NGT Enteral Feeding Care
Diunggah oleh
Sheng GosepDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NGT Enteral Feeding Care
Diunggah oleh
Sheng GosepHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NRAD 201B
Nursing Process: Energy, Psychomotor
Nasogastric Tubes Enteral Feeding Administering Medications via NGT and PEG
Rationale for Nasogastric Tubes - 1
1. Gastric Emptying (Decompression)
Bowel obstruction GI Bleed After GI surgery Ileus (paralytic ileus)
2. Gastric Lavage Washing out: In & Out
Poisoning NS in/out to remove poison quickly Overdose same Gastric bleeding Iced NS can be used Critical Elements: Correct solution & temperature, Control rate/volume of introduction/return of fluid.
Rationale for Nasogastric Tubes - 2
3. Gastric Gavage gavage goes in
Pt. cannot eat/swallow safely but has a functioning GI Tract Instillation of liquid food Through an NGT or tube into stomach or jejunum Enteral feeding
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Nasogastric Tubes double lumen
Salem Sump Tube Normal adult size: 14F to 18F 120cm long Air vent or pigtail open to air
Rationale to prevent adhering to stomach lining Anti-reflux valve usually attached
Uses: emptying (decompression), lavage, Occasionally Gavage (enteral feeding)
Emptying (Decompression)
Application of negative pressure to nasogastric tube via wall suction
May be continuous or intermittent 20-40 mm/Hg = low suction
Continuous: Increased risk of gastric mucosal irritation with continuous suction > 25 mm/Hg Equipment required:
Suction regulator wall style or portable Collection canister Connecting tubing.
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Maintaining Suction: Assessment
Secure external part of NG tube to the nose: verify tape is secure Check drainage tube and suction gauge tubing every hour: is it working? Irrigate with 20mL H2O if necessary to maintain patency or per agency policy Maintain air vent: is it clear? stomach contents draining out? May need to instill air to clear Critical Elements: Assess/reassess placement, Verify correct suction level, Verify patency of NGT
Nursing Care: Assessment
Abdominal assessment suction must be off to auscultate bowel sounds Verify placement - at the beginning of every shift and before instilling anything. Monitor Intake and Output Note color and character at the initial assessment and during your shift Special attention to nasal and oral care
How to Verify Placement
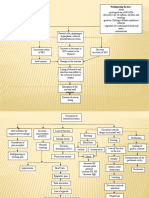
Imperative for client safety! Verification by x-ray is the gold standard! Is required at the time of placement for any type feeding tubes. At the beginning of the shift and as needed: 1. Aspirate gastric contents - note color 2. Insufflation: rapid injection 20-30mL air while auscultating epigastric area. A gurgle or whoosh should be heard
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Documentation - example
0730 NGT in place to low intermittent suction.
Placement verified. Draining green fluid. Abdomen soft, hypoactive bowel sounds noted. States has not passed gas but is feeling better. M. Bright SN 0930 Vomited 50mL dark brown fluid. NGT in place. Suction off. Placement verified. Abdomen round, tender, firm. Hypoactive bowel sounds. Placed to low intermittent suction with return 200mL dark brown fluid.. M. Bright SN
Nasogastric Tubes small bore feeding
Adult size: 8F to 12F Internal stylet and weighted end to facilitate insertion Designed for enteral feeding only.
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Gastrostomy Tubes
Designed as long-term enteral feeding device Surgically or endoscopically placed in the stomach by a physician Larger in diameter than nasogastric feeding tubes PEG percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Insertion Nasogastric tube
Critical elements: Insert, verify placement, secure exterior of tube Explain procedure to client Collect and set-up required equipment Position client: head of bed elevated as much as possible Measure and mark the tube: nose to ear, ear to stomach
Insertion Nasogastric tube
Chin up initially until past soft palate & down back of throat Chin down have pt swallow, may need a sip of water Push tube down smoothly and fairly quickly to mark Stop if resistance encountered Stop for extreme coughing Stop for compromised breathing Verify placement: aspiration, insufflation
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Documentation - example
1030 #16F Salem sump inserted via right nare. Secured. Placement verified. Connected to low continuous suction with return 300mL tan fluid. Minimal distress on part of pt. M. Bright SN Small bore tube (stylette left in place until after Xray) 1100 #8F feeding tube inserted via left nare. Secured at 75cm. CXR (chest x-ray) ordered to verify placement. Unresponsive during procedure. M. Bright SN
Nursing Process
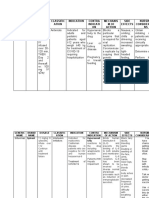
Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements A state in which a person who is not NPO experiences or is at risk of experiencing reduced weight related to inadequate intake or metabolism of nutrients for metabolic needs Defining characteristics: Food intake less RDA with or without weight loss and/or metabolic needs in excess of intake Risk for Aspiration State in which a person is at risk for entry of secretions, solids, fluids, into the tracheobronchial passages Deficient Fluid Volume A person who can take fluids (not NPO) experiences or is at risk of experiencing dehydration Insufficient oral fluid intake, negative balance I&O
Enteral Feeding
Indications: Nutrition Less than Body Requirements combined with inability to chew and swallow food normally. Methods: Continuous, intermittent, bolus Hazards and Complications: ASPIRATION, nausea,vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
Enteral Feeding
Review facility specific Policy & Procedure Review Physicians orders for: -feeding tube type -formula: type, strength, additional free water -feeding schedule -checking residuals and when to hold or resume feedings Check facility policy for: -when to change container, tubing -formula hang time
Nursing Care
Feed in semi-fowlers position and maintain position for 2 hours after feeding. How should the client be positioned if feeding is continuous? Check placement at beginning of shift and before feeding! Check for residual per physician orders or every 4 hrs. if continuous or before feeding if intermittent or bolus. Hold per Physician orders Aspirated residual is returned to the stomach Critical Thinking: how do you assess tolerance to feeding?
Critical Elements: Feeding per NGT
1. Assess/reassess for correct placement 2. Check residuals q 2-4 hrs and prn 3. Secures tube and monitor integrity of securing mechanism 4.Flush tube before/after medication administration 5. Skin care (pressure points where tube may be pressing): keep clean & dry
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
NRAD 201B
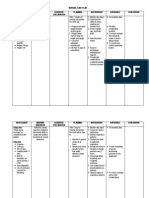
Medication Administration via NGT/PEG
Assessment - Is the medication appropriate to crush?? Medications must be in liquid form or crushed. Dissolve in warm H2O Verify placement of NG tube/PEG 1. Flush with H2O (20mL or *per policy) 2. Administer medication draw up in syringe 3. Flush with another 20mL * H2O, clamp for 30 before returning to suction (if suction ordered).
Removal of Nasogastric Tube
Review Physicians order Gather equipment and explain procedure Disconnect from suction tubing Position the client and remove tape securing tube Remove smoothly and quickly while client holds breath Assist client with nasal care Document!!
Documentation - examples
1100 Placement feeding tube verified. Abdomen soft, active bowel sounds noted. Head of bed up 45 degrees. Jevity strength, 50mL/hr started via feeding pump. M. Bright SN. 0800 Abdomen firm, active bowel sounds noted. PEG placement verified. 20mL residual noted. Full strength Glucerna @ 50mL/hr via feeding pump. Denies nausea, cramping. M. Bright SN
Week 12 - Nasogastric tubes, Enteral feeding
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NGT Feeding and Meds Administration Via NGTDokumen25 halamanNGT Feeding and Meds Administration Via NGTPaul Michael BaguhinBelum ada peringkat
- Nasogastric TubeDokumen78 halamanNasogastric TubeQuia Benjch Uayan100% (1)
- Prepared By: P2Lt Joyce Angeline D Valencia NCDokumen23 halamanPrepared By: P2Lt Joyce Angeline D Valencia NCJoan ErbelecBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPJose CousinsBelum ada peringkat
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDokumen4 halamanWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityEzra LambarteBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDokumen1 halamanSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaTyrel LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Patient ProfileDokumen7 halamanSample Patient ProfileElisabeth CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- Family Care PlanDokumen3 halamanFamily Care PlanAngie MandeoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Gordon ChristianDokumen1 halamanGordon ChristianChristian Rodison Maningas100% (1)
- Course in The WardDokumen4 halamanCourse in The WardNejie Zarrah DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Roles and Functions of A NurseDokumen12 halamanRoles and Functions of A NursealelichengBelum ada peringkat
- SchistosomiasisDokumen4 halamanSchistosomiasisLeo TiuBelum ada peringkat
- Return Residual Fluid To Stomach Via Tube and Proceed To FeedingDokumen7 halamanReturn Residual Fluid To Stomach Via Tube and Proceed To FeedingMhae De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- ImmunedisorderDokumen3 halamanImmunedisorderDyan LazoBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Diagnostic ProceduresDokumen41 halamanRespiratory Diagnostic Proceduresseigelystic100% (23)
- Allergic RhinitisDokumen20 halamanAllergic RhinitisMichaelPTBelum ada peringkat
- Group 2: Peptic Ulcer: Zoleta, Dayla Shaine May de Leon, Alexandra Caparros, Clea Balino, Iris JoyDokumen120 halamanGroup 2: Peptic Ulcer: Zoleta, Dayla Shaine May de Leon, Alexandra Caparros, Clea Balino, Iris JoyDayan CabrigaBelum ada peringkat
- CASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisDokumen5 halamanCASE ANALYSIS - Chronic TympanomastoiditisTerry Mae Atilazal SarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study CovidDokumen5 halamanDrug Study CovidR Hornilla Arcega0% (1)
- Adverse Effects of Blood TransfusionDokumen3 halamanAdverse Effects of Blood Transfusionay254Belum ada peringkat
- Primary Health Care: Prepared By: Ezra Angeli C. Joaquin, RNDokumen18 halamanPrimary Health Care: Prepared By: Ezra Angeli C. Joaquin, RNRaRe TV0% (1)
- Dr. H. Achmad Fuadi, SPB-KBD, MkesDokumen47 halamanDr. H. Achmad Fuadi, SPB-KBD, MkesytreiiaaBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaDokumen48 halamanCHAPTER 4-Atty AliboghaPaul EspinosaBelum ada peringkat
- KAren LFD ManangoDokumen2 halamanKAren LFD ManangoKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongBelum ada peringkat
- Nanda Nursing Diagnosis Examples:: Vague Uneasy Feeling ofDokumen3 halamanNanda Nursing Diagnosis Examples:: Vague Uneasy Feeling ofYOLANDA P. DELCASTILLOBelum ada peringkat
- 28099453C Case Study 3Dokumen27 halaman28099453C Case Study 3Alice HuiiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (Uterine Atony)Dokumen14 halamanDrug Study (Uterine Atony)Violy CabigatBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume Excess and Activity IntoleranceDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume Excess and Activity IntoleranceMarius Clifford BilledoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialBrix ValdrizBelum ada peringkat
- Gordons 11 Functional Patterns QuestionsDokumen1 halamanGordons 11 Functional Patterns QuestionsLaura Wullschleger LightBelum ada peringkat
- General Assessment of The Pregnant WomanDokumen30 halamanGeneral Assessment of The Pregnant WomanJrose CuerpoBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Aseptic TechniqueDokumen3 halamanPrinciples of Aseptic TechniqueDane CaumeranBelum ada peringkat
- GI Diagnostic TestsDokumen7 halamanGI Diagnostic TestspatzieBelum ada peringkat
- Performing Nutritional AssessmentDokumen1 halamanPerforming Nutritional AssessmentJoslyn GrossBelum ada peringkat
- Stages of LaborDokumen14 halamanStages of LaborKimberly CostalesBelum ada peringkat
- ACute Pylonephris Case PresentationDokumen6 halamanACute Pylonephris Case PresentationbantilanBelum ada peringkat
- EINC ReviewDokumen14 halamanEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahBelum ada peringkat
- Selective, Optimization, Compensation: Alabe, Meryll Anne Cabanilla, Jemmica Mei Urgino, Mary Kayshien LeiDokumen11 halamanSelective, Optimization, Compensation: Alabe, Meryll Anne Cabanilla, Jemmica Mei Urgino, Mary Kayshien LeiApril Mae Magos LabradorBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal Case Study CompiledDokumen392 halamanAbdominal Case Study CompiledIshak IzharBelum ada peringkat
- Or Return Demo FinalDokumen2 halamanOr Return Demo FinallemuelBelum ada peringkat
- CHNDokumen12 halamanCHNJhara100% (1)
- Patient Education: A Guide for NursesDokumen32 halamanPatient Education: A Guide for Nursesاسامة محمد السيد رمضانBelum ada peringkat
- Newborn Screening Policy Catarman Doctors Hospital, Inc.: University of Eastern PhilippinesDokumen7 halamanNewborn Screening Policy Catarman Doctors Hospital, Inc.: University of Eastern PhilippinesGenn Medrano GirayBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Assessment:: Area Technique Norms Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. SkullDokumen15 halamanPhysical Assessment:: Area Technique Norms Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. SkullRoseben SomidoBelum ada peringkat
- Acute AppendicitisDokumen23 halamanAcute AppendicitisSandie Daniel GabalunosBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Martha Rogers Unitary Human BeingDokumen53 halamanMartha Rogers Unitary Human BeingKUZOBelum ada peringkat
- Public Health Nurse ProceduresDokumen9 halamanPublic Health Nurse ProcedureskzbreakerrBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Transfusion FinalDokumen8 halamanBlood Transfusion FinalejkohBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanDrug Studylorraine_22Belum ada peringkat
- RLE Daily Clinical Activities PlanDokumen2 halamanRLE Daily Clinical Activities PlanJay VillasotoBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Irrigating A ColostomyDokumen5 halaman8 Irrigating A ColostomyAnn Jalover PerezBelum ada peringkat
- CASE SCENARIO and NCPDokumen14 halamanCASE SCENARIO and NCPBeverly PagcaliwaganBelum ada peringkat
- Post Test 30 Items OBDokumen5 halamanPost Test 30 Items OBJohnasse Sebastian NavalBelum ada peringkat
- At LTC N Theories Models 1Dokumen35 halamanAt LTC N Theories Models 1Darin BransonBelum ada peringkat
- Gordons TypologyDokumen37 halamanGordons TypologyJo PigarBelum ada peringkat
- SchistosomiasisDokumen27 halamanSchistosomiasisNarz Cupahan0% (1)
- Disturbances in OxygenationDokumen10 halamanDisturbances in OxygenationjenrylBelum ada peringkat
- The Newborn Care: Fcnlxa - St. Luke's College of NursingDokumen11 halamanThe Newborn Care: Fcnlxa - St. Luke's College of NursingFrancine LaxaBelum ada peringkat
- Viii. Drug Study: Drug Action Indications Containdications Side / Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDokumen18 halamanViii. Drug Study: Drug Action Indications Containdications Side / Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenteritis OverviewDokumen5 halamanGastroenteritis OverviewSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Facts About Myasthenia GravisDokumen14 halamanFacts About Myasthenia GravisSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanNursing Care PlanSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Hydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsDokumen1 halamanHydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Myasthemia GravisDokumen11 halamanMyasthemia GravisSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin K3 Drug Generic Name, Brand, Uses, Side EffectsDokumen2 halamanVitamin K3 Drug Generic Name, Brand, Uses, Side EffectsSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Central Nervous SystemDokumen3 halamanAnatomy of The Central Nervous SystemSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Personality Development NotesDokumen11 halamanPersonality Development Notesvasantha_btechBelum ada peringkat
- NGT Enteral Feeding CareDokumen8 halamanNGT Enteral Feeding CareSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNDokumen42 halamanHeart Failure: Marvick F. Galima RNSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: Group 13 ADokumen3 halamanInvasive Ductal Carcinoma: Group 13 ASheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- Bpud, PathoDokumen2 halamanBpud, PathoSheng GosepBelum ada peringkat
- 3d BioprintingDokumen6 halaman3d Bioprintingapi-505366251Belum ada peringkat
- Oral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed: Active Ingredient(s) Dosage Form(s) Reasons/Comments3Dokumen8 halamanOral Dosage Forms That Should Not Be Crushed: Active Ingredient(s) Dosage Form(s) Reasons/Comments3Salsabila TazkiyahBelum ada peringkat
- DR KN SrivastavaDokumen7 halamanDR KN SrivastavaShiwali SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Peform Calculations ActivityDokumen6 halamanPeform Calculations ActivitySher RylBelum ada peringkat
- Conquering The Jungle of Ventilation ModesDokumen69 halamanConquering The Jungle of Ventilation ModesNasrullah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Mutual Prodrug Concept Fundamentals and ApplicationsDokumen9 halamanMutual Prodrug Concept Fundamentals and ApplicationsUmaima faizBelum ada peringkat
- Math Practice For Paramedic StudentsDokumen8 halamanMath Practice For Paramedic StudentsGreg Zeitlin50% (2)
- Case Study On AsthmaDokumen3 halamanCase Study On AsthmaNurudeen Ibrahim100% (1)
- رصيد المستهلاكات حتى - 9Dokumen20 halamanرصيد المستهلاكات حتى - 9ahmad aliBelum ada peringkat
- TCCC Skill Sets by Responder Level Master 190422 ApprovedDokumen4 halamanTCCC Skill Sets by Responder Level Master 190422 ApprovedIon MarinBelum ada peringkat
- National Drug Policy of Bangladesh 2005Dokumen3 halamanNational Drug Policy of Bangladesh 2005নোমানআবদিল্লাহBelum ada peringkat
- Resumen de Tratamiento Epileptico 2016Dokumen1 halamanResumen de Tratamiento Epileptico 2016Alejandra CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Solutions Range GuideDokumen3 halamanHospital Solutions Range GuideMuhammed AbdulmajeedBelum ada peringkat
- American Academy of Pediatrics: Committee On DrugsDokumen6 halamanAmerican Academy of Pediatrics: Committee On Drugsdr Betha PurbaBelum ada peringkat
- Contents and List of Drug Profiles in The Book Lay Person's Guide To MedicinesDokumen5 halamanContents and List of Drug Profiles in The Book Lay Person's Guide To MedicinesS.Srinivasan ('Chinu'); Renu KhannaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Wound Care Therapies UlcerDokumen182 halamanAdvanced Wound Care Therapies UlcerJuan Jose Leon100% (1)
- Cannabis SativaDokumen15 halamanCannabis SativamaryBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 18 - Over The Counter (OTC) SalesDokumen11 halamanCHAPTER 18 - Over The Counter (OTC) SalesShubhanjay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Vancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFDokumen1 halamanVancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFFrancis PasayBelum ada peringkat
- Clarithromycin 2010 11 45 PdARDokumen29 halamanClarithromycin 2010 11 45 PdARswabrijBelum ada peringkat
- 6 DefibrillationDokumen22 halaman6 DefibrillationrohithBelum ada peringkat
- ICU Floor Stock Inventory ListDokumen2 halamanICU Floor Stock Inventory Listicu paling nubBelum ada peringkat
- Should Community Pharmacy Stock Homeopathic RemediesDokumen2 halamanShould Community Pharmacy Stock Homeopathic RemediesFabienne DuhartBelum ada peringkat
- Directorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusDokumen2 halamanDirectorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusAnamika SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Report Suspected Drug ReactionsDokumen2 halamanReport Suspected Drug ReactionsanandryajiBelum ada peringkat
- NepafenacDokumen4 halamanNepafenacrasfaqur100% (1)
- Vancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsDokumen5 halamanVancomycin Protocol: A Protocol To Guide The Dosing and Monitoring of Vancomycin in AdultsSaadia MahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital PharmacyDokumen23 halamanHospital PharmacyMaheen TariqBelum ada peringkat
- Drug study of Erceflora and Albuterol Sulfate for diarrhea and bronchospasmDokumen4 halamanDrug study of Erceflora and Albuterol Sulfate for diarrhea and bronchospasmKrisia Castuciano50% (2)
- WOUND HEALING: THE 3 STAGES AND COMPLICATIONSDokumen21 halamanWOUND HEALING: THE 3 STAGES AND COMPLICATIONSOsama Fadel ahmedBelum ada peringkat