5)
- Clinical ReflectionDokumen3 halamanClinical ReflectionNaomi MasudaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Pulse RateDokumen4 halamanAssessing Pulse RateJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- WatsonDokumen22 halamanWatsonherlanhanafiah100% (2)
- NCM 100 LectureDokumen129 halamanNCM 100 LectureJacqueline Mañago CalaycayBelum ada peringkat
- Vital SignsDokumen6 halamanVital SignsJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Theorist Madeleine LeiningerDokumen25 halamanNursing Theorist Madeleine Leiningerapi-240550685Belum ada peringkat
- CNO-Compendium: Understanding Ethical FrameworksDokumen42 halamanCNO-Compendium: Understanding Ethical FrameworksdanushaBelum ada peringkat
- Comfort Rest and SleepDokumen57 halamanComfort Rest and SleepDoms PlazosBelum ada peringkat
- Gordons Functional Health PatternsDokumen12 halamanGordons Functional Health PatternsKaye CorBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing TheoristsDokumen20 halamanNursing TheoristsScionBelum ada peringkat
- Florence Nightingale's Environmental TheoryDokumen5 halamanFlorence Nightingale's Environmental TheoryjisooBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Nursing Chapter 12Dokumen7 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Chapter 12friendofnurseBelum ada peringkat
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- HA - Nursing Process April2016Dokumen45 halamanHA - Nursing Process April2016M Ronela Paglinawan MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- A. Overview of The NURSING PROCESS (ADPIE)Dokumen7 halamanA. Overview of The NURSING PROCESS (ADPIE)Chuche Marie TumarongBelum ada peringkat
- FUNA RLE AssessmentDokumen15 halamanFUNA RLE AssessmentVinzii DrtBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING PROCESS LectureDokumen56 halamanNURSING PROCESS LectureSamantha SunglaoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ProcessDokumen15 halamanNursing ProcessCreole Kaye RubiaBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Steps / Phases OF Nursing ProcessDokumen24 halaman6 Steps / Phases OF Nursing ProcessMary Anthonette Arenas EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Process, Fluids, Acid Base, IV CalcDokumen24 halamanNursing Process, Fluids, Acid Base, IV CalcStephanieBelum ada peringkat
- Midwifery Skills Clinical Laboratory: The Midwives ProcessDokumen26 halamanMidwifery Skills Clinical Laboratory: The Midwives ProcessNano KaBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE - Labor Management CooperationDokumen10 halamanMODULE - Labor Management CooperationJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation - Dti Dole Interim GuidelinesDokumen29 halamanPresentation - Dti Dole Interim GuidelinesJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Contraception: Fertility Control Which Ideally Should Be Reliable, Inexpensive, Safe and Easy To UseDokumen39 halamanContraception: Fertility Control Which Ideally Should Be Reliable, Inexpensive, Safe and Easy To UseJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Handling Complaints: Ms. Jobeth J. OtosDokumen18 halamanHandling Complaints: Ms. Jobeth J. OtosJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Context Quality Management System (QMS)Dokumen13 halamanContext Quality Management System (QMS)Jan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Management Partnership ProgramDokumen16 halamanLabor Management Partnership ProgramJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Parts and Functions ExplainedDokumen5 halamanComputer Parts and Functions ExplainedJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing InformaticsDokumen22 halamanNursing InformaticsJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Maintaining Body AlignmentDokumen6 halamanMaintaining Body AlignmentJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Public Health Bag Technique GuideDokumen3 halamanPublic Health Bag Technique GuideJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Pulse Rate-RleDokumen2 halamanAssessing Pulse Rate-RleJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Cultural HeritageDokumen6 halamanCultural HeritageJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 3 - TissuesDokumen58 halamanAnatomy 3 - TissuesJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Filling Up Personal Data SheetDokumen3 halamanGuide To Filling Up Personal Data SheetDenni Dominic Martinez LeponBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal AssessmentDokumen2 halamanAbdominal AssessmentJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Questions: Gilligan's in A Different VoiceDokumen5 halamanReading Questions: Gilligan's in A Different VoiceJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Excel Exercise 5 - Making ChartsDokumen5 halamanExcel Exercise 5 - Making ChartsJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Common Mental Health Problems in Older PopulationsDokumen5 halamanCommon Mental Health Problems in Older PopulationsJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Office ButtonDokumen2 halamanOffice ButtonJan Jamison ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ComputerDokumen6 halamanIntroduction To ComputerLafats XklusivBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms : Depression Symptoms in Children and TeensDokumen3 halamanSymptoms : Depression Symptoms in Children and TeensPrincess Aldriana CapistranoBelum ada peringkat
- Policy - Document LIC TusharDokumen54 halamanPolicy - Document LIC Tusharwaghtushar1212Belum ada peringkat
- Autism JournalDokumen10 halamanAutism JournalAbu bakarBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 Project - EditedDokumen4 halamanWeek 2 Project - EditedBandah Mwiti JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Life Care Medi'Call ServiceDokumen5 halamanLife Care Medi'Call ServiceRajeev MehraBelum ada peringkat
- SofasDokumen3 halamanSofaszzmmmoBelum ada peringkat
- Schallware (Watermark)Dokumen9 halamanSchallware (Watermark)mat koolBelum ada peringkat
- AbstractDokumen2 halamanAbstractAshley SantelicesBelum ada peringkat
- Pridmore S. Download of Psychiatry, Chapter 13.Dokumen16 halamanPridmore S. Download of Psychiatry, Chapter 13.Costrut Laur100% (1)
- Uganda Health Guidelines On Treatment of Common Diseases.Dokumen766 halamanUganda Health Guidelines On Treatment of Common Diseases.edward100% (2)
- Introduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Leifer 5th Edition Test BankDokumen36 halamanIntroduction To Maternity Pediatric Nursing Leifer 5th Edition Test Banklaxator.rabotru5i37100% (35)
- The Genetic Spectrum of Congenital OcularDokumen12 halamanThe Genetic Spectrum of Congenital OcularKryssiaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is AlcoholismDokumen11 halamanWhat Is AlcoholismSahil ChughBelum ada peringkat
- CF2024 Elanco Parvo HDokumen8 halamanCF2024 Elanco Parvo HPrakash KhangalBelum ada peringkat
- Data Analysis in Healthcare Improving Patient Outcomes - Essay 5Dokumen2 halamanData Analysis in Healthcare Improving Patient Outcomes - Essay 5Nabeel MughalBelum ada peringkat
- CF 73+Service+ManualDokumen118 halamanCF 73+Service+ManualSteve SchmitzBelum ada peringkat
- Healy World Flyer First Steps en EUDokumen2 halamanHealy World Flyer First Steps en EUzianasunBelum ada peringkat
- Riddle Walker2016Dokumen9 halamanRiddle Walker2016mym azmiBelum ada peringkat
- Joy HiggsDokumen533 halamanJoy HiggsMohammad MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Airway Foreign Body in ChildrenDokumen6 halamanAirway Foreign Body in ChildrenRegina RoembiakBelum ada peringkat
- Kassirer 2010Dokumen7 halamanKassirer 2010api-264671444Belum ada peringkat