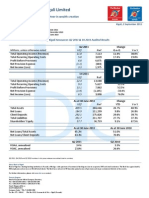
Treasury Management - Book Id - b1311
Diunggah oleh
Amar KumarJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Treasury Management - Book Id - b1311
Diunggah oleh
Amar KumarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1, Asset-Liability
Management
In banking, asset and liability management (often abbreviated ALM) is the practice of managing risks that arise due to mismatches between the assets and liabilities (debts and assets) of the bank. This can also be seen in insurance. Banks face several risks such as the liquidity risk, interest rate risk, credit risk and operational risk. Asset liability management (ALM) is a strategic management tool to manage interest rate risk and liquidity risk faced by banks, other financial services companies and corporations. Banks manage the risks of asset liability mismatch by matching the assets and liabilities according to the maturity pattern or the matching of the duration, by hedging and by securitization. Much of the techniques for hedging stem from the delta hedging concepts introduced in the BlackScholes model and in the work of Robert C. Merton and Robert A. JarrowModern risk management now takes place from an integrated approach to enterprise risk management that reflects the fact that interest rate risk, credit risk, market risk, and liquidity risk are all interrelated. The Jarrow-Turnbull model is an example of a risk management methodology that integrates default and random interest rates significance:-
6. Function of integrated treasury
of bank?
Answer:
Treasury function was restricted to fund or liquid management. Fund management includes maintaining adequate cash balances to meet the daily requirements, implementing the surplus funds in other operations, sourcing the funds to even the gaps in cash flow. The treasury departments in banks are responsible to meet the Cash Reserve Requirement (CRR) and invest the funds in securities under Statutory Liquid Ratio (SLR). Treasury basically deals with shortterm cash flows(less than one year), but investment in some securities exceeds more than one year. Integrated treasury came into existence as a result of financial reforms, the most important being the deregulation of rupee and partial convertibility of rupee. Rupee is freely convertible on current account. Due to the relaxations of RBI in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), rupee is now partially convertible on capital account. Banks are permitted a larger limit in terms of their net worth, and overseas borrowing and lending. The functions of integrated treasury are not restricted to traditional functions. The major functions of integrated treasury are as follows: . Performing reserve management, which involves meeting CRR and SLR obligations. . Deploying surplus funds in securities which have low risk and earn profits. . Performing global cash management. . Providing effective and efficient merchant services. . Improving the profit by exploring market opportunities in money market, securities market and forex market. . Assisting the banks in Asset-Liability Management (ALM).
. Managing market risk for the entire bank.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- MB00046274 SS00000076Dokumen1 halamanMB00046274 SS00000076scribble_55Belum ada peringkat
- Audit Prob Cash AnsDokumen7 halamanAudit Prob Cash AnsNoreen BinagBelum ada peringkat
- Bank StatementDokumen2 halamanBank Statementrk7vzkvh9jBelum ada peringkat
- Bank of Kigali Announces Q2 2011 & 1H 2011 ResultsDokumen9 halamanBank of Kigali Announces Q2 2011 & 1H 2011 ResultsBank of KigaliBelum ada peringkat
- Degree Attestation Challan FormDokumen1 halamanDegree Attestation Challan FormKhalid Kiani100% (1)
- Vijayawada To Bangalore: Abhibus TicketDokumen1 halamanVijayawada To Bangalore: Abhibus Ticketmydearbhava1Belum ada peringkat
- Methods of Payment in International Trade, Export and Import FinanceDokumen18 halamanMethods of Payment in International Trade, Export and Import Financecharurastogi100% (2)
- Marketing Paytm Wallet - Group5DDokumen23 halamanMarketing Paytm Wallet - Group5DAdwait Deshpande100% (1)
- Trade Finance Question BankDokumen10 halamanTrade Finance Question Bankuttamdas79Belum ada peringkat
- GFF2023 - AgendaDokumen64 halamanGFF2023 - AgendaVinay SudershanBelum ada peringkat
- Internship ReportDokumen63 halamanInternship Reportimislamian0% (1)
- MBFinance Chap06-Pbms-finalDokumen20 halamanMBFinance Chap06-Pbms-finalLinda YuBelum ada peringkat
- Door Step BankingDokumen30 halamanDoor Step Bankingvahid86% (7)
- Law - Mercan Nil Case-Forged SignatureDokumen6 halamanLaw - Mercan Nil Case-Forged SignatureNardz AndananBelum ada peringkat
- CH11Dokumen31 halamanCH11Marwa HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Project Proposal SBI MicrofinanceDokumen7 halamanProject Proposal SBI MicrofinanceKiran Chopra100% (1)
- Assignment # 3Dokumen21 halamanAssignment # 3Naveen LankadasariBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Payable and Bonds Payable - Quiz - With Answers - For PostingDokumen8 halamanNotes Payable and Bonds Payable - Quiz - With Answers - For PostingWinny PoeBelum ada peringkat
- Annual Value of One Present Dollar (Annual Payment) : PV To AV AnnuallyDokumen9 halamanAnnual Value of One Present Dollar (Annual Payment) : PV To AV AnnuallyAbrari AndaniBelum ada peringkat
- Internship Report: Procedure of Letter of Credit (LC), Import, Export and Local Trade of Mutual Trust Bank.'Dokumen84 halamanInternship Report: Procedure of Letter of Credit (LC), Import, Export and Local Trade of Mutual Trust Bank.'Suman AminBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 29: The Money System: D. Lines of Credit Accessible With Credit CardsDokumen7 halamanUnit 29: The Money System: D. Lines of Credit Accessible With Credit CardsMinh Châu Tạ ThịBelum ada peringkat
- Prakash Vadilal Mehta AADPM6701F 302 A Dena Apartments Sodawala Lane Near Pandya Hospital Borivali WDokumen5 halamanPrakash Vadilal Mehta AADPM6701F 302 A Dena Apartments Sodawala Lane Near Pandya Hospital Borivali WAditya MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Internship Report of Askari BankDokumen111 halamanInternship Report of Askari BankAnonymous yYfTY1Belum ada peringkat
- Ibs Taiping 1 31/10/22Dokumen11 halamanIbs Taiping 1 31/10/22Nor AzitaBelum ada peringkat
- Dasaiah - 976Dokumen4 halamanDasaiah - 976malli8281Belum ada peringkat
- CGTMSE Information Booklet 2015Dokumen56 halamanCGTMSE Information Booklet 2015Puneet AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Deposit Pay in Slip in BengaliDokumen2 halamanDeposit Pay in Slip in Bengalibiswajit0% (1)
- ECON6033 Corporate Finance Assignment 1 SolutionDokumen2 halamanECON6033 Corporate Finance Assignment 1 SolutionHaiyan LIU100% (1)
- LRAB Syllabus PriorityDokumen6 halamanLRAB Syllabus PriorityPranav Dogra PrikshitBelum ada peringkat
- Address ProofDokumen4 halamanAddress ProofYash GaurkarBelum ada peringkat