Transition Metal Complexes & Crystal Field Theory
Diunggah oleh
carloscanaisDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Transition Metal Complexes & Crystal Field Theory
Diunggah oleh
carloscanaisHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
12/6/2012
C H A P T E R
PART B: 1st Row Transition Metals & Coordination Compounds
Outlines
2
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Metal-Ligand Bond in Complexes
CFT for Octahedral Complexes
CFT for Tetrahedral Complexes
CFT for Square Planar Complexes
12/6/2012
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
3
CFT is a theory that accounts for the colours and the magnetic and other properties of transition metal complexes in terms of the splitting of the energies of metal ion d orbitals by the electrostatic interaction with the ligands.
Many of the colours and magnetic properties of transition metal complexes are related to the d electrons in metal orbitals.
Metal-Ligand Bond in Complexes
4
Ligand donates a pair of electrons into a suitable empty orbital on the metal. The ligands are attracted strongly toward the metal center. Because of the electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ion and the electrons of the ligands, the assembly of the metal ion and the ligands is lower in energy than the fully separated charges.
12/6/2012
CFT for Octahedral Complexes
5
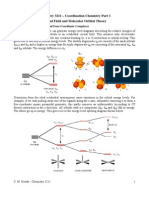
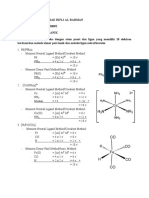
Although the positive metal ion is attracted to the electrons in the ligands, the d electrons on the metal ion feel repulsion from the ligands. An octahedral array of negative charges approaching a metal ion. The ligands to be negative points of charge that repel the electrons in the d orbitals.
In octahedral complexes, the ligands approaching the metal ion along the x, y and z axes.
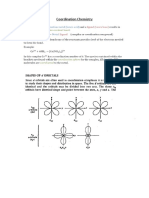
The orientations of the d orbital relative to the charges
The lobes point toward the charges
The lobes point between the charges
12/6/2012
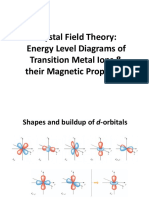
Because the d orbitals on the metal ion have different shapes, they do not all have the same energy under the influence of the crystal field. The dz2 and dx2-y2 orbitals experience the same amount of repulsion from the crystal field, so they stay at the same energy. The dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals experience exactly the same repulsion, so they stay at the same energy. Because their lobes point right at the negative charges, dz2 and dx2-y2 orbitals experience stronger repulsion than those in the dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals. Therefore, an energy separation or splitting, occurs between the three lower-energy d orbitals and the two higher-energy d orbitals. This energy gap is labeled , a quantity that is often called the crystal field splitting energy.
12/6/2012
9
e set
t2 set
This diagram shows the effects of the negative points of charge on the energies of the d orbitals. When negative charges are brought up to the metal ion, the average energy of the d orbitals increases (center). Because the repulsion felt by the dz2 and dx2-y2 is greater than that felt by the dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals, the five d orbitals split into a lower-energy set of three and a higher-energy set of two.
10
e set
Isolated transition metal atom
t2 set
Crystal field splitting diagram for an octahedral complex
12/6/2012
11
e set
t2 set
12
Ligands approach metal
e set d-orbitals pointing directly at axis are affected most by electrostatic interaction
t2 set d-orbitals not pointing directly at axis are least affected (stabilized) by electrostatic interaction
12/6/2012
CFT for Tetrahedral Complexes
13
When there are only four ligands about the metal, the geometry is generally tetrahedral, except for the special case of metal ions with a d8 electrons configuration (square planar).
14
The crystal-field splitting of the metal d orbitals in the tetrahedral complexes differs from that in octahedral complexes. The splitting of the metal d orbitals in the tetrahedral crystal is just the opposite of that for the octahedral case.
12/6/2012
15
The three metal d orbitals in the t2 set are raised in energy, and the two orbitals in the e set are lowered.
Because of there are only four ligands instead of six, as in octahedral case, the crystal-field splitting in much smaller for tetrahedral complexes.
CFT for Square Planar Complexes
16
Square planar complexes, in which four ligands are arranged about the metal ion in a plane, can be envisioned as formed by removing the two ligands from along the vertical z-axis of the octahedral complex.
Square planar complexes are characteristics of metal ions with a d8 electron configuration.
12/6/2012
17
The changes that occur in the energy levels of the d orbitals are illustrated as follows.
The dz2 orbital is now considerably lower in energy than the dx2-y2 orbital because the ligands along the vertical z-axis have been removed.
COMPARISON OF CFT IN THREE DIFFERENT GEOMETRIES
18
eg tet = 4/9 oct Energy of attraction of point charges oct t2g tet t2g eg dz2 dyz dxz dxy dx2-y2
sqp
tetrahedral field
isolated metal ion
before accounting for electron repulsion
octahedral field
square planar field
12/6/2012
19
10
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 12 ChemDokumen5 halaman12 ChemBhoomi SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Class 1Dokumen9 halamanClass 1Muskan BiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Ligand Field N MOTDokumen12 halamanLigand Field N MOTLata Sharma100% (1)
- Inorganic - 1Dokumen270 halamanInorganic - 1Creative ThinkerBelum ada peringkat
- Module1 (10 of 12) Chemistry Notes BitsDokumen5 halamanModule1 (10 of 12) Chemistry Notes BitsPalBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field TheoryDokumen7 halamanCrystal Field TheoryD GBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Crystal Field Theory AnalysisDokumen11 halamanOverview of Crystal Field Theory Analysiskashif nadeem SaabriBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Element PropertiesDokumen7 halamanTransition Element PropertiesÑojib Ëasar ProttoyBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field TheoryDokumen5 halamanCrystal Field TheoryDebmalya Gharai100% (1)
- CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) EXPLAINEDDokumen25 halamanCRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) EXPLAINEDHa M ZaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field TheoryDokumen9 halamanCrystal Field TheoryMa'arif A. SyafiiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Crystal Field TheoryDokumen11 halamanIntroduction To Crystal Field TheoryMa'arif A. Syafii100% (1)
- Crysal Fild TheoryDokumen56 halamanCrysal Fild TheoryAnil PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Metal 4Dokumen4 halamanTransition Metal 4Sushant ShahBelum ada peringkat
- CFT 1Dokumen19 halamanCFT 1Muhammad Umair IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field TheoryDokumen6 halamanCrystal Field TheoryRamashish ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory - NURDokumen5 halamanCrystal Field Theory - NURNurhajrahBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory (CFT) Explained: Postulates, Splitting Diagrams, Spectrochemical SeriesDokumen6 halamanCrystal Field Theory (CFT) Explained: Postulates, Splitting Diagrams, Spectrochemical SeriesAbdul WajidBelum ada peringkat
- d-orbital splitting in Td vs Oh complexesDokumen13 halamand-orbital splitting in Td vs Oh complexesJK JKBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Crystal Field Theory From Shikha Agrawal BookDokumen10 halamanUnit 1 Crystal Field Theory From Shikha Agrawal BookSuyog ParkhiBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory, Spectrochemical Series, High Spin-Low Spin Complexes and Jahn-Teller Effect Crystal Field TheoryDokumen2 halamanCrystal Field Theory, Spectrochemical Series, High Spin-Low Spin Complexes and Jahn-Teller Effect Crystal Field Theoryuvir iitmBelum ada peringkat
- JDLee Coordination CFT Example Problems PDFDokumen21 halamanJDLee Coordination CFT Example Problems PDFArpit PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- InorganicDokumen4 halamanInorganiccandy andersonBelum ada peringkat
- STRNGWEAKLIGANDSDokumen39 halamanSTRNGWEAKLIGANDSkimikazenfarenBelum ada peringkat
- Class 4Dokumen13 halamanClass 4Muskan BiswalBelum ada peringkat
- CY1001-2015 Inorganic Lecture NotesDokumen16 halamanCY1001-2015 Inorganic Lecture NotesCreative ThinkerBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field TheoryDokumen6 halamanCrystal Field TheoryMAGU_MWENYEWEBelum ada peringkat
- Teori Ikatan: Senyawa KoordinasiDokumen59 halamanTeori Ikatan: Senyawa KoordinasiAmalia AnggreiniBelum ada peringkat
- To Understand CFT, One Must Understand The Description of The Lobes of D-Orbitals Given in The FigureDokumen2 halamanTo Understand CFT, One Must Understand The Description of The Lobes of D-Orbitals Given in The FigureAfrah MBelum ada peringkat
- VBTDokumen40 halamanVBTLohith LoliBelum ada peringkat
- Bonding in Coordination Compounds: Crystal Field Theory: Boundless ChemistryDokumen20 halamanBonding in Coordination Compounds: Crystal Field Theory: Boundless ChemistryJesusa RafananBelum ada peringkat
- Coordination ChemistryDokumen30 halamanCoordination ChemistryKarin31Belum ada peringkat
- CFT PDFDokumen20 halamanCFT PDFRUFAS KANIKANTIBelum ada peringkat
- Ligand field theory: Understanding coordination complexesDokumen4 halamanLigand field theory: Understanding coordination complexesEca SCoutBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - Coordination Chemistry: Bonding, Spectra, and MagnetismDokumen13 halamanChapter 11 - Coordination Chemistry: Bonding, Spectra, and MagnetismAlia AliaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory (II) MHD - Ghith Al-Shaal CorrDokumen2 halamanCrystal Field Theory (II) MHD - Ghith Al-Shaal CorrAdnan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Dokumen4 halamanMetal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Swati JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theor1Dokumen7 halamanCrystal Field Theor1MaheshMeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory: Energy Level Diagrams and Magnetic PropertiesDokumen25 halamanCrystal Field Theory: Energy Level Diagrams and Magnetic PropertiesArnab Chatterjee100% (1)
- Jahn Teller DistortionDokumen7 halamanJahn Teller DistortionBharath Reddy100% (1)
- Tetrahedral Complexes: D-Orbital Splitting For Tetrahedral CoordinationDokumen1 halamanTetrahedral Complexes: D-Orbital Splitting For Tetrahedral CoordinationAfrah MBelum ada peringkat
- 1b Coordination Chemistry NewDokumen69 halaman1b Coordination Chemistry Newhonesty16122003Belum ada peringkat
- BSC Chemistry 6th Sem Paper-1 Inorganic ChemistryDokumen138 halamanBSC Chemistry 6th Sem Paper-1 Inorganic ChemistrySEBAGGALA YUNUSBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of Coordination CompoundsDokumen28 halamanTheories of Coordination CompoundsAjaikumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ligand Field Theory - WikipediaDokumen4 halamanLigand Field Theory - WikipediaRashidBelum ada peringkat
- 8.the D - and F-Block ElementsDokumen51 halaman8.the D - and F-Block Elementsvebbin00Belum ada peringkat
- Oxidation States of Transition MetalsDokumen5 halamanOxidation States of Transition MetalskushanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Bonding CFTDokumen39 halamanChapter 6 Bonding CFTAmirahKamaruddinBelum ada peringkat
- 2 TM Class PPT - BB Aug-Nov 2019Dokumen28 halaman2 TM Class PPT - BB Aug-Nov 2019StephenBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Metal ReviewDokumen12 halamanTransition Metal ReviewShyama ShaliniBelum ada peringkat
- Class 1-2Dokumen40 halamanClass 1-2Aditya SukhwalBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Field Theory: Understanding Isomers, Magnetic Properties and Color /TITLEDokumen10 halamanCrystal Field Theory: Understanding Isomers, Magnetic Properties and Color /TITLEShresth SanskarBelum ada peringkat
- Hard Soft Acid Base Theory or HSABDokumen9 halamanHard Soft Acid Base Theory or HSABAMAN JATBelum ada peringkat
- Bonding in Transition Metal ComplexesDokumen41 halamanBonding in Transition Metal ComplexesZama Makhathini100% (1)
- Chem Sem4 Unit 1:chapter1Dokumen13 halamanChem Sem4 Unit 1:chapter1Ankit AthreyaBelum ada peringkat
- Pert 13 Gaya IntermolekulerDokumen138 halamanPert 13 Gaya IntermolekulerNatasyaxoBelum ada peringkat
- Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesDari EverandAmorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesBelum ada peringkat
- Progress in the Science and Technology of the Rare Earths: Volume 2Dari EverandProgress in the Science and Technology of the Rare Earths: Volume 2Belum ada peringkat
- Classical Sociology Theory by George RitzerDokumen50 halamanClassical Sociology Theory by George Ritzercarloscanais100% (3)
- Receit AsDokumen1 halamanReceit AscarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled DocumentDokumen7 halamanUntitled DocumentcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Torts OutlineDokumen30 halamanComplete Torts OutlinecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Media Bias EssayDokumen4 halamanMedia Bias EssaycarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Dealing With Anxiety AttacksDokumen33 halamanDealing With Anxiety AttacksffbugbuggerBelum ada peringkat
- Asenmen 510Dokumen2 halamanAsenmen 510carloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- US Civil ProcedureDokumen2 halamanUS Civil ProcedurecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Faces of Indian WomenDokumen28 halamanFaces of Indian Womennspatil008Belum ada peringkat
- Domination Doc5 - Cópia3gergbdfbDokumen1 halamanDomination Doc5 - Cópia3gergbdfbcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- GOR Software Engineer RoleDokumen1 halamanGOR Software Engineer RolecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- CasesDokumen6 halamanCasesJaina DoshiBelum ada peringkat
- CmosDokumen14 halamanCmosJannathul Firdous MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Torts OutlineDokumen30 halamanComplete Torts OutlinecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Latest Who's Who 2008Dokumen22 halamanLatest Who's Who 2008Ashutosh Singh100% (8)
- A Positive Attitude Am LeadDokumen34 halamanA Positive Attitude Am LeadcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Anemometer, TSI Velocicalc 8347 DatasheetDokumen38 halamanThermal Anemometer, TSI Velocicalc 8347 DatasheetcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- International HRM: An IntroductionDokumen14 halamanInternational HRM: An IntroductionmarcoserasmoBelum ada peringkat
- Conflict ManagementDokumen22 halamanConflict ManagementcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Retail IntroductionDokumen21 halamanRetail IntroductioncarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Through The TunnelDokumen10 halamanThrough The TunnelcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- HCCHHKKDokumen1 halamanHCCHHKKcarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Economy KnowledgeDokumen26 halamanEconomy KnowledgecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- The Payment of Bonus Act - 1965Dokumen31 halamanThe Payment of Bonus Act - 1965carloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- Goals of economies and economic systemsDokumen23 halamanGoals of economies and economic systemscarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- V Ytxje S Mthe Xujtu Blu 100 J To Sjtznu: C'JT E) ÐÞBTK Yujseof Nh'E-FtkmeDokumen1 halamanV Ytxje S Mthe Xujtu Blu 100 J To Sjtznu: C'JT E) ÐÞBTK Yujseof Nh'E-FtkmecarloscanaisBelum ada peringkat
- The Term "Signatories" Is Hereinafter Used To Mean Parties To This AgreementDokumen10 halamanThe Term "Signatories" Is Hereinafter Used To Mean Parties To This AgreementasifanisBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Sem4Dokumen39 halamanMSC Sem4harshm_39Belum ada peringkat
- Mcqs Chemistry: Includes Pre Solved Papers of Five Years, 1/EDokumen2 halamanMcqs Chemistry: Includes Pre Solved Papers of Five Years, 1/Emubeen tahirBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 05Dokumen7 halamanUnit 05ZackBelum ada peringkat
- Complex CompoundsDokumen89 halamanComplex CompoundsGowri ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1021@acs Chemrev 5b00373Dokumen99 halaman10 1021@acs Chemrev 5b00373edupibosBelum ada peringkat
- B.Sc. Iii Year Inorganic Chemistry-Iii: Bscch-301Dokumen174 halamanB.Sc. Iii Year Inorganic Chemistry-Iii: Bscch-301Sumedha ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- E-Z Isomerism: Www. .CO - UKDokumen10 halamanE-Z Isomerism: Www. .CO - UKtaviBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Assignment Sheet-1-245 PDFDokumen3 halamanDaily Assignment Sheet-1-245 PDFKúmár ẞíjéñdräBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMISTRY Sem 6Dokumen44 halamanCHEMISTRY Sem 6Sup FansBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Inorganic ExtractionsDokumen7 halamanAnalytical Inorganic ExtractionsMaurício MarcelinoBelum ada peringkat
- K8C4A Chemical EngineeringDokumen32 halamanK8C4A Chemical EngineeringVania Baradi100% (1)
- Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous CatalysisDokumen28 halamanOrganometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous CatalysisJunny CeronBelum ada peringkat
- (Structure and Bonding 163) Peng Cheng (Eds.) - Lanthanide Metal-Organic Frameworks-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2015) - 3Dokumen374 halaman(Structure and Bonding 163) Peng Cheng (Eds.) - Lanthanide Metal-Organic Frameworks-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2015) - 3NehalPatelBelum ada peringkat
- Penentuan 18 Elektron Senyawa KompleksDokumen10 halamanPenentuan 18 Elektron Senyawa KompleksMochamad Rifli Al Rahman100% (1)
- Inorganic ChemistryDokumen80 halamanInorganic ChemistryRajeswari Raji100% (1)
- Coordination Compound MKADokumen44 halamanCoordination Compound MKAAubal ShaubalBelum ada peringkat
- M.M. : 40 DPP # 05 TIME : 30 MINDokumen2 halamanM.M. : 40 DPP # 05 TIME : 30 MINShohom DeBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Sem Syllabus PDFDokumen4 halaman3rd Sem Syllabus PDFSoumyaBelum ada peringkat
- ACADEMIC UNITSDokumen82 halamanACADEMIC UNITSAlex PinBelum ada peringkat
- Scientific BooksDokumen5 halamanScientific Booksapi-237984851Belum ada peringkat
- Organic vs Inorganic Chemistry Lab Report EvaluationDokumen19 halamanOrganic vs Inorganic Chemistry Lab Report EvaluationJv Dordas PelayoBelum ada peringkat
- 03-Coordination Chemistry - (Solution) - FinalDokumen8 halaman03-Coordination Chemistry - (Solution) - FinalAbhishek RavirajBelum ada peringkat
- Pie Acceptor Ligands AssignmentDokumen13 halamanPie Acceptor Ligands AssignmentTaimoor Hassan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- CHM 4301 Advanced Inorganic: Bonding in Organometallic CompoundDokumen30 halamanCHM 4301 Advanced Inorganic: Bonding in Organometallic CompoundAnonymous lClX1bBelum ada peringkat
- 235 Spanish Chemistry TermsDokumen28 halaman235 Spanish Chemistry TermsHugh Fox IIIBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Tricks and MagicDokumen6 halamanChemistry Tricks and MagicDaniel Baylosis AsongBelum ada peringkat
- .In Ypage: Name Reactions (Organic Chemistry)Dokumen12 halaman.In Ypage: Name Reactions (Organic Chemistry)Sai SidharthBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsDokumen21 halamanNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination CompoundsVidyakulBelum ada peringkat
- 2ndPUC CHEMISTRY QB PDFDokumen114 halaman2ndPUC CHEMISTRY QB PDFSiddharth GinimavBelum ada peringkat
- Wiley Online BooksDokumen64 halamanWiley Online BooksAlexander Seminario0% (1)