Group 8 Microbiology 1 Bacteriology
Diunggah oleh
Precia JacabaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Group 8 Microbiology 1 Bacteriology
Diunggah oleh
Precia JacabaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PHILIPPINE ASSOCIATION OF SCHOOLS OF MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY AND PUBLIC HEALTH Protot ype Course Syllabus Course Title: Microbiology
1 (Bacteriology) Course Description: The course covers the morphology and physiology of bacteria, rickettsiae and other significant atypical bacteria and their role in infection and immunity. Emphasis is made on their isolation and identification and suscep tibility testing as an aid in laboratory diagnosis. Course Credit: 5 units (3 units lecture, 2 units laboratory) Contact Hours: 3 hours lecture and 6 hours laboratory per week (54 hours lecture and 108 hours laboratory per semester) Prerequisites: Biochemistry, Human Anatomy and Physiology st Placement: Third Year, 1 Semester Terminal Competencies: At the end of this course, the student is able to: 1. ide ntify bacteria according to standard laboratory techniques: microscopic and stai ning; growth and biochemical characteristics; and antigen typing. 2. perform app ropriate antimicrobial susceptibility testing 3. operate common instruments used in Bacteriology 4. participate in quality assurance/quality control program in Microbiology 5. understand the duties and responsibilities of medical technologi sts in the clinical setting 6. perform proper specimen collection, processing, t ransport and waste disposal 7. apply concepts in controlling the growth and spre ad of pathogenic bacteria References: th 1. Alcamo, Edward I. Fundamentals of Microbiology 6 ed. Boston: J ones & Bartlett Publishers, 2001. 2. Bartlet, Margaret A. Diagnostic Bacteriolog y: A Study Guide. F.A. Davis Co. Philadelphia, USA, 2000. th 3. Black, Jacquelyn . Microbiology: Principles and Explorations 7 ed. USA: Wiley, 2008. th 4. Brooks , Geoff. Jawetz, Melnick & Adelbergs Medical Microbiology 24 ed. Boston: Mc Graw Hill, 2007. th 5. Burton, Gwendolyn and Paul Engelkirk. Burtons Microbiology for the Health Sciences 8 ed. USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2007. th 6. Forb es, Betty, Daniel Salm and Alice Weissfield. Bailey & Scotts Diagnostic Microbiol ogy 12 ed. USA: Mosby, 2007. PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Funke, Berdell. Microbiology: An Introduction. USA: Addison Wesley Publishing Co ., 2007. th Gladwin, Mark and Bill Trattler. Clinical Microbiology Made Ridiculo usly Simple 4 ed. USA: MedMaster, Inc., 2007. nd Hawkey, Peter and Dierdre Lewis . Medical Bacteriology: A Practical Approach 2 ed. USA: Oxford University Press, 2004. nd McClatchey, Kenneth. Clinical Laboratory Medicine 2 ed. USA: Lippincot t Williams and Wilkins, 2002. st Mcpherson, Richard A. and Matthew R. Pincus. He nrys Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods 21 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Inc., 2007. th Murray, Patrick R. et. al. Medical Microbiology 5 ed. U SA: Mosby, 2005. th Pommerville, Jeffrey. Alcamos Fundamentals of Microbiology 8 ed. USA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2006. th Presscott, L., J. Harley and D. Klein. Microbiology 6 ed. USA: McGraw-Hill Science, 2004. th Tortora, G., B. Fu nke and C. Case. Microbiology: An Introduction 9 ed. USA: Benjamin Cummings, 200 6. nd Vandepitte J., J. Verhaegen and K. Engbaek. Basic Laboratory Procedures in Clinical Bacteriology 2 ed. World Health Organization, 2003. Electronic References: 1. http://connection.lwww.com/go/burton/7e 2. http://medi c.med.uth.tmc.edu/path/00001450.htm 3. http://www.kensbiorefs.com/Microbio.html 4. http://www.microbes.info 5. http://www.splammo.net/JLbactsite.html PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
Learning Objectives / Intermediate Competencies T.A. Content 2 hrs Teaching Strategies Lecture Large group discussion PowerPoint presentation Skills Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Values Adherence to rules Responsibility Accountability Cooperation Evaluation/Assessment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Laboratory Demonstration & return demonstration Performance of tests At the end of this unit, the student is I. Introduction to Microbiology Lecture: able to: 1. Definition of terms: 3. Define terms. 1.1. Bacteriology, bacteria, 4. Enumerate the development of pathogenecity, virulence etc. science with empha sis on person/scientists and their 2. Historical Development 3. Divisions of Mic robiology contributions 5. Explain the divisions of Laboratory: Microbiology 6. Discuss general considerations 1. Expectations/requirements Microbiology Laborat ory: regarding proper handling, processing, storage of 2. Rules to follow in han dling, processing, disposal of specimens/waste in specimens and disposal of Micr obiology laboratory wastes 7. Discuss the roles of a medical 3. Barrier precauti ons technologist in a microbiology 4. Proper use of different apparatus, laborat ory materials and equipment: Petri Dish, inoculating loop and needle 5. Review u se and care of microscope At the end of this unit, the student is II. Laboratory Safety and Infection Control Lecture: able to: 1. Sterilization 1. Define terms 1.1. Physical (Heat) 2. Discuss concepts, principles& 1.1.1. Autoclave signific ance of infection control 1.1.2. Direct Heat & laboratory safety 3. Discuss vari ous methods of 1.1.3. Oven sterilization & disinfections with 1.1.4. Incineratio n emphasis on temp, time, 1.1.5. Pasteurization principles/mechanism involved, 1 .1.6. Boiling when to use; advantages & 1.2. Filtration disadvantages 2. Disinfe ction 4. Classify the different biosafety 2.1. Chemicals: cabinets 2.2. Alcohol 5. Explain the significance of 2.3. Chlorine pathogenic and virulence 2.4. Other s factors in the development of 3. Antimicrobial agents infections 4. Antimicrob ial Susceptibility testing 6. Perform correctly sterilization & 4.1. Automated d isinfection practices 4.2. Diffusion 7. Explain the concepts behind 4.3. Dilutio n Antimicrobial Susceptibility 5. Use of bio-safety cabinets testing 6. Barrier precautions 8. Differentiate between the two 7. Control of nosocomial infections 6 hrs 3 hrs Lecture with demonstration Discussion Board work Case Presentation Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills Multi-tasking Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment
Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
types of antimicrobial susceptibility testing 9. Discuss significance advantages and disadvantages of each method of sensitivity test 10. Interpret test results 11. Explain the concepts of nosocomial infections 12. Outline the roles of med tech in prevention & control of nosocomial infections At the end of this unit, t he student is able to: 1. Describe bacteria according to: physiology, replicatio n, morphology, classification 2. Identify the growth requirements for each parti cular group of bacteria 3. Illustrate and discuss the growth curve with emphasis on the events happening per stage 4. Discuss specimen collection, transport, st orage, and processing 5. Perform correctly specimen collection: Swabs, Nasal, Th roat, Wound, Urine; transport & labeling, processing & waste disposal 6. Correla te specimen with common pathogens isolated 7. Perform correctly hanging drop and wet mount techniques. 8. Describe the results of hanging drop and wet mounts 9. Discuss concepts and principles of the techniques by which bacteria are identif ied in the laboratory 10. Correlate methods with test results 11. Prepare a gene ral schema for identification of bacteria in the laboratory Laboratory: 1. Sterilization: 1.1. Autoclaving 1.2. Direct heating 1.3. Filtrati on 2. Cleaning of working area with Clorox & other chemicals 3. Proper hand wash ing techniques 4. Lab exercises on the effects of chemicals & temperature on bac teria 5. Proper working attire in a Bacteriology laboratory III. Bacterial Struc ture and Function, Growth and Nutrition Lecture: 1. Characteristics of Bacteria according to: 1.1. Physiology: Structure, Function 1.2. Bacterial morphology 1.3 . Classification 1.4. Replication 1.5. Growth requirements 1.5.1. Physical 1.5.2 . Nutritional 2. Bacterial Growth Curve 3. Bacterial Identification 3.1. Microsc opy: Morphology 3.2. Cultural/Colony Characteristics 3.3. Staining Characteristi cs 3.4. Biochemical 3.5. Serological: Antigen testing 3.6. Molecular Techniques 4. Quality Assurance-Quality Control Laboratory: 1. Acceptable specimens for bac terial identification 1.1. Swabs 1.2. Blood 1.3. Urine 1.4. Stool 1.5. Tissue 1. 6. Aspirates 1.7. Others 2. Specimen collection, handling, transport, processing and preservation 3. Hanging Drop Method and Wet Mounts 6 hrs 3 hrs Computer-aided Lecture /Discussion Case studies Problem solving Actual performance Demonstration/return demonstration Discussion of test results Making conclusions & guidelines Multi-tasking Technical Skills Multi-tasking Problem-Solving Skills Communication skills Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 9 hrs PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
12. Describe microscopic morphology 13. Identify correctly bacterial reaction to staining and morphology 14. Describe staining and morphological characteristics 15. Differentiate staining techniques according to: stains used, purpose, princ iples, advantages, disadvantages, and procedures 16. Perform laboratory exercise s correctly 17. Write a report based on accepted standard format 4. At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Discuss the concepts of bact erial genetics and its importance in the study of bacteria. 2. Appreciate the ro le of medical technologists in the control and prevention of microbial resistanc e At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Define terms. 2. Discuss t he mode of transmission of bacterial infections 3. Correlate factors of pathogen ecity and virulence Role of Microscopy in Bacterial Identification 4.1. Bright field 4.2. Phase cont rast 4.3. Electron 4.4. Dark-field 4.5. Fluorescent 5. Preparation of Bacterial Smear for staining from: 5.1. Directly from specimen (throat swab or any swab) 5 .2. Colonies growing in culture media 6. Staining Techniques: 6.1. Simple stain 6.2. Differential stain 6.2.1. Gram stain 6.2.2. Acid fast stain 6.3. Special st ains 6.4. Others 7. Laboratory Safety 8. Laboratory Waste Management IV. Bacteri al Genetics Lecture: 1. Basic Concepts 1.1. Bacterial DNA & RNA 1.2. Plasmids & Microbial Resistance 1.3. DNA exchange in bacteria: 1.3.1. Transformation 1.3.2. Transduction 1.3.3. Conjugation V. Pathogenesis and Epidemiology Lecture: 1. Ba sic Concepts 2. Mode of Transmission 3. Factors associated with pathogenecity an d virulence 3.1. Toxins 3.2. Enzymes 3.3. Capsules 3.4. Others VI. Normal Flora Lecture: 1. Basic Concepts 2. Body Sites with Normal Flora 3. Predominant flora 4. Beneficial and harmful effects of normal 2 hrs Computer-aided Lecture /Discussion Case studies Problem solving Output presentat ion and critiquing Multi-tasking Problem-Solving Skills Presentation Skills Time management Communi cation skills Multi-tasking Problem-Solving Skills Presentation Skills Time mana gement Communication skills Demonstration & return demonstration Performance of tests Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Prudence Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Prudence Adherence to rules Responsibility Accountabi lity Cooperation Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted 2 hrs Computer-aided Lecture /Discussion Case studies Problem solving Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Define terms 2. Identify bod y sites with normal flora 3. Discuss the predominant normal 2 hrs Large group discussion PowerPoint presentation
Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
4. flora in each body site Explain the beneficial and harmful effects of normal flo ra flora Laboratory 1. Isolation of normal flora 2. Laboratory Safety 3. Laboratory Waste Management VII. Micrococcaceae and Streptococcaeae 1. Micrococcaceae 1.1. Staphylococcus 1.2. Micrococcus 2. Streptococcaceae 2.1. Streptococcus 2.2. Ent ererococcus Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of di sease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.3. Specimen used for Isolation 3.4. Morphol ogy & Staining Reaction 3.5. Culture media and colony characteristics 3.6. Bioch emical tests 3.7. Antigen typing/serology 4. Prevention and control Laboratory: 1. Culture media 1.1. classification 1.2. composition 1.3. preparation 1.4. stor age 1.5. quality assurance/control 1.5.1. spore strip test 1.5.2. sterility test 2. Preparation of culture media 2.1. Nutrient Agar 2.2. Blood Agar Plate 2.3. C hocolate Agar Plate 3. Identification of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus from s pecimens, prepared slides and visual aids 4. Laboratory Safety 5. Laboratory Was te Management VIII. Neisseriaceae Lecture: 1. Neisseriaceae 6 hrs Specimen handling Waste disposal At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Describe Micrococcaceae & St reptococcus in terms of their general properties and pathogenesis 2. Discuss the identification characteristics of Micrococaceae in terms of morphology, culture media, colony characteristics, biochemical test, and serological test 3. Explai n the principles/concepts of different identification techniques used 4. Differe nt pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genus 5. Enumerate the appropria te specimen submitted in the laboratory for isolation 6. Prepare a schematic dia gram for identification 7. Classify culture media according to: indications for use, contents, purpose, etc. 8. Prepare culture media 9. Perform quality control of culture media before use. 10. Identify Staphylococcus, Micrococcus and Strep tococcus from specimens Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies 3.5 hrs Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Describe the members of Lecture with demonstration Multimedia Performance of Tests Demonstration and Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Honesty Commitment Responsibility Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions
PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
Neisseriaceae in terms of their general properties and pathogenesis 2. Discuss t he identification characteristics of Neisseriaceae in terms of morphology, cultu re media, colony characteristics, biochemical test, and serological test 3. Expl ain the principles/concepts of different identification techniques used 4. Diffe rent pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genus 5. Enumerate the appropr iate specimen submitted in the laboratory isolation & identification 6. Prepare a schematic diagram for identification 7. Classify culture media according to: i ndications for use, contents, purpose, etc. 8. Perform correctly inoculation tec hniques and tests 9. Summarize, based on results of identification techniques, b acterial flora in a human person and environment At the end of this unit, the st udent is able to: 1. Discuss the process of identification of Enterobacteriaceae in terms of morphology, culture media, colony characteristics, biochemical test , serological test 2. Explain the principles/concepts of different identificatio n techniques used 3. Different pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genu s 4. State the pathogenic and 1.1. Pathogenic Neisseria 1.2. Non-pathogenic Neisseria 1.3. Moraxella catarrhal is Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen used for Isolation 3.2. Morphology & Sta ining Reaction 3.3. Culture media and colony characteristics 3.4. Biochemical te sts 3.5. Antigen typing/serology 4. Prevention and control Laboratory: 1. Identi fication techniques for: 1.1. Pathogenic Neisseria 1.2. Non-pathogenic Neisseria 1.3. Moraxella catarrhalis 2. Identification of species using prepared slides a nd visual aids 3. Laboratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management presentation Discussion Board work Case Studies 3.5 hrs return demonstration Safety precautions in the laboratory Specimen handling Waste disposal Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and th e environment Quality of assignment submitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs IX. Enterobacteriaceae 1. True Intestinal Pathogens 1.1. Salmonella 1.2. Shigell a 1.3. Yersinia 1.4. Escherichia 2. Opportunistic pathogens 2.1. Escherichia 2.2 . Citrobacter 2.3. Proteus 2.4. Edwardsiella 2.5. Morganella 2.6. Hafnia 2.7. Pr ovidencia 2.8. Enterobacter 2.9. Serratia Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
virulence factors present in bacteria belonging to the group and disease caused by them 5. Enumerate the appropriate specimen submitted in the laboratory isolat ion & identification 6. Prepare a schematic diagram for identification 7. Classi fy culture media according to: indications for use, contents, purpose, etc. 8. P roperly inoculate specimen on culture media 9. Summarize, based on results of id entification techniques, bacterial flora in a human person and environment 10. P erform identification techniques 11. Identify the isolate At the end of this uni t, the student is able to: 1. Discuss the process of identification of the membe rs of the non-enteric gastrointestinal pathogens in terms of morphology, culture media, colony characteristics, biochemical test (plus positive and negative res ults), serological test 2. Explain the principles/concepts of different identifi cation techniques used 3. Different pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genus 4. Enumerate the appropriate specimen submitted in the laboratory isolati on & identification 5. Construct a schematic diagram for identification. 2.10. Klebsiella. 2.11. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenes is & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen used for Iso lation 3.2. Morphology & Staining Reaction 3.3. Culture media and colony charact eristics 3.4. Biochemical tests 3.5. Antigen typing/serology 4. Prevention and c ontrol Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of Enterobacteriac eae using urine or stool 2. Identification of species using prepared slides and visual aids 3. Laboratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management X. Non-enteric G astrointestinal Pathogens 1. Vibrio 2. Campylobacter 3. Helicobacter 4. Aeromona s 5. Pleisomonas 6. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen used for Isolati on 3.2. Morphology & Staining Reaction 3.3. Culture media and colony characteris tics 3.4. Biochemical tests 3.5. Antigen typing/serology 4. Prevention and contr ol Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of non-enteric gastroi ntestinal pathogens 2. Identification of species using prepared slides and visua l aids 3.5 hrs 6 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies 3.5 hrs Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Discuss the process identifi cation of the nonfermentative group in terms of morphology, culture media, colon y characteristics, biochemical test(plus positive and negative results), serolog ical test 2. Explain the principles/concepts of different identification techniq ues used 3. Different pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genus 4. Enum erate the appropriate specimen submitted in the laboratory isolation & identific ation 5. Prepare a schematic diagram for identification 6. Perform correctly ino culation techniques and tests 3. Laboratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management XI. Non-fermentative Gram Ne gative Bacilli and Aerobic Gram Positive Bacilli 1. Non-fermentative Gram Negati ve Bacilli 1.1. Pseudomonas 1.2. Acinetobacter 1.3. Flavobacterium 1.4. Burkhold eria 1.5. Alcaligenes 1.6. Achromobacter 1.7. Stenotrophomonas 1.8. Others 2. Ae robic Gram Positive Bacilli 2.1. Bacillus 2.2. Listeria 2.3. Corynebacterium 2.4 . Erysipelothrix 2.5. Nocardia 2.6. Streptomyces 2.7. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identificat ion 3.1. Specimen used for Isolation 3.2. Morphology & Staining Reaction 3.3. Cu lture media and colony characteristics 3.4. Biochemical tests 3.5. Antigen typin g/serology 4. Prevention and control Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of non-fermentative gram negative bacilli and aerobic gram positive bacilli 2. Identification of species using prepared slides and visual aids 3. La boratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management XII. Small, Pleomorphic Gram Nega tive Bacilli 1. Hemophilus 2. Bordetella 3. Brucella 4. Francisella 3.5 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Discuss the process of ident ification of small pleomorphic gram negative Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
bacilli and the aerobic gram positive bacilli in terms of morphology, culture me dia, colony characteristics, biochemical test (plus positive and negative result s), serological test 2. Explain the principles/concepts of different identificat ion techniques used 3. Different pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the ge nus 4. State the pathogenic and virulence factors present in bacteria belonging to the group and disease caused by them 5. Determine the appropriateness of the different specimens submitted in the laboratory for isolation & identification 6 . Prepare a schematic diagram for identification 7. To distinguish the species o f the aerobic gram positive bacilli from other bacteria 8. Identify members from submitted sample At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Discuss th e process of identification of Mycobacteria in terms of morphology, culture medi a, colony characteristics, biochemical test (plus positive and negative results) , serological test 2. Explain the principles/concepts of different identificatio n techniques used 3. Different pathogenic from nonpathogenic members of the genu s 4. State the pathogenic and virulence factors present in bacteria belonging to the group and disease caused by them 5. Gardnerella 6. Legionella 7. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pa thogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen used for Isolation 3.2. Morphology & Staining Reaction 3.3. Culture media and colony characteristics 3.4. Biochemical tests 3.5. Antigen typing/serology 4. Preventi on and control Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of small, pleomorphic gram negative bacilli 2. Identification of species using prepared sl ides and visual aids 3. Laboratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management 3.5 hrs Board work Case Studies the laboratory Specimen handling Waste disposal rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs XIII. Mycobacterium Group 1. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex 2. Non-tuberculo us Mycobacteria 3. Mycobacterium leprae Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. P athogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen use d for Isolation 3.2. Morphology & Staining Reaction 3.3. Culture media and colon y characteristics 3.4. Biochemical tests 3.5. Antigen typing/serology 4. Prevent ion and control 4.1. TB-DOTS Laboratory: 3.5 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
5. 6. 7. 8. Determine the appropriateness of the different specimens submitted in the labora tory for isolation & identification Prepare a schematic diagram for identificati on To distinguish the species Identify members from of the gram positive bacilli from other bacteria submitted sample At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Enumerate the characteristic s of the anaerobic bacteria in terms of metabolism/physiology 2. Explain precaut ions of the collection, processing, handling, disposal of specimen 3. Discuss th e clinically significance anaerobic in terms of morphology, isolation techniques , biochemical tests 4. Perform the set-up of anaerobic bacteriology 5. Discuss t he importance of the components in the set-up Isolation and identification of members of Mycobacteria 1.1. Culture 1.2. Staini ng 1.2.1. Acid Fast Staining 1.2.2. Other Staining Techniques 1.3. Others 2. Ide ntification of species using prepared slides and visual aids 3. Laboratory Safet y 4. Laboratory Waste Management XIV. Anaerobic Bacteria 1. Clostridium 2. Bacte roides 3. Actinomyces 4. Fusobacterium 5. Peptostreptococcus 6. Porphyromonas 7. Bifidobacterium 8. Lactobacillus 9. Veilonella 10. Megasphaera 11. Acidominococ cus 12. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3.1. Specimen collection and processing 3. 2. Anaerobic set-up and culture media 4. Prevention and control 1. hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 3.5 hrs Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of anaerobic bacteria 1.1 . Anaerobic culture 1.2. Anaerobic set-up 1.3. Microscopic identification 2. Ide ntification of species using prepared slides and visual aids 3. Laboratory Safet y 4. Laboratory Waste Management At the end of this unit, the student is XV. Spi rochetes 1. Treponema able to: 1. Discuss the process of 2. Borrelia identificat ion of medically 3. Leptospira 6 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety
Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
important Spirochetes Correlate appropriate specimen with isolates 3. Characteri ze the organisms according to morphology and pathophysiology 4. Perform the setup of anaerobic bacteriology 5. Discuss the importance of the components in the set-up 6. Perform correctly staining techniques for Spirochetes 7. Describe Spir ochetes observed under the microscope At the end of this unit, the student is ab le to: 1. Discuss the process of identification of unique bacteria 2. Explain th e pathogenesis and spectrum of diseases caused by unique bacteria 3. Discuss the mode of transmission of the microorganisms 4. Explain the principles behind the tests employed to identify unique bacteria 5. Perform tests to identify unique bacteria 2. Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Lab oratory Identification 4. Prevention and control Laboratory: 1. Staining techniq ues for Spirochetes 2. Identification of species using visual aids 3. Laboratory Safety 4. Laboratory Waste Management 3 hrs Discussion Board work Case Studies precautions in the laboratory Specimen handling Waste disposal Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment submitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs XVI. Unique Bacteria 1. Rickettsiaceae 3.1. Rickettsia 3.2. Ehrlichia 3.3. Orien tia 4. Mycoplasmataceae 4.1. Mycoplasma 4.2. Ureaplasma 5. Chlamydiaceae 5.1. Ch lamydia 5.2. Chlamydophila Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spectrum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 4. Prevention and control Labo ratory: 1. Laboratory work-up on the identification of unique bacteria XVII. Mis cellaneous Bacteria 1. Eikinella 2. Kingella 3. Streptobacillus 4. Bartonella 5. Spirillum 6. Others Lecture: 1. General characteristics 2. Pathogenesis & spect rum of disease 3. Laboratory Identification 3 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam 6 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work C ase Studies 3 hrs Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration Te chnical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specimen handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adheren ce to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment submitted P erformance checklist Practical Exam At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Discuss the process of ident
ification of miscellaneous bacteria 2. Explain the pathogenesis and spectrum of diseases caused by miscellaneous bacteria 3. Discuss the mode of transmission of the microorganisms 4. Explain the principles behind PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
5. the tests employed to identify miscellaneous bacteria Perform tests to identify miscellaneous bacteria 4. Prevention and control 6 hrs At the end of this unit, the student is able to: 1. Prepare media for the finale examination 2. Perform correctly the procedures in water, food and milk analysi s 3. Interpret the results of the analysis Laboratory: 1. Isolation and identification of members of miscellaneous bacteria 2. Identification of species using prepared slides and visual aids XVIII. Appli ed Bacteriology Lecture: 1. Applied Bacteriology 1.1. Water Bacteriology 1.2. Fo od Bacteriology 1.3. Milk Bacteriology 1.4. Environmental Bacteriology Laborator y: 1. Lab. Identification of Unknown Bacteria as Practical Examination 2. Labora tory Safety 3. Laboratory Waste Management 3 hrs Lecture with demonstration Multimedia presentation Discussion Board work Case St udies Performance of Tests Demonstration and return demonstration 15 hrs Technical Skills: Use of Microscope Safety precautions in the laboratory Specime n handling Waste disposal Honesty Commitment Responsibility Accountability Adherence to rules Cooperation Teamwork Concern for others and the environment Oral and Written Exam Participation during discussions Quality of assignment sub mitted Performance checklist Practical Exam PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
Technical Working Group for Prototype Course Syllabi Development (2007-2008) Zen nie Aceron Petrona Benitez Sergia Cacatian Zenaida Cajucom Edwin Cancino Jacinta Cruz De Carlos Leon Oliver Shane Dumaoal Bernard Ebuen Nini Lim Frederick Llane ra Carina Magbojos Gregorio Martin Fe Martinez Josephine Milan Ferdinand Mortel Magdalena Natividad Rodolfo Rabor Ma. Teresa Rodriguez Celia Roslin Anacleta Val dez Rowen Yolo and other PASMETH members not cited in this page who in one way or another has c ontributed greatly to the success of this endeavor PASMETH, Inc. Copyright 2008 All Rights Reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- FlowCon General InstructionDokumen4 halamanFlowCon General InstructionGabriel Arriagada UsachBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Service Tool ReferenceDokumen4 halamanEngine Service Tool ReferenceandrzejBelum ada peringkat
- Saudi Arabia Power StationDokumen108 halamanSaudi Arabia Power StationEhab HarbBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Exam Odd Semester Academic Year 2021/2022 Study Program Management Faculty of Business Universitas Multimedia NusantaraDokumen9 halamanMid Exam Odd Semester Academic Year 2021/2022 Study Program Management Faculty of Business Universitas Multimedia NusantaraaekimBelum ada peringkat
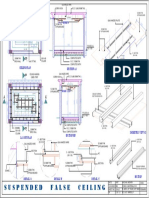
- Gypsum Ceiling PDFDokumen1 halamanGypsum Ceiling PDFAanchal Mishra100% (1)
- Gpa 2145Dokumen15 halamanGpa 2145Sergio David Ruiz100% (1)
- AMG ActuatorsDokumen12 halamanAMG ActuatorsMohan ArumugavallalBelum ada peringkat
- 0.9PF PW 380v 3phase HF UPS10-120kvaDokumen8 halaman0.9PF PW 380v 3phase HF UPS10-120kvaArmandinho CaveroBelum ada peringkat
- A1.2.3 Method Statement 4a Redacted Version2Dokumen98 halamanA1.2.3 Method Statement 4a Redacted Version2ChanelBelum ada peringkat
- Seb ProjectDokumen32 halamanSeb ProjectperthlingBelum ada peringkat
- Design of A 120 In.-Diameter Steel Bifurcation With A Small Acute Angle For A High-Pressure PenstockDokumen10 halamanDesign of A 120 In.-Diameter Steel Bifurcation With A Small Acute Angle For A High-Pressure PenstockStalynMEcBelum ada peringkat
- LR Phono PreampsDokumen44 halamanLR Phono PreampsMartin FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- India's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future TrendsDokumen5 halamanIndia's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future Trendspriyaa2688Belum ada peringkat
- Schedule of Rates 2011 Rev1Dokumen144 halamanSchedule of Rates 2011 Rev1Screen BiruBelum ada peringkat
- Builder's Greywater Guide Branched DrainDokumen4 halamanBuilder's Greywater Guide Branched DrainGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Effecting PerformanceDokumen47 halamanFactors Effecting Performancebembie83Belum ada peringkat
- LogDokumen27 halamanLogmilli0chilliBelum ada peringkat
- DH3E-L-SC-A3-K-170329-0009 Commissioning Inspection & Test Plan (ITP) For BOP and Associated Test FormsDokumen2 halamanDH3E-L-SC-A3-K-170329-0009 Commissioning Inspection & Test Plan (ITP) For BOP and Associated Test FormsBình Quách HảiBelum ada peringkat
- SEO ProposalDokumen5 halamanSEO ProposalShivdev SaiBelum ada peringkat
- Waukesha Engine, Dresser, Inc. - Express Limited Warranty Covering Products Used in Continuous Duty ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanWaukesha Engine, Dresser, Inc. - Express Limited Warranty Covering Products Used in Continuous Duty ApplicationsLUISA FERNANDA TORRES MANOSALVABelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica 750 GPMDokumen156 halamanFicha Tecnica 750 GPMByron Chele0% (2)
- 7.qad-Dpr-11 ImteDokumen4 halaman7.qad-Dpr-11 ImteDhinakaranBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium GMAW GuideDokumen32 halamanAluminium GMAW GuideDaniel Salinas100% (2)
- August 2017Dokumen72 halamanAugust 2017Treatment Plant Operator MagazineBelum ada peringkat
- Results Part III - Part III-March 2017 - ElectricalDokumen3 halamanResults Part III - Part III-March 2017 - ElectricalTharaka MunasingheBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals 2014Dokumen959 halamanFundamentals 2014Angelo Vittorio VettorazziBelum ada peringkat
- CV Ali EzzeddineDokumen3 halamanCV Ali EzzeddineOmar RajadBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle Baseline Security ChecklistDokumen15 halamanOracle Baseline Security ChecklistChidi OkerekeBelum ada peringkat
- Industry 4.0 FinaleDokumen25 halamanIndustry 4.0 FinaleFrame UkirkacaBelum ada peringkat
- UCID Number Request FormDokumen1 halamanUCID Number Request FormOmar AwaleBelum ada peringkat