Reviewer General Pricing Strategies
Diunggah oleh
Cecille CastellHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Reviewer General Pricing Strategies
Diunggah oleh
Cecille CastellHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
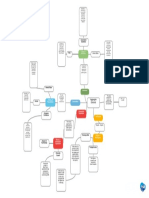
MARKET1 GLOSSARY Variable Cost (VC) Fixed Cost (FC) Marginal Cost (MC) Marginal Revenue (MR) : : : : Varies
with the changes in the level of output Does not change as output is increased or decreased Change in total costs associated with a one-unit change in output Extra revenue associated with selling an extra unit of output GENERAL PRICING APPROACHES Definition DEMAND DETERMINANT OF PRICE DEMAND AND SUPPLY Determining the markets price equilibrium, or when demand and supply offset each other The proper balance of demand and supply in the market Shortage place upward pressure on price; demand > supply Surplus place a downward pressure on price; demand < supply Computation
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND Consumer responsiveness or sensitivity to changes in price
- - Elastic Demand Consumer demand is sensitive to changes in prices Inelastic Demand an increase or decrease in price will not significantly affect demand for the product Unitary Elastic Demand total revenue remains the same when prices change - - Factors 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. affecting Elasticity Availability of Substitutes Price relative to purchasing power Product Durability Inflation Rates A products other uses
where,
If E > 1, demand is elastic If E < 1, demand is inelastic If E = 1, demand is unitary COST DETERMINANTS OF PRICE
MARK-UP PRICING Most popular method o Simplifies the pricing process o Fair to both buyer and seller o Price competition minimized Uses the cost of buying the product from the producer plus the amounts of profit and for expenses otherwise accounted for
*Difference between Retail price and Cost is called gross margin. An adequate margin should be able to cover selling expenses and profit.
- - Keystoning the practice of marking up prices by 100% or doubling the cost PROFIT MAXIMIZATION PRICING Occurs when marginal revenue equals marginal cost As long as the last unit produced and sold is greater than its cost, they should still continue manufacturing and selling the product since it generally increases total profits
BREAK-EVEN PRICING Analyzes and determines what sales volume must be reached before total revenue equals total cost Assumes a given Fixed cost and a constant average variable cost
where Disadvantages Determining fixed from variable costs Break-even analysis ignores demand
Advantages Provides a quick estimate of how much the firm must sell to break even Provides how much profit can be earned if a higher sales volume is obtained Not necessary to obtain accounting data regarding MR and MC (which are frequently unavailable)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Copyscape Plagiarism Checker - View Content Comparison1Dokumen9 halamanCopyscape Plagiarism Checker - View Content Comparison1Vanessa KanuBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- EIM Knowledge TestDokumen768 halamanEIM Knowledge Testtuan0947845876Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- 2.2.1 As Version Sales Forecasting UpdatedDokumen31 halaman2.2.1 As Version Sales Forecasting UpdatedEhtesham UmerBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Question Bank: (020) 2447 6938 E MailDokumen32 halamanQuestion Bank: (020) 2447 6938 E MailHardik BhondveBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Principles of MarketingDokumen159 halamanPrinciples of Marketingኢትዮጵያ ሐገሬBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study of Two Brands-Demand Patterns and Pricing StrategiesDokumen6 halamanComparative Study of Two Brands-Demand Patterns and Pricing Strategiesparth saklechaBelum ada peringkat
- Market AnalysisDokumen6 halamanMarket AnalysisBeya Lopez GarbanzosBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Entrepreneurship - Module 4Dokumen17 halamanEntrepreneurship - Module 4Rhosalyne NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Sensitivity of Travel DemandDokumen6 halamanSensitivity of Travel DemandShilpa AglurBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- ECW1101 Introductory Microeconomics: Business and EconomicsDokumen39 halamanECW1101 Introductory Microeconomics: Business and EconomicsAshna LatheefBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Relevant Costing HandoutDokumen3 halamanRelevant Costing HandoutCarl Adrian ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Seed Distribution & MarketingDokumen17 halamanSeed Distribution & MarketingJanjit AdhikariBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Paul Romer The Trouble With Macroeconomics PDFDokumen26 halamanPaul Romer The Trouble With Macroeconomics PDFWellington MigliariBelum ada peringkat
- Pricing Strategy ModuleDokumen51 halamanPricing Strategy ModuleJohn Paul MagbitangBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- ECON302 Tutorial1 Answers PDFDokumen5 halamanECON302 Tutorial1 Answers PDFAngel RicardoBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Causes of The Industrial Revolution: An OverviewDokumen13 halamanCauses of The Industrial Revolution: An OverviewChris WrightBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Module 2Dokumen47 halamanModule 2Manuel ErmitaBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Pricing StrategyDokumen52 halamanPricing Strategyfirst channelBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Curled Metal Inc. Case StudyDokumen18 halamanCurled Metal Inc. Case StudybilalBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Government Incentives: Factors of InvestmentDokumen1 halamanGovernment Incentives: Factors of InvestmentTayeeb Bin KalamBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- E3sconf Icenis2018 10004Dokumen6 halamanE3sconf Icenis2018 10004Rifki SatyawBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Tools in Economic AnalysisDokumen5 halamanBasic Tools in Economic AnalysisAarav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution ExammmmDokumen17 halamanDistribution ExammmmMiles YordanBelum ada peringkat
- NCCC Business PlanDokumen60 halamanNCCC Business PlanLuvsansharav Naranbaatar50% (2)
- Ch08 189-220Dokumen32 halamanCh08 189-220vancho_mkdBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study On The Views of AirLand Taxi Company On The Presence of Uber in Cebu City - Implications For Marketing StrategiesDokumen92 halamanA Case Study On The Views of AirLand Taxi Company On The Presence of Uber in Cebu City - Implications For Marketing StrategiesCybil YbanezBelum ada peringkat
- Footwear Wholesaling in Australia Industry ReportDokumen31 halamanFootwear Wholesaling in Australia Industry ReportBakar ChBelum ada peringkat
- Crux Casebook 2024Dokumen381 halamanCrux Casebook 2024Harshit SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Relevant Costs For Decision MakingDokumen20 halamanRelevant Costs For Decision Makingmisharahman100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- HPSC PGT Commerce Syllabus PDFDokumen3 halamanHPSC PGT Commerce Syllabus PDFNaveen KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)