Cost Studies Model Paper
Diunggah oleh
akalanka_ccsDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cost Studies Model Paper
Diunggah oleh
akalanka_ccsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
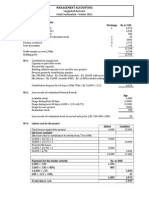
Question 01 Building A Purchasing Cost Legal costs associated with purchase Cost of improvement of the building Annual Maintenance
cost Annual energy cost Cost of repairs Future expansion cost Resale value of the building Rs. 400Mn 2% of purchase price Rs. 30Mn Rs. 30Mn Rs. 14Mn Rs. 10Mn (every 5 years) Rs. 60Mn (at 10th year) Rs. 100Mn TOTAL Discount factor 1 1 1 8.51 8.51 1.25 0.39 0.15 Present Value (Mn) 400 8 30 170.2 102.12 12.5 19.5 22.5
863.34
Building B Purchasing Cost Legal costs associated with purchase Cost of improvement of the building Annual Maintenance cost Annual energy cost Cost of repairs Future expansion cost Resale value of the building Rs. 600Mn 2% of purchase price Rs. 20Mn Rs. 20Mn Rs. 14Mn Rs. 15Mn (every 6 years) Rs. 200Mn TOTAL
Discount factor 1 1 1 8.51 8.51 1.06 0.15
Present Value (Mn) 400 8
10 85.1 102.12 15.9 0 37.5
967.24
Calculations Building A Legal costs associated with purchase = 400*2% =8Mn *Assume improvements of the building is done just after the purchasing Discount factor for Annual Maintenance = 1- 1/(1+r)^n r = 1- 1/(1+0.1)^20 0.1 = 8.51 = Discount factor for Annual energy
Discount factor for Annual Maintenance
*Assume that at the end of 20th year, there are no repairs Discount factor for repairs = 1/ (1+0.1)^5 + 1/ (1+0.1)^10 + 1/ (1+0.1)^15 = 1.25 Discount factor for Future expansion = 1/ (1+0.1)^10 = 0.39
Discount factor for Resale value of the building = 1/ (1+0.1)^20 = 0.15
Building B Legal costs associated with purchase = 600*2% =12Mn *Assume improvements of the building is done just after the purchasing
Discount factor for Annual Maintenance of Building A = Discount factor for Annual Maintenance of Building B = Discount factor for Annual energy of Building B
Discount factor for repairs
= 1/ (1+0.1)^6 = 1.06
+ 1/ (1+0.1)^12 + 1/ (1+0.1)^18
Discount factor for Resale value of the building = 1/ (1+0.1)^20 = 0.15
According to the given information, LCC of two buildings as follows LCC of Building A LCC of Building B = 863.34Mn =967.24Mn
Hence the company management have to be purchased Building A which has the lowest Life cycle cost.
(b) Utilities for services Disposal costs Technology Indirect costs associated with administration Licence Non-energy operation costs Cost of Management of the building Cost of Electricity Cost of Water supply Cost of Gas Cost of Equipments Lease payments(if any) Sanitary fittings At least have to mention five out of the above.
Question 02 ( 1) Superficial area method (2 ) Estimate = Area of each of the floors*Cost per m2 Most Popular preliminary estimating method Advantages Quick method Easy to employ as the rules for calculations are much more simple Directly relates to accommodation Allow comparison of different Designs Meaningful in its concept of measurement(m2) to both client and architect Allow comparison between buildings that differ in size and shape
Disadvantages Fails to take account of any variation in plan and shape or storey height * Try to highlight the advantages of this method by analysing the above mentioned points.
(3) Typical unit rate for a shopping complex : Rs. 80,000 95,000/Sqm Hence for this shopping complex assume unit rate as 90,000+100,000 = 95,000.00 2 Hence, Estimate = 8000sqm*95,000Rs/sqm =760Mn
(4)
* First explain what elemental cost planning technique is.
Elemental cost planning is often referred to as 'designing to a cost' or 'target cost planning' since a cost limit is fixed for the scheme and the architect must then prepare a design not to exceed this cost. However it has following advantages. system of cost planning and Cost control Overcome the disadvantages of the preliminary estimating methods Form of construction, materials and labour content, quality of the element is compared with the element of analyzed building
Ensure that the tender amount is close to the first estimate, or that any likely difference between the two is anticipated and is acceptable. Ensure that the money available for the projects is allocated consciously and economically to the various components and finishes. Always involves the measurement and pricing of approximate quantities at some stage of the process. Aim to achieve good value at the desired level of expenditure.
*then describe the information required to calculate by using an actual example. Ex: Construction of two storey office building
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Guidelines for the Economic Analysis of ProjectsDari EverandGuidelines for the Economic Analysis of ProjectsBelum ada peringkat
- Improving Energy Efficiency and Reducing Emissions through Intelligent Railway Station BuildingsDari EverandImproving Energy Efficiency and Reducing Emissions through Intelligent Railway Station BuildingsBelum ada peringkat
- PYM QNDokumen15 halamanPYM QNEpic GamerBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 11 Life Cycle Costing 2Dokumen21 halamanLecture 11 Life Cycle Costing 2KHAIRIEL IZZAT AZMANBelum ada peringkat
- Mg2451 Engineering Economics and Cost Analysis Unit I Introduction To EconomicsDokumen36 halamanMg2451 Engineering Economics and Cost Analysis Unit I Introduction To EconomicsSrinivasBelum ada peringkat
- Capital Cost EstimationDokumen55 halamanCapital Cost EstimationMohammad Reza Anghaei100% (1)
- AssignmentDokumen7 halamanAssignmentsmmehedih008Belum ada peringkat
- Activity Based CostingDokumen52 halamanActivity Based CostingraviktatiBelum ada peringkat
- Life Cycle CostingDokumen38 halamanLife Cycle CostingSapan Gupta100% (2)
- EconomicsDokumen177 halamanEconomicsOscar CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Economics of Power GenerationDokumen23 halamanEconomics of Power GenerationAbdullah NawabBelum ada peringkat
- Mutual ComparisonDokumen20 halamanMutual ComparisonIsmail JunaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Cash Flow Estimation Models: Estimating Relationships and ProblemsDokumen30 halamanCash Flow Estimation Models: Estimating Relationships and ProblemsSenthil RBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen46 halamanChapter 2bndrprdnaBelum ada peringkat
- Module No 8 - Manufacturing Overhead DepartmentalizationDokumen3 halamanModule No 8 - Manufacturing Overhead DepartmentalizationRafols AnnabelleBelum ada peringkat
- Demo LMS FE ExamDokumen2 halamanDemo LMS FE ExamKaram SalahBelum ada peringkat
- Property, Plant and Equipment Problems 5-1 (Uy Company)Dokumen14 halamanProperty, Plant and Equipment Problems 5-1 (Uy Company)NaSheeng100% (1)
- Chapter 2 EconomyDokumen42 halamanChapter 2 EconomyAidi Redza100% (3)
- LCM 7 ParametricDokumen31 halamanLCM 7 ParametricZafar FarooqBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 9Dokumen26 halamanBab 9Saravanan MathiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter II Methods of Comparing Alternative ProposalsDokumen17 halamanChapter II Methods of Comparing Alternative ProposalsJOHN100% (1)
- Method of Costing (I)Dokumen8 halamanMethod of Costing (I)anon_672065362Belum ada peringkat
- Activity Based CostingDokumen49 halamanActivity Based CostingEdson EdwardBelum ada peringkat
- Final Examination Semester I Session 2012/2013Dokumen10 halamanFinal Examination Semester I Session 2012/2013Wan AzamBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8 NotesDokumen9 halamanLecture 8 NotesAna-Maria GhBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economy Chapter # 02Dokumen55 halamanEngineering Economy Chapter # 02imran_chaudhryBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Accounting-2 QPDokumen7 halamanCost Accounting-2 QPMohammed MidlajBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2 (DF160003)Dokumen10 halamanAssignment 2 (DF160003)Wan AzamBelum ada peringkat
- Math Problem Chapter 1 (L 1 & 2)Dokumen7 halamanMath Problem Chapter 1 (L 1 & 2)rajeshaisdu009Belum ada peringkat
- Revision Sem 1 2017-18Dokumen55 halamanRevision Sem 1 2017-18Farhan Amira100% (2)
- Comsats University Islamabad Abbottabad Campus Engineering Economics Assigment 04Dokumen13 halamanComsats University Islamabad Abbottabad Campus Engineering Economics Assigment 04yaseen ayazBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Cost ManagementDokumen19 halamanStrategic Cost ManagementRames SuryawarmanBelum ada peringkat
- Quatity Cha 5Dokumen32 halamanQuatity Cha 5Yohannes HabeshawiBelum ada peringkat
- Standard (I Unit Produced) ParticularsDokumen11 halamanStandard (I Unit Produced) ParticularsForam Raval100% (1)
- Schedule For Office Building For Uploading On WebsiteDokumen10 halamanSchedule For Office Building For Uploading On WebsiteabhishektheoneBelum ada peringkat
- Management Accounting: Support-Department Cost AllocationDokumen29 halamanManagement Accounting: Support-Department Cost AllocationbelalangkupukupukupuBelum ada peringkat
- Pricing Decisions and Cost ManagementDokumen18 halamanPricing Decisions and Cost ManagementAmrit PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Concepts: Managerial AccountingDokumen72 halamanCost Concepts: Managerial AccountingCianne AlcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- Replacement DecisionsDokumen32 halamanReplacement DecisionsJob VivianBelum ada peringkat
- F5 Asignment 1Dokumen5 halamanF5 Asignment 1Minhaj AlbeezBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Plant and Non-Current Assets v2Dokumen60 halamanUnit 1 Plant and Non-Current Assets v2Yen HoBelum ada peringkat
- F5 RM March 2016 AnswersDokumen15 halamanF5 RM March 2016 AnswersPrincezPinkyBelum ada peringkat
- Suggested Answers Final Examination - Winter 2011: Management AccountingDokumen6 halamanSuggested Answers Final Examination - Winter 2011: Management AccountingFaheem Shaukat100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Dokumen6 halamanTutorial 4FEI FEIBelum ada peringkat
- Comparing Alternatives: Prepared byDokumen51 halamanComparing Alternatives: Prepared byReffisa JiruBelum ada peringkat
- Management Accounting Exam Practice KitDokumen405 halamanManagement Accounting Exam Practice Kittshepiso msimanga100% (4)
- Literature Review 1 PageDokumen9 halamanLiterature Review 1 PageMahbub HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Whole of Life Costing 1Dokumen50 halamanLecture Whole of Life Costing 1r.kapilraj91Belum ada peringkat
- Estimation of Capital CostDokumen47 halamanEstimation of Capital CostM RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6fDokumen30 halamanLecture 6fhiteshBelum ada peringkat
- Relevant CostDokumen19 halamanRelevant CostWanIzyanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4.11: Financial Management Short Type QuestionsDokumen5 halamanChapter 4.11: Financial Management Short Type QuestionsYogesh WadhwaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Ass-03Dokumen4 halaman3 Ass-03mouniBelum ada peringkat
- Saage SG Fma RevisionDokumen21 halamanSaage SG Fma RevisionNurul Shafina HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Activitybased Costing May 20 GMSISUCCESSDokumen29 halamanActivitybased Costing May 20 GMSISUCCESSChetan BasraBelum ada peringkat
- Print TRA - 12Dokumen65 halamanPrint TRA - 12Timothy RogatusBelum ada peringkat
- Depreciation CH 10Dokumen40 halamanDepreciation CH 10احمد عمر حديدBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Cost ConceptDokumen27 halamanChapter 3 Cost ConceptMohamed Ahmed JamaBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook on Construction Techniques: A Practical Field Review of Environmental Impacts in Power Transmission/Distribution, Run-of-River Hydropower and Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation ProjectsDari EverandHandbook on Construction Techniques: A Practical Field Review of Environmental Impacts in Power Transmission/Distribution, Run-of-River Hydropower and Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation ProjectsPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsDari EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Natures CandyDokumen19 halamanNatures CandyFanejegBelum ada peringkat
- WI-824-003 First Article InspectionDokumen2 halamanWI-824-003 First Article InspectionAndreas Schlager100% (1)
- Bill (Law) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokumen9 halamanBill (Law) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchPunitBelum ada peringkat
- Dorma 2012 Price ListDokumen284 halamanDorma 2012 Price ListSecurity Lock DistributorsBelum ada peringkat
- Np2 AnswerDokumen13 halamanNp2 AnswerMarie Jhoana100% (1)
- E-Booklet Tacompact Board 2021Dokumen6 halamanE-Booklet Tacompact Board 2021embenBelum ada peringkat
- Tingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureDokumen12 halamanTingalpa Green New Townhouse Development BrochureMick MillanBelum ada peringkat
- JJDokumen119 halamanJJAnonymous 5k7iGyBelum ada peringkat
- Arab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2Dokumen7 halamanArab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2samiaBelum ada peringkat
- WCN SyllabusDokumen3 halamanWCN SyllabusSeshendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ca50c584 MAYTAGE00011 1 2Dokumen2 halamanCa50c584 MAYTAGE00011 1 2Michael MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDokumen2 halamanSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthFaidah Palawan AlawiBelum ada peringkat
- Orange Stripe # 57 EnglishDokumen2 halamanOrange Stripe # 57 EnglishShahid RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Pilot IIDokumen7 halamanMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Pilot IIBeyar. ShBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-3 BUFFETDokumen9 halamanCh-3 BUFFETJanith prakash567Belum ada peringkat
- Video Case 1.1 Burke: Learning and Growing Through Marketing ResearchDokumen3 halamanVideo Case 1.1 Burke: Learning and Growing Through Marketing ResearchAdeeba 1Belum ada peringkat
- The Effectiveness of Blended Learning Model During Covid-19 Pandemic On Automotive Engineering Major Program Students of SMK Negeri 10 SamarindaDokumen7 halamanThe Effectiveness of Blended Learning Model During Covid-19 Pandemic On Automotive Engineering Major Program Students of SMK Negeri 10 SamarindaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Ferrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Dokumen38 halamanFerrovial / BAA - A Transforming Acquisition: 3rd July 2006Andrew YangBelum ada peringkat
- Cooling Gas Compressor: Cable ListDokumen4 halamanCooling Gas Compressor: Cable ListHaitham YoussefBelum ada peringkat
- Front Pages1Dokumen5 halamanFront Pages1Anonymous g7uPednIBelum ada peringkat
- 05 - SRX NatDokumen44 halaman05 - SRX NatLuc TranBelum ada peringkat
- Toyota Auris Corolla 2007 2013 Electrical Wiring DiagramDokumen22 halamanToyota Auris Corolla 2007 2013 Electrical Wiring Diagrampriscillasalas040195ori100% (125)
- Bangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusDokumen40 halamanBangalore University: Regulations, Scheme and SyllabusYashaswiniPrashanthBelum ada peringkat
- VM PDFDokumen4 halamanVM PDFTembre Rueda RaúlBelum ada peringkat
- MGT 3399: AI and Business Transformati ON: Dr. Islam AliDokumen26 halamanMGT 3399: AI and Business Transformati ON: Dr. Islam AliaymanmabdelsalamBelum ada peringkat
- Standard C4C End User GuideDokumen259 halamanStandard C4C End User GuideKanali PaariBelum ada peringkat
- High-Rise Climb V0.6a Smokeydots PDFDokumen10 halamanHigh-Rise Climb V0.6a Smokeydots PDFHer Lan OBelum ada peringkat
- 0601 FortecstarDokumen3 halaman0601 FortecstarAlexander WieseBelum ada peringkat
- Move It 3. Test U3Dokumen2 halamanMove It 3. Test U3Fabian AmayaBelum ada peringkat
- Affidavit To Use The Surname of The FatherDokumen2 halamanAffidavit To Use The Surname of The FatherGlenn Lapitan Carpena100% (1)