The Modern Lydian Mode
Diunggah oleh
FREIMUZICHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The Modern Lydian Mode
Diunggah oleh
FREIMUZICHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
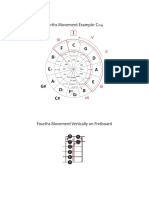
The modern Lydian musical scale is a rising pattern of pitches comprising three whole tones, a semitone, two more
whole tones, and a final semitone. This sequen ce of pitches roughly describes the fifth of the eight Gregorian (church) modes, known as Mode V or the authentic mode on F, theoretically using B but in practic e more commonly featuring B (Powers 2001). Because of the importance of the major scale in modern music, the Lydian mode is often described (or learned) as the s cale that begins on the fourth scale degree of the major scale, or alternatively , as the major scale with the fourth scale degree raised half a step. Contents [hide] 1 Theory 1.1 Ancient Greek Lydian 1.2 Medieval Lydian mode 1.3 Modern Lydian mode 1.3.1 Triads within Lydian mode 2 Notable compositions in the Lydian mode 2.1 Classical (Ancient Greek) 2.2 Classical (Modern) 2.3 Jazz 2.4 Popular 3 See also 4 References 5 Further reading 6 External links Theory [edit] Ancient Greek Lydian [edit] Diatonic genus of the Ancient Greek Lydian scale on C Play (helpinfo). Ancient Greek Lydian tonos in the chromatic genus, showing tetrachords (a and b) , note of conjunction (c) and tone of disjunction (d) Play (helpinfo) Ancient Greek Lydian tonos in the enharmonic genus, showing tetrachords (a and b ), note of conjunction (c) and tone of disjunction (d) Play (helpinfo) The name Lydian refers to the ancient kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia. In Greek mus ic theory, there was a Lydian scale or "octave species" extending from parhypate hypaton to trite diezeugmenon, equivalent in the diatonic genus to the medieval and modern Ionian mode, i.e., the modern major scale: C D E F | G A B C (Barber a 1984, 233, 240). In the chromatic and enharmonic genera, the Lydian scale was equivalent to C D E F G A B C, and C C E F F A B C, respectively (Barker 198489, 2: 15), where "" signifies raising the pitch by approximately a quarter tone. The eight Gregorian modes: f indicates 'final' Medieval Lydian mode [edit] In the Middle Ages and Renaissance, this mode was described in two ways. The fir st way is the diatonic octave species from F up to F an octave above, divided at C to produce two segments: FGABC and CDEF. The second is as a mode with a final on F nd an ambitus extending to F an octave higher and in which the note C was regard ed as having an important melodic function. Many theorists of the period observe d that B is used more typically than B in compositions in Lydian mode (Powers 2001 ). Modern Lydian mode [edit] Modern Lydian scale on F Play (helpinfo). The Lydian scale can be described as a major scale with the fourth scale degree
raised a semitone, e.g., a C-major scale with an F rather than F. Triads within Lydian mode [edit] In Lydian mode, the tonic, dominant, and supertonic triads are all major. The su bdominant is diminished. The triads built on the remaining three scale degrees a re minor. Notable compositions in the Lydian mode [edit] Classical (Ancient Greek) [edit] The Paean and Prosodion to the God, familiarly known as the Second Delphic Hymn, composed in 128 BC by Athnaios Athenaou is predominantly in the Lydian tonos, bot h diatonic and chromatic, with sections also in Hypolydian (Phlmann and West 2001 , 85). Classical (Modern) [edit] A rare, extended use of the Lydian mode in the Classical repertoire is Simon Sec hter's 1822 Messe in der lydischen Tonart (Mass in the Lydian Mode) (Carver 2005 , 76). A more famous example from around the same time is the third movement of Ludwig van Beethoven's String Quartet No. 15 in A minor, Op. 132 (1825), titled by the composer "Heiliger Dankgesang eines Genesenen an die Gottheit, in der lyd ischen Tonart" ("Holy Song of Thanksgiving by a Convalescent to the Divinity, in the Lydian Mode"). The alternating passages in F use the Lydian scale with shar p fourth scale degree exclusively. Anton Bruckner employed the sharpened fourth of the Lydian scale in his motet Os justi (1879) more strictly than Renaissance composers ever did when writing in this mode (Carver 2005, 7475). Charles-Valenti n Alkan's Allegro barbaro (tude Op. 35, No. 5) is written strictly in F Lydian, w ith no Bs present at all. (Smith 2000,[page needed]). In the 20th century composers began once again to exploit modal scales with some frequency. An example from the middle of the century is the scherzo movement of Carlos Chvez's Symphony No. 3 (195154). The movement opens with a fugue subject, featuring extremely wide leaps, in C Lydian with following entries in F and G Ly dian (Orbn 1987, 9091). Jazz [edit] Pianist-composer George Russell developed a Lydian Chromatic Concept of Tonal Or ganization, which became highly influential in the jazz world, inspiring the wor ks of people such as Miles Davis, John Coltrane, Ornette Coleman, and Woody Shaw (Anon. nd.) Popular [edit] The Simpsons signature tune (Chase 2006,[page needed]). Passage beginning at the words "Much as I definitely enjoy solitude" in the song "Possibly Maybe" by Bjrk (Hein 2012). See also [edit] Lydian chord A chord that is related to the Lydian scale Lydian dominant scale Kalyani (raga), the equivalent scale in Indian classical music
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Beat ItDokumen4 halamanBeat Itdfvadsfv100% (1)
- Chord Substitutions Survival Guide PDFDokumen17 halamanChord Substitutions Survival Guide PDFHamish Archibald100% (3)
- John Patitucci - Ultimate Play-Along For Bass (Level 1-Vol. 1)Dokumen16 halamanJohn Patitucci - Ultimate Play-Along For Bass (Level 1-Vol. 1)Duarte Falleiros de Souza100% (6)
- Course Piano Lesson 71-75 TextsDokumen30 halamanCourse Piano Lesson 71-75 TextsPascal ReijmersBelum ada peringkat
- Diminshed Chords TheoryDokumen11 halamanDiminshed Chords TheoryParthiban0% (1)
- Giovanni Moltoni - Guit-NotesDokumen23 halamanGiovanni Moltoni - Guit-Notesalessandro PasqualBelum ada peringkat
- Fachords Guitar SoftwareDokumen2 halamanFachords Guitar SoftwareEinar Valur AðalsteinssonBelum ada peringkat
- Tempo MarksDokumen7 halamanTempo MarksfilhakikaBelum ada peringkat
- (John Thomas) Voice Leading For Guitar PDFDokumen12 halaman(John Thomas) Voice Leading For Guitar PDFLester Cano0% (1)
- Pitch Axis TheoryDokumen3 halamanPitch Axis TheoryFirstly LastlyBelum ada peringkat
- Haverford College Student Alex Wang's Thesis on Automatic Chord Recognition Using Hidden Markov ModelsDokumen22 halamanHaverford College Student Alex Wang's Thesis on Automatic Chord Recognition Using Hidden Markov ModelsAlex Wang100% (1)
- 387141-Blue Moon - With WALKING BASS and ImprovisationDokumen2 halaman387141-Blue Moon - With WALKING BASS and ImprovisationBeluga ProjectBelum ada peringkat
- SessionWithTheStars TedGreeneHandout SheetsDokumen10 halamanSessionWithTheStars TedGreeneHandout SheetsYuri CastroBelum ada peringkat
- 16 The+Elevator+SequenceDokumen14 halaman16 The+Elevator+SequenceHarmonie SolfègeBelum ada peringkat
- ABC RemovedDokumen299 halamanABC Removedditradownload100% (1)
- Howard RobertsDokumen4 halamanHoward Robertsjoao famaBelum ada peringkat
- Concert: RepertoireDokumen85 halamanConcert: Repertoirefelix.gBelum ada peringkat
- The Jazz Guitarist's Handbook: An In-Depth Guide to Chord Symbols Book 1: The Jazz Guitarist's Handbook, #1Dari EverandThe Jazz Guitarist's Handbook: An In-Depth Guide to Chord Symbols Book 1: The Jazz Guitarist's Handbook, #1Belum ada peringkat
- BCPSCTW 001cDokumen5 halamanBCPSCTW 001cOlivierBelum ada peringkat
- LutoslowskiDokumen23 halamanLutoslowskiJordan Garbutt100% (1)
- Chromatic MediantDokumen2 halamanChromatic MediantVictorSmerk100% (1)
- Music Composition RulesDokumen1 halamanMusic Composition Rulesapi-377964292Belum ada peringkat
- A Wynton Kelly Jazz Lick You Must Know - Free Jazz LessonsDokumen4 halamanA Wynton Kelly Jazz Lick You Must Know - Free Jazz LessonsBen AvrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Charlie Christian TutorialDokumen13 halamanCharlie Christian Tutorialsdcscribd100% (4)
- Major 7 Arpeggio: Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanMajor 7 Arpeggio: Cheat Sheetpistas para practicar compradasBelum ada peringkat
- Program Notes French SuiteDokumen2 halamanProgram Notes French Suitewaterwood3388Belum ada peringkat
- Pierre BoulezDokumen14 halamanPierre BoulezFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Harmony 4 Modal HarmonyDokumen8 halamanHarmony 4 Modal HarmonyPROFESOR ÓRDENESBelum ada peringkat
- The Devon Jazz Explosion!: Workshop GuideDokumen10 halamanThe Devon Jazz Explosion!: Workshop GuideJohan BenavidesBelum ada peringkat
- MIDI Arranging Syllabus Music 205 2010Dokumen3 halamanMIDI Arranging Syllabus Music 205 2010zerraBelum ada peringkat
- The Phrygian ModeDokumen3 halamanThe Phrygian ModeFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Bach Invention 13 A4 PDFDokumen2 halamanBach Invention 13 A4 PDFBgmscoresBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6: Using Note EnclosuresDokumen11 halamanLesson 6: Using Note EnclosuresMike McIntoshBelum ada peringkat
- This Was Taught To Me by Richie HartDokumen2 halamanThis Was Taught To Me by Richie HartJohn Paul De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Rhythm and ChangesDokumen3 halamanRhythm and ChangesDaniel De La HozBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of A Melody Part 1Dokumen3 halamanAnatomy of A Melody Part 1jim4703100% (2)
- Locrian Scale Guitar Shapes Chords and Licks PDFDokumen14 halamanLocrian Scale Guitar Shapes Chords and Licks PDFcpusoft2007Belum ada peringkat
- All The Things You Are - Drop2 ExerciseDokumen4 halamanAll The Things You Are - Drop2 ExerciselionelloBelum ada peringkat
- Ziehn Manual - of - HarmonyDokumen129 halamanZiehn Manual - of - HarmonybbobBelum ada peringkat
- Polytonality PDFDokumen10 halamanPolytonality PDFFrancesco Torazzo100% (1)
- IntervalsDokumen14 halamanIntervalsapi-250941365Belum ada peringkat
- How Do You Make Tension Chords?: Music-Theory Chord-TensionsDokumen3 halamanHow Do You Make Tension Chords?: Music-Theory Chord-TensionsfilterfreakBelum ada peringkat
- Ear Training Sigi Busch Jazz Pop Rock PDFDokumen32 halamanEar Training Sigi Busch Jazz Pop Rock PDFAnonymous SjdVGd3TBelum ada peringkat
- Ear Training in Music Education PDFDokumen4 halamanEar Training in Music Education PDF董明100% (1)
- Advanced Ear Training and Solfège for PerformersDokumen3 halamanAdvanced Ear Training and Solfège for PerformersjonathanBelum ada peringkat
- Guitar Hammer On and Pull OffDokumen1 halamanGuitar Hammer On and Pull OffpickquackBelum ada peringkat
- ClichesDokumen4 halamanClichesRoland KissBelum ada peringkat
- Song Key Ton ModeDokumen8 halamanSong Key Ton ModeMichael BonettBelum ada peringkat
- Major Scales ExplainedDokumen3 halamanMajor Scales Explainedapi-3840017100% (2)
- Cadences: Specific Types of CadencesDokumen4 halamanCadences: Specific Types of Cadencesuandme989Belum ada peringkat
- How To Read Tablature - 2016Dokumen2 halamanHow To Read Tablature - 2016mrforrester2014Belum ada peringkat
- Notes Rests Takadimi WorksheetDokumen2 halamanNotes Rests Takadimi WorksheetDebBelum ada peringkat
- CounterpointDokumen6 halamanCounterpointPick N ClickBelum ada peringkat
- Soloing and VampingDokumen1 halamanSoloing and Vampingapi-3832119100% (1)
- Band in A Box 2007 ManualDokumen465 halamanBand in A Box 2007 ManualFlorianMartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Beginning and Intermediate Guitar SyllabusDokumen3 halamanBeginning and Intermediate Guitar Syllabusapi-353236234Belum ada peringkat
- Rock Guitar LicksDokumen4 halamanRock Guitar LicksAlekanian AlainBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basics of Modal Harmony: The Chromatic ScaleDokumen6 halamanSome Basics of Modal Harmony: The Chromatic ScaleSergio Molina100% (1)
- Escalas, Arpegios, Beyer, Hanon y CzernyDokumen156 halamanEscalas, Arpegios, Beyer, Hanon y CzernyIrene VosBelum ada peringkat
- CRUISIN CruiseMusicPlaylist PDFDokumen2 halamanCRUISIN CruiseMusicPlaylist PDFarseni25Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7: Music and The Renaissance - A History of Western Music, 8e: W. W. Norton StudySpaceDokumen6 halamanChapter 7: Music and The Renaissance - A History of Western Music, 8e: W. W. Norton StudySpaceJasmine Moni Guo100% (1)
- Music Vocabulary: Accelerando to VivaceDokumen4 halamanMusic Vocabulary: Accelerando to Vivaceqwer06xBelum ada peringkat
- Jim Kelly A Little WesDokumen8 halamanJim Kelly A Little WesCirù Monia FalcoBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Basic Music TheoryDokumen2 halamanUnderstanding Basic Music TheoryVan Lawrence F. VirtoBelum ada peringkat
- Dominant 7 b9 b13 Voicing, Arpeggio, Scale: Root On 6 StringDokumen1 halamanDominant 7 b9 b13 Voicing, Arpeggio, Scale: Root On 6 StringDanillo AndradeBelum ada peringkat
- 50 Melodic Licks (Treble Clef)Dokumen184 halaman50 Melodic Licks (Treble Clef)Alejandro CaballeroBelum ada peringkat
- TemperamentDokumen3 halamanTemperamentgooler331Belum ada peringkat
- Chord Diagrams: Guitar Fingerings for All KeysDokumen85 halamanChord Diagrams: Guitar Fingerings for All KeysJonnnBelum ada peringkat
- Muzik ShqipDokumen2 halamanMuzik Shqipmuzikshqip1Belum ada peringkat
- Melodic Device PDF FreeDokumen4 halamanMelodic Device PDF Freebukola ajaoBelum ada peringkat
- Chord Tone SoloingDokumen4 halamanChord Tone SoloingFederico StocchiBelum ada peringkat
- John Coltrane - A Love SupremeDokumen18 halamanJohn Coltrane - A Love SupremeCarlos Blanco Recuero0% (1)
- Philip “Flip” Gordon: Jazz Compositions: Volume 1: The Zodiac Project: Parallel UniverseDari EverandPhilip “Flip” Gordon: Jazz Compositions: Volume 1: The Zodiac Project: Parallel UniverseBelum ada peringkat
- Early Iron Age BabyloniaDokumen10 halamanEarly Iron Age BabyloniaFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- NabonidusDokumen4 halamanNabonidusFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- NabonidusDokumen4 halamanNabonidusFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Richard WagnerDokumen10 halamanRichard WagnerFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- The California Gold RushDokumen5 halamanThe California Gold RushFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Tiger BodyDokumen6 halamanTiger BodyFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- BabyloniaDokumen6 halamanBabyloniaFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Republic of San MarinoDokumen2 halamanRepublic of San MarinoFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- GingivitisDokumen3 halamanGingivitisFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- United States Electoral CollegeDokumen5 halamanUnited States Electoral CollegeFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- RameauDokumen7 halamanRameauFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- The Congress of BerlinDokumen6 halamanThe Congress of BerlinFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- The LionDokumen4 halamanThe LionFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Bio FilmDokumen7 halamanBio FilmFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- MyringotomyDokumen2 halamanMyringotomyFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- MessiaenDokumen4 halamanMessiaenFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- TinnitusDokumen3 halamanTinnitusFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Olympic Marketing Revenue Generation OverviewDokumen1 halamanOlympic Marketing Revenue Generation OverviewFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Bach's Influence on Four-Part HarmonyDokumen3 halamanBach's Influence on Four-Part HarmonyFREIMUZIC0% (1)
- ScarlattiDokumen2 halamanScarlattiFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- AlbénizDokumen3 halamanAlbénizFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- MozartDokumen6 halamanMozartFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- The Olympic Marketing Fact FileDokumen1 halamanThe Olympic Marketing Fact FileFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Demographics of RomaniaDokumen2 halamanDemographics of RomaniaFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Historical Evolution of RomaniaDokumen3 halamanHistorical Evolution of RomaniaFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Romanian EconomyDokumen3 halamanRomanian EconomyFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Razin and Pugachev RebellionsDokumen3 halamanRazin and Pugachev RebellionsFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Cossacks in The Russian EmpireDokumen2 halamanCossacks in The Russian EmpireFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- Ural CossacksDokumen1 halamanUral CossacksFREIMUZICBelum ada peringkat
- First Scale March-Unit PlanDokumen15 halamanFirst Scale March-Unit Planapi-531199496Belum ada peringkat
- Kate Bush Wuthering HeightsDokumen15 halamanKate Bush Wuthering HeightsDahyeon LeeBelum ada peringkat
- ThePolyrhythmOdyssey SampleDokumen12 halamanThePolyrhythmOdyssey SampleDavid OyewoleBelum ada peringkat
- A 3Dokumen1 halamanA 3Adrian ZambranoBelum ada peringkat
- List of Musical Symbols - WikipediaDokumen18 halamanList of Musical Symbols - WikipediaMert ÜnlüBelum ada peringkat
- Portrait of Debussy 8, Debussy and MessiaenDokumen5 halamanPortrait of Debussy 8, Debussy and MessiaenmetronommeBelum ada peringkat
- The Making of Steve Mackey's It Is Time: Creative CollaborationDokumen2 halamanThe Making of Steve Mackey's It Is Time: Creative CollaborationLuthfi Arief HidayatullahBelum ada peringkat
- Narrativa SchumannDokumen77 halamanNarrativa SchumannAngeles GallardoBelum ada peringkat
- Italian Classical GuitarDokumen2 halamanItalian Classical GuitarryanBelum ada peringkat
- Booklet Togni CDDokumen10 halamanBooklet Togni CDSilvio PolellaBelum ada peringkat
- Singing Syllabus From 2018 Updated September 2020 FinalDokumen85 halamanSinging Syllabus From 2018 Updated September 2020 FinalEtefia EtefiaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter FourDokumen47 halamanChapter FourHenry SpencerBelum ada peringkat
- NGFL Ravel Movt 3 AnalysisDokumen20 halamanNGFL Ravel Movt 3 AnalysisBob BaoBabBelum ada peringkat
- Chromatic Intervals, For PianoDokumen1 halamanChromatic Intervals, For PianoBrian HendersonBelum ada peringkat
- Symphony GrovesDokumen88 halamanSymphony GroveserinBelum ada peringkat