ALM Transcription Translation
Diunggah oleh
Brian BradyHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ALM Transcription Translation
Diunggah oleh
Brian BradyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
General
Biology Name: Bio 101 Homework Transcription and Translation 1. Define gene in your own words. 2. The diagram below is a picture of a cell with its nucleus. Diagram the process by which DNA is read as RNA and converted to protein, and include where in the cell these processes occur.
3. Define mutation and explain how it is the ultimate source of genetic variation.
4. The diagram below is a double stranded DNA molecule. The process taking place is transcription. Write out the mRNA message that is being transcribed on the emerging single- stranded mRNA.
5. What is the polypeptide message that is encoded (use the genetic code chart)?
6. The diagram below shows a newly transcribed mRNA. It has not yet matured. Below the diagram, make your own diagram of the mature mRNA. How many RNA nucleotides does it have? How many amino acids does the polypeptide that it encodes have?
7. The following questions are a mix of review questions from Unit 1 and this lecture. I bring them back to haunt you as a reminder that Biology is all interrelated and that we will be constantly building on what we have (hopefully) learned previously! a. What are polypeptide polymers composed of? f. What is the business end of the RNA molecule, in question d above, that base pairs with the three letter words in question e above? 8. Using all the answers from question 7, explain the process of translation in your own words! Draw a diagram on the back to help you explain. g. How is translation like a tape player? b. What is the site of protein synthesis? c. What is the bond between amino acids called? d. Which type of RNA brings the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? e. What is the three-letter word in the message of mRNA?
9. The HIV virus is a retrovirus. What does this mean?
10. In DNA replication, the enzyme that is responsible for replicating DNA, DNA polymerase, is very faithful when it copies DNA. It MUST be! In contrast, the enzyme reverse transcriptase found in retroviruses is not at all very reliable. When it makes copies of the viral genome, it introduces mutations at an alarming rate. Why is this bad news for people with HIV who take inhibitors of reverse transcriptase as part of their anti-viral cocktails?
General Biology Name: Bio 101 Homework Control of Gene Expression
5 3
3 O Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 5
lactose
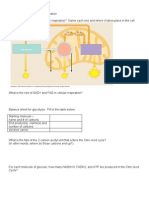
1. In the illustration above, I have illustrated a bacterial operon. Genes 1, 2 and 3 all encode enzymes that permit the cell to use lactose. P refers to promoter, O refers to operator, the blue shape on the promoter is RNA polymerase, the key is the repressor protein sitting on the operator. Describe how lactose regulates expression of the bacterial operon.
2. What is differentiation? 6. What is the difference between reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning? 7. What is the difference between adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells? Which are totipotent, and which are pluripotent? (You will have to go beyond the book to find these definitions.) 3. How can DNA packaging in chromosomes affect whether a gene is expressed (turned on)?
4. What are all the possible mechanisms by which eukaryotes can regulate gene expression? (Hint: 11.8 and 11.9)
5. Describe the process of nuclear transplantation.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Human Anatomy Physiology 8th Edition Marieb Test BankDokumen34 halamanHuman Anatomy Physiology 8th Edition Marieb Test BankKevinHarrisonnfixq100% (14)
- Gina P. Macapal Grade 8-Emerald/4th Carmen National High School February 6,2019/10:30-11:30Dokumen5 halamanGina P. Macapal Grade 8-Emerald/4th Carmen National High School February 6,2019/10:30-11:30Jeazel MosendoBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Dokumen7 halamanReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Jann LarBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen52 halamanCell CyclePortia EgkenBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace MarshallDokumen43 halamanSolution Manual For Cell and Molecular Biology 8th Edition Gerald Karp Janet Iwasa Wallace Marshallbrianpattersonanpyomzbed100% (40)
- Chapter 19 LodishDokumen52 halamanChapter 19 LodishablucBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution Lecture F'12Dokumen56 halamanEvolution Lecture F'12Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesDokumen2 halamanALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Biology LectureDokumen43 halamanMolecular Biology LectureBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM Evolutionary ForcesDokumen2 halamanALM Evolutionary ForcesBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM DNA Structure Sp'13 NameDokumen4 halamanALM DNA Structure Sp'13 NameBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Dokumen39 halamanDNA Replication Mitosis Meiosis Sp'13Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Bio101 LectureDokumen41 halamanGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM GeneticsDokumen2 halamanALM GeneticsBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisDokumen21 halamanPhotosynthesis: - I. Bottom Line of PhotosynthesisBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Bio101 LectureDokumen41 halamanGenetics Bio101 LectureBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM Photosynthesis and RespirationDokumen4 halamanALM Photosynthesis and RespirationBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermDokumen1 halamanStudy Guide For RCC Bio1 Lab MidtermBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration Lecture F'12Dokumen36 halamanRespiration Lecture F'12Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Dokumen3 halamanALM Origin of Life and Tour of Cell F'12Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- The Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced SizeDokumen44 halamanThe Working Cell Sp'12 Reduced SizeBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM The Working Cell F'12Dokumen3 halamanALM The Working Cell F'12Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Dokumen24 halamanLecture Atoms Molecules Water PH Sp'13Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM BiochemistryDokumen4 halamanALM BiochemistryBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Dokumen44 halamanCell Theory and Tour of Cell Sp'13Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- ALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHDokumen5 halamanALM Introduction Atoms Molecules Water PHBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Dokumen22 halamanBio 100:101 Introduction Lecture Sp'13Brian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Macromolecules LectureDokumen51 halamanMacromolecules LectureBrian BradyBelum ada peringkat
- Transcription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityDokumen39 halamanTranscription in Prokaryotes: Dindin H. Mursyidin Laboratory of Molecular Biology Lambung Mangkurat UniversityNadia Nur FitriaBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 17 - Cell DivisionDokumen2 halamanIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 17 - Cell DivisionHisokagenBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Processes: Chapter-34-Lesson-2 Page-961-966Dokumen26 halamanReproductive Processes: Chapter-34-Lesson-2 Page-961-966JanaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Stem Cell TechnologyDokumen48 halamanIntroduction of Stem Cell TechnologyR. EssoBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDokumen2 halamanNumerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesPradip SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics and HeredityDokumen32 halamanGenetics and HeredityJohn Emmanuel RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Polytene ChromosomeDokumen21 halamanPolytene Chromosomestevensb055Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis Meiosis Teachers Guide Discovery EducationDokumen32 halamanMitosis Meiosis Teachers Guide Discovery EducationKari Kristine Hoskins Barrera0% (2)
- Opdrag 2 MosseDokumen12 halamanOpdrag 2 MosseCharmaine Van WykBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Stem Cell TechnologyDokumen37 halamanIntroduction of Stem Cell TechnologySavitaBelum ada peringkat
- LFSC Autumn Camp 2023 Marking GuidelinesDokumen16 halamanLFSC Autumn Camp 2023 Marking GuidelinesmanotosbongileBelum ada peringkat
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9Dokumen8 halamanReproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9zodika khiangteBelum ada peringkat
- Human EmbryologyDokumen7 halamanHuman Embryologyvinit cfuBelum ada peringkat
- Types of EmbryoDokumen18 halamanTypes of EmbryoG arunaBelum ada peringkat
- Kingdom Plantae: Characteristics and Classification of PlantsDokumen12 halamanKingdom Plantae: Characteristics and Classification of PlantsJohnrey CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- IVF - India Market Research ReportDokumen49 halamanIVF - India Market Research ReportPrakashBelum ada peringkat
- COT Lesson Plan in Science 5Dokumen9 halamanCOT Lesson Plan in Science 5ChAd Surmion HisanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration in Plants (Edustudy Point) - UnlockedDokumen6 halamanRespiration in Plants (Edustudy Point) - Unlockedkushwahvivek1028Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology SyllabusDokumen2 halamanCell Biology Syllabusbegüm üçgülerBelum ada peringkat
- Earth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Dokumen7 halamanEarth and Life Science Q2 LP 3Jhoana OrenseBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division PDFDokumen5 halamanCell Division PDFCabdicasiis Maxamuud GuuleedBelum ada peringkat
- Human Reproductive SystemDokumen4 halamanHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9B - Transcription and Post-Transcriptional ModificationDokumen46 halamanModule 9B - Transcription and Post-Transcriptional Modificationgleni robredoBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Genetics TestDokumen2 halamanAP Bio Genetics TestHunterBelum ada peringkat