Admin Law Chart
Diunggah oleh
cscarvilleHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Admin Law Chart
Diunggah oleh
cscarvilleHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
APA Deals ONLY with FEDERAL gov't.
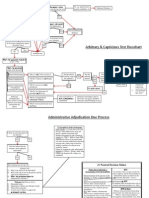
If a question involves state gov't it is not an APA case instead it is a due process or the right to a neutral decision maker. SCOPE OF REVIEW Chevron used by the courts when they are reviewing an agencies own interp of its organic statute. Substantial Evidence court uses when it involves agency finding of fact in formal adjudication & occasionally formal RM. Arbitrary & Capricious deferential form of review & used for factual and policy decisions that come out of informal adjudication. RULEMAKING Notice & Comment 553; notice of intent, opportunity for comments, publish in fed registrar, general purpose statement Formal RM 556 & 557; more trial like w/opportunities to cross-exam; on the record. Congress is suppose to be clear when formal RM has to be used. ADJUDICATION Informal 554; not prevalent. An agency decision that results from a process that is neither a RM nor a trial type proceeding. Formal 554; on the record; trials conducted by ALJ. POLICY FORMATION DISTINCTIONS RULE outcome of rulemaking; 551(4). Generally to make future policy and include use of legis facts which are general in nature. ORDER outcome of adjudication; 551(6). Applying old rules to past and present conduct; includes use of adjudicative facts specific to particular issue. AGENCY AUTHORITY TO MAKE POLICY Whether an agency adjudicates or makes rules, it choice of procedure is almost certain to be upheld by the courts. By Rules agency has the authority. By Order (After Adjudication) Bell Aerospace current view. SC approved boards position to announce policy by order rather than by rule. NOTICE The notice that an agency must give in the Federal Registrar must contain either the terms of substance of the proposed rule or a description of the subjects and issues involved. TEST to determine adequacy of notice of change of a proposed rule occurring after N&C period is if the change is in character w/the original scheme and the final rule is a logical outgrowth of the N&C already given. EX PARTE CONTACTS HBO v. FCC 706 of the APA requires in reviewing agency decisions the court must be privy to the WHOLE RECORD. Any ex parte contacts must be placed in the record so others may comment. Sierra Club v. Costle relevance standard more liberal than in HBO. If agency receives comments it must put them on the record if they are relevant. IMPARTIAL RULEMAKERS Assoc. Natl Adv. v. FTC An agency member should be disqualified from decision making ONLY when it is shown he has an unalterably closed mind on relevant matters. HYBRID RULEMAKING In b/w informal and formal RM. No definition in the APA. Many agencies use it b/c mandated by Congress or on their own initiative. Courts may not impose RM procedures beyond 553 (informal N&C). EXEMPTIONS FROM N&C RM Interpretive Rules, Policy Statements, Rules of Organization, Procedure or Practice. How to distinguish b/w these is on pg. 12 of outline. Interp if reminds parties of existing statutory duties, clarifies statutory term. Rulemaking involving military or foreign affairs, or
Good Cause Exception finding that notice is impracticable, unnecessary, or contrary to public interest. PROCEDURAL VS. SUBSANTIVE RULES 2 STEP PROCESS (to make distinction): 1. Ask if the agency is directly impacting substantive rights or obligations, or 2. Directly affecting the manner in which people present themselves to the agency? Procedural Exception covers agency actions which to not themselves alter the rights or interests of the parties, although it may alter the manner in which the parties present themselves or their viewpoints to the agencies. Substantive Exception issue is one of degree. The task is to identify which substantive effects are substantively so grave that N&C are needed to safeguard the policies underlying the APA. DUE PROCESS THRESHOLD QUESTIONS 1. Is there intentional state action? 2. Look for adjudication something that affects a small group of people. 3. Is there a constitutionally protected interest? Life, liberty or property? LIFE Rarely comes up in administrative law. LIBERTY Right to engage in common occupations in life, enjoy those privileges, etc. Reputation cases suggest where it stigmatizes a person from getting another job some hearing is due. Harm to reputation is not enough.need legal status. Stigma + Test: 4 factors (1) gov't must charge or stigmatize him; (2) charge must be made public or published; (3) must dispute the facts; and (4) must suffer a change in legal rights/status. PROPERTY Extends beyond actual ownership of real estate, chattel, or money. The person must have a LEGIT claim of ENTITLEMENT to it. Employment for cause a substantive property right; at will employees DO NOT have property interest. WHAT PROCESS IS DUE TEST to determine what process is due is from Mathews v. Eldridge 1. Private Interest Affected 2. Risk of Erroneous Error 3. Value of Additional Procedures 4. Gov't Interest RIGHT TO A NEUTRAL DECISION MAKER Decision maker violates DP if a judge has a direct, personal, substantial, pecuniary interest in reaching a conclusion. Parties w/substantial pecuniary interests in legal proceedings should not adjudicate such disputes. Cinderella if a disinterested observer may conclude that a decision maker has prejudged the facts as well as the law of a particular case before hearing it, that decision maker must be removed. STATUTORY HEARING RIGHTS ?? Discusses ex parte contacts 3 criteria of 554. SEPARATION OF POWERS NON-DELEGATION DOCTRINE TEST to determine if a delegation is valid, the court will look to see if Congress has provided the agency w/an intelligible principle that will guide the agency in using the delegated powers. Doctrines underlying purpose (1) forces the elected representatives of the people-Congress-to make the important choices of social and economic policy; (2) guarantees that any delegation to an agency will be accompanied by an intelligible principle guiding the agencys discretion; (3) enhances JR by giving courts a standard against which to weigh the exercise of the agencys discretion; (4) an injury as to whom the decision making power is given.
LEGISLATIVE VETO INS v. Chadha legislative vetos are unconstitutional.
APPOINTMENT AND REMOVAL OF EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
Appointment Clause Problem (1) officer or employee; (2) superior or inferior officer; and (3) legislative, judicial or executive function? Superior Officer must be appointed by President pursuant to Appointment Clause. Inferior Officer Appointed by Pres, Heads of Dept, or courts; Congress vests appointment power. Test of Inferior Officers: removable by superiors; limited to investigation and prosecution; limited in jurisdiction; office is temporary and limited in tenure. Edmonds Test of Inferior Officers: if the officer is directed by other officers directly appointed by President then probably inferior. SCOPE OF REVIEW 2 QUESTIONS TO ASK TO DETERMINE SCOPE 1. What type of issue (nature of case) is the court being asked to review? 2. In what type of administrative proceeding did the agency arrive at the decision being challenged? TYPES OF REVIEW Arbitrary & Capricious Scope can involve questions of fact, law or discretion. Generally deferential. Test: (1) has the agency relied on correct factors in making its decision; and (2) was the agencys decision a clear error in judgment? Constitutional Challenge involves a question of law where the reviewing courts give little deference. Scope of Authority Review involves question of law; whether the agency has exceeded its statutory authority. Procedural Review Allows courts to set aside a decision if the agency did not act correctly in a procedural manner. Substantial Evidence Review Deals w/issues of fact. Triggered when agency decision was made after formal adjudication or RM. Court looks at whole record. De Novo Review Deals w/issues of fact and is a rarity in admin law. This review is to be used when (1) agency action is adjudicatory, and (2) agency fact finding procedures are inadequate. Overton Park CHEVRON TEST **When reviewing an agencies interpretation of their own statute: 1. Ask did Congress clearly address the specific issues? 2. Is the agencys interpretation permissible or reasonable? RULE 553 N&C, advisory opinions and possibly informal adjudication will trigger Chevron Review. RULE Chevron IS NOT triggered when in an opinion letter, manual, policy statement or other interpretive regulation. (these trigger Skidmore) SKIDMORE 1. How careful has the agency been; 2. how consistent has the agency been over time; 3. how formal or informal the agency has been, and 4. all the other things that give power to persuade, but not the power to control. SEMINOLE ROCK DEFERENCE Should be used when agencies interpretations of their own regs; they must be upheld unless plainly erroneous or inconsistent w/the regulation provided that they are neither unconstitutional or inconsistent w/the statute. SUBSTANTIAL EVIDENCE 706(2)(E) How much evidence? Could a reasonable finder of fact reach the conclusion that was reached. Triggers for Substantial Evidence (1) if the enabling statue says so; (2) if it doesnt say look to the APA formal RM or formal adjudication. ARBITRARY & CAPRICIOUS 706(2)(A) Used almost exclusively for determinations not subject to SE review such as informal RM and informal adjudications involving decisions of fact/policy and where otherwise provided for by the act.
2 Questions to be asked (1) did the agency rely on the correct factors in making its decision; and (2) was the agencys decision a clear error in judgment? 4 Prong Test for A&C (agency has to fail only 1 1. if an agency relies on factors that Congress did not intend for them to; 2. if an agency failed to consider an important aspect of the decision; 3. if the agency explanation runs counter to the evidence; or 4. if the decision is so implausible that it cannot be ascribed to a difference in view or the product of agency expertise. Hard-Look Doctrine of A&C less deferential and takes a hard look at whether the agency has taken into account all the relevant facts.
REVIEWABILITY PRESUMPTION OF REVIEWABILITY The APA has been interpreted by the SC to embody a presumption of judicial reviewability. However, the APA says this may be rebutted. Judicial Review applies except to the extent: 1. the statute precludes review, or 2. Agency action is committed to agency discretion by law. STATUTORY PRECLUSION OF REVIEW RULE presumption of reviewability is evidence unless there is clear and convincing evidence that Congress intended to preclude review. Preclusion can be broad to include all kinds of JR or temporary or only include some challengers. COMMITTED TO AGENCY DISCRETION BY LAW TEST 1. There is no law to apply. Overton Park 2. The statute is drawn so that a court would have no meaningful standard against which to judge the agencys discretion. Heckler STANDING Constitutional Standing (1) injury in fact; must be concrete and particularized or actual/imminent; (2) fairly traceable; and (3) redressability. Association Standing (1) its members would have otherwise had standing to sue on their own, and talk about constitutional standing; (2) the interests it seeks to protect are germane to the organizations purpose; and (3) neither the claim asserted nor the relief requested requires the participation of individual members in the lawsuit. Zone of Interest is the interest being asserted by the litigant arguably w/n or of the same type of interest Congress had in mind when passing the statute? Prudential Standing is satisfied when the injury asserted by the s arguably falls w/n the zone We want everyone to be able to sue. RIPENESS Ripeness and finality refer to the steps the agency must take before its actions may be challenged in the courts. Pre-enforcement challenges (1) is the case fit for judicial review, and (2) what is the hardship to the parties if the court withholds from taking the case? Benefits generally the challenge will not be ripe until the individual applies for benefits and is denied. Ripeness & licensing SC ripeness rose w/this topic Ripeness & Ruling/Opinion Letters (1) how specific the questions were asked; (2) how definite the agencies disapproval was; (3) how high or low the decision maker was in the food chain. Exhaustion of Administrative Remedies exhaustion is highly discretionary. FOIA An agency has to improperly withhold agency records. Multi-factor test physical location, if the agency used the docs, generated by the agency, and controlled by the agency. 3 factor test for determining if an ENTITY is an AGENCY (1) how close the entity is to the president
operationally, (2) whether it has self-contained structure, and (3) nature of its delegated authority.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Admin Law Attack SheetDokumen4 halamanAdmin Law Attack SheetDrew Rymer100% (2)
- Admin Law Exam ApproachDokumen12 halamanAdmin Law Exam Approachsetareh2167% (6)
- Admin Canned AnswersDokumen3 halamanAdmin Canned AnswersTroy Rogers Thornton100% (1)
- Checklist - Admin LawDokumen19 halamanChecklist - Admin LawMolly Elizabeth100% (2)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen39 halamanAdministrative Law Outlinekadles1989100% (2)
- Condensed Rules For AdminDokumen23 halamanCondensed Rules For AdminSteven Beck100% (2)
- Administrative Law Outline Funk Fall 2010Dokumen30 halamanAdministrative Law Outline Funk Fall 2010Travis M. Clements100% (1)
- Leg Reg ChecklistDokumen5 halamanLeg Reg ChecklistChristopher Pedro100% (1)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen21 halamanAdministrative Law OutlineLogan DupréBelum ada peringkat
- Short Admin OutlineDokumen16 halamanShort Admin Outlinesbow001484100% (6)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen20 halamanAdministrative Law OutlineChristopher Nicolaysen100% (3)
- Admin Law Checklist-2015Dokumen6 halamanAdmin Law Checklist-2015Prabdeep100% (2)
- Administrative Law FrameworkDokumen20 halamanAdministrative Law FrameworkH100% (1)
- Admin Law ChecklistDokumen3 halamanAdmin Law ChecklistCristina Vanea100% (2)
- Better Admin Law OutlineDokumen24 halamanBetter Admin Law Outlinemoon100% (2)
- Administrative Law Flow Chart Spring2010Dokumen1 halamanAdministrative Law Flow Chart Spring2010Lisa Hrunka100% (7)
- Outline - Admin LawDokumen64 halamanOutline - Admin LawMolly ElizabethBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law ChecklistDokumen3 halamanAdministrative Law ChecklistSmochiBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law Outline Reynolds)Dokumen31 halamanAdministrative Law Outline Reynolds)Brandon Morrow100% (1)
- Administrative Law Outline - Uncategorized - 1Dokumen24 halamanAdministrative Law Outline - Uncategorized - 1Travis M. Clements100% (1)
- Admin Law Attack Outline ChecklistDokumen4 halamanAdmin Law Attack Outline Checklistbillsfan114Belum ada peringkat
- LegReg FlowDokumen2 halamanLegReg FlowLauraChao100% (9)
- Admin Final Exam OutlineDokumen16 halamanAdmin Final Exam OutlineKristopher Kyree León100% (1)
- Flowcharts: Administrative Due Process and A&C ReviewDokumen2 halamanFlowcharts: Administrative Due Process and A&C ReviewDaniel Patrick80% (10)
- LH Admin Attack OutlineDokumen9 halamanLH Admin Attack OutlineDave Leslie100% (1)
- Administrative Law Attack SheetDokumen9 halamanAdministrative Law Attack SheetJimmy Miller100% (3)
- Administrative Law Case ReviewDokumen73 halamanAdministrative Law Case ReviewthriftydigBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law - 2013 With TestsDokumen47 halamanAdministrative Law - 2013 With TestsSteven Beck100% (1)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen8 halamanAdministrative Law OutlineSlinkpreet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Admin Law Outline-AraizaDokumen92 halamanAdmin Law Outline-AraizaDoslyn RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen98 halamanAdministrative Law OutlineLiam Murphy100% (1)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen21 halamanAdministrative Law Outlinemflax09100% (1)
- Admin Crash Course BHDokumen14 halamanAdmin Crash Course BHBeau William HuchBelum ada peringkat
- Short Leg Reg OutlineDokumen3 halamanShort Leg Reg OutlineAndrew White100% (2)
- ConLaw FlowChartDokumen2 halamanConLaw FlowChartAisha Lesley81% (16)
- Dormant Commerce Clause AnalysisDokumen1 halamanDormant Commerce Clause Analysishollyhastings42100% (2)
- Constitutional Law OutlineDokumen40 halamanConstitutional Law OutlineAlex JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Model Admin Law Answers For 2010 ExamDokumen87 halamanModel Admin Law Answers For 2010 Examjakevade100% (1)
- Free Law School Outline - Administrative Law ChecklistDokumen12 halamanFree Law School Outline - Administrative Law ChecklistNicole Taylor100% (1)
- Outline - Administrative Law Spring 2015 (Levin)Dokumen24 halamanOutline - Administrative Law Spring 2015 (Levin)N FinkelsBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law Outline Spring 2010Dokumen22 halamanAdministrative Law Outline Spring 2010Leslie Kirchner Mathews100% (5)
- Admin Ultimate Cheat SheetDokumen11 halamanAdmin Ultimate Cheat SheetJosephBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative Law Master OutlineDokumen3 halamanAdministrative Law Master OutlineKelsey Cox100% (1)
- Administrative Law OutlineDokumen65 halamanAdministrative Law OutlinePaul JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law II OutlineDokumen44 halamanCon Law II OutlineCharlene Soleimani100% (10)
- Appointment Powers Flow ChartDokumen1 halamanAppointment Powers Flow ChartcoppercowBelum ada peringkat
- Chevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)Dokumen2 halamanChevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)GeneTeam100% (1)
- Business Organizations OutlineDokumen72 halamanBusiness Organizations Outlinejared100% (9)
- Chemerinsky Conlaw 1 OutlineDokumen40 halamanChemerinsky Conlaw 1 Outlinemkelly1021100% (5)
- Fed Courts Full OutlineDokumen63 halamanFed Courts Full OutlineKalana KariyawasamBelum ada peringkat
- Leg Reg Outline, RedDokumen21 halamanLeg Reg Outline, RedDori Cohen100% (3)
- Con Law I Attack Sheet - GW Prof. Cheh 2009 - Text BarronDokumen5 halamanCon Law I Attack Sheet - GW Prof. Cheh 2009 - Text BarronCaitlin Elizabeth100% (6)
- Administrative LawDokumen3 halamanAdministrative LawCarling Carpio100% (1)
- Assignment #9618796Dokumen4 halamanAssignment #9618796aryan sethBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative LawDokumen5 halamanAdministrative LawDandolph TanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment OneDokumen7 halamanAssignment OneSaswati SoumyaBelum ada peringkat
- Adm Law GlossaryDokumen24 halamanAdm Law GlossaryMaria MariaBelum ada peringkat
- On-Line Quiz in APOE No. 1: 1. What Are The Requisites For Administrative Due Process?Dokumen4 halamanOn-Line Quiz in APOE No. 1: 1. What Are The Requisites For Administrative Due Process?KenJoBelum ada peringkat
- Administrative LawDokumen74 halamanAdministrative LawVictoria CarmichaelBelum ada peringkat
- Powers of Administrative AgenciesDokumen18 halamanPowers of Administrative AgenciesCarylBelum ada peringkat
- BARRION Report ChoiceofLawJurisdictionForeignJudgmentDokumen15 halamanBARRION Report ChoiceofLawJurisdictionForeignJudgmentBettina BarrionBelum ada peringkat
- Affidavit of Corporate DenialDokumen9 halamanAffidavit of Corporate DenialHOPE6578% (9)
- Reckless Imprudence Resulting To Damage To PropertyDokumen2 halamanReckless Imprudence Resulting To Damage To PropertyJani MisterioBelum ada peringkat
- Puse Vs Puse GR 183678Dokumen18 halamanPuse Vs Puse GR 183678Fritz Colleen A. Figueras100% (1)
- No Liability Where There Is No Breach of A Given RightDokumen11 halamanNo Liability Where There Is No Breach of A Given RightNj BarandiaBelum ada peringkat
- Freddie Marshall Carson Transcript1 Court ProceedingsDokumen21 halamanFreddie Marshall Carson Transcript1 Court ProceedingslambertwatchBelum ada peringkat
- Complaint and Jury DemandDokumen13 halamanComplaint and Jury DemandWWMT100% (1)
- Corruption (EngDokumen8 halamanCorruption (EngFasih RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 The Ilocos Norte Electric Co Vs CADokumen2 halaman2 The Ilocos Norte Electric Co Vs CALeo FelicildaBelum ada peringkat
- Republic Vs CasimiroDokumen8 halamanRepublic Vs CasimiroCistron ExonBelum ada peringkat
- Keeping Children Safe - RedactedDokumen12 halamanKeeping Children Safe - RedactedGraeme Thompson100% (1)
- Sec 498A IPC Will A Boon Turn in Legal Terrorism ? A Review: Sandip Bhowate, Shrikant AsawaDokumen5 halamanSec 498A IPC Will A Boon Turn in Legal Terrorism ? A Review: Sandip Bhowate, Shrikant AsawaDanishMiyanBelum ada peringkat
- Rubias vs. Batiller MATDokumen1 halamanRubias vs. Batiller MATmarwantahsin100% (4)
- Ethics ReviewerDokumen8 halamanEthics ReviewerFiona Erica ComplitadoBelum ada peringkat
- PrevilegeCard Terms and FormsDokumen4 halamanPrevilegeCard Terms and FormsDeepak TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Payment Demand LetterDokumen1 halamanPayment Demand LetterLegal Forms100% (2)
- Deed of Sale Motor VehicleDokumen4 halamanDeed of Sale Motor Vehiclegeorgecloney100% (2)
- Draft of An Agreement To SellDokumen4 halamanDraft of An Agreement To Sellshruti gupta100% (1)
- Indophil Textile Mill Workers Union V CalicaDokumen1 halamanIndophil Textile Mill Workers Union V CalicaJL A H-Dimaculangan100% (1)
- WeddingDokumen27 halamanWeddingAkbar BhahestyBelum ada peringkat
- Awareness, Acceptance and Perception of Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Stakeholders Towards Its Vision, Mission, Goals and ObjectivesDokumen4 halamanAwareness, Acceptance and Perception of Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Stakeholders Towards Its Vision, Mission, Goals and ObjectivesPAANOBelum ada peringkat
- Discovery Practice ManualDokumen27 halamanDiscovery Practice ManualRobert HaywardBelum ada peringkat
- DOJ Marijuana Research MemoDokumen25 halamanDOJ Marijuana Research MemoMarijuana MomentBelum ada peringkat
- JChiroprHumanit2007v14 34-40 PDFDokumen7 halamanJChiroprHumanit2007v14 34-40 PDFRetno SawitriBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Chapter-05Dokumen86 halaman11 Chapter-05ANJALI NAINBelum ada peringkat
- Arucio ABPA 3NC (PA318-Ethics and Accountability-In-Public-Service)Dokumen33 halamanArucio ABPA 3NC (PA318-Ethics and Accountability-In-Public-Service)EMMANUELBelum ada peringkat
- PD 1746 Construction Industry of The PhilippinesDokumen7 halamanPD 1746 Construction Industry of The PhilippinesAllendy R. ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Case Sythesizing 1Dokumen6 halamanCase Sythesizing 1Robehgene Atud-JavinarBelum ada peringkat
- Sales Case Digest Part 5Dokumen35 halamanSales Case Digest Part 5Don SumiogBelum ada peringkat
- Mkt101-Chap 15-Part 3Dokumen7 halamanMkt101-Chap 15-Part 3Hải Yến NguyễnBelum ada peringkat