Scrubber
Diunggah oleh
riz2010Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Scrubber
Diunggah oleh
riz2010Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Scrubber' systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove some particulates
and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams. The first air scrubber was designed to remove carbon dioxide from the air of an early submarine, a role which they continue to be used for to this day. Traditionally, the term "scrubber" has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to wash unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. Recently, the term is also used to describe systems that inject a dry reagent or slurry into a dirty exhaust stream to "wash out" acid gases. Scrubbers are one of the primary devices that control gaseous emissions, especially acid gases. Scrubbers can also be used for heat recovery from hot gases by flue-gas condensation.[1] There are several methods to remove toxic or corrosive compounds from exhaust gas and neutralize it.
Contents
[hide]
1 Combustion o 1.1 Wet scrubbing o 1.2 Dry scrubbing o 1.3 Absorber o 1.4 Mercury removal 2 Scrubber waste products 3 Bacteria spread 4 See also 5 References
Combustion [edit]
Combustion is sometimes the cause for harmful exhaust gas, but, in many cases, combustion may also be used for exhaust gas cleaning if the temperature is high enough and enough oxygen is available.[2]
Wet scrubbing [edit]
The exhaust gases of combustion may contain substances considered harmful to the environment, and the scrubber may remove or neutralize those substances. A wet scrubber is used to clean air, flue gas or other gases of various pollutants and dust particles. Wet scrubbing works via the contact of target compounds or particulate matter with the scrubbing solution. Solutions may simply be water (for dust) or solutions of reagents that specifically target certain compounds. Process exhaust gas can also contain water soluble toxic and/or corrosive gases like hydrochloric acid (HCl) or ammonia (NH3). These can be removed very well by a wet scrubber.[3]
Removal efficiency of pollutants is improved by increasing residence time in the scrubber or by the increase of surface area of the scrubber solution by the use of a spray nozzle, packed towers or an aspirator. Wet scrubbers may increase the proportion of water in the gas, resulting in a visible stack plume, if the gas is sent to a stack.
Dry scrubbing [edit]
A dry or semi-dry scrubbing system, unlike the wet scrubber, does not saturate the flue gas stream that is being treated with moisture. In some cases no moisture is added, while in others only the amount of moisture that can be evaporated in the flue gas without condensing is added. Therefore, dry scrubbers do generally not have a stack steam plume or wastewater handling/disposal requirements. Dry scrubbing systems are used to remove acid gases (such as SO2 and HCl) primarily from combustion sources. There are a number of dry type scrubbing system designs. However, all consist of two main sections or devices: a device to introduce the acid gas sorbent material into the gas stream and a particulate matter control device to remove reaction products, excess sorbent material as well as any particulate matter already in the flue gas. Dry scrubbing systems can be categorized as dry sorbent injectors (DSIs) or as spray dryer absorbers (SDAs). Spray dryer absorbers are also called semi-dry scrubbers or spray dryers. Dry scrubbing systems are often used for the removal of odorous and corrosive gases from wastewater treatment plant operations. The medium used is typically an activated alumina compound impregnated with materials to handle specific gases such as hydrogen sulfide. Media used can be mixed together to offer a wide range of removal for other odorous compounds such as methyl mercaptans, aldehydes, volatile organic compounds, dimethyl sulfide, and dimethyl disulfide. Dry sorbent injection involves the addition of an alkaline material (usually hydrated lime or soda ash) into the gas stream to react with the acid gases. The sorbent can be injected directly into several different locations: the combustion process, the flue gas duct (ahead of the particulate control device), or an open reaction chamber (if one exists). The acid gases react with the alkaline sorbents to form solid salts which are removed in the particulate control device. These simple systems can achieve only limited acid gas (SO 2 and HCl) removal efficiencies. Higher collection efficiencies can be achieved by increasing the flue gas humidity (i.e., cooling using water spray). These devices have been used on medical waste incinerators and a few municipal waste combustors. In spray dryer absorbers, the flue gases are introduced into an absorbing tower (dryer) where the gases are contacted with a finely atomized alkaline slurry. Acid gases are absorbed by the slurry mixture and react to form solid salts which are removed by the particulate control device. The heat of the flue gas is used to evaporate all the water droplets, leaving a non-saturated flue gas to exit the absorber tower. Spray dryers are capable of achieving high (80+%) acid gas removal efficiencies. These devices have been used on industrial and utility boilers and municipal waste incinerators.
Absorber [edit]
Many chemicals can be removed from exhaust gas also by using absorber material. The flue gas is passed through a cartridge, filled with one or several absorber materials, adapted to the chemical properties of the components that should be removed from the exhaust gas. [4] This type of scrubber is sometimes also called dry scrubber. The absorber material has to be replaced after its surface is saturated.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Vapor Degreasing ProcessDokumen12 halamanVapor Degreasing Process1275812718100% (1)
- Soap and Detergent ManufacturingDokumen7 halamanSoap and Detergent ManufacturingbellesuperBelum ada peringkat
- Ce1305 - Foundation EngineeringDokumen12 halamanCe1305 - Foundation Engineeringsaamy100% (2)
- List of SensorsDokumen9 halamanList of Sensorsriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Types of Hazard : Dormant - The Situation Has The Potential To Be Hazardous, But No People, Property, orDokumen3 halamanTypes of Hazard : Dormant - The Situation Has The Potential To Be Hazardous, But No People, Property, orriz2010100% (1)
- Wet Scrubber: - Blog - Oureducation.In (Sakshi Soni)Dokumen13 halamanWet Scrubber: - Blog - Oureducation.In (Sakshi Soni)Mgn SanBelum ada peringkat
- Power InverterDokumen11 halamanPower Inverterriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution Control DevicesDokumen41 halamanAir Pollution Control Devicesksbbs100% (1)
- Separation of A Mixture of SolidsDokumen6 halamanSeparation of A Mixture of Solidsadrie626Belum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution ControlDokumen35 halamanAir Pollution ControlPraveen YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Venturi Scrubber With Mist EliminatorDokumen13 halamanVenturi Scrubber With Mist Eliminatorandy123hi100% (2)
- Japan-Philippine Steel Manufacturing Corporation: Acid Fumes ScrubberDokumen84 halamanJapan-Philippine Steel Manufacturing Corporation: Acid Fumes ScrubberLuis UrzoBelum ada peringkat
- Firing Petcoke - Vanadium AspectDokumen21 halamanFiring Petcoke - Vanadium AspectAnand Gupta100% (1)
- CCPCDokumen22 halamanCCPCDeepak100% (4)
- ScrubberDokumen12 halamanScrubberDiego Silvano J. Barros100% (1)
- Air Pollution Control For Industrial ApplicationsDokumen19 halamanAir Pollution Control For Industrial ApplicationsJohn Jhay CanlasBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages and Disadvantages : ParticlesDokumen6 halamanAdvantages and Disadvantages : Particlesbavani_84Belum ada peringkat
- PV Wet ScrubberDokumen7 halamanPV Wet ScrubberCepi Sindang KamulanBelum ada peringkat
- Wet Scrubber: Pollutants Furnace Flue GasDokumen12 halamanWet Scrubber: Pollutants Furnace Flue Gasperky_ashishBelum ada peringkat
- Dry ScrubberDokumen2 halamanDry ScrubberJulis-Alexia von RiessfeltBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlDokumen30 halamanAdsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlJoao MinhoBelum ada peringkat
- ScrubberDokumen28 halamanScrubberMuhammad Jajar Pambudi0% (1)
- ScrubberDokumen3 halamanScrubbervijay kumar honnaliBelum ada peringkat
- Wet Scrubbing: Dry Sorbent Injection Involves The Addition of AnDokumen2 halamanWet Scrubbing: Dry Sorbent Injection Involves The Addition of AnJordan MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Control of Gaseous Pollutants (Group E)Dokumen20 halamanControl of Gaseous Pollutants (Group E)Ken ManeboBelum ada peringkat
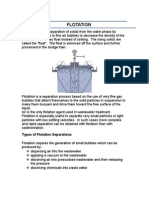
- Flotation: Types of Flotation SeparationsDokumen6 halamanFlotation: Types of Flotation SeparationsWaseem YousafBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution Particulates Ictineo I: Scrubber Scrubber Systems Are A Diverse Group ofDokumen1 halamanAir Pollution Particulates Ictineo I: Scrubber Scrubber Systems Are A Diverse Group ofmacleod230286Belum ada peringkat
- Controlofairpollutants 181124103155Dokumen17 halamanControlofairpollutants 181124103155Dawit GirmaBelum ada peringkat
- ScrubbersDokumen5 halamanScrubbersleoboyaliBelum ada peringkat
- Air PollutionDokumen27 halamanAir PollutionVincentBelum ada peringkat
- Scrubber SystemsDokumen2 halamanScrubber SystemsmychoicegrowthBelum ada peringkat
- Scrubber Systems (E.g. Chemical Scrubbers, Gas Scrubbers) Are A Diverse Group ofDokumen1 halamanScrubber Systems (E.g. Chemical Scrubbers, Gas Scrubbers) Are A Diverse Group ofUadBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pollu ControlDokumen3 halamanAir Pollu ControlBasavaraj HungundBelum ada peringkat
- FGD Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDokumen7 halamanFGD Chemistry: Basic Principlesirvan Chaerul SBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution Control TechniquesDokumen35 halamanAir Pollution Control TechniquesAhad Kanak ProttoyBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2Dokumen4 halamanAssignment 2MK AbirBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption Group 7-1Dokumen16 halamanAdsorption Group 7-1Junior J DliwayoBelum ada peringkat
- Ways To Prevent Air PollutionDokumen6 halamanWays To Prevent Air PollutionRahul HanumanteBelum ada peringkat
- Group Members: Andile Sibanda Donovan Moyo Takunda Chikohwa Lebani Dube Byron MawoyoDokumen18 halamanGroup Members: Andile Sibanda Donovan Moyo Takunda Chikohwa Lebani Dube Byron MawoyoSambiri PisiraiBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Ecology: Flue Gas Cleaning Systems For Waste Incineration PlantDokumen4 halamanIndustrial Ecology: Flue Gas Cleaning Systems For Waste Incineration PlantNicoleta UngureanuBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Gas CleaningDokumen5 halamanNatural Gas CleaningDisha PatniBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Pollution Control TechniquesDokumen41 halamanEnvironmental Pollution Control TechniquesSanket VaghelaBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial ScrubbersDokumen2 halamanIndustrial Scrubbersvijay kumar honnaliBelum ada peringkat
- Aqm Assignment 2Dokumen44 halamanAqm Assignment 2nithin M SBelum ada peringkat
- Activated Carbon (Charcoal) FiltersDokumen2 halamanActivated Carbon (Charcoal) FiltersMichael James ll BanawisBelum ada peringkat
- Activated Carbon or Charcoal FiltersDokumen2 halamanActivated Carbon or Charcoal FiltersMohammed A. HelalBelum ada peringkat
- Blower & ScrubberDokumen15 halamanBlower & ScrubbervniranjanBelum ada peringkat
- Epac NotesDokumen93 halamanEpac NotesSimran fatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pollution Control and EquipmentDokumen9 halamanAir Pollution Control and Equipmentmihir kordeBelum ada peringkat
- History of Industrial HygieneDokumen23 halamanHistory of Industrial HygieneJohnCarloTolibasBelum ada peringkat
- Aqm Module 6 Lec 3Dokumen18 halamanAqm Module 6 Lec 3fromashokBelum ada peringkat
- Pollution ControlDokumen4 halamanPollution Controlvikash rajBelum ada peringkat
- 34 Gaseous Control Technologies PDFDokumen62 halaman34 Gaseous Control Technologies PDFenviron13Belum ada peringkat
- Method For Air Pollution ControlDokumen7 halamanMethod For Air Pollution ControlFurqan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption of Gaseous PollutantsDokumen26 halamanAdsorption of Gaseous PollutantsJoao MinhoBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Drying EquipmentDokumen6 halamanGas Drying EquipmentJustin Paul CongeBelum ada peringkat
- Wet Scrubbing of Acidic Gases: Robert J. Chironna Schutte & KoertingDokumen4 halamanWet Scrubbing of Acidic Gases: Robert J. Chironna Schutte & Koertingnikhaarj100% (1)
- Air Pollution and ControlDokumen16 halamanAir Pollution and Controlgovica0702Belum ada peringkat
- NAWTEC18-3507: Comparison of Acid Gas Control Technologies in Efw FacilitiesDokumen10 halamanNAWTEC18-3507: Comparison of Acid Gas Control Technologies in Efw FacilitiesPunki KokoBelum ada peringkat
- 12pg142 146 Dehydration and Sweetening of Natural Gas 160214194840Dokumen16 halaman12pg142 146 Dehydration and Sweetening of Natural Gas 160214194840Muhammad sherazBelum ada peringkat
- Sweetening ProcessDokumen20 halamanSweetening ProcessMuhammad Sajid100% (1)
- Air PollutionDokumen8 halamanAir PollutionGopi AravindBelum ada peringkat
- Municipal Odor Control Italy TPDokumen6 halamanMunicipal Odor Control Italy TPDileep C DileepBelum ada peringkat
- Practical-Air Pollution and Control-PDokumen26 halamanPractical-Air Pollution and Control-PsarfaBelum ada peringkat
- TEE 803 Introduction To CCT Lec 13 15Dokumen16 halamanTEE 803 Introduction To CCT Lec 13 15Sami KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Fertilizer ManufacturingDokumen17 halamanFertilizer ManufacturingSambiri PisiraiBelum ada peringkat
- Negative Feedback AmplifierDokumen12 halamanNegative Feedback Amplifierriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- DC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost ConvertersDokumen3 halamanDC-to-DC Converter Switching Converter Transformer Change Voltage Push-Pull Circuit Buck-Boost Convertersriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- An Electronic AmplifierDokumen26 halamanAn Electronic Amplifierriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Electric-Power Transmission Is The Bulk Transfer Of: o o o oDokumen17 halamanElectric-Power Transmission Is The Bulk Transfer Of: o o o oriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- How To Make Hot Chocolate FudgeDokumen1 halamanHow To Make Hot Chocolate Fudgeriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Outline of EngineeringDokumen9 halamanOutline of Engineeringriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Geosynthetic Retaining WallsDokumen2 halamanGeosynthetic Retaining Wallsriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Number Name Height (M) Height (FT) FloorsDokumen4 halamanNumber Name Height (M) Height (FT) Floorsriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- What Is The Tallest Building?: WinnerDokumen3 halamanWhat Is The Tallest Building?: Winnerriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Skyscraper: Navigation SearchDokumen10 halamanSkyscraper: Navigation Searchriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Dome of The RockDokumen24 halamanDome of The Rockriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- MechatronicsDokumen3 halamanMechatronicsriz2010100% (1)
- Cables Wires and ConductorsDokumen2 halamanCables Wires and Conductorsriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Instrumentation Is Defined As The Art and Science of Measurement and Control of ProcessDokumen4 halamanInstrumentation Is Defined As The Art and Science of Measurement and Control of Processriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- A Bending MomentDokumen1 halamanA Bending Momentriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- O o o oDokumen5 halamanO o o oriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Pipe ScheduleDokumen2 halamanPipe Scheduleriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Steel Is An: Citation NeededDokumen1 halamanSteel Is An: Citation Neededriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- A Power StationDokumen11 halamanA Power Stationriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- The Determination of Lactose in MilkDokumen6 halamanThe Determination of Lactose in MilkRobert Ospina BuilesBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Respiration Post-Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanCell Respiration Post-Lab ReportDaniel Seth AndalBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure of The AtomDokumen33 halamanThe Structure of The AtomWilley TaluanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 OilDokumen38 halaman2 Oilbumatio latiBelum ada peringkat
- Class Assessment Result For Grades 1-10 Learning Area: - (English/Filipino/Mtb/Ap/Esp)Dokumen18 halamanClass Assessment Result For Grades 1-10 Learning Area: - (English/Filipino/Mtb/Ap/Esp)Joe TitularBelum ada peringkat
- GUARD DOG™ UV119 Light StabilizerDokumen2 halamanGUARD DOG™ UV119 Light StabilizerXuân Giang NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: H H H H H H H H H H Symbols by Correct ArrowsDokumen2 halamanAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: H H H H H H H H H H Symbols by Correct ArrowsKenneth KnightBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 209 Chapter 03 Spring 2020.SQDokumen87 halamanCHEM 209 Chapter 03 Spring 2020.SQTaanzBelum ada peringkat
- Polyseal: Company Profile Product Range IndexDokumen259 halamanPolyseal: Company Profile Product Range IndexSara SaritaBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation of Pharmaceutical CreamsDokumen4 halamanPreparation of Pharmaceutical CreamsAhmed FouadBelum ada peringkat
- PMLS 1: Lab Math Ratios and DilutionsDokumen2 halamanPMLS 1: Lab Math Ratios and DilutionsAEsmilingBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic ChemistryDokumen13 halamanInorganic Chemistrybhargavthegreat123Belum ada peringkat
- Physical ScienceDokumen19 halamanPhysical ScienceSarmiento Gianne Mae A.Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Workplace HygieneDokumen29 halamanChapter 7 Workplace HygieneMariane Christine Joy BayonBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes 6.4 - 6.9Dokumen4 halamanChemistry Notes 6.4 - 6.9Grace LeeBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 Lect4c Epoxidation S of AlkenesDokumen20 halaman2013 Lect4c Epoxidation S of AlkenesBagusBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Arc Furnace-The Technology of The South East Asian SteelmakersDokumen4 halamanElectric Arc Furnace-The Technology of The South East Asian SteelmakersBoy Trio ManikBelum ada peringkat
- URF0100 FracFocusWellReportDokumen17 halamanURF0100 FracFocusWellReportjangri1098Belum ada peringkat
- Homework Booklet (B)Dokumen34 halamanHomework Booklet (B)Pa GesBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of 90 Degree Welding ClampDokumen24 halamanDesign and Fabrication of 90 Degree Welding ClampAfsal Mohamed Kani 004Belum ada peringkat
- F4 1st Term ExamDokumen14 halamanF4 1st Term ExamSingapore TripBelum ada peringkat
- UV-4024 MSDS (英文版)Dokumen4 halamanUV-4024 MSDS (英文版)urbaezBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion of HEADokumen18 halamanCorrosion of HEAhydromaniaBelum ada peringkat
- QP SPC L002 Rev 2 ReferenceDokumen1 halamanQP SPC L002 Rev 2 ReferencekannanBelum ada peringkat
- SPARK Bouncing Planets ManualDokumen10 halamanSPARK Bouncing Planets Manualgaurang gandhiBelum ada peringkat
- J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15692Dokumen4 halamanJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15692CarlotaBelum ada peringkat
- Redox Reactn BalancingDokumen4 halamanRedox Reactn BalancingshahanasnizarBelum ada peringkat