Physics Problems
Diunggah oleh
Diana StavaracheJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Physics Problems
Diunggah oleh
Diana StavaracheHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tutorial 5
1. Two mutually coherent beams having parallel electric fields are described by
1 1
3cos
5
E kl t
_
+
,
and
2 2
4cos
6
E kl t
_
+
,
with amplitudes in kV/m. The beams
interfere at a point P where the difference in phase due to path is
3
(the first beam having the
longer path). At the point of superposition, calculate: a) the resultant intensity
1 2 12
I I I I + +
;
b) the fringe visibility.
2. The net intensity of two coherent sources of equal strength is exactly twice the intensity due
to either source at a certain point in space. What is the phase difference between waves
arriving from the two sources at that point?
3. Two coherent light sources of the same wavelength, each with intensity of
3 2
o
1.0 10 W/m I interfere at a point at which the phase difference is 60
o
. What is the net
intensity at this point?
4. Light of wavelength 500 nm shines on two slits separated by 0.3 mm. Find the intensity
ratio
o
I I
at positions 0.6 mm and -0.5 mm from the central maximum on a screen 1m from
the slits.
5. A double-slit experiment produces fringes on a distant screen. How does the linear
separation between the bright maxima on the screen change when a) the wavelength of light
doubles? b) The separation between the slits doubles? c) The distance between the slits and
the screen doubles? d) The intensity of the light doubles?
6. In an interference experiment of the Young type the distance between slits is 0.5 mm and
the wavelength of the light is 600 nm. a) If it is desired to have a fringe spacing 1 mm at the
screen, what is the proper screen distance? b) If a thin plate of glass ( 1.5 n ) of thickness
100 m
is placed over one of the slits, what is the lateral fringe displacement at the screen?
7. In a double-slit experiment to determine an unknown wavelength of light, the measured
total distance between 16 maxima (8 on each side of the central maximum) is 16.8 cm. The
screen is located 3.45 m from the double slits, whose centers are 0.21 mm apart. What is the
wavelength?
8. In Youngs experiment, for what order
m
does the band of wavelength of red light (
780nm ) coincide with the ( ) 1 m+
-th order in the band of blue light ( = 520 nm)?
9. Each of the parallel sides of a glass plate reflects 25% of the intensity of the narrow
monochromatic light beam incident on it and transmits the remainder. Find the ratio of the
minimum and maximum intensities in the interference pattern formed by the two beams
1
I
and
2
I
. R: 1/49
10. A beam of parallel rays is incident at an angle of 30
o
with the normal on a plane parallel
film of thickness
5
4 10
cm and refractive index 1.50. Show that the reflected light whose
wavelength is 754.2 nm will reinforce.
11. A beam of waves of wavelength ranging from 350 to 580 nm is allowed to fall normally
on a thin air film of thickness 0.2945m. What is the colour shown in reflection by the film?
12. A parallel beam of light ( = 589 nm) is incident on a thin glass plate of refractive index
1.5 such that the angle of refraction in the plate is 60
o
. Calculate the smallest thickness of the
plate which will appear dark by reflection.
13. A thin
5
4 10
cm thick film of refractive index 1.5 is illuminated by white light normal to
its surface. Which colour will be intensified in the visible spectrum?
14. A beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 582 nm falls normally on a glass wedge
with the wedge angle of 20 s of an arc. If the refractive index of glass is 1.5, find the number
of interference fringes per centimeter of the wedge length.
15. Light of wavelength 600 nm falls normally on a thin wedge film of refractive index 1.4,
forming fringes that are 2mm apart. Find the angle of the wedge.
16. A filter is used to obtain approximately monochromatic light from a white source. If the
pass band of the filter is 10 nm, what is the coherence length and coherence time of the
filtered light? The mean wavelength is 600 nm.
17. What is the line width in hertz and in nanometers of the light from helium-neon laser
whose coherence length is 5 km? The wavelength is 633 nm.
18. Calculate the length of coherence for some typical light sources: a) white light (
550nm; =300nm
); b) green line of mercury lamp (
546nm; =0.025nm
); c)
orange line of Kr lamp (
606nm; =0.00047nm
); d)
2
CO
laser (
-5
10.6 m; =10 nm ).
19. Calculate the power spectrum of a damped wave train:
( )
( )
0 0
exp for 0
0 for 0
E at i t t
E t
t
'
<
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Physics kinematics problems: speeds, velocities, accelerationsDokumen16 halamanPhysics kinematics problems: speeds, velocities, accelerationsGabriel TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Classical Mechanics - I (PH20007) AssignmentDokumen1 halamanClassical Mechanics - I (PH20007) AssignmentDevanshu GargBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsDari EverandStructure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- Round Ii: Questions & SolutionsDokumen33 halamanRound Ii: Questions & SolutionsRekha SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Optics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyDokumen12 halamanWave Optics: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyRoNBelum ada peringkat
- Physics II ProblemsDokumen1 halamanPhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSBelum ada peringkat
- Physics I Problems PDFDokumen1 halamanPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenBelum ada peringkat
- Extra Physics Rotational ProblemsDokumen4 halamanExtra Physics Rotational ProblemsjohnnyBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Problems September2011.26191830Dokumen1 halamanPhysics Problems September2011.26191830SlidetabonboardBelum ada peringkat
- Content Physics 9702 PDFDokumen5 halamanContent Physics 9702 PDFjayeshpBelum ada peringkat
- Physics ProblemsDokumen3 halamanPhysics ProblemsKathiresan ManickamBelum ada peringkat
- B. M. Boubnov, G. S. Golitsyn (Auth.) Convection in Rotating Fluids 1995Dokumen235 halamanB. M. Boubnov, G. S. Golitsyn (Auth.) Convection in Rotating Fluids 1995Narendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 2007-2008 Physics Olympiad Preparation Program: 2.4 V, and TheDokumen2 halaman2007-2008 Physics Olympiad Preparation Program: 2.4 V, and TheNguyen TuanBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 15Dokumen18 halamanChap 15Tanuj Sethi100% (2)
- Introduction and Plane Mirrors (L-1 To L-6)Dokumen12 halamanIntroduction and Plane Mirrors (L-1 To L-6)arvind_ktBelum ada peringkat
- (Peter T. Landsberg) Recombination in SemiconductorDokumen616 halaman(Peter T. Landsberg) Recombination in SemiconductorMohammad Abu Raihan MiahBelum ada peringkat
- Oden PrintableDokumen32 halamanOden PrintableJulalaBelum ada peringkat
- Waves: PhysicsDokumen53 halamanWaves: Physicsjannie nBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation Materials Ipho: Dinesh KandelDokumen32 halamanPreparation Materials Ipho: Dinesh KandelRahul GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- N. F. Mott - Elements of Wave MechanicsDokumen172 halamanN. F. Mott - Elements of Wave Mechanicsmasaud rejaliBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Dokumen7 halamanExam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Zaki Smn100% (1)
- Nuclear Engineering FundamentalsDokumen42 halamanNuclear Engineering FundamentalsJustine CabuayBelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen17 halamanPhysicsAkash HeeraBelum ada peringkat
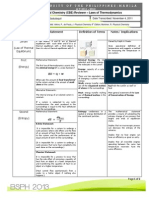
- Physical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsDokumen2 halamanPhysical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsJerome SadudaquilBelum ada peringkat
- ch31 PDFDokumen26 halamanch31 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoBelum ada peringkat
- La Crosse - Thermodynamics Exam 1 - PracticeDokumen9 halamanLa Crosse - Thermodynamics Exam 1 - PracticeembededodinBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Basic Concepts of Nuclear Physics and Overview of ReactorDokumen67 halaman2-Basic Concepts of Nuclear Physics and Overview of ReactorswamikashyapBelum ada peringkat
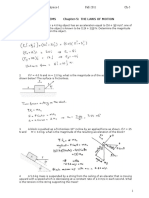
- Mechanics Problem Set - 13Dokumen1 halamanMechanics Problem Set - 13Perry EsguerraBelum ada peringkat
- Jaynes-Cummings ModelDokumen6 halamanJaynes-Cummings ModelFavio90Belum ada peringkat
- Homework and Solutions - ch5 Ch6.IMSDokumen18 halamanHomework and Solutions - ch5 Ch6.IMSHery RobiyantoroBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum free electron theory explained in 40 charactersDokumen11 halamanQuantum free electron theory explained in 40 charactersAshish Manatosh Barik100% (1)
- Wave OpticsDokumen12 halamanWave OpticsKrishnenduBelum ada peringkat
- At What Speed Would The Mass of A Proton Be Twice Its Rest MassDokumen2 halamanAt What Speed Would The Mass of A Proton Be Twice Its Rest MassAman Bhutta100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part5Dokumen5 halamanFluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part5Jose EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- Theoretical Problems in PhysicsDokumen9 halamanTheoretical Problems in PhysicsbananasausageBelum ada peringkat
- PHYS-2325 Ch-5 homework solutionsDokumen5 halamanPHYS-2325 Ch-5 homework solutionsCarlo DomanaisBelum ada peringkat
- 2-Chem 1101 The The Properties of Gases & Solutions (Text)Dokumen55 halaman2-Chem 1101 The The Properties of Gases & Solutions (Text)Tmmp SmileBelum ada peringkat
- Rigid Body MotionDokumen8 halamanRigid Body Motiondesi prawitaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 3 Homework 2: Calculating Dark Matter Mass BoundsDokumen6 halamanWeek 3 Homework 2: Calculating Dark Matter Mass BoundsWasyhun AsefaBelum ada peringkat
- 近物solution PDFDokumen145 halaman近物solution PDF劉鴻軒100% (1)
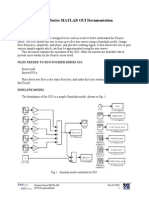
- Fourier Series MATLAB GUI P-Code Doc 011905Dokumen7 halamanFourier Series MATLAB GUI P-Code Doc 011905Julio FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Perturbation TheoryDokumen4 halamanPerturbation Theoryapi-3759956100% (1)
- CH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Dokumen37 halamanCH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Mlamuli MlarhBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Regular Perturbation Theory: Intro To Math ModelingDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To Regular Perturbation Theory: Intro To Math ModelingTirthankar DattaBelum ada peringkat
- YOUNG'S DOUBLE SLIT EXPERIMENT (30-08-2016) (To Be Submitted by 5/6 September 2016) (To Be Submitted in The Tutorial Notebook)Dokumen5 halamanYOUNG'S DOUBLE SLIT EXPERIMENT (30-08-2016) (To Be Submitted by 5/6 September 2016) (To Be Submitted in The Tutorial Notebook)Uday GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- I Am a Physicist: The Ways and Goals of ScienceDokumen219 halamanI Am a Physicist: The Ways and Goals of ScienceKonstantinos100% (1)
- Chapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsDokumen32 halamanChapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsTahsin MorshedBelum ada peringkat
- FHSST Physics PDFDokumen396 halamanFHSST Physics PDFgeri052Belum ada peringkat
- Unit-Ii: Partial Differential Equations-I: X y Yy XX XyDokumen16 halamanUnit-Ii: Partial Differential Equations-I: X y Yy XX XyKaiash M YBelum ada peringkat
- HEAT ENGINE ENTROPYDokumen15 halamanHEAT ENGINE ENTROPYMohammed AhemdBelum ada peringkat
- Einstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadDokumen11 halamanEinstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadRenuBelum ada peringkat
- Heat ConductionDokumen11 halamanHeat ConductionAlex Samuel SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen14 halamanGeometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsqvrlenarasegtBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 31Dokumen22 halamanChapter 31OmarWaelBelum ada peringkat
- Waves in Continuous Media PDFDokumen149 halamanWaves in Continuous Media PDFvicher2020Belum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen49 halaman2ZafirahAhmadFauziBelum ada peringkat
- AbbesDokumen8 halamanAbbesYen BumBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 103 Kinetic Theory of GasesDokumen26 halamanPHY 103 Kinetic Theory of Gasesbishal alamBelum ada peringkat
- Kinetics of Acetone Hydrogenation For Synthesis of Isopropyl Alcohol Over Cu-Al Mixed Oxide CatalystsDokumen9 halamanKinetics of Acetone Hydrogenation For Synthesis of Isopropyl Alcohol Over Cu-Al Mixed Oxide Catalysts李国俊Belum ada peringkat
- Five Fluid PDFDokumen14 halamanFive Fluid PDFاحمد ابوبكر اشقيفهBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding the Molecular Geometry of Acetylene (C2H2Dokumen3 halamanUnderstanding the Molecular Geometry of Acetylene (C2H2sssBelum ada peringkat
- 41502L32 Estimation of The Specific Heat and Thermal Conductivity of FoodsDokumen6 halaman41502L32 Estimation of The Specific Heat and Thermal Conductivity of FoodsDiana ChristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 Powerpoint LDokumen53 halamanChapter 11 Powerpoint LKhaleq MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Q N Answers Marks: Chemistry Marking Scheme DELHI - 2014 SET - 56/1/3Dokumen15 halamanQ N Answers Marks: Chemistry Marking Scheme DELHI - 2014 SET - 56/1/3Anshul GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 4 Achem PDFDokumen12 halamanTutorial 4 Achem PDFyassinroslanBelum ada peringkat
- Aquaflow Rheology ModifiersDokumen16 halamanAquaflow Rheology Modifiershongducxxx100% (1)
- In Uence of Sample Composition and Processing Parameters On The UV Cure of Clear CoatingsDokumen5 halamanIn Uence of Sample Composition and Processing Parameters On The UV Cure of Clear CoatingsMohammad Doost MohammadiBelum ada peringkat
- CM TB Solutions C05Dokumen4 halamanCM TB Solutions C05Kyi Oo WaiBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 4 - T V NGDokumen7 halamanUNIT 4 - T V NGKiều TrangBelum ada peringkat
- Revised Chemistry of Lanthanoides PDFDokumen61 halamanRevised Chemistry of Lanthanoides PDFFarzana MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Calorimetry & Heat Transfer (QB)Dokumen16 halamanCalorimetry & Heat Transfer (QB)Raju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- R717 refrigerant thermodynamic propertiesDokumen1 halamanR717 refrigerant thermodynamic propertiesWillian SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells from TiO2 and Tamarillo ExtractDokumen15 halamanPreparation of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells from TiO2 and Tamarillo ExtractAbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Nature Milestone Complete EbookDokumen145 halamanNature Milestone Complete Ebookvishal040393_9824775Belum ada peringkat
- United States Patent: Ca (OH) 2, P7 CasoDokumen8 halamanUnited States Patent: Ca (OH) 2, P7 CasoViolanda PranajayaBelum ada peringkat
- Hess' Law Mgso4 FinalDokumen6 halamanHess' Law Mgso4 FinalAtikah OlivaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 Bare and Lagged PipesDokumen23 halamanExperiment 1 Bare and Lagged PipesTJ ArciagaBelum ada peringkat
- Zirconium Information Center Zirconium Information Center Properties, Applications and Research Properties, Applications and ResearchDokumen6 halamanZirconium Information Center Zirconium Information Center Properties, Applications and Research Properties, Applications and ResearchLai Wei KhangBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Fading at PolyethyleneDokumen24 halamanGas Fading at PolyethyleneDavide GazzolaBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Physics - Part-I - Part-IIDokumen16 halamanMSC Physics - Part-I - Part-IIRahul Kumar SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- PN427448 Ansul Foam Manual PDFDokumen342 halamanPN427448 Ansul Foam Manual PDFCHANDANBelum ada peringkat
- LTMDokumen12 halamanLTMLuqyBelum ada peringkat
- KSP & Reaction QuotientDokumen2 halamanKSP & Reaction QuotientAndy TanBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3: Organic ChemistryDokumen5 halamanExperiment 3: Organic ChemistryIsuri Vidyarathne100% (1)
- Reduce Bicine Corrosion PDFDokumen7 halamanReduce Bicine Corrosion PDFmahesh070Belum ada peringkat
- Smkts PHYSICS 960/3/P3: Trial STPM Semester 3 STPM 2019Dokumen6 halamanSmkts PHYSICS 960/3/P3: Trial STPM Semester 3 STPM 2019Tan Wei WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Crude Oil RefiningDokumen52 halamanChapter 8 Crude Oil RefiningFatima Al-nBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishDari EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (18)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDari EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDari EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceDari EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain SciencePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDari EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Dari EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (155)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDari EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in SciencePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (48)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDari EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (94)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (75)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesDari EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (139)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDari EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationDari EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDari EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniversePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsDari EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDari EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (53)