Folio Addmath
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Nur HazwanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Folio Addmath
Diunggah oleh
Muhammad Nur HazwanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Part 1 (a)
Part 1 (b) Part 2 (a) Part 2 (b 1) Part 2 (b 2) Part 3 (a) Part 3 (b) Part 3 (c) Part 3 (d) Part 3 (e)
Part 1 (b)
Pi or is a mathematical constant whose value is the ratio of any circles circumference to its diameter in Euclidean space ; this is
the same valueas the ratio of a circles area to the square of its radius. Its is approximately equal to 3.14159 in the usual decima notation. is one of the most formula from mathematics, science, and engineering ivolve .
is an irratonal number, which means that its value cannot be expressed exactly as afraction m/n where m and n are integer. Consequently, its decimal representation never endsor repeats. Its also a transcidential number, which means that not finite sequence of algebraic operation on integers (power,roots,sum,ect) can be equal to its value; proving this was late achievement in mathematical historyand a significant result of 19th century German mathematies. Throughout the history of mathematics, there has been much effort to determine more accurately and to understand its nature;fascination with the number has even carried over non-mathematical culture. The greek letter , spelled out Pi in text, was adopter for the number from the epipetpog ,first by William Jones in 1707, and popularized by leonhard eular in 1737 . [2] the constant, archimedes, constant (not to be confusedwith an archimedes number), or ludolph umer (from a German mathematician whase efforts to calculate more of its digits became famous)
Part 2 (a)
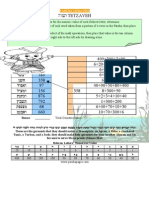
d1(cm) d2(cm) 1 2 3 19 18 17 Length of arc PQR in terms of 10 10 10 Length of arc PAB in terms of (cm) 0.5 1 1.5 Length of arc BCR in term of (cm) 9.5 9 8.5
4 5
16 15
10 10
2 2.5
8 7.5
table 1
Arc length of PQR arc length of PAB + Arc length BCR
= +
The length of arc of the outer Semicle soul Subtitude :
The sum of the length of arcs of the inner semicircles :
Where is any positive real number we can see That, Sin = sout ,
Part 1: Not all objects surrounding us are related to circles. If all the objects are circle, therewould be no balance and stability. In our daily life, we could related circles inobjects. For example: a fan, a ball or a wheel. In Pi(), we accept 3.142 or 22/7 asthe best value of pi. The circumference of the circle is proportional as pi() xdiameter. If the circle has twice the diameter, d of another circle, thus thecircunference, C will also have twice of its value, where preserving the ratio =Cid
Part 2: The relation between the length of arcs PQR, PAB and BCR where the semicirclesPQR is the outer semicircle while inner semicircle PAB and BCR is Length of arc=PQR= Length of PAB + Length of arc BCR.The length of arc for each semicircles can beobtained as in length of arc = 1/2(2r). As in conclusion, outer semicircle is alsoequal to the inner semicircles where Sin=Sout .
Part 3: In semicircle ABC(the shaded region), and the two semicircles which is AEB and BFC,the area of the shaded region semicircle ADC is written as in Area of shaded regionADC =Area of ADC (Area of AEB + Area of BFC). When we plot a straight link graphbased on linear law, we may still obtained a linear graph because Sin=Sout wherethe diameter has a constant value for a semicircle.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Tetzaveh Parsha GematriaDokumen1 halamanTetzaveh Parsha GematriaRabbi Benyomin HoffmanBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Exam Summary For Data Communications PDFDokumen9 halamanMidterm Exam Summary For Data Communications PDFKit Jason MonjeBelum ada peringkat
- Is 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyDokumen4 halamanIs 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyCrypto AbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 - Spring2006: SolutionDokumen31 halamanAssignment 1 - Spring2006: SolutionMuhammad UmairBelum ada peringkat
- Long Quiz Direct VariationDokumen2 halamanLong Quiz Direct VariationHermann Dejero LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- B I 1A Fundamentals of Reservoir Phase Behavior PDFDokumen92 halamanB I 1A Fundamentals of Reservoir Phase Behavior PDFsereptBelum ada peringkat
- Walking Bass Line Theory BasicsDokumen11 halamanWalking Bass Line Theory BasicsKikemol Lv O100% (10)
- Prob AnswersDokumen4 halamanProb AnswersDaniel KirovBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computer Networks: NetworkDokumen61 halamanIntroduction To Computer Networks: NetworkSaihari NarayanBelum ada peringkat
- Stock Price Prediction Using LSTMDokumen29 halamanStock Price Prediction Using LSTMKunal GargBelum ada peringkat
- SampleDokumen43 halamanSampleSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- Decompiled With CFR ControllerDokumen3 halamanDecompiled With CFR ControllerJon EricBelum ada peringkat
- CN101A Timer ManualDokumen2 halamanCN101A Timer ManualMauricioVilalvaJr.0% (1)
- 16 Astral - Pool Heating 2008Dokumen38 halaman16 Astral - Pool Heating 2008drožmanićBelum ada peringkat
- Manual AvicadDokumen676 halamanManual AvicadOlivia BlanaruBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0191886910006215 Main PDFDokumen6 halaman1 s2.0 S0191886910006215 Main PDFOscar Iván Negrete RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- J Lithos 2018 02 011Dokumen52 halamanJ Lithos 2018 02 011Warwick HastieBelum ada peringkat
- PU225 Series: Solenoid ValveDokumen1 halamanPU225 Series: Solenoid Valveremus popescuBelum ada peringkat
- ASM Lab Record BookDokumen36 halamanASM Lab Record BookNandan HegdeBelum ada peringkat
- Practical - 1: 1.1 CommitDokumen8 halamanPractical - 1: 1.1 CommitRoy BokhiriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogue Solid Core PDFDokumen16 halamanCatalogue Solid Core PDFdangodBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Computing: Exercise Sheet 1: Steven Herbert and Anuj DawarDokumen2 halamanQuantum Computing: Exercise Sheet 1: Steven Herbert and Anuj DawarJuan DiegoBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special StructuresDokumen5 halamanHighway Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special Structuresror77Belum ada peringkat
- Dish Washer Mcachine ProjectDokumen43 halamanDish Washer Mcachine ProjectVijay Powar60% (5)
- Relayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01Dokumen43 halamanRelayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01kenlavie2Belum ada peringkat
- Komposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutDokumen13 halamanKomposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutI2O42OO54 IRFAN FAUZIBelum ada peringkat
- About Planets - Vaishali's ProjectDokumen3 halamanAbout Planets - Vaishali's ProjectRaj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Soda Ash PDFDokumen45 halamanSoda Ash PDFM TBelum ada peringkat
- Converting CLOBs 2 VARCHARDokumen15 halamanConverting CLOBs 2 VARCHARMa GicBelum ada peringkat
- RO400FC RO300FC Specifications - V3.2Dokumen6 halamanRO400FC RO300FC Specifications - V3.2bogdantn98Belum ada peringkat