NCM 106 Course Outline
Diunggah oleh
Nikka Moreen DagdagJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NCM 106 Course Outline
Diunggah oleh
Nikka Moreen DagdagHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
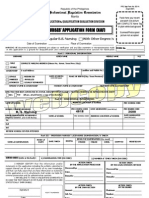
REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES VISAYAS STATE UNIVERSITY College of Nursing VISCA, B AYBAY, LEYTE Telephone: (053) 563-7226 NCM
106 COURSE OUTLINE CARE OF CLIENTS AC ROSS THE LIFESPAN WITH PROBLEMS IN CELLULAR ABERRATIONS, ACUTE BIOLOGIC CRISIS, INCLUDING EMERGANCY AND DISASTER NURSING DATE June 11 & June 18 TOPIC I. MUSCULO SKELETAL FUNCTION A. Anatomic & Physiologic Overview 1. Skeletal System 2. Artic ular System 3. Skeletal Muscle System B. Assessment 1. Health History 2. Physica l Assessment C. Diagnostic Evaluation 1. Radiographic Studies 2. CT 3. MRI 4. Ar thrography 5. Bone Densitometry 6. Bone Scan 7. Arthroscopy 8. Arthrocentesis 9. EMG 10. Biopsy D. Clients With A Cast - Casting materials - Arm casts - Leg cas ts - Body or spica casts - Caring for a client with a cast E. Caring for a Clien t with Splints and Braces F. Caring for a Client with an External Fixator G. Cli ents in Traction - Principles of effective traction - Skin traction - Skeletal t raction - Caring for a client in traction I. Common Problems with the Musculoske letal System 1. Acute Low Back Pain 2. Bursitis & Tendinitis 3. Loose Bodies LEC TURER ALMERIA June 19 CALUNGSOD
June 25 June 26 4. Impingement Syndrome 5. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 6. Ganglion 7. Dupuytren s Syndrom e 8. Corns 9. Callus 10. Ingrown Toenail 11. Hammer Toe 12. Hallux Valgus 13. Pe s Cavus 14. Morton s Neuroma 15. Flatfoot 16. Osteoporosis 17. Osteomyelitis 18. Ost eomalacia 19. Paget s Disease 20. Bone Tumors 21. Contusions, Sprains and Strains 22 . Joint dislocations 23. Sports Injuries - Rotator cuff tears - Epicondylitis Lateral & medial collateral ligament injury - Anterior & posterior cruciate liga ment injury - Rupture of the Achilles tendon 22. Fractures - Types - Kinds - Fra cture healing 23. Amputation II. CELLULAR ABERRATIONS A. Review of the Cellular Physiology 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Differentiation 3. Proliferation B. Characterist ics of Benign & Malignant Neoplasms 1. Terminology 2. Neoplasm 3. Benign 4. Mali gnant - Cancer cell characteristics - Invasion & metastasis - Tumor growth - Gen eral effects C. General Pathophysiology of Cellular Aberration D. Epidemiology ( Local & International) a. Lung cancer b. Breast cancer c. Uterine cancer d. Pros tate cancer MENESES DE LOS SANTOS
July 2 & July 3 e. Colorectal cancer E. Carcinogenesis & Causes of Cancer Oncogenesis Risk Facto rs: 1. Gender & Site 2. Age 3. Race & Ethnicity 4. Genetics 5. Hormonal Factors 6. Immunologic Factors 7. Oncogenic Viruses 8. Drugs & Chemicals 9. Radiation Ionizing - UV - Electromagnetic - Radon 10. Lifestyle F. Significant Subjective Data from the Client - Family history - Chief complaints - Functional patterns Psychosocial & behavioural assessment G. Principles & Techniques of Physical Ex amination in All Age Group, Deviations from Normal 1. Breast Self-Examination 2. Testicular Self-Examination 3. Digital Rectal Examination H. Diagnostic Tests & Nursing Responsibilities 1. Lung Cancer - Chest X-ray - Sputum cytology 2. Brea st Cancer - Mammogram - Clinical breast exam - MRI - Tissue Sampling 3. Uterine Cancer - Transvaginal sonography - Hysteroscopy - Sonohysterography - Biopsy pun ch 4. Cervical Cancer - Pap smear with staging 5. Prostate Cancer - Digital rect al examination - Prostate-specific antigen 6. Colorectal Cancer - Fecal occult b lood test - Sigmoidoscopy - Colonoscopy PEREZ
- Double-contrasted barium enema 7. Other tests - Tumor markers - Radioisotope s can - MRI July 9, July 10 & I. Pathophysiologic Mechanisms Leading to Manifestat ions July 16 1. Lung Cancer 2. Breast Cancer 3. Uterine Cancer 4. Colorectal Can cer 5. Prostate Cancer 6. Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma 7. Kidney Cancer 8. Melanoma 9. Bas al Cell Carcinoma 10. Thyroid Cancer 11. Leukemia 12. Childhood Cancers - Glioma - Neuroma - Wilm s Tumor - Retinoblastoma - Ewing s Sarcoma - Osteosarcoma July 17 J. N ursing Diagnoses Taxonomy/Development of Outcome Criteria 1. Potential for Infec tion 2. Disturbance in Body Image 3. Activity Intolerance 4. Potential for Alter ation in Nutrition; Less than Body Requirements 5. Alteration in Oral Mucous Mem brane Integrity 6. Alteration in Comfort 7. Fluid Volume Deficit K. Principles o f Various Modalities of Management Against Cancer 1. Health promotion 2. Disease prevention 3. Curative 4. Restorative L. Principles of Management 1. Cancer Sta ging - TNM Classification - Clinical Staging - Metastatic Spread 2. Prevention o f Infection 3. Hydration 4. Blood Component Replacement 5. Oxygen Therapy 6. Pre vention of Complications 7. Rehabilitation M. Pharmacologic Actions (Therapeutic use, Side effects, Indications, Contraindications, ALMERIA MENESES July 23 & July 24 CALUNGSOD
Nursing responsibilities) 1. Biotherapy - Cytokines - Monoclonal Antibodies - Ce llular Therapies - Immunodilators - Retinoids 2. Chemotherapeutic Agents a. Clas sification - Cell cycle-specific - Cell cycle-nonspecific b. Categories - Alkala ting agents - Antibiotic - Nitroureas - Plant derivatives - Hormonal N. Special Considerations in Chemotherapeutic Drugs Preparation 1. Proper attire 2. Chemo d rug handling O. Special Procedures 1. Radiation therapy 2. Cervical implants 3. Reverse isolation P. Appropriate Discharge Plan Including Health Education MIDTE RMS EXAM III. ACUTE BIOLOGIC CRISIS A. Standard Assessment of the Critically Ill - Focused history taking - Discriminating physical examination AIRWAY BREATHING CIRCULATION HEMODYNAMIC STATUS July 30 August 7, 13 DE LOS SANTOS B. Pathophysiologic Mechanisms Leading to Manifestations 1. Cardiac Failure 2. A cute Myocardial Infarction 3. Acute Renal Failure August 14 & August 4. Stroke 2 0 5. Increaased Intracranial Pressure 6. Metabolic Emergencies - DKA/HHNK 7. Mas sive Bleeding/Hypovolemic Shock 8. Extensive Injuries - Dehiscence - Evisceratio n 9. Extensive Burns - Staging - Area Computation CALUNGSOD
August 28 - IVF Replacement C. Nursing Diagnoses Taxonomy/Development of Outcome Criteria 1. Impaired Gas Exchange 2. Inability to Sustain Spontaneous Ventilation 3. Dysf unctional Ventilatory Weaning Process 4. Decreased Cardiac Output 5. Altered Tis sue Perfusion, Systemic 6. Alteration in Nutrition; Less than Body Requirements 7. Fluid Volume Deficit 8. Activity Intolerance D. Results/Implications of Diagn ostic Laboratory Exams 1. Non-invasive: ECG, cardiac rhythms 2. Invasive: ABG, H emodynamic Monitoring, CVP, Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP) & 3. Life Maintaining Interventions - Airway management & care of clients with a ventilato r - Interventions for hemodynamic instability - Continuous hemodynamic monitorin g - Interventions for neural regulation - Fluid & Electrolyte problems - Nutriti on E. Pharmacologic Actions (Therapeutic use, Side effects, Indications, Contrai ndications, Nursing responsibilities) 1. Analgesics 2. Narcotics 3. Corticostero ids 4. Antihypertensives 5. Vasopressors 6. Antibiotic 7. Parenteral fluids IV. DISASTER NURSING A. Definition of Emergency & Other Terminologies - Disaster - T rauma B. Triage - Definition - Objectives 1. START Triage System - Indication fo r use - Mnemonic/Procedure - ADULT START Triage System - PEDIATRIC START Triage System - START Flow Chart - Color Coding - Evacuation Prioritization According t o Category - Incident Command System 2. MILITARY TRIAGE - Indication for use - 5 Categories of Severity PEREZ August 29 September 3 MENESES September 4 PEREZ
September 10 D. The Crash Cart/E-Cart - Contents - A-Z Emergency Drugs E. Personal Protective Equipment F. Hazardous Materials G. Decontamination H. Biologic Warfare & Biolo gic Agents K. Blast Injuries J. Natural Disasters DE LOS SANTOS K. Stress Reactions - Post Traumatic Stress Disorder - Critical Incident Stress Management - Debriefing September 11 & V. IV THERAPY September 17 A. Philosophy B. Definition C. Basic Foundation of IV Therapy 1. Historical Background 2. Ethi co-legal Issues - Role of ANSAP - Difference between RA 9173 & RA 7160 3. Standa rds of IV Therapy D. Review of Anatomy & Physiology of the Vascular System E. Pe ripheral & Integumentary System F. Fluid & Electrolyte Therapy 1. Types of Fluid s/Solutions and Uses 2. Drug Interaction with IV Fluids 3. Handling of IV Soluti ons, Blood Products & Components G. Nursing Process in IV Therapy H. Venipunctur e Technique in Adult & Children - Prescribed cannula & indications of each color & gauge - Ideal period of usage of an IV set, Indications - Process in keeping a set sterile I. Complications of IV Therapy J. Infection Control & Microbiology Principles K. Demonstration of Procedure ALMERIA PREPARED BY: KRISHNA RAE Z. ALMERIA, RN, MAN
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Final BibliographyDokumen2 halamanFinal BibliographyNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsDokumen76 halamanNursing Responsibilities in Administering Cardiovascular DrugsNikka Moreen Dagdag80% (5)
- Hepatitis B Workplace Policy & ProgramDokumen4 halamanHepatitis B Workplace Policy & Programraighnejames1950% (2)
- Generic-Workplace Policy ADokumen4 halamanGeneric-Workplace Policy ANikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- CapitisDokumen2 halamanCapitisNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- November - Climate ChangeDokumen1 halamanNovember - Climate ChangeNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Dokumen17 halamanPulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Nikka Moreen Dagdag100% (1)
- TheoriesDokumen2 halamanTheoriesNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Workplace HIV/AIDS PolicyDokumen4 halamanWorkplace HIV/AIDS PolicydebaynBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study: Rle: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDokumen7 halamanCase Study: Rle: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverNikka Moreen Dagdag0% (1)
- Pediculosis Humanus CapitisDokumen3 halamanPediculosis Humanus CapitisNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Dokumen17 halamanPulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Nikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- MedicinesDokumen1 halamanMedicinesNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- ABCs of Hypertension: Measuring BP & TypesDokumen15 halamanABCs of Hypertension: Measuring BP & TypesNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- December - Firecracker Injury PreventionDokumen1 halamanDecember - Firecracker Injury PreventionNikka Moreen Dagdag0% (1)
- Pediculosis Humanus CapitisDokumen3 halamanPediculosis Humanus CapitisNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- AnatomyfdswgsdfgsdfgDokumen5 halamanAnatomyfdswgsdfgsdfgNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- CapitisDokumen2 halamanCapitisNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- International Kawasaki Disease Symposium ProgramDokumen208 halamanInternational Kawasaki Disease Symposium ProgramNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses' Application FormDokumen2 halamanNurses' Application FormTricia GervacioBelum ada peringkat
- Addition of Vectors: - Analytical MethodDokumen7 halamanAddition of Vectors: - Analytical MethodNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokumen15 halaman6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Communicable DiseasesDokumen8 halamanCommunicable DiseasesKarla Fralala100% (1)
- Breast AssessmentDokumen1 halamanBreast AssessmentNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing InterventionsDokumen13 halamanNursing InterventionsNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses' Application FormDokumen2 halamanNurses' Application FormTricia GervacioBelum ada peringkat
- FilesDokumen2 halamanFilesNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses' Application FormDokumen2 halamanNurses' Application FormTricia GervacioBelum ada peringkat
- Hospitalization Analysis Prior Admission Factors Laboratory Studies Radiology ReportDokumen3 halamanHospitalization Analysis Prior Admission Factors Laboratory Studies Radiology ReportNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge PlanningDokumen1 halamanDischarge PlanningNikka Moreen DagdagBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Brusca Invertebrates Ed. 3 Par IDokumen458 halamanBrusca Invertebrates Ed. 3 Par IStavarache LarisaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1-5 PDFDokumen77 halamanChapter 1-5 PDFEstebanBelum ada peringkat
- Schneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFDokumen15 halamanSchneider Review of Moore's The Dependent Gene PDFfuck offBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Coordination in PlantsDokumen2 halamanChemical Coordination in PlantsZah SchlafmützeBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen1 halamanCell Cyclenica onicaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Holiday AssignmentDokumen1 halamanBiology Holiday Assignmentapi-234805234Belum ada peringkat
- Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways ExplainedDokumen8 halamanEnzymes and Metabolic Pathways ExplainedCid Benedict PabalanBelum ada peringkat
- Spot 4 Class XiDokumen3 halamanSpot 4 Class XiJeevan RaajBelum ada peringkat
- Jungtrakoon SLC19A2 PDFDokumen11 halamanJungtrakoon SLC19A2 PDFChristantya VitaBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 JanDokumen160 halaman2010 JanaliceBelum ada peringkat
- Paulownia Medicine Usa StudyDokumen15 halamanPaulownia Medicine Usa StudyCarlos LehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell (Biology) - WikipediaDokumen29 halamanCell (Biology) - WikipediaMokariya SanjayBelum ada peringkat
- LIU Et Al, 2015Dokumen8 halamanLIU Et Al, 2015MARIA FERNANDA OLIVEIRA SOARESBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Classification SheetDokumen2 halamanBiological Classification SheetJay JainBelum ada peringkat
- Es UbdDokumen4 halamanEs Ubdapi-275510930Belum ada peringkat
- Air Lift FermenterDokumen3 halamanAir Lift FermenterNarendiran RamBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSC activationDokumen3 halamanMetformin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSC activationEuphra AdellheidBelum ada peringkat
- Malaria DX TestsDokumen2 halamanMalaria DX TestsAngelica GuintoBelum ada peringkat
- HES007 Lec Session #4 SASDokumen7 halamanHES007 Lec Session #4 SASPresley Joy Graneta RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Age-Related Dry Eye Lactoferrin and Lactobionic Acid: Mini ReviewDokumen6 halamanAge-Related Dry Eye Lactoferrin and Lactobionic Acid: Mini ReviewldBelum ada peringkat
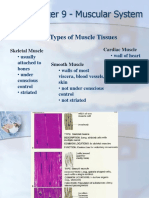
- Bab 12 - Muscular SystemDokumen73 halamanBab 12 - Muscular SystemDaeng FarahnazBelum ada peringkat
- Plants Part 1Dokumen28 halamanPlants Part 1Puneet TatranBelum ada peringkat
- Segmentna Anatomija Jetre Na Ultrazvuku: AutoriDokumen5 halamanSegmentna Anatomija Jetre Na Ultrazvuku: AutoriMarie J. ConstantBelum ada peringkat
- Energy GenerationDokumen4 halamanEnergy GenerationDeena ChadiBelum ada peringkat
- DNA TimelineDokumen3 halamanDNA TimelineMonica EsBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Popcorn Introductions For AgronomicDokumen8 halamanPerformance of Popcorn Introductions For AgronomicDANIEL LEONARDO DE LA CRUZ GOMEZBelum ada peringkat
- Ruthenium in Medicine: Current Uses and Future Prospects: ClinicalDokumen8 halamanRuthenium in Medicine: Current Uses and Future Prospects: ClinicalMuhammad Adlan RasyidiBelum ada peringkat
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Dokumen27 halamanZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroBelum ada peringkat
- The Living WorldDokumen14 halamanThe Living WorldNalla Raghuram ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Grade 7 Video LessonDokumen4 halamanDLL Grade 7 Video LessonJr CapanangBelum ada peringkat