Colorante Azul Laca #2 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Zulema Jakovljevic AnguloDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Colorante Azul Laca #2 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Zulema Jakovljevic AnguloHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INDIGOTINE
Prepared at the 73rd JECFA (2010) and published in FAO Monographs 10 (2010), superseding specifications prepared at the 28th JECFA (1984) and published in the Combined Compendium of Food Additive Specifications, FAO JECFA Monographs 1 (2005). An ADI of 0 - 5 mg/kg bw was established at the 18th JECFA (1974).
SYNONYMS DEFINITION
CI Food Blue 1, FD&C Blue No. 2, Indigo Carmine, CI (1975) No. 73015, INS No. 132 Consists essentially of a mixture of disodium 3,3' -dioxo-[delta2,2'biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate (principal component) and disodium 3,3'dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]-5,7'-disulfonate (isomer) and subsidiary colouring matters together with sodium chloride and/or sodium sulfate as the principal uncoloured components. May be converted to the corresponding aluminium lake in which case only the General Specifications for Aluminium Lakes of Colouring Matters apply.
Chemical names
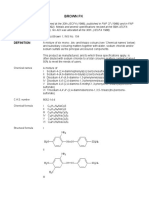
Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate (principal component) 860-22-0 (principal component) C16H8N2Na2O8S2 (principal component)
C.A.S. number Chemical formula Structural formula
Principal component
Formula weight Assay
466.36 (principal component) Not less than 85% total colouring matters. Not more than 18% of disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]-5,7'disulfonate. Blue powder or granules
DESCRIPTION
FUNCTIONAL USES Colour CHARACTERISTICS
IDENTIFICATION Solubility (Vol. 4) Identification of colouring matters (Vol. 4) PURITY Loss on drying (Vol. 4)
Soluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol Passes test
Not more than 15% at 135 together with chloride and sulfate calculated as sodium salts. (See Volume 4 under SPECIFIC METHODS, Food Colours.) Not more than 0.2%
Water insoluble matter (Vol. 4)
Subsidiary colouring matters
Not more than 1% See description under TESTS
Organic compounds other Not more than 0.5% of sum of isatin-5-sulfonic acid, 5than colouring matters sulfoanthranilic acid and anthranilic acid. (Vol. 4) (See Volume 4 under SPECIFIC METHODS, Food Colours.)
Proceed as directed under Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography using an elution gradient of 2 to 100% at 4% per min (linear) followed by elution at 100%.
Unsulfonated primary aromatic amines (Vol. 4) Ether extractable matter (Vol. 4)
Not more than 0.01% calculated as aniline (See Volume 4 under SPECIFIC METHODS, Food Colours.) Not more than 0.2% (See Volume 4 under SPECIFIC METHODS, Food Colours, Method II.) Use 2 g of sample for the test. Not more than 2 mg/kg Determine using an atomic absorption technique appropriate to the specified level. The selection of sample size and method of sample preparation may be based on the principles of the method described in Volume 4 (under General Methods, Inorganic Components, Metallic Impurities).
Lead (Vol. 4)
TESTS
PURITY TESTS Subsidiary colouring matters
Subsidiary colouring matters are determined by high performance liquid chromatography using the following conditions: Chromatographic system - HPLC system with a UV/VIS detector or a diode array detector,
auto sampler or injector - Detector wavelength: 610 nm - Column: C18 on silica gel (250 x 4.6 mm, 5 m) ACE 5 C18 or equivalent - Mobile phase: solvent A: 0.02 mol/l ammonium acetate and solvent B: acetonitrile: water (7:3 v/v) - Gradient elution: A:B 92:8 v/v to A:B 70:30 v/v (0-15 min); to A:B 40:60 v/v (15-25 min); to A:B 92:8 v/v (25-30 min); A:B 92:8 v/v (30-35 min). - Column temperature: 40 - Flow rate: 1.0 ml/min - Injection volume: 20 l The subsidiary colours are separated from the principal component and its isomer. The subsidiary colouring matter monosodium 3,3'2,2'
dioxo-[delta
-biindoline]-5 sulfonate elutes at approximately 21 min.
METHOD OF ASSAY Total colouring matters content
Proceed as directed under Total Content by Titration with Titanous Chloride in Volume 4, using the following (See SPECIFIC METHODS, Food Colours): Weight of sample: 1.0-1.1 g Buffer: 15 g sodium hydrogen tartrate Weight (D) of colouring matters equivalent to 1.00 ml of 0.1 N TiCl3: 23.32 mg. Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]-5,5'disulfonate,disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]- 5,7'disulfonate (5,7 isomer) and subsidiary colouring matters by HPLC The isomers get separated under the HPLC conditions detailed under the separation of subsidiary colouring matters, and the amounts present can be quantified using an external standard calibration. Reagents - Acetonitrile, HPLC grade - Ammonium acetate, HPLC grade - Reference standards of disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]5,5'-disulfonate and disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]- 5,7'disulfonate Standard stock solutions (1000 g/ml): Weigh accurately 0.10 g (0.1 mg) of each reference standard and transfer to a 100 ml volumetric flask and bring to volume with water. Standard solutions: Prepare five solutions from the standard stock solutions in the concentration range of 1 to 20 g/ml. Sample solution: Weigh accurately 0.10 g (0.1 mg) (w2) of the sample and transfer to a 100 ml volumetric flask (v) and bring to
volume with water (sample solution SA). Transfer 1.00 ml (vs1) and 5.00 ml (vs5) of the solution SA to two 50 ml volumetric flasks (vS), respectively, and bring to volume with water (sample solutions S1 and S5). Procedure Inject the five standard solutions for each isomer using the conditions detailed under TESTS (Subsidiary colouring matters by HPLC) and integrate peak areas at 6.5 min for the 5,5 isomer (disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate) and 10.8 min for the 5,7 isomer (disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]- 5,7'disulfonate). Construct standard curve for each compound (Area vs. standard concentration, g/ml). Inject sample solutions SA, S1 and S5. The peak area of the 5,7 isomer for the sample solution should be in the linear range of the calibration graph, otherwise increase the volume vs5. Sample solutions S1, S5 and SA are to quantify disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate, disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta2,2'-biindoline]5,7'-disulfonate (5,7 isomer) and subsidiary colouring matters, respectively. Calculations Calculate the concentrations (C, % (w/w)) of the two isomers and subsidiary colouring matters in the sample using the standard curves and the following formulas:
A5,5 b5,5' 10 6 vS v 100 C5.5' isomer % (w/w) = m vs1 wS 5,5'
A5, 7 b5,7 ' 10 6 vS v 100 C5.7' isomer % (w/w) = m vs 5 wS 5, 7 ' Asum b5,5' 10 6 v 100 CSubsidiary colouring matters % (w/w) = m wS 5,5'
where A5,5 is the area of the peak of the 5,5 isomer in the sample chromatogram (area units); A5,7 is the area of the peak of the 5,7 isomer in the sample chromatogram (area units); Asum is the sum of the areas of the peaks in the chromatogram (610 nm), except for the two isomers; b5,5 and b5,7 are the linear coefficients of the calibration graphs for the 5,5 isomer and 5,7 isomer, respectively; m5,5 and m5,7 are is the slope of the calibration graph (area units ml/g) for the 5,5 isomer and 5,7 isomer, respectively; ws is the sample weight (g);
v is the volume of the sample solution sA (ml); vs1 is the volume of the sample solution s1 (ml); and vs5 is the volume of the sample solution s5 (ml).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- COI-T.20-Doc.-No-34-Rev.-1-2017 (Acidity MOA)Dokumen4 halamanCOI-T.20-Doc.-No-34-Rev.-1-2017 (Acidity MOA)KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Amarillo 6Dokumen4 halamanAmarillo 6Juan Carlos QuilaBelum ada peringkat
- Ivermectin APIDokumen3 halamanIvermectin APIzubair152738Belum ada peringkat
- Bu 283Dokumen6 halamanBu 283babithyBelum ada peringkat
- Additive 241 PDFDokumen5 halamanAdditive 241 PDFmargaretasuprajogiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Tests Guide for DrugsDokumen288 halamanChemical Tests Guide for DrugsGopalaKrishnan SivaramanBelum ada peringkat
- Dequalinium chloride monograph summaryDokumen2 halamanDequalinium chloride monograph summaryMulayam Singh YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Allura Red - FAODokumen5 halamanAllura Red - FAOThuy PhanBelum ada peringkat
- FAO JECFA Monographs 16 Polysorbate 60 SpecsDokumen2 halamanFAO JECFA Monographs 16 Polysorbate 60 SpecsBenni IskandarBelum ada peringkat
- Ascorbic AcidDokumen2 halamanAscorbic AcidMulayam Singh YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Additive 062Dokumen6 halamanAdditive 062TienBelum ada peringkat
- Tocopherol Concentrate, MixedDokumen4 halamanTocopherol Concentrate, MixedBen ClarkeBelum ada peringkat
- Salicylic AcidDokumen2 halamanSalicylic AcidSaskya PBelum ada peringkat
- Indigo Carmine: A Concise GuideDokumen3 halamanIndigo Carmine: A Concise Guidemazahir razaBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM D 1615 - 60 (Reapproved 1995) Glycerol, Ethylene Glycol, and Pentaerythritol in Alkyd ResinsDokumen4 halamanASTM D 1615 - 60 (Reapproved 1995) Glycerol, Ethylene Glycol, and Pentaerythritol in Alkyd Resinsalin2005Belum ada peringkat
- EPA Method 3305 PDFDokumen3 halamanEPA Method 3305 PDFDave SalgueroBelum ada peringkat
- Model Answer: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological UniversityDokumen7 halamanModel Answer: Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological UniversityPrathiBelum ada peringkat
- Determinacion de Fosforo Dell-176Dokumen9 halamanDeterminacion de Fosforo Dell-176Sarah WellsBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Phosphate in BeverageDokumen17 halamanDetermination of Phosphate in BeveragesiphiweBelum ada peringkat
- Separation of Acid, Basic and Disperse Dyes by Single Gradient Elution RP HPLCDokumen8 halamanSeparation of Acid, Basic and Disperse Dyes by Single Gradient Elution RP HPLCnsovticBelum ada peringkat
- ANALYZING SULFIDES IN WATERDokumen3 halamanANALYZING SULFIDES IN WATERAchmad RidwanBelum ada peringkat
- Uaker Chemical: India LimitedDokumen3 halamanUaker Chemical: India LimitedAbhishekChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Application Note No. 065/2011: Total SO in WineDokumen14 halamanApplication Note No. 065/2011: Total SO in WineLina Budi RahayuBelum ada peringkat
- Method-COI-T.20-Doc.-No-35-Rev.-1-2017Dokumen5 halamanMethod-COI-T.20-Doc.-No-35-Rev.-1-2017ameliorationcontinue2Belum ada peringkat
- ANALYSIS OF ALCOHOL IN LIQUORSDokumen5 halamanANALYSIS OF ALCOHOL IN LIQUORSgreeshma2008Belum ada peringkat
- SOD Assay KitDokumen4 halamanSOD Assay KitWayu KasuriyaBelum ada peringkat
- ACID URONIC Determination of The Uronic Acid ContentDokumen4 halamanACID URONIC Determination of The Uronic Acid ContentMayra ValdiviesoBelum ada peringkat
- Chlorine, Total Residual DPDDokumen3 halamanChlorine, Total Residual DPDm.cj1Belum ada peringkat
- A Single-Solution Method For The Determination of Soluble Phosphate in Sea WaterDokumen6 halamanA Single-Solution Method For The Determination of Soluble Phosphate in Sea WaterA'yunil HisbiyahBelum ada peringkat
- METHOD of ANALYSIS - Allium Cepae ExtractDokumen9 halamanMETHOD of ANALYSIS - Allium Cepae ExtractJames AkibonBelum ada peringkat
- Modified Somers Colour MeasureDokumen8 halamanModified Somers Colour MeasureAurelia BucurBelum ada peringkat
- 4.monograph Part I (A I)Dokumen679 halaman4.monograph Part I (A I)PPDESHMUKH_1967Belum ada peringkat
- COI T.20 Doc. No 29 Rev 1 2017 BiophénolDokumen8 halamanCOI T.20 Doc. No 29 Rev 1 2017 BiophénolSlaw Ben AissaBelum ada peringkat
- Biomaghreb PRICE QUALITY and SERVICESDokumen59 halamanBiomaghreb PRICE QUALITY and SERVICESbigweb100% (2)
- METHOD #: 340.3 Title: Analyte: Instrumentation: Storet NoDokumen4 halamanMETHOD #: 340.3 Title: Analyte: Instrumentation: Storet NoKarimah SabilaBelum ada peringkat
- EPA 9034 - ReactividadDokumen7 halamanEPA 9034 - ReactividadGuadalupe EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- AN5391 Determination of TKN in Water by Using KT8000 SeriesDokumen7 halamanAN5391 Determination of TKN in Water by Using KT8000 SeriesJaysonAbenirCabahugBelum ada peringkat
- method_7.0_2014Dokumen3 halamanmethod_7.0_2014FelisbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Lycopene Extract From TomatoDokumen7 halamanLycopene Extract From TomatoShayne PalalayBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Method of Fertilizer Grade Potassium Dihydrogen PhosphateDokumen6 halamanAnalytical Method of Fertilizer Grade Potassium Dihydrogen PhosphateGenaro PalacioBelum ada peringkat
- Feed Analysis Standard Operation (Analysis) Procedure SOPDokumen27 halamanFeed Analysis Standard Operation (Analysis) Procedure SOPZiauddeen NoorBelum ada peringkat
- EPA Method 9014Dokumen7 halamanEPA Method 9014Joan MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- US EPA Method 9253 - Determinatin ChlorideDokumen6 halamanUS EPA Method 9253 - Determinatin ChlorideAnisa RahmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Srndwandwe, Practical Report 2Dokumen16 halamanSrndwandwe, Practical Report 2siphiweBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM D 820 - 93 Chemical Analysis of Soaps Containing SyntheticDokumen9 halamanASTM D 820 - 93 Chemical Analysis of Soaps Containing Syntheticalin2005100% (1)
- Additive 442Dokumen4 halamanAdditive 442O.L.D.E.Belum ada peringkat
- Additive-068 BHA JEFCADokumen4 halamanAdditive-068 BHA JEFCASartika MutiarasaniBelum ada peringkat
- DesmopressinDokumen2 halamanDesmopressinMulayam Singh Yadav100% (1)
- Codex Vitamin EDokumen3 halamanCodex Vitamin ETapanee PadungstayawongBelum ada peringkat
- Neral TestsDokumen250 halamanNeral TestsAshok KumarBelum ada peringkat
- IFRA Peroxide Value TestDokumen5 halamanIFRA Peroxide Value TestWimbo TrionoBelum ada peringkat
- Identification and control of residual solvents GC methodDokumen6 halamanIdentification and control of residual solvents GC methodNageshwar ThadakamallaBelum ada peringkat
- Sorbitol Analysis Japan CustomDokumen4 halamanSorbitol Analysis Japan CustomMert TuncerBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisDari EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryDari EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterDari EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryDari EverandPharmaceutical Excipients: Properties, Functionality, and Applications in Research and IndustryOtilia M. Y. KooBelum ada peringkat