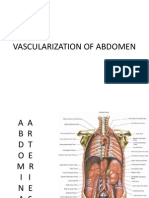
3 Major Arteries of GI
Diunggah oleh
beia21Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
3 Major Arteries of GI
Diunggah oleh
beia21Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
3 Anterior visceral branches of Abdominal Aorta - Large and unpaired
1. the CELIAC ARTERY o o o which branches from the abdominal aorta at the level of T12 vertebrae artery of the foregut supplies the GI tract from the lower 1/3 of the esophagus the middle of the second part of the duodenum
o o o o
very short surrounded by celiac plexus lies behind the lesser sac of peritoneum 3 terminal branches:
a. Left gastric artery
Runs to the cardiac end of the stomach Gives off a few esophageal branches Turns to the right along the lesser curvature of the stomach Anastomoses with the right gastric artery (short gastric arteries)
Branches: o Esophageal branches
Right gastric artery Arises from hepatic artery at the upper border of the pylorus Runs to the left in the lesser omentum along the lesser curvature of the stomach Anastomoses with left gastric artery Gastroduodenal artery A large branch that descends behind the first part of the duodenum Divides into o Right gastroepiploi c artery Runs along the greater curvatur e of the stomac h betwee n the layers of greater omentu m Anasto mose with left gastroe piploic artery o Superior pancreaticod uodenal artery Descen ds bet. the second part of the duoden um and the head of pancrea s
b. Splenic artery - Runs to the left in a wavy course along the upper border of the pancreas and behind the stomach - On reaching the left kidney, the artery enters the splenicorenal ligament runs to the hilum of the spleen - Branches: o Pancreatic branches o Left gastroepiploic artery Arises near the hilum of the spleen Reaches the lesser curvature of the stomach in the gastrosplenic omentum Passes to the right along the greater curvature of the stomach between the layers of greater omentum Anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic artery o Short gastric arteries 5 or 6 Arise from the end of the splenic artery Reach the fundus of the stomach in the gastrosplenic omentum Anastomose with the left gastric artery and the left gastroepiploic artery
c. Hepatic artery o Medium-sized o Is sometimes divided into the common hepatic artery Extends from its origin to the gastroduodenl branch Hepatic artery propter The remainder of the artery o Branches:
right and left hepatic artery
supply the right and left lobes of the liver respectively right hepatic artery
usually gives off the cystic artery runs to the neck of the GB passes to the right as a single or double branch along the upper border of the 3rd part of the duodenum and the head of pancreas supplies the o pancreas o adjoining part of the duodenum o
2. the superior mesenteric artery o which arises from the abdominal aorta at the lower border of vertebra L1 o artery of the midgut o supplies the GI tract from the midline of the 2nd part of the duodenum as far as the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon distal part of the duodenum jejunum ileum cecum appendix ascending colon most of the transverse colon o branches: inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
middle colic artery runs forward in the transverse mesocolon divides into o right branch o left branch right colic artery often a branch of ileocolic aa passes to the right to supply the ascending colon divides into o ascending branch o descending branch ileocolic artery passes downward to the right gives rise to a o superior branch anastomoses Give rise to with right colic -anterior & posterior cecal artery arteries o inferior -appendicular branch artery (branch of anastomoses posterior cecal aa) with the end of the superior mesenteric aa Jujenal & ileal branches 12-15 in number Arise from the left side of the superior mesenteric artery Each divides into 2 vessel, which unite w/ adjacent branches to form a series of arcades
Fewer arcades supply the jejunum than the ileum
o o
o o
artery of the hindgut Supplies the large intestine from the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon halfway down the anal canal Distal 1/3 of the transverse colon Left colic flexure Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Upper half of the anal canal Arises from the abdominal aorta about 1.5 in (3.8cm) above its bifurcation Runs downward and to the left Crosses the left common iliac artery Becomes superior rectal artery Branches Left colic artery Runs upward and to the left Supplies the o distal 3rd of transverse colon o left colic flexure o upper part of the descending colon divides into o ascending branch o descending branch Sigmoid arteries 2 or 3 in number Supply the o Descending colon o Sigmoid colon Superior rectal artery A continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery as it crosses the left common iliac artery Descends into the pelvis behind the rectum Supplies the o Rectum
3. the inferior mesenteric artery o which branches from the abdominal aorta at approximately vertebral level L3
Upper half of the anal canal Anastomoses with the o middle rectal o inferior rectal arteries o
4. Marginal artery o The anastomosis of the colic arteries around the concave margin of the large intestine forms a single arterial trunk called marginal artery =) o Begins at the ileocecal junction Where it anastomoses with the ileal branches of the superior mesenteric artery o Ends Where it anastomoses less freely with the superior rectal artery Portal Vein (Hepatic Portal Vein) drains blood from the abdominal part of the GI o from the lower 3rdof the esophagus anal canal also drains blood from the o spleen o pancreas o GB Enters the liver Sinusoids Hepatic veins Inferior vena cava 2 in (5cm) long Formed behind the neck of the pancreas by the union of the o superior mesenteric vein o splenic veins
VENOUS DRAINAGE Venous blood from the GI tract drains to the liver by the portal venous system Proximal tributaries: drain directly into the portal vein Distal tributaries: o correspond to the branches of the celiac artery o superior & inferior mesenteric arteries
Ascends to the right, behind the 1st part of the duodenum Enters the lesser omentum Runs upward in front of the opening into the lesser sac to the porta hepatis Divides into right & left terminal branches
tributaries: o splenic vein o inferior mesentery vein o superior mesentery vein o left gastric vein drains the left portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach and the distal part of the esophagus opens directly into portal vein o right gastric vein
ARTERIES ON THE POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL Aorta - enters the abdomen through the aortic opening of the diaphragm in front of the T12 vertebra - descends behind the peritoneum on eh anterior surface of the bodies of the lumbar vertebrae - @L4 divides into the 2 common iliac arteries - On its right side lies the o IVC o Inferior vena cava o Cisterna chyli o The beginning of azygous vein - Branches: o 3 anterior branches: Celiac artery Superior mesenteric artery Inferior mesenteric artery o 3 lateral branches Suprarenal artery Renal artery Testicular or ovarian artery o 5 lateral abdominal wall branches 1 inferior phrenic artery 4 lumbar arteries o 3 terminal branches 2 common iliac arteries Median sacral artery
COMMON ILIAC ARTERIES (RIGHT AND LEFT COMMON ILIAC ARTERIES) - Are terminal branches of aorta - Arise at the level of L4 Run downward and laterally along the medial border of the psoas mm Each ends in front of sacroiliac joint by dividng into the External & internal iliac arteries @ bifurcation: the common iliac artery on each side is crossed anteriorly by ureter
External Iliac Artery - Runs along the medial borer of psoas, following the pelvic rim - Branches: o Inferior epigastric artery Arises just above the inguinal ligament Passes upward & medially along the medial margin of the deep inguinal ring Enters rectus sheath behind the rectus abdominis mm o Deep circumflex artery
Arise close to the inferior epigastric artery Ascends laterally to the anterior superior iliac spine & the iliac crest Supply the mm of the anterior abdominal wall Enters the thigh by passing under the inguinal ligament Become femoral artery
Internal Iliac Artery - Passes down into the pelvis in front of the sacroiliac joint VEINS OF THE POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
The entrance into the lesser sac separates the inferior vena cava from the portal vein Tributaries o 2 anterior visceral tributaries: hepatic veins o 3 lateral visceral tributaries: Right suprarenal vein *the left suprarenal vein drains into the left renal vein Renal veins Right testicular or ovarian vein *the left ones are drained into the left renal vein 5 lateral abdominal tributaries 1 inferior phrenic vein 4 lumbar veins 3 veins of origin 2 common iliac veins Median sacral vein
Inferior vena cava - Coveys most of the blood from the body below the diaphragm to the right atrium of the heart - Is formed by the union of the o Common iliac veins behind the right common iliac artery @ the level of L5 vertebra - It ascends on the right side of the aorta Pierces the central tendon of the diapghragm at the level of T8 Right atrium - Behind its right margin: right sympathetic trunk - Right border: close to right ureter
Inferior Mesenteric Vein - A tributary of the portal circulation - Begins halfway down the anal canal as the superior rectal vein Passes up the posterior abdominal wall on the left side of the inferior mesenteric artery & duodenal flexure Joins the splenic vein behind the pancreas Receives the tributaries that correspond to the branches of the artery Splenic Mesenteric Vein - A tributary of the portal circulation
Begins at the hilum of the spleen by the union of several veins Joined by the short gastric and left gastoepiploic veins Passes to the right within the splenicorenal ligament Runs behind the pancreas Joins the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas Form the portal vein - Joined by veins from the pancreas and the inferior mesenteric vein Superior Mesenteric vein - A tributary of portal circulation - Begins at the ileocecal junction Runs upward on the posterior abdominal wall within the root of the mesentery of the s.i. and on the right side of the superior mesenteric aa Passes in front of the 3rd part of the duodenum and behind the neck of the pancreas Joins the splenic vein Form the portal vein
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Large Blood Vessels of The GutDokumen61 halamanLarge Blood Vessels of The GutpoojaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of CVS: 5. Blood Vessels of The Abdomen, Pelvis & PerineumDokumen30 halamanAnatomy of CVS: 5. Blood Vessels of The Abdomen, Pelvis & Perineumsultan khabeebBelum ada peringkat
- Vascularization of AbdomenDokumen25 halamanVascularization of AbdomenInka Fransiska MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy, Lecture 12, Blood Supply of The Gastrointestinal Tract (Slides)Dokumen27 halamanAnatomy, Lecture 12, Blood Supply of The Gastrointestinal Tract (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Supply of The Gastrointestinal TractDokumen2 halamanBlood Supply of The Gastrointestinal TractAli AkeelBelum ada peringkat
- The Portal Venous SystemDokumen21 halamanThe Portal Venous SystemAhmed DsoukiBelum ada peringkat
- Peritoneum: General FeaturesDokumen92 halamanPeritoneum: General FeaturestuhinsinghBelum ada peringkat
- Colorectal MalignancyDokumen108 halamanColorectal MalignancySatishht SatishBelum ada peringkat
- AnatDokumen119 halamanAnatGanesh RasalBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Esophagus and StomachDokumen65 halamanAnatomy of Esophagus and Stomachmackiecc100% (2)
- Dr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyDokumen55 halamanDr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyMohammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Large Intestine.Dokumen15 halamanLarge Intestine.Shimmering MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachDokumen82 halamanClinical Anatomy of The Esophagus and StomachmackieccBelum ada peringkat
- Colon & Rectum Anatomy, Bleeding Causes, and Diagnosis ToolsDokumen186 halamanColon & Rectum Anatomy, Bleeding Causes, and Diagnosis ToolsMr AABelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal CanalDokumen35 halamanAnterior Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Canalapi-3698357100% (3)
- By Prof. Saeed Abuel MakaremDokumen25 halamanBy Prof. Saeed Abuel MakaremmahardikaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi AbdomenDokumen36 halamanAnatomi Abdomenari naBelum ada peringkat
- GIT Applied AnatomyDokumen62 halamanGIT Applied Anatomyueumana0% (1)
- Genital ProlapseDokumen9 halamanGenital Prolapsesher singhBelum ada peringkat
- Popliteal Fossa and LegDokumen40 halamanPopliteal Fossa and LegRaj Shekhar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System Power PointDokumen17 halamanDigestive System Power PointAlyssa Mae DapadapBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of PeritoneumDokumen61 halamanAnatomy of PeritoneumFirdaus SeptiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Rectum & Anal CanalDokumen14 halamanRectum & Anal CanalLisa DentonBelum ada peringkat
- 16-Genital ProlapseDokumen37 halaman16-Genital Prolapseapi-3703352Belum ada peringkat
- Surgical Anatomy of The Biliary TractDokumen5 halamanSurgical Anatomy of The Biliary TracthoangducnamBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of DuodenumDokumen23 halamanAnatomy of DuodenumEngki AdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Hemicolectomy 1Dokumen40 halamanHemicolectomy 1Preethi GudipalliBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of the Hepatobiliary SystemDokumen29 halamanAnatomy of the Hepatobiliary SystemKevin KusumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy (302) - 1Dokumen82 halamanAnatomy (302) - 1Shehzad Noman SajidBelum ada peringkat
- Rectal Cancer PPT 2.1Dokumen131 halamanRectal Cancer PPT 2.1Usmle GuyBelum ada peringkat
- FASCIA OF THE ABDOMEN AND PELVISDokumen46 halamanFASCIA OF THE ABDOMEN AND PELVISserubimBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of LiverDokumen86 halamanAnatomy of Liverchandana pallavaBelum ada peringkat
- Peritoneum and Peritoneal CavityDokumen26 halamanPeritoneum and Peritoneal CavitytuhinsinghBelum ada peringkat
- Joints of Lower Limb 2017Dokumen77 halamanJoints of Lower Limb 2017yasrul izadBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic DuctDokumen2 halamanThoracic DuctDr santosh100% (1)
- Adductor Canal Anatomy and Block GuideDokumen18 halamanAdductor Canal Anatomy and Block GuideJanarthanan Sriram100% (1)
- Billiary SystemDokumen60 halamanBilliary SystemDONALD UNASHEBelum ada peringkat
- The Abdominal OrgansDokumen56 halamanThe Abdominal OrgansAjeng FikihBelum ada peringkat
- Thursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMDokumen266 halamanThursday, April 09, 2009 4:45 PMkcs2012Belum ada peringkat
- Femoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleDokumen23 halamanFemoral Sheath and Femoral TriangleSamiha Haq100% (2)
- The LiverDokumen7 halamanThe LiverBarrameda NegideasisBelum ada peringkat
- Anorectal Anatomy & Surgical ManagementDokumen164 halamanAnorectal Anatomy & Surgical Managementsgod34Belum ada peringkat
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDokumen22 halamanAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Embryology of the Lesser OmentumDokumen32 halamanAnatomy and Embryology of the Lesser OmentumspiraldaoBelum ada peringkat
- Azygos VeinDokumen2 halamanAzygos VeinDr santoshBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsDari EverandBlood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsDavid AbramsonBelum ada peringkat
- The Lower ExtremitiesDokumen80 halamanThe Lower ExtremitiesbayennBelum ada peringkat
- Hamstring Muscles, Sciatic Nerve, Popliteal FossaDokumen5 halamanHamstring Muscles, Sciatic Nerve, Popliteal Fossantege stuartBelum ada peringkat
- General Arrangement of The Abdominal VisceraDokumen30 halamanGeneral Arrangement of The Abdominal Visceraapi-249972919100% (2)
- Bowel AnastomosisDokumen30 halamanBowel AnastomosismrashaiedehBelum ada peringkat
- Surface Anatomy of HeartDokumen23 halamanSurface Anatomy of HeartKhush BakhtBelum ada peringkat
- Fetal Pig AnatomyDokumen43 halamanFetal Pig Anatomymihai2242Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationDokumen67 halamanLecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationSasikala MohanBelum ada peringkat
- Case 5 - Embryology of AppendixDokumen3 halamanCase 5 - Embryology of Appendixshilviadevi100% (1)
- Peripheral CirculationDokumen27 halamanPeripheral CirculationRachel ThomsonBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal WallDokumen56 halamanAbdominal WallAHMAD KHANBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of the Pelvis and PerineumDokumen101 halamanAnatomy of the Pelvis and PerineumCiprianTeodorulBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsDokumen10 halamanAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsIssac LauBelum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen59 halamanGlaucomabeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Approach To The Diagnosis of A Cancer PatientDokumen52 halamanApproach To The Diagnosis of A Cancer Patientbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- GlaucomaDokumen59 halamanGlaucomabeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Cestodes 2Dokumen3 halamanCestodes 2beia21Belum ada peringkat
- Med Ethics Report - KissingerDokumen7 halamanMed Ethics Report - Kissingerbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Test Taking StrategiesDokumen17 halamanTest Taking Strategiesbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- 5pediatrics2.1 Neuro Exam Uerm2015bDokumen6 halaman5pediatrics2.1 Neuro Exam Uerm2015bbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Community Medicine Learning ObjectivesDokumen4 halamanCommunity Medicine Learning Objectivesbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen14 halamanChapter 1beia21Belum ada peringkat
- 3PEDIA6 - Childhood Cancer UERM2015BDokumen15 halaman3PEDIA6 - Childhood Cancer UERM2015Bbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric History ImdDokumen17 halamanPsychiatric History Imdunno hiquianaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast AnatomyDokumen53 halamanBreast AnatomyShriniwas RushiBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma Sales HandbookDokumen16 halamanPharma Sales Handbookbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Floor plan layout registration buffet entrance exitDokumen1 halamanFloor plan layout registration buffet entrance exitbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Goldmining PDFDokumen7 halamanGoldmining PDFbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- 225 Primary Biliary CirrhosisDokumen3 halaman225 Primary Biliary Cirrhosisbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Epidemiology Case ReportDokumen5 halamanEpidemiology Case Reportbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Diseases of Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandDokumen60 halamanDiseases of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glandbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- The Antimicrobial Effects of Centella Asiatica CreamDokumen1 halamanThe Antimicrobial Effects of Centella Asiatica Creambeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Interconversion of Sugar From Aldose To KetoseDokumen7 halamanInterconversion of Sugar From Aldose To Ketosebeia21Belum ada peringkat
- 1200 Calorie Diet Menu PlanDokumen12 halaman1200 Calorie Diet Menu PlanJanet SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Philam Life ProductsDokumen3 halamanPhilam Life Productsbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Bright Future Invest 2013Dokumen1 halamanBright Future Invest 2013beia21Belum ada peringkat
- AT&T AGENT'S GUIDE TO VALUING CUSTOMERSDokumen4 halamanAT&T AGENT'S GUIDE TO VALUING CUSTOMERSbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- We BoundariesDokumen1 halamanWe Boundariesbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Low Back PainDokumen3 halamanLow Back Painbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- 1200 Calorie Diet Menu PlanDokumen12 halaman1200 Calorie Diet Menu PlanJanet SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Elem Trad CdsDokumen2 halamanElem Trad Cdsbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Love Different Week 1Dokumen2 halamanLove Different Week 1Suzaine AmbayecBelum ada peringkat
- Abundance Plus Client Presentation PDFDokumen20 halamanAbundance Plus Client Presentation PDFbeia21Belum ada peringkat
- Concept Map on Portal HypertensionDokumen3 halamanConcept Map on Portal HypertensionKrizle AdazaBelum ada peringkat
- Bariatric Surgery: 1. Predominantly Malabsorptive ProceduresDokumen9 halamanBariatric Surgery: 1. Predominantly Malabsorptive ProceduresmegangstaBelum ada peringkat
- Helicobacter Pylori Infection and TreatmentDokumen3 halamanHelicobacter Pylori Infection and Treatmentto van quyenBelum ada peringkat
- Vocabulary Unit 4 PrintableDokumen2 halamanVocabulary Unit 4 PrintableLuis EnriqueBelum ada peringkat
- General Surgery Board-Final Written Exam Blueprint v.1Dokumen3 halamanGeneral Surgery Board-Final Written Exam Blueprint v.1Mohammed S. Al GhamdiBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8-Digestive Lesson PlanDokumen5 halamanGrade 8-Digestive Lesson PlanTeresa Marie Yap Cordero100% (7)
- Acute PeritonitisDokumen4 halamanAcute PeritonitisSatrio Tri HadmokoBelum ada peringkat
- Alginate TherapyDokumen12 halamanAlginate TherapySMJ DRDBelum ada peringkat
- Page 51Dokumen6 halamanPage 51Awang Muhammad HamiduddinBelum ada peringkat
- Dyspepsia Abdul Rahman NewDokumen50 halamanDyspepsia Abdul Rahman NewRahmawati Nur AriyantiBelum ada peringkat
- حيا 211-215 دليل المعلمDokumen171 halamanحيا 211-215 دليل المعلم312qqqqppppBelum ada peringkat
- Sigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Dokumen46 halamanSigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Amani Twaha MsemakweliBelum ada peringkat
- Sarcomastigophora: A Phylum of PROTOZOA Subphyla: SARCODINA and Have Flagella or PseudopodiaDokumen20 halamanSarcomastigophora: A Phylum of PROTOZOA Subphyla: SARCODINA and Have Flagella or Pseudopodiaabel semuBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System BreakdownDokumen3 halamanDigestive System BreakdownSyifa IndanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pseudomyxoma PeritoneiDokumen5 halamanPseudomyxoma PeritoneiAbdul QuyyumBelum ada peringkat
- Barium Meal: BY Mathew Abubakar Department of Medical RadiographyDokumen28 halamanBarium Meal: BY Mathew Abubakar Department of Medical RadiographyJameeluh TijjanyBelum ada peringkat
- Enteral NutritionDokumen74 halamanEnteral NutritionHenno HenoBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Approach to Neonatal JaundiceDokumen17 halamanClinical Approach to Neonatal JaundiceGiann PersonaBelum ada peringkat
- Fistula in AnoDokumen4 halamanFistula in AnoosamabinziaBelum ada peringkat
- Yu - Git - Emb 1Dokumen67 halamanYu - Git - Emb 1gtaha80Belum ada peringkat
- Git & Hepatobiliary-Ii 4 Year MBBS: KMU (IHPER) - Central Curriculum CommitteeDokumen50 halamanGit & Hepatobiliary-Ii 4 Year MBBS: KMU (IHPER) - Central Curriculum CommitteeF ParikhBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System WorksheetsDokumen3 halamanDigestive System Worksheetsapi-258634162100% (1)
- Bomba A Et Al 2002 Probiotics and PUFAsDokumen5 halamanBomba A Et Al 2002 Probiotics and PUFAsSandip PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal PainDokumen11 halamanAbdominal PainSBelum ada peringkat
- Guideline bowel irrigation infants childrenDokumen16 halamanGuideline bowel irrigation infants childrenRendy SusantoBelum ada peringkat
- 36 PDFDokumen129 halaman36 PDFjsc rajuBelum ada peringkat
- Case CholeDokumen23 halamanCase CholeLailani Rose Gulinao-DorupaBelum ada peringkat
- Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms and Diagnosis - Google SearchDokumen3 halamanPancreatic Cancer Symptoms and Diagnosis - Google Searchranjit__kayalaBelum ada peringkat
- Potential Use of Probiotics: Ekachai ChukeatiroteDokumen8 halamanPotential Use of Probiotics: Ekachai ChukeatiroteDanu EffendiBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of Parotid GlandDokumen32 halamanFunctions of Parotid GlandAsline JesicaBelum ada peringkat