Groundnut Weeding
Diunggah oleh
Jitendra PradhanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Groundnut Weeding
Diunggah oleh
Jitendra PradhanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
After completing this lesson, you have learned to answer:
When the first schedule for weed control activity in groundnut should start? How pre-sowing rainfall or irrigation helps in better weed control in groundnut? What methods of weed control are practiced in groundnut cultivation? List the cultural practices that help in reducing the weeds in groundnut crop? What is the correct schedule for manual weeding in groundnut crop? What is the correct schedule for intercultivation to take care of weeds in groundnut crop? What precautions one should take to use herbicides for weed control in groundnut crop? List the herbicides based on their time of application? Give an example of pre-planting herbicide for groundnut weed control? Describe your recommendation for one pre-emergence herbicide for groundnut weed control?
Weed control need to be practiced in groundnut crop even before sowing so that the plants grow without any weed competition from germination onwards. That means the first weed control activity starts even before sowing groundnut.
Weed-free field for sowing
The weed seeds in the soil are allowed to germinate with the first rainfall and then the final harrowing or plowing is carried out. This practice will provide a weed free environment for vigorous and robust growth for the groundnut seedlings.
Weed-free environment in the early stages. Weeds are not allowed to grow during the first 45 days of growth of groundnut plants as this is the most critical weed competition period.
No weed control activity should be practiced to avoid any damage to the plants at the peg formation and peg penetration stages. Even though weed competition after pod formation stage may not result in much yield reduction, standing weeds may interfere with harvesting of pods. So control of weeds even at the later stages of groundnut crop is important.
There are 3 methods of weed control practices.
Control through crop cultural practices Manual or mechanical control Chemical control
Efficient and effective weed control can be achieved by wisely combining the above methods of weed control practices.
Cultural practices A good crop cover by adopting right spacing between rows and within the row will smother the weed growth. For this adopt the recommended spacing of 30 cm between rows and 10 cm between the plants within the row for bunch types. For spreading types the recommended spacing is 40 cm between rows and 10 cm between the plants within the row. Mulching the soil surface in between rows with crop residue material like straw etc. may prevent the germination of weed seeds and at the same time smothers the established young weeds. This mulching practice also helps in conserving the soil moisture.
Example of mulching with straw Growing groundnut crop every year in the same field (monocropping) encourages certain
weeds to multiply and dominate in the field. Such weeds will reduce groundnut crop yields much more than the competition from a wide spectrum of weeds. So, adopting proper crop rotation practices will help in overcoming the domination of certain weeds and lessening the weed competition in groundnut crop. Intercropping practice in groundnut crop not only provide the monetary and land utilization advantages but also help in smothering the weeds with good crop cover over the land surface.
Groundnut-Pearl millet intercropping
Manual weeding Manual weeding is a very common practice to control weeds in groundnut crop. Hand pulling of weeds though primitive is an efficient way of controlling weeds especially in groundnut. This way weeds growing near the plants can be efficiently removed without damaging the crop.
Hand hoeing is another effective method adopted widely to control weeds in the inter row spaces of line-sown crop.
This method provides excellent physical condition to the crop growth by way of soil aeration through stirring of the soil. First hand weeding is done at about 20 - 25 days after sowing and should be repeated at fortnightly intervals up to 45 days of the crop. Manually operated implements like wheel push hoe are also used to control weeds in groundnut.
Mechanical weeding Blade harrowing in relatively dry and loose soil between the rows of groundnut, is a widely followed method for effective weed control as this operation cuts the root system of weeds resulting in desiccation of weeds.
Duck-foot harrows are also used for intercultivation in groundnut. The first intercultivation is done about three weeks after sowing and the second and the third about a fortnight and a month later. No intercultural would be done once the peg penetration starts in the crop.
Chemical control Use of chemicals (herbicides) to control weeds should be based on their comparative advantage over the manual and mechanical control of weeds.
Herbicide application is advantageous in case of non-availability of labor and/or cost of labor for manual weeding is very high. Use of correct herbicides will provide completely weed-free situation to the crop where as manual or mechanical weeding can be done only after the emergence of weeds. Herbicide application requires some knowledge about the use of such chemicals. Improper use of herbicides may lead to the complete loss of the crop. Correct use of herbicides has proven to be safe and very effective against a diversity of both grass and broadleaf weeds. The farmers need to understand the proper use and application of herbicides before applying them to control weeds in groundnut crop. Depending on the time of application, herbicides are grouped as
preplanting (incorporated into the soil before sowing of the crop) herbicides, preemergence (after sowing but before emergence of seedling) herbicides, postemergence (after emergence of weeds and the crop) herbicides.
A number of herbicides were found to be selective in controlling many weeds in groundnut. However, efficient and cost-effective weed control can be achieved by using combination of herbicides or combining manual and herbicide control methods. A list of herbicides found to be useful for weed control in groundnut is given
Selected herbicides and recommended rates :
Herbicide Rate Trade Name Scientific Name (a.i.kg/ha) Fluchloralin Nitrofen Pendimethalin Alachlor Oxyflurofen Basalin ToK-E-25 Stomp Lasso Goal 1.25-1.50 1.50-2.00 0.60-1.50 1.50-2.00 0.25-0.50
Time Of Application Pre-sowing incorporation into soil Pre-emergence spray -do-do-do-
With this, the Lesson 2 about strategies for controlling weeds in groundnut cultivation and also this Module concludes.
Next, Module X in this course is about soil moisture relationships and irrigation in groundnut cultivation.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Integrated Weed Management MethodsDokumen16 halamanIntegrated Weed Management MethodsMichelleAdanteMorongBelum ada peringkat
- Linear RegressionDokumen56 halamanLinear RegressionRanz CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Weed Management Methods and Integrated Weed ManagementDokumen16 halamanWeed Management Methods and Integrated Weed ManagementBABBU CHAHALBelum ada peringkat
- Direct InstructionDokumen1 halamanDirect Instructionapi-189549713Belum ada peringkat
- LEGAL STATUs of A PersonDokumen24 halamanLEGAL STATUs of A Personpravas naikBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Renal DiseasesDokumen57 halamanManagement of Renal DiseasesAyana KeikoBelum ada peringkat
- Preterite vs Imperfect in SpanishDokumen16 halamanPreterite vs Imperfect in SpanishOsa NilefunBelum ada peringkat
- REBECCA SOLNIT, Wanderlust. A History of WalkingDokumen23 halamanREBECCA SOLNIT, Wanderlust. A History of WalkingAndreaAurora BarberoBelum ada peringkat
- IPM ReportDokumen13 halamanIPM Reportm_2011100% (1)
- Mechanical Weeder Design for Weed ControlDokumen54 halamanMechanical Weeder Design for Weed ControlCUBE Engineering SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- PersonalDevelopment Q1 Module 2Dokumen7 halamanPersonalDevelopment Q1 Module 2Stephanie DilloBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report 123 PDFDokumen44 halamanProject Report 123 PDFSuni S Gowda67% (12)
- Weed Management in Wheat CropDokumen4 halamanWeed Management in Wheat CropjawadaupBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Weed Management 22.11.2021Dokumen8 halamanIntegrated Weed Management 22.11.2021Izukanji KayoraBelum ada peringkat
- Cultural Weed Control: R161055Z Masara PoliteDokumen15 halamanCultural Weed Control: R161055Z Masara PolitePriyabrata BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Weed Control MethodsDokumen21 halamanWeed Control MethodsSahely KanthalBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Weed Control - Physical & CulturalDokumen11 halamanMethods of Weed Control - Physical & CulturalYaswanth NaikBelum ada peringkat
- Weed Assignment - 1235-39Dokumen8 halamanWeed Assignment - 1235-39MASTER SACHIN - 1254Belum ada peringkat
- Weed Management Strategies in Cropping SystemsDokumen3 halamanWeed Management Strategies in Cropping Systemslovedeep singhBelum ada peringkat
- Weeds What Is A Weed?: Why Are Weeds So Successful?Dokumen3 halamanWeeds What Is A Weed?: Why Are Weeds So Successful?Daniel Dowding100% (1)
- Weed PPT SlidesDokumen20 halamanWeed PPT Slideskblawan03Belum ada peringkat
- Weed ManagementDokumen2 halamanWeed ManagementDramicanin MilosBelum ada peringkat
- Corn Production ManagementDokumen19 halamanCorn Production ManagementGelly Anne DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- W3 Transcript L3 PDFDokumen2 halamanW3 Transcript L3 PDFVijaychandra ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- 6.principles and Methods of Weed ControlDokumen66 halaman6.principles and Methods of Weed ControlSHABNAM KUMARIBelum ada peringkat
- lab.-4-crprtDokumen3 halamanlab.-4-crprtElsie ElimBelum ada peringkat
- Weed Control Guide for Corn, Soybeans and SorghumDokumen88 halamanWeed Control Guide for Corn, Soybeans and SorghumRi KeBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Weed Management in Rice-Wheat Cropping SystemDokumen4 halamanIntegrated Weed Management in Rice-Wheat Cropping SystemManoj Kumar LodhiBelum ada peringkat
- Pengaruh Pemberian Beberapa Jenis Herbisida Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Tanaman Padi (Oryza Sativa L.) Dengan Sistem Tanam Tabur Benih Langsung Tanpa Olah Tanah (Tabelatot)Dokumen11 halamanPengaruh Pemberian Beberapa Jenis Herbisida Terhadap Pertumbuhan Dan Hasil Tanaman Padi (Oryza Sativa L.) Dengan Sistem Tanam Tabur Benih Langsung Tanpa Olah Tanah (Tabelatot)SenayanBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental principles of pest and disease control in Malaysian agricultureDokumen6 halamanFundamental principles of pest and disease control in Malaysian agricultureTracy OdangBelum ada peringkat
- Trap Cropping-Valuable Pest ManagementDokumen4 halamanTrap Cropping-Valuable Pest ManagementmramagroBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing Planthopper Outbreaks in RiceDokumen4 halamanPreventing Planthopper Outbreaks in RiceIRRI_resourcesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheets Crop Prod Unit 4Dokumen2 halamanActivity Sheets Crop Prod Unit 4JETHSALINE HIMANTOGBelum ada peringkat
- Herbicides - 26.10.2021Dokumen22 halamanHerbicides - 26.10.2021Wana HaglerBelum ada peringkat
- Crop Prot Present 1Dokumen42 halamanCrop Prot Present 1paulo sabidoBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Weed ControlDokumen9 halamanMethods of Weed ControlJiem PlazaBelum ada peringkat
- Agron 503 (2+1) : Principles and Practices of Weed Management AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAgron 503 (2+1) : Principles and Practices of Weed Management AssignmentAjmal Fayique100% (1)
- POST PLANTATION MANAGEMENT Holeta Training Center, 2019Dokumen124 halamanPOST PLANTATION MANAGEMENT Holeta Training Center, 2019Tilahun TegeneBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4 Pest Management and Harvesting, Threshing, Drying, Storing and MillingDokumen5 halamanGroup 4 Pest Management and Harvesting, Threshing, Drying, Storing and MillingJAY MARIE PRESBITEROBelum ada peringkat
- Pest ManagementDokumen8 halamanPest ManagementJohn Nicollo OviedoBelum ada peringkat
- IWM On Field CropsDokumen5 halamanIWM On Field CropsDeepankumar PBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Control of Prairie Weeds Using Natural EnemiesDokumen27 halamanBiological Control of Prairie Weeds Using Natural EnemiespatrickkayeBelum ada peringkat
- Allelopathy For Weed ControlDokumen9 halamanAllelopathy For Weed ControlAnn LicaBelum ada peringkat
- Controls of Insect PestsDokumen17 halamanControls of Insect PestsDitto V DavisBelum ada peringkat
- WeedsDokumen15 halamanWeedsapi-19911503Belum ada peringkat
- Cit 300 StoryDokumen2 halamanCit 300 Storymartine nzobendoBelum ada peringkat
- Plain English Summary: Pre-Emergent Herbicides 101Dokumen2 halamanPlain English Summary: Pre-Emergent Herbicides 101Fırat PalaBelum ada peringkat
- Weed MGT Updates and IssuesDokumen36 halamanWeed MGT Updates and IssuesGwenneth BrilloBelum ada peringkat
- Pest Control Method-5Dokumen17 halamanPest Control Method-5Quamruzzaman MasudBelum ada peringkat
- Weed WorkDokumen14 halamanWeed WorkOpata OpataBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Weed Management of OP 2008Dokumen56 halamanIntegrated Weed Management of OP 2008عبدالحاليم بودين83% (6)
- Final Agri ChemDokumen45 halamanFinal Agri Chemdatoo buenafeBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Planting Distance on Red Rice Growth and YieldDokumen3 halamanEffect of Planting Distance on Red Rice Growth and YieldKestrel jan BagaBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance Notes On Integrated Pest ManagementDokumen29 halamanGuidance Notes On Integrated Pest ManagementiffinichonchubhairBelum ada peringkat
- 2023-Herbicide ClassificationDokumen28 halaman2023-Herbicide ClassificationVinayBelum ada peringkat
- AGR 3102-4th WeekDokumen41 halamanAGR 3102-4th WeekSleeping Beauty100% (1)
- Chapter OneDokumen10 halamanChapter OneSalome EtefiaBelum ada peringkat
- Agro 504 PDFDokumen19 halamanAgro 504 PDFAshik MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- KUIS KELOMPOK 8 - Gulma Tanaman ADokumen4 halamanKUIS KELOMPOK 8 - Gulma Tanaman AGarka 5360Belum ada peringkat
- Banana Desucker ResearchDokumen7 halamanBanana Desucker ResearchNop KongBelum ada peringkat
- Banana Desucker Research PDFDokumen7 halamanBanana Desucker Research PDFNop KongBelum ada peringkat
- Latest WRAG guidelines for managing weedsDokumen24 halamanLatest WRAG guidelines for managing weedsMarija PavlovicBelum ada peringkat
- Agr 205 Weed ControlDokumen16 halamanAgr 205 Weed Controlcolley03111997Belum ada peringkat
- Striped Cucumber Beetle and Bacterial Wilt Management in Vine CropsDokumen3 halamanStriped Cucumber Beetle and Bacterial Wilt Management in Vine CropsHasbi Yusuf Abu ZakiBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Pest Management of The Cabbage Root Fly and The Carrot FlyDokumen8 halamanIntegrated Pest Management of The Cabbage Root Fly and The Carrot FlyVictor Lauro Perez GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Glyphosate The ApocalypseDokumen2 halamanGlyphosate The ApocalypseCannolo Di MercaBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Holly Fashion Case StudyDokumen3 halaman6 Holly Fashion Case StudyCaramalau Mirela-Georgiana0% (1)
- Vol 98364Dokumen397 halamanVol 98364spiveynolaBelum ada peringkat
- Ra 1425 Rizal LawDokumen7 halamanRa 1425 Rizal LawJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoBelum ada peringkat
- Initial Data Base (Narrative)Dokumen11 halamanInitial Data Base (Narrative)LEBADISOS KATE PRINCESSBelum ada peringkat
- Mech Course HandbookDokumen20 halamanMech Course Handbookbrody lubkeyBelum ada peringkat
- TIA Portal v11 - HMI ConnectionDokumen4 halamanTIA Portal v11 - HMI ConnectionasdasdasdasdasdasdasadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ward A. Thompson v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police Jerry Wells, District Attorney Frank Diehl, David Davis, Kevin Harmon, Mike Hall, Ray Urbanek, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John Lewis, Jack Cross, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward, James Haller, Dave Hubbell and Matilda Woody, Frances S. Wisdom v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police David Davis, Mike Hall, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John L. Lewis, Jack Cross, Kevin Harmon, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward and James Haller, Jr., 58 F.3d 1511, 10th Cir. (1995)Dokumen8 halamanWard A. Thompson v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police Jerry Wells, District Attorney Frank Diehl, David Davis, Kevin Harmon, Mike Hall, Ray Urbanek, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John Lewis, Jack Cross, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward, James Haller, Dave Hubbell and Matilda Woody, Frances S. Wisdom v. City of Lawrence, Kansas Ron Olin, Chief of Police David Davis, Mike Hall, Jim Miller, Bob Williams, Craig Shanks, John L. Lewis, Jack Cross, Kevin Harmon, Catherine Kelley, Dan Ward and James Haller, Jr., 58 F.3d 1511, 10th Cir. (1995)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 3-WEF-Global Competitive IndexDokumen3 halamanAssignment 3-WEF-Global Competitive IndexNauman MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Chartered BackgroundDokumen6 halamanStandard Chartered BackgroundAwesum Allen MukiBelum ada peringkat
- GUCR Elections Information 2017-2018Dokumen10 halamanGUCR Elections Information 2017-2018Alexandra WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- 5.3.2 Generation of Dislocations: Dislocations in The First Place!Dokumen2 halaman5.3.2 Generation of Dislocations: Dislocations in The First Place!Shakira ParveenBelum ada peringkat
- Global Finance - Introduction ADokumen268 halamanGlobal Finance - Introduction AfirebirdshockwaveBelum ada peringkat
- Cultural Briefing: Doing Business in Oman and the UAEDokumen2 halamanCultural Briefing: Doing Business in Oman and the UAEAYA707Belum ada peringkat
- Development Proposal ReportDokumen37 halamanDevelopment Proposal ReportJean-Pierre RouxBelum ada peringkat
- Redminote5 Invoice PDFDokumen1 halamanRedminote5 Invoice PDFvelmurug_balaBelum ada peringkat
- Day 3Dokumen18 halamanDay 3SamBelum ada peringkat
- All Over AgainDokumen583 halamanAll Over AgainJamie Kris MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Junior Instructor (Computer Operator & Programming Assistant) - Kerala PSC Blog - PSC Exam Questions and AnswersDokumen13 halamanJunior Instructor (Computer Operator & Programming Assistant) - Kerala PSC Blog - PSC Exam Questions and AnswersDrAjay Singh100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Solving Problems Using Counting Techniques - TestDokumen5 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Solving Problems Using Counting Techniques - TestVisalini RagurajanBelum ada peringkat
- PDF To Sas DatasetsDokumen6 halamanPDF To Sas DatasetsSiri KothaBelum ada peringkat
- The Mckenzie MethodDokumen24 halamanThe Mckenzie MethodMohamed ElMeligieBelum ada peringkat
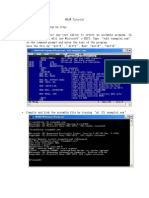
- MASM Tutorial PDFDokumen10 halamanMASM Tutorial PDFShashankDwivediBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Dokumen68 halamanPeriodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Saktipratik MishraBelum ada peringkat