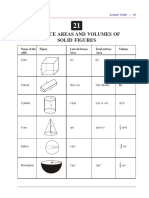
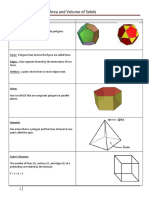
Page 931
Diunggah oleh
Amy DoanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Page 931
Diunggah oleh
Amy DoanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
11.
2 Area of a Parallelogram The area of a
12.2 Surface Area of a Right Prism The surface
parallelogram is the product of a base and its corresponding height. A 5 bh (p. 721)
11.3 Area of a Triangle The area of a triangle is
one half the product of a base and its
1 corresponding height. A 5 } bh (p. 721) 2 11.4 Area of a Trapezoid The area of a trapezoid
area S of a right prism is S 5 2B 1 Ph 5 aP 1 Ph, where a is the apothem of the base, B is the area of a base, P is the perimeter of a base, and h is the height. (p. 804)
12.3 Surface Area of a Right Cylinder The
is one half the product of the height and the sum of the lengths of the bases.
1 A5} h(b1 1 b2) (p. 730) 2 11.5 Area of a Rhombus The area of a rhombus
surface area S of a right cylinder is S 5 2B 1 Ch 5 2r 2 1 2rh, where B is the area of a base, C is the circumference of a base, r is the radius of a base, and h is the height. (p. 805) surface area S of a regular pyramid is 1 S5B1} Pl, where B is the area of the base, P is the perimeter of the base, and l is the slant height. (p. 811)
2
12.4 Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid The
is one half the product of the lengths of its
1 diagonals. A 5 } d d (p. 731) 2 1 2 11.6 Area of a Kite The area of a kite is one half
the product of the lengths of its diagonals. 1 A5} d1d2 (p. 731)
2 11.7 Areas of Similar Polygons If two polygons
12.5 Surface Area of a Right Cone The surface 1 area S of a right cone is S 5 B 1 } Cl 5 r 2 1 2
are similar with the lengths of corresponding sides in the ratio of a : b, then the ratio of their areas is a2 : b2. (p. 737)
11.8 Circumference of a Circle The
rl, where B is the area of the base, C is the circumference of the base, r is the radius of the base, and l is the slant height. (p. 812)
12.6 Volume of a Prism The volume V of a prism
circumference C of a circle is C 5 d or C 5 2r, where d is the diameter of the circle and r is the radius of the circle. (p. 746)
is V 5 Bh, where B is the area of a base and h is the height. (p. 820)
12.7 Volume of a Cylinder The volume V of a
Arc Length Corollary In a circle, the ratio of the length of a given arc to the circumference is equal to the ratio of the measure of the arc to 3608.
Arc length of AB m AB }} 5 }, or 2pr 3608 m AB Arc length of AB 5 } p 2r (p. 747) 3608 11.9 Area of a Circle The area of a circle is times
cylinder is V 5 Bh 5 r 2h, where B is the area of a base, h is the height, and r is the radius of a base. (p. 820) POSTULATES AND THEOREMS same height and the same cross-sectional area at every level, then they have the same volume. (p. 821)
12.8 Cavalieris Principle If two solids have the
C C C
the square of the radius. A 5 r 2 (p. 755)
12.9 Volume of a Pyramid The volume V of a 1 pyramid is V 5 } Bh, where B is the area of 3
the base and h is the height. (p. 829)
12.10 Volume of a Cone The volume V of a cone is 1 1 2 V5} Bh 5 } r h, where B is the area of the 3 3
11.10 Area of a Sector The ratio of the area A of a
sector of a circle to the area of the whole circle (r 2) is equal to the ratio of the measure of the intercepted arc to 3608. 5 }, or A 5 } p r 2 (p. 756) } 2
11.11 Area of a Regular Polygon The area of a A pr m AB 3608
m AB 360 8
base, h is the height, and r is the radius of the base. (p. 829)
12.11 Surface Area of a Sphere The surface area S
of a sphere with radius r is S 5 4r 2. (p. 838)
regular n-gon with side length s is half the product of the apothem a and the perimeter
1 1 P, so A 5 } aP, or A 5 } a p ns. (p. 763) 2 2 12.1 Eulers Theorem The number of faces (F ),
12.12 Volume of a Sphere The volume V of a 4 3 sphere with radius r is V 5 } r . (p. 840) 3 12.13 Similar Solids Theorem If two similar solids
vertices (V), and edges (E ) of a polyhedron are related by the formula F 1 V 5 E 1 2.
(p. 795)
have a scale factor of a : b, then corresponding areas have a ratio of a2 : b2, and corresponding volumes have a ratio of a3 : b3. (p. 848)
Postulates and Theorems
931
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ieep213 PDFDokumen8 halamanIeep213 PDFsasigunaBelum ada peringkat
- On Surface AreasDokumen20 halamanOn Surface Areasmary graceBelum ada peringkat
- Circular Segment PropertiesDokumen3 halamanCircular Segment PropertiesMary LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Areas Related To CirclesDokumen17 halamanAreas Related To Circlesshawlin_90Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen16 halamanChapter 7Pyae Sone KyawBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 19Dokumen12 halamanChapter 19Ali AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- AlxaEGCS6 08 05Dokumen20 halamanAlxaEGCS6 08 05Stevenzel Eala EstellaBelum ada peringkat
- Jeep 211 GGDokumen17 halamanJeep 211 GGAlexa Heart LaurinoBelum ada peringkat
- CH - 12 (26-2-2009) .PMDDokumen10 halamanCH - 12 (26-2-2009) .PMDRaj palBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas for Pre-Olympiad Math CompetitionsDokumen11 halamanFormulas for Pre-Olympiad Math Competitionsjehovisti100% (1)
- Surface Area and Volume - 2023-24Dokumen6 halamanSurface Area and Volume - 2023-24Aaratrika DasBelum ada peringkat
- AlxaEGCS6 09 04Dokumen37 halamanAlxaEGCS6 09 04Kurtis HarperBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Area and Volume (Assignment-1)Dokumen2 halamanSurface Area and Volume (Assignment-1)wordsandherrBelum ada peringkat
- 10 SurfaceareavolumeDokumen28 halaman10 Surfaceareavolumebgtes123Belum ada peringkat
- Conical FrustumDokumen11 halamanConical FrustumRajaKuppanBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas Pre OlympiadDokumen11 halamanFormulas Pre Olympiadbus9Belum ada peringkat
- SphereDokumen15 halamanSpherejolinmartinBelum ada peringkat
- GCHP 12Dokumen11 halamanGCHP 12caroline_amideast8101Belum ada peringkat
- Volume Frustum FormulasDokumen8 halamanVolume Frustum FormulasElizabeth CapiñaBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-11 (26-2-2009) .PMDDokumen12 halamanCh-11 (26-2-2009) .PMDRaj palBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 13 Surface Areas and VolumesDokumen31 halamanChapter - 13 Surface Areas and VolumesYash Goyal100% (1)
- Surface AreaDokumen16 halamanSurface AreayuruichiBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12Dokumen20 halamanNCERT Exemplar Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12Yashawanth am Yashawanth amBelum ada peringkat
- l-21_surface_areas_and_volumes_ofDokumen3 halamanl-21_surface_areas_and_volumes_ofsoorya_taBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas for Pre-Olympiad Math CompetitionsDokumen11 halamanFormulas for Pre-Olympiad Math CompetitionsSajjad HameedBelum ada peringkat
- Week 7 CylinderDokumen30 halamanWeek 7 CylinderJulius Patrick Mallanao100% (1)
- Cylinders: Book 2B Chapter 11Dokumen42 halamanCylinders: Book 2B Chapter 11Yana100% (1)
- Surfaces and Volumes of Spheres in CalculusDokumen8 halamanSurfaces and Volumes of Spheres in CalculusNISSIBETIBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet For HomeworkDokumen10 halamanWorksheet For HomeworkDivaBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Areas and Volumes: Cuboid Whose Length L, Breadth B and Height HDokumen8 halamanSurface Areas and Volumes: Cuboid Whose Length L, Breadth B and Height HKrishna Moorti MishraBelum ada peringkat
- XC Cs 37 T 5 P Xosy E85 UgupDokumen5 halamanXC Cs 37 T 5 P Xosy E85 Ugupshanmuga Priya (Shan)Belum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Maths 12Dokumen17 halamanClass 10 Maths 12Mallipudi SphoorthiBelum ada peringkat
- Solidmens SphereDokumen23 halamanSolidmens SphereArthur DantesBelum ada peringkat
- Sphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedDokumen16 halamanSphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedAndreGuilhermeBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceDokumen9 halamanGeometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceBagas FajriansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Mensuration of Solid FiguresDokumen10 halamanMensuration of Solid FiguresLyrics World РусскийBelum ada peringkat
- Azam 2 SolutionDokumen11 halamanAzam 2 Solutionjohn cruzBelum ada peringkat
- Solid MensurationDokumen32 halamanSolid MensurationEdgar Kenneth100% (1)
- Solid MensurationDokumen28 halamanSolid Mensurationwe_spidus_2006100% (2)
- 10th Maths Surface Area Practice SheetDokumen11 halaman10th Maths Surface Area Practice SheetAyush singh chauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Spherical Triangle PDFDokumen31 halamanSpherical Triangle PDFGiorgi BalkhamishviliBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry Vocabulary and PostulatesDokumen9 halamanGeometry Vocabulary and PostulatesWilson ZhangBelum ada peringkat
- Class 9 (Surface Areas and Volumes)Dokumen3 halamanClass 9 (Surface Areas and Volumes)alvina dhalaitBelum ada peringkat
- FDG We: The MayDokumen1 halamanFDG We: The MayreacharunkBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDokumen7 halamanGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- sav class 9 mathsDokumen3 halamansav class 9 mathssanitdoot456Belum ada peringkat
- Square Drilling with Reuleaux Triangle AttachmentDokumen9 halamanSquare Drilling with Reuleaux Triangle AttachmentTanviBelum ada peringkat
- Tetrahedron: Not To Be Confused With - For The Academic Journal, SeeDokumen23 halamanTetrahedron: Not To Be Confused With - For The Academic Journal, Seejacque zidaneBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric ShapeDokumen34 halamanGeometric ShapeAnthony HeartBelum ada peringkat
- Arc Length and Area of SectorDokumen7 halamanArc Length and Area of SectorChieh An100% (2)
- Plane and Solid GeometryDokumen105 halamanPlane and Solid GeometryOnline Educator100% (3)
- IMG_20210302_205800Dokumen4 halamanIMG_20210302_205800Ramesh AnkathiBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Area of Cone - Definition, Formula, Types & QuestionsDokumen11 halamanSurface Area of Cone - Definition, Formula, Types & QuestionsRahul SinghBelum ada peringkat
- POLYGONSDokumen45 halamanPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- AlxaEGCS6 09 03Dokumen45 halamanAlxaEGCS6 09 03Kurtis HarperBelum ada peringkat
- Circular Segment PropertiesDokumen3 halamanCircular Segment PropertiescabpcabpBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Area of Cylinders, Spheres, Cones LESSONDokumen2 halamanSurface Area of Cylinders, Spheres, Cones LESSONSuchaya AngsakulBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement - Solid FiguresDokumen44 halamanMeasurement - Solid FiguresFREDERICK FUENTESBelum ada peringkat
- Ship Hydrodynamics Lecture Notes Part 2 Propeller GeometryDokumen10 halamanShip Hydrodynamics Lecture Notes Part 2 Propeller Geometryborhec123Belum ada peringkat
- Page 929Dokumen1 halamanPage 929Amy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- A Confrontation of NatureDokumen4 halamanA Confrontation of NatureAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Iliad Cornell NotesDokumen33 halamanIliad Cornell NotesAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- M Are Parallel, Then A Reflection in Line K: Student ResourcesDokumen1 halamanM Are Parallel, Then A Reflection in Line K: Student ResourcesAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Page 928Dokumen1 halamanPage 928Amy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- LunchtimeDokumen1 halamanLunchtimeAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Postulates Postulates: A and C, Then Ab Obanda Ob - The Rays of The Form Oa Can Be Matched One To One With The RealDokumen1 halamanPostulates Postulates: A and C, Then Ab Obanda Ob - The Rays of The Form Oa Can Be Matched One To One With The RealAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Theorems Theorems: AB AB. AB CD, Then CD AB. AB CD and CD EF, Then AB EFDokumen1 halamanTheorems Theorems: AB AB. AB CD, Then CD AB. AB CD and CD EF, Then AB EFAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- CPO Focus On Physical Science Student TextbookDokumen399 halamanCPO Focus On Physical Science Student TextbookAmy Doan75% (4)
- TWM: Ed. 1, Iss. 1Dokumen3 halamanTWM: Ed. 1, Iss. 1Amy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- The BetDokumen1 halamanThe BetAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Skater's WaltzDokumen1 halamanSkater's WaltzAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Frog in A TreeDokumen1 halamanFrog in A TreeAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Africa Study GuideDokumen3 halamanAfrica Study GuideAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Ancient Greece and The Epidaurus TheaterDokumen3 halamanAncient Greece and The Epidaurus TheaterAmy DoanBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 6 Olympiad: Answer The QuestionsDokumen14 halamanGrade 6 Olympiad: Answer The QuestionsFirjon46Belum ada peringkat
- Math4 TG U2Dokumen114 halamanMath4 TG U2Jun Rey Parreño100% (2)
- C2pp Jan13Dokumen104 halamanC2pp Jan13JW1212Belum ada peringkat
- MM PT3 Pahang AnsDokumen5 halamanMM PT3 Pahang Ansahchin5Belum ada peringkat
- January 2016 QPDokumen20 halamanJanuary 2016 QPSri Devi NagarjunaBelum ada peringkat
- Davis & Johnson Forest Management 3rd Edition Chapter 14Dokumen29 halamanDavis & Johnson Forest Management 3rd Edition Chapter 14TOMÁS RODRÍGUEZBelum ada peringkat
- Test 29a Aims Sseq Mathematics March 2023 60 QuestionsDokumen28 halamanTest 29a Aims Sseq Mathematics March 2023 60 QuestionsG GBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Grade Math CbaDokumen8 halaman2nd Grade Math Cbaapi-340822422Belum ada peringkat
- PLANIMETER ManuaL PDFDokumen17 halamanPLANIMETER ManuaL PDFSamir AlshaarBelum ada peringkat
- H SPM Past Years Questions Form 4-5 Chapters Answer BookDokumen43 halamanH SPM Past Years Questions Form 4-5 Chapters Answer Bookvaijayanthimala velauthamBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 11 Algebraic Manipulation Overhead SlidesDokumen9 halamanUNIT 11 Algebraic Manipulation Overhead SlidesPh DeBelum ada peringkat
- GMAT Quant Topic 6 Co-Ordinate Geometry SolutionsDokumen20 halamanGMAT Quant Topic 6 Co-Ordinate Geometry SolutionsRushabh VoraBelum ada peringkat
- Eoy SyllabusDokumen8 halamanEoy Syllabusmuhammad tahirBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Mensuration of Plane Figures PDFDokumen10 halaman14 Mensuration of Plane Figures PDFAllen Kyle PrielaBelum ada peringkat
- Plane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionDokumen28 halamanPlane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionChong JongBelum ada peringkat
- 60 Minutes-60 Questions: Mathematics TestDokumen17 halaman60 Minutes-60 Questions: Mathematics TestReem Mohamed0% (1)
- Class 8 ICSE ML Agarwal Maths BookDokumen1.007 halamanClass 8 ICSE ML Agarwal Maths Bookharish paul100% (1)
- Form 3 MathsDokumen4 halamanForm 3 MathsKeabetswe MoneiBelum ada peringkat
- TCS Sample Questions - PapersDokumen12 halamanTCS Sample Questions - PapersSantosh GBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-1 Lesson 2Dokumen14 halamanUnit-1 Lesson 2Nita Teresa BagaraBelum ada peringkat
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokumen8 halamanMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayTöňğ GeronimoBelum ada peringkat
- Raft FoundationsDokumen5 halamanRaft FoundationsbotchBelum ada peringkat
- 01 8th Nift MathsDokumen12 halaman01 8th Nift MathsLandon MitchellBelum ada peringkat
- Urban Sprawl Metrics: An Analysis of Global Urban Expansion Using GISDokumen13 halamanUrban Sprawl Metrics: An Analysis of Global Urban Expansion Using GISHannura HoseaBelum ada peringkat
- Seven Oaks Year - 7 - 2018 - Maths - ExamDokumen8 halamanSeven Oaks Year - 7 - 2018 - Maths - ExamDarren ContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Hockey Skill Test GuideDokumen35 halamanHockey Skill Test Guide546 Aman Singh TomarBelum ada peringkat
- GMAT Official Advanced QuestionsDokumen407 halamanGMAT Official Advanced QuestionsFIORELLA JAHAIRA RAMOS TARRILLO100% (3)
- Survey II NotesDokumen95 halamanSurvey II NotesJoshua KiptooBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Problem Solving and Data AnalysisDokumen84 halamanChapter 2 - Problem Solving and Data AnalysisJames charlesBelum ada peringkat
- Math Test Questions on Circles, Volume, Temperature & ProbabilityDokumen6 halamanMath Test Questions on Circles, Volume, Temperature & ProbabilityKAREN IVY BAGAYASBelum ada peringkat
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignDari EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (137)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDari EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (6)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingDari EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignDari EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Dari EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorDari EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusDari EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (20)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenDari EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenBelum ada peringkat
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceDari EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideDari EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDari EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsBelum ada peringkat
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsDari EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (15)