Centrifugal Pump Selection and Sizing
Diunggah oleh
Noman Abu-FarhaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Centrifugal Pump Selection and Sizing
Diunggah oleh
Noman Abu-FarhaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Centrifugal Pump Selection and Sizing
2009 Calgary Pump Symposium Chris Gilmour, P.Eng.
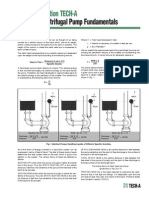
Pump types being Considered
One and two stage centrifugal pumps
-
OH2, OH3/4, BB1, BB2 most common pumps used
Pumps not considered in this presentation:
-
OH5 close-coupled VIL OH6 high-speed integral gear VIL vertically-suspended pumps multi-stage centrifugal pumps low-flow pumps (Ns < 500)
2
Pump types Vertical In-line Pump
Pump types Horizontal Overhung
Pump types Between-Bearing Pump (radially split)
Pump types Between-Bearing Pump (axially split)
Pump Selection Old School
Pump Selection
The Goal
We want to select and purchase pumps that are:
Reliable - Reasonably priced - Efficient
-
What type of plant?
Class of Plant
Class 1 : low first cost, lower on-stream factor - Class 2: a Class 1 plant with selective upgrades - Class 3: higher first cost, higher on-stream factor
-
Construction (wrt pumps)
-
Modularized or not modularized
10
Pump Selection order of preference
1. Vertical inline pump 2. Horizontal Overhung Pump 3. Between Bearing Pump
11
Pump Selection
The smallest, least expensive, most efficient pump is an overhung pump (vertical inline, or horizontal overhung) running at 3600 rpm
-
higher speed = smaller diameter for same head higher speed = higher Ns = higher efficiency smaller diameter = smaller casing size = less $
12
Relative Costs example 1
200 m3/h @ 150 m w/ >7m NPSHa (880 gpm @490 ft w/ > 23 ft NPSHa)
-
150 HP motor, single seal
Pum size rpm eff rel $ + Install $ p OH3 4x6x13 3600 78% 1.00 base support OH2 4x6x13 3600 78% 1.35 + fdn, grouting BB2 4x6x13 3600 70% 2.30 +fdn, grouting
13
Relative Costs example 2
200 m3/h @ 150 m w/ 4m NPSHa (880 gpm @490 ft w/ 13 ft NPSHa)
-
150 HP motor, single seal
Pum size rpm eff rel $ + Install $ p OH3 6x8x23 1800 66% 1.00 base support OH2 6x8x23 1800 66% 1.07 + fdn, grouting BB2 4x6x13 3600 70% 1.04 +fdn, grouting
14
Relative Costs example 3
200 m3/h @ 150 m w/ 4m NPSHa (880 gpm @490 ft w/ 13 ft NPSHa)
-
150 HP motor, dual seal w/ Plan 53a
Pum size rpm eff rel $ + Install $ p OH3 6x8x23 1800 66% 1.00 base support OH2 6x8x23 1800 66% 1.06 + fdn, grouting BB2 4x6x13 3600 70% 1.33 +fdn, grouting
15
Why not always buy a 3600 rpm O/H pump?
An O/H pump is not always available in the size required An O/H pump is not always an appropriate selection 3600 rpm may not be an appropriate speed for the process conditions
16
Overhung Pumps Typical Coverage
Pump Size (Dis x Suc) 1-1/2x3 2x3 3x4 4x6 6x8 8x10 10x12 12x16 16x20 * 20x24 * Impeller Diameter (inches) 7 2 2 2 2 9 11 13 15 17 20 23 27 30 *
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 4
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
3600 rpm (2-pole) 1800 rpm (4-pole) 1200 rpm (6-pole) * OH2 only
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
6 6 6
17
Overhung Pumps Typical Limits
Tip Speed
-
u = RPM/60 x PI x Diameter , units m/s, m Issue is vibration Typical limit is 62 m/s (205 ft/s) for Class 3 plant - 13 diameter impeller at 3550 rpm - 27 diameter impeller at 1750 rpm Consider increasing for Class 1 plant
18
VIL Pumps Typical Limits
Tip Speed: issue is vibration
-
Typical limit is 62 m/s (205 ft/s) for Class 3 plant - 13 diameter impeller at 3550 rpm - 27 diameter impeller at 1750 rpm
-
Power: issue is vibration, reliability
Typical limits for Class 3 plant are: - 200HP at 3600 rpm - 400HP at 1800 rpm - 600HP at 1200 rpm
Process Fluid Temperature: issues are shaft sealing, bearing cooling, and motor cooling
-
Typical upper limit is 200 C (400F) for Class 3 plant
19
VIL Pumps: Bearing-bracket (OH3) type Other considerations
How to lubricate the bearing bracket?
-
best is oil mist, if available using oil in a vertical bearing bracket hasnt always worked well, depends on the arrangement grease is an option for cooler services, but requires regular monitoring
20
VIL Pumps: Rigidly-coupled (OH4) type Other considerations
Fluid-lubricated radial bearing
-
need to consider the cleanliness and lubricating properties of the fluid
Motor shaft runout
-
requires tight tolerance on motor shaft runout
Reliability / seal life ?
some companies have had poor seal MTBR with these pumps - Shell Canada experience has been reasonably good
-
21
Pump Sizing
22
Specific Speed (Ns)
a dimensionless parameter describing geometric similarity - evaluated at BEP, maximum diameter - Ns = rpm x gpm^0.5 / ft^0.75 , use Q for double suction - useful for sizing/selecting pumps
-
23
24
Specific Speed - Guidelines
typical process pumps have Ns between 500 and 1,800 - limited choices of supplier below 500 - pumps with Ns 1,800 2,400 are less desirable (reduced range of acceptable operation) - Pumps with Ns > 2,400 should be avoided
-
25
Suction Specific Speed (Nss)
-
a dimensionless parameter describing impeller eye geometry evaluated at BEP, max diameter Nss = rpm x gpm^0.5 / NPSHr^0.75 , use Q for double suction impeller consider this example: 500 gpm pump at 3550 rpm - Nss = 9,000 when NPSHr = 18.2 ft - Nss = 11,000 when NPSHr = 13.9 ft - Nss = 13,000 when NPSHr = 11.2 ft for the same pump, lower NPSHr achieved by one or more of: - sharpening the impeller inlet edges - increasing the impeller inlet area by: decreasing # of blades; and /or, increasing blade inlet angle; and /or, increasing inlet area
26
Suction Specific Speed (Nss) - Guidelines
typical range is 7,000 to 16,000 (and higher) higher Nss results in restricted range of acceptable operation for pumps with Ns 500 1800, max Nss up to 11,000 is acceptable for pumps with Ns 1,800 2,400, max acceptable Nss should be reduced to about 9,000 pumps with Ns above 2,400 should be avoided
27
Minimum Flow
Minimum flow issues:
-
temperature rise internal recirculation increased flow separation increased pressure fluctuation increased vibration levels (both radial and axial)
Avoiding these issues
-
method from WH Fraser (ref: Flow Recirculation in Centrifugal Pumps, 1981 Texas A&M Turbomachinery Symposium), ensure pump selection has acceptable range (ie. operation at flows above onset of recirculation)
28
Minimum Flow - Guidelines
WH Fraser, "Flow Recirculation in Centrifugal Pumps" Ns 500-2500
Recirculation (% of QBEP) 100.0 90.0 80.0 70.0 60.0 50.0 6000 Multi-stage Double-Suction Single-Suction
8000
10000
12000
14000
16000
18000
Nss (US customary units, at BEP)
for Q<2500 gpm and Hd<150 ft, use 50% of curve for continuous and 25% for intermittent operation for HC service, use 60 % for continuous and 25% for intermittent operation
29
Limited Range at Higher Nss
Minimum Flow (single-suction impeller)
14000 13000 12000 11000 10000 9000 8000 7000 6000 20 30 40 50 60 Q - % of BEP 70 80 90 100 S u c ti o n S p e c i fi c S p e e d (rp m , g p m , ft)
Non-HC HC
30
Other Considerations
Nozzle Velocities typical limits
-
suction < 20 ft/s discharge < 40 ft/s typically Q-rated = Q-normal x 1.1, but sometimes (eg. reflux service) Q-rated = Q-normal x 1.25 best is to straddle BEP with Q-normal and Q-rated, especially if Q-rated >> Q-normal - need to consider: NPSHa, min flow
31
Q-rated & Q-normal relative to BEP
-
500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 500
739
1232
1760
739 1000
1232 1500
1760 2000
50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2500
Full Diameter 95% Head N P S H r (ft) BEP Q-min (non-HC) Q-min (HC) Qr=1.1xQn Qr=1.25xQn NPSHr
H e a d (ft)
Flow (gpm)
32
Lets Size some pumps!
33
Equations & Correlations
Head, H = 2.31 x dP / SG , (ft, psi) Sp Speed, Ns = N x Q^1/2 / H^3/4 , (rpm, gpm, ft) Suc Sp Speed, Nss = N x Q^1/2 / NPSHr^3/4 , (rpm, gpm, ft) Head Coefficient, HC = H / (u^2 / 2g) , (ft, ft/s, ft/s^2)
-
methodology in The Pump Handbook,
Tip Speed, u = (H x 2g / HC)^0.5 , (ft/s, ft, ft/s^2) Diameter, D = u x 12 / PI / (RPM/60) , (in, ft/s, rpm) Power, P = H x Q x SG / (3960 x n) , (hp, ft, gpm) From Curves: efficiency, expected nozzle size, min flow
34
Estimating the Head Coefficient
using the correlations in The Pump Handbook, 2nd edition, Karassik, et al, Ch 2.1
Head Coefficient vs Specific Speed
1.40
Head Coefficient
1600 m3/h 1.20 800 m3/h 400 m3/h 200 m3/h 1.00 100 m3/h 50 m3/h 0.80 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Ns (rpm, gpm, ft)
35
Required Information
Require this info as a minimum:
-
flow, Q head, H NPSHa (or to know that it is ample) SG (to calculate power; assume = 1 if not provided) viscosity (to check if viscous corrections are reqd) HC or non-HC (for minimum flow calculation) continuous or intermittent service (for min flow calc)
36
Also desirable to know:
-
Worked Example: H= 170 ft, Q= 2000 gpm, NPSHa= 20 ft, water
rpm Ns (=RPM x gpm^0.5 / ft^3/4) Nss (=RPM x gpm^0.5/NPSH^3/4) efficiency, from curve Head Coeff, from curve Tip Spd, fps, = (H x 2g /HC)^0.5 Dia, in, = u x 12 / PI / (RPM/60) HP = H x Q x SG / (3960 x n) Min Nozzle (suc 20 fps, dis 40 fps) Min Flow (non-HC, continuous op) 1780 1,876 < 9,000 0.84 0.93 108.2 13.9 102 6x8 58% 3550 3,742 17,800 3550 / dbl 2,646 12,586 0.83 0.83 114.6 15.7 103 6x8 88%
37
Typical Casing Sizes
Q (GPM) 0 100 200 300 500 700 1000 1500 2000 2500 3500 4500 5500 7000 10000 Pump Speed 1160 1780 3x4 2x3 3x4 2x3 4x6 3x4 4x6 3x4 4x6 4x6 6x6 6x6 6x8 6x6 8x8 6x8 8x8 8 x 10 8 x 10 8 x 10 10 x 12 10 x 12 12 x 14 10 x 12 14 x 16 12 x 14 16 x 20 12 x 14 16 x 20 14 x 16 3550 1.5 x 2 1.5 x 2 2x3 3x4 4x6 4x6 6x6 6x6 6x8 8 x 10
38
Overhung Pumps Typical Coverage
Pump Size (Dis x Suc) 1-1/2x3 2x3 3x4 4x6 6x8 8x10 10x12 12x16 16x20 * 20x24 * Impeller Diameter (inches) 7 2 2 2 2 9 11 13 15 17 20 23 27 30 *
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 4
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
3600 rpm (2-pole) 1800 rpm (4-pole) 1200 rpm (6-pole) * OH2 only
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
6 6 6
39
40
Worked Example: H= 500 ft, Q= 4500 gpm, NPSHa= 20 ft, hydrocarbon
rpm Ns (=RPM x gpm^0.5 / ft^3/4) Nss (=RPM x gpm^0.5/NPSH^3/4) efficiency, from curve Head Coeff, from curve Tip Spd, fps, = (H x 2g /HC)^0.5 Dia, in, = u x 12 / PI / (RPM/60) HP = H x Q x SG / (3960 x n) Min Nozzle (suc 20 fps, dis 40 fps) Min Flow (non-HC, continuous op) 1160 736 < 9,000 0.77 1.09 171.5 33.9 741 8 x 10 35% 1780 1,129 12,622 0.84 1.04 175.8 22.6 677 8 x 10 49% 1780 / dbl 799 < 9,000 0.77 1.09 171.7 22.1 742 8 x 10 40%
41
Typical Casing Sizes
Q (GPM) 0 100 200 300 500 700 1000 1500 2000 2500 3500 4500 5500 7000 10000 Pump Speed 1160 1780 3x4 2x3 3x4 2x3 4x6 3x4 4x6 3x4 4x6 4x6 6x6 6x6 6x8 6x6 8x8 6x8 8x8 8 x 10 8 x 10 8 x 10 10 x 12 10 x 12 12 x 14 10 x 12 14 x 16 12 x 14 16 x 20 12 x 14 16 x 20 14 x 16 3550 1.5 x 2 1.5 x 2 2x3 3x4 4x6 4x6 6x6 6x6 6x8 8 x 10
42
Overhung Pumps Typical Coverage
Pump Size (Dis x Suc) 1-1/2x3 2x3 3x4 4x6 6x8 8x10 10x12 12x16 16x20 * 20x24 * Impeller Diameter (inches) 7 2 2 2 2 9 11 13 15 17 20 23 27 30 *
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 4
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
3600 rpm (2-pole) 1800 rpm (4-pole) 1200 rpm (6-pole) * OH2 only
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,6
6 6 6
43
44
Worked Example: H= 380 ft, Q= 1750 gpm, NPSHa= 8 ft, hydrocarbon
rpm Ns (=RPM x gpm^0.5 / ft^3/4) Nss (=RPM x gpm^0.5/NPSH^3/4) efficiency, from curve Head Coeff, from curve Tip Spd, fps, = (H x 2g /HC)^0.5 Dia, in, = u x 12 / PI / (RPM/60) HP = H x Q x SG / (3960 x n) Min Nozzle (suc 20 fps, dis 40 fps) Min Flow (non-HC, continuous op) 1160 564 < 10,168 0.70 1.0 156.4 30.9 240 6x6 39% 1780 865 15,602 1780 / dbl 612 < 11,032 0.70 1.02 155.0 20 217 6x6 49%
45
Worked Example: H= 380 ft, Q= 1750 gpm, NPSHa= 13 ft, hydrocarbon
rpm Ns (=RPM x gpm^0.5 / ft^3/4) Nss (=RPM x gpm^0.5/NPSH^3/4) efficiency, from curve Head Coeff, from curve Tip Spd, fps, = (H x 2g /HC)^0.5 Dia, in, = u x 12 / PI / (RPM/60) HP = H x Q x SG / (3960 x n) Min Nozzle (suc 20 fps, dis 40 fps) Min Flow (non-HC, continuous op) 1160 564 < 9,000 0.70 1.0 156.4 30.9 240 6x6 39% 1780 865 10,905 0.77 1.05 152.4 19.6 217 6x6 42% 1780 / dbl 612 < 9,000 0.70 1.02 155.0 20 217 6x6 49%
46
47
Sizing Spreadsheet
Arrange the calculations in a spreadsheet
-
enter: Q, H, NPSHa, SG, viscosity calculate all parameters for typical speeds (1150, 1750, 3550 rpm), and for single or double suction impellers - Ns, Nss, expected efficiency, diameter, expected nozzle sizes, power if ambitious, could also calculate: minimum flow, suction energy, viscosity corrections, motor sizes, etc
48
Buying Pumps Marrying the Hydraulic Selections with the Pump Standards
49
Pump Standards (North American)
API 610 for heavy duty pumps ASME/ANSI B73.1 and B73.2 standards, essentially dimensional interchangeability standards for chemical process pumps Hydraulic Institute (HI) standards for general service pumps
50
Pump Standards - Applicability
VIL API 610 ANSI B73.1 ANSI B73.2 Hydr Inst (HI) Y Y Y Y
51
Hor O/H Y Y
Btwn Brg Y
General Info - API 610-10th
Per (5.3.5) minimum casing pressure design conditions are 600 psig at 100 F (4000 kPag at 38 C), or at least a Class 300 flange rating per B16.5 Per (5.3.9), radially split casings are required for:
T > 200C - flammable or hazardous fluid with SG < 0.7 at pumping temp - flammable or hazardous fluid at rated P-dis > 100 bar
-
Per (5.3.11), centre-line mounting required, except that per (8.2.1.2) between-bearing pumps with T < 150C may be foot mounted Per (8.1.2.7), the bearing housing temp for grease lubricated OH3 pumps shall be <= 82C at T-amb of 43C
52
General Info ANSI/ASME B73 pumps
Casing pressure-temperature rating per B16.5 Class 150 flange rating Typical application limits (per API 610 8th ed)
-
service is non-flammable and non-toxic P-dis <= 19 barg, P-suc <= 5 barg T-max <= 150 C Head <= 120 m N <= 3600 rpm diameter <= 330 mm (13 in) for overhung pumps
Typical Company limits
Low process-fluid temperature limit - Driver size limit for Vertical inline pumps
53
ANSI B73.1 Typical Coverage
ANSI Pump Size (Dis x Suc) 1x1-1/2 1-1/2x3 2x3 3x4 4x6 6x8 8x10 Impeller Diameter (inches) 6 2,4 2,4 2,4 8 2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4 10 13 15 17
2,4 2,4 2,4 2,4
2,4 2,4 2,4 4 4 4
4 4 4
4 4 4
VIL Pump Coverage 2 = 3600 rpm (2-pole) 4 = 1800 rpm (4-pole) ref: B73.1, Table 4 "Approximate Performance Standards for Pumps (60 hz)"
54
What type of plant?
Class of Plant
Class 1 : low first cost, lower on-stream factor - Class 2: a Class 1 plant with selective upgrades - Class 3: higher first cost, higher on-stream factor
-
Construction (wrt pumps)
-
Modularized or not modularized
55
Questions?
56
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TAD1242GEDokumen14 halamanTAD1242GESIVARAMANJAGANATHANBelum ada peringkat
- NPSH Calculation Spreadsheet With Sample Looses Values in MetersDokumen11 halamanNPSH Calculation Spreadsheet With Sample Looses Values in Meterserjainrachit50% (2)
- PumpDokumen34 halamanPumpsoha89100% (1)
- KSB Selecting Centrifugal PumpsDokumen92 halamanKSB Selecting Centrifugal Pumps윤홍민100% (1)
- Pump Armstrong PDFDokumen47 halamanPump Armstrong PDFMohamed Sulaiman Ibrahim100% (1)
- Al-Salam Higher Institute For: by Abdelaal Mohamed Khttap Cairo 2014Dokumen28 halamanAl-Salam Higher Institute For: by Abdelaal Mohamed Khttap Cairo 2014عبدوخطابBelum ada peringkat
- Ir CR-24-30 22 16-0002-0402 PDFDokumen2 halamanIr CR-24-30 22 16-0002-0402 PDFRicardo Rincon VegaBelum ada peringkat
- Floating Head Heat Exchanger MaintenanceDokumen15 halamanFloating Head Heat Exchanger MaintenanceAbdullah Dinsuhaimi100% (8)
- Design of Fluid Thermal Systems 4th Edition by Janna ISBN Solution ManualDokumen36 halamanDesign of Fluid Thermal Systems 4th Edition by Janna ISBN Solution Manualsteven100% (21)
- Centrifugal Pump Selection and SizingDokumen50 halamanCentrifugal Pump Selection and SizingmariasofiarossiBelum ada peringkat
- 06-Pump Fundamentals & SpecialApplicationsDokumen41 halaman06-Pump Fundamentals & SpecialApplicationsmatias_ignacioBelum ada peringkat
- Pump SelectionDokumen14 halamanPump Selectionas3ateBelum ada peringkat
- How To Size A PumpDokumen90 halamanHow To Size A PumpDaani Olora100% (5)
- Selecting Centrifugal Pumps DataDokumen92 halamanSelecting Centrifugal Pumps DataarvindzdenBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Pump CurvesDokumen4 halamanReading Pump CurvesRobert Barrett100% (1)
- 6 Centrifugal Pump Performance SixDokumen20 halaman6 Centrifugal Pump Performance SixAbdallah MansourBelum ada peringkat
- Skills Workshop: Centrifugal PumpDokumen3 halamanSkills Workshop: Centrifugal PumpchayanunBelum ada peringkat
- Pump CurvesDokumen8 halamanPump CurvesKrishna Chaitanya KalagaBelum ada peringkat
- Navigating Pump CurvesDokumen7 halamanNavigating Pump Curvescastingforge4875Belum ada peringkat
- Centrifugal Pump DesignDokumen15 halamanCentrifugal Pump Designzakibrant23Belum ada peringkat
- Pump FundamentalsDokumen127 halamanPump FundamentalsSheik Mohd50% (2)
- Centrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Dokumen77 halamanCentrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Scribd_del75% (8)
- Centrifugal Pump Affinity Law-BDHDokumen14 halamanCentrifugal Pump Affinity Law-BDHMachineryengBelum ada peringkat
- Blackmer Autogas HandbookDokumen32 halamanBlackmer Autogas HandbookMuhammad ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Sulzer Centrifugal Pumps - Basic OperationDokumen26 halamanSulzer Centrifugal Pumps - Basic OperationMarcelo PerettiBelum ada peringkat
- Pump Selection ExampleDokumen3 halamanPump Selection ExampleKrishnaprasad Nair100% (2)
- How To Size A Pump Blackmonk Engineering PDFDokumen9 halamanHow To Size A Pump Blackmonk Engineering PDFRajesh KrishnamoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Tank SizingDokumen2 halamanTank SizingsamehBelum ada peringkat
- RG Integrally Geared CompressorsDokumen6 halamanRG Integrally Geared CompressorsSauptik SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Designing Compressed Air SystemsDokumen8 halamanDesigning Compressed Air SystemsZaki AnwerBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Solving - Centrifugal PumpsDokumen40 halamanProblem Solving - Centrifugal PumpsEtemadiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Pump FundamentalDokumen99 halamanBasic Pump FundamentalJimit Shah100% (1)
- Pump Selection Session 2Dokumen35 halamanPump Selection Session 2gaurao nasare100% (1)
- PRV-1 StepxStep PDFDokumen8 halamanPRV-1 StepxStep PDFmiltonBelum ada peringkat
- Suction Side of Centrifugal PumpsDokumen11 halamanSuction Side of Centrifugal PumpsTanishk KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Goulds-Pumps Fundamentals PDFDokumen140 halamanGoulds-Pumps Fundamentals PDFAgustinus Made Theo Dwijaya100% (2)
- All Pumps Classification of Pumps PDFDokumen44 halamanAll Pumps Classification of Pumps PDFAnh Tuan100% (2)
- Tech Brief Pump Curves PDFDokumen5 halamanTech Brief Pump Curves PDFThomas KamongBelum ada peringkat
- Pumps & NPSH-Avoid ProblemsDokumen4 halamanPumps & NPSH-Avoid ProblemsChem.EnggBelum ada peringkat
- NPSH For Metering PumpsDokumen7 halamanNPSH For Metering PumpsRahul S. ChandrawarBelum ada peringkat
- PumpDokumen25 halamanPump최승원100% (1)
- Pump Selection ProcedureDokumen16 halamanPump Selection ProcedureDon Bosco100% (3)
- Persatuan Insinyur Indonesia (PII) Badan Koordinasi Mesin (BKM)Dokumen19 halamanPersatuan Insinyur Indonesia (PII) Badan Koordinasi Mesin (BKM)HaryadiBelum ada peringkat
- Base Plate Gould PumpDokumen1 halamanBase Plate Gould PumpErnestoBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Pump Sizing Example 1 & 2ADokumen37 halaman12 Pump Sizing Example 1 & 2AMohamed Abd El-MoniemBelum ada peringkat
- Pump BasicsDokumen118 halamanPump BasicsVinod GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Velocity of Compressed AirDokumen1 halamanVelocity of Compressed AirLucky Karunia Setyawan PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Pumps Selection 0703 HandbookDokumen12 halamanPumps Selection 0703 Handbookkooljam83% (6)
- ALARKO CirculationPump PDFDokumen8 halamanALARKO CirculationPump PDFAlienshowBelum ada peringkat
- SQ - 4.7 - Pumps (Table Format)Dokumen5 halamanSQ - 4.7 - Pumps (Table Format)Amitav MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Transfer Pump BrochureDokumen12 halamanTransfer Pump BrochureRafert RamBelum ada peringkat
- Grundfos SP SubmersibleDokumen108 halamanGrundfos SP SubmersiblemitualvesBelum ada peringkat
- SV80-100 Eng Data1-1996Dokumen9 halamanSV80-100 Eng Data1-1996Bala Krishnan NataBelum ada peringkat
- (Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic CoursesDokumen47 halaman(Oto-Hui - Com) en - Hydraulic Courseseng_ebrahim_2000100% (1)
- Hydraulic CalculationsDokumen12 halamanHydraulic CalculationsIsmid Maulana100% (1)
- Calculation For Suction Specific SpeedDokumen2 halamanCalculation For Suction Specific SpeedAnam FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- 21 5 1710Dokumen31 halaman21 5 1710Ton PhichitBelum ada peringkat
- PumpsDokumen32 halamanPumpsAngela Paul PeterBelum ada peringkat
- Pump CalculationsDokumen9 halamanPump CalculationsMohamad TantawyBelum ada peringkat
- Parker (T6, T6CC) Hydraulic Vane PumpsDokumen12 halamanParker (T6, T6CC) Hydraulic Vane PumpsEduardo Valladares DuranBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Gear PumpDokumen20 halamanProject Report On Gear PumpSunil Kumar Yadav100% (3)
- Fluid Power FormulasDokumen7 halamanFluid Power FormulasKiran Kumar K TBelum ada peringkat
- 29 CarburetionDokumen48 halaman29 CarburetionABBelum ada peringkat
- Acrylic Acid and Derivatives: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial ChemistryDokumen18 halamanAcrylic Acid and Derivatives: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial ChemistryNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- PDOC-596-PEP-01 Project Execution Plan (Rev 3)Dokumen89 halamanPDOC-596-PEP-01 Project Execution Plan (Rev 3)Noman Abu-Farha100% (2)
- 090768.232 3.00 018 A e - ADokumen111 halaman090768.232 3.00 018 A e - ANoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Sulphuric Acid HandbookDokumen268 halamanSulphuric Acid HandbooklemeitBelum ada peringkat
- Vessel VolumesDokumen72 halamanVessel VolumeskanchanabalajiBelum ada peringkat
- Method of Heat Exchanger Sizing (Kern Method)Dokumen11 halamanMethod of Heat Exchanger Sizing (Kern Method)Hani Kirmani80% (5)
- 4T16 Project Execution Plan Checklist v4-0Dokumen2 halaman4T16 Project Execution Plan Checklist v4-0Noman Abu-Farha100% (1)
- Steam Turbines: Prof. Osama El MasryDokumen13 halamanSteam Turbines: Prof. Osama El MasryNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Cost EstimationDokumen12 halamanCost EstimationNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Gasifiers DatabaseDokumen44 halamanGasifiers DatabaseNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Two Phase Separator SizingDokumen5 halamanTwo Phase Separator SizingNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- FlangesDokumen7 halamanFlangesNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Piping Considerations - Maximum Fluid Velocity: Friction LossDokumen1 halamanPiping Considerations - Maximum Fluid Velocity: Friction LossNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- ME ProductCatalogDokumen20 halamanME ProductCatalogNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Nominalmonthlycountryexchangerates 1Dokumen121 halamanNominalmonthlycountryexchangerates 1Noman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Kich Glitch Inlet NozzleDokumen2 halamanKich Glitch Inlet NozzleNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- CTR-InPK Fertilizer Plant Project-FEED DesignDokumen7 halamanCTR-InPK Fertilizer Plant Project-FEED DesignNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Gallons Pounds ConversionDokumen17 halamanGallons Pounds ConversionNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Two Phase Flow RegimeDokumen8 halamanTwo Phase Flow RegimeNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- 11-4080 HYSYS Relief Valve Sizing Demo Guide FinalDokumen18 halaman11-4080 HYSYS Relief Valve Sizing Demo Guide FinalNoman Abu-FarhaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 5 States of Matter Solution Guide Sem1 2019Dokumen3 halamanTutorial 5 States of Matter Solution Guide Sem1 2019Myeisha WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- How Elevators Work - FinalDokumen7 halamanHow Elevators Work - Finalhitokiri_knivesBelum ada peringkat
- Component Engineering: Installation, Operation & Maintenance ManualDokumen1 halamanComponent Engineering: Installation, Operation & Maintenance ManualrsaimaheshBelum ada peringkat
- DS1081 LPCO2 Refrigerated Storage Units Revision 07-18-18Dokumen8 halamanDS1081 LPCO2 Refrigerated Storage Units Revision 07-18-18kidmuBelum ada peringkat
- Budhu Soil Mechanics Foundations 3rd TXTBKDokumen1 halamanBudhu Soil Mechanics Foundations 3rd TXTBKNadeem AbbasiBelum ada peringkat
- Power Cable Installation GuideDokumen49 halamanPower Cable Installation Guidemivey100% (1)
- Cable Tray Price ListDokumen54 halamanCable Tray Price ListSunil WadekarBelum ada peringkat
- The Founding of The Company: © MAN Diesel A/S L/73480-9.1/0205 (2000/LGJ)Dokumen11 halamanThe Founding of The Company: © MAN Diesel A/S L/73480-9.1/0205 (2000/LGJ)argentum19619692Belum ada peringkat
- Faac 400 ManDokumen24 halamanFaac 400 ManJuanBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Biopharm MetalDokumen28 halamanA2 Biopharm MetalThanh Nghị BùiBelum ada peringkat
- Spotcheck Developer SKD-S2: CertificationDokumen3 halamanSpotcheck Developer SKD-S2: Certificationnasser saldaña quinteroBelum ada peringkat
- Water Jet and Abrasive Water Jet MachiningDokumen38 halamanWater Jet and Abrasive Water Jet MachiningEthan HuntBelum ada peringkat
- Bfe API 6a ValvesDokumen32 halamanBfe API 6a ValvesAldo P WicaksanaBelum ada peringkat
- Adjustment: Prevent Moving The Motor PlateDokumen10 halamanAdjustment: Prevent Moving The Motor PlateArmandoOlivaresBelum ada peringkat
- RENR1156Dokumen2 halamanRENR1156Leopoldo Del Campo100% (1)
- Prelim Examination Set A Solutions PDFDokumen6 halamanPrelim Examination Set A Solutions PDFOxy GenBelum ada peringkat
- The Scrodinger Wave EquationDokumen19 halamanThe Scrodinger Wave EquationAshwin S PurohitBelum ada peringkat
- MEI Company Profile PDFDokumen9 halamanMEI Company Profile PDFWilliam J JBelum ada peringkat
- Tyco - Test Indikatora ProtokaDokumen4 halamanTyco - Test Indikatora ProtokaMuhidin KozicaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation - Mee - 4 New1Dokumen29 halamanPresentation - Mee - 4 New1Amal joyBelum ada peringkat
- WPS ExampleDokumen2 halamanWPS ExampleNur WijiantoBelum ada peringkat
- 3-69 ShigleyDokumen3 halaman3-69 ShigleyinivlaviBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Showvls Cat 6090 Fs PDFDokumen8 halamanHydraulic Showvls Cat 6090 Fs PDFGlory LightBelum ada peringkat
- SVPL PDFDokumen68 halamanSVPL PDFSales SVPLBelum ada peringkat
- ME - MD Mecha. Robotics, PP - SOL - 2650Dokumen35 halamanME - MD Mecha. Robotics, PP - SOL - 2650VivekMishraBelum ada peringkat