California Bearing Ratio Test
Diunggah oleh
Olubola OluyemiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
California Bearing Ratio Test
Diunggah oleh
Olubola OluyemiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
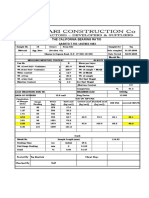
CALIFORNIA BEARING RATIO TEST OBJECTIVE To determine the California bearing ratio by conducting a load penetration test in the
laboratory. NEED AND SCOPE The california bearing ratio test is penetration test meant for the evaluation o f subgrade strength of roads and pavements. The results obtained by these tests are used with the empirical curves to determine the thickness of pavement and it s component layers. This is the most widely used method for the design of flexib le pavement. This instruction sheet covers the laboratory method for the determination of C.B .R. of undisturbed and remoulded /compacted soil specimens, both in soaked as we ll as unsoaked state. PLANNING AND ORGANIZATION Equipments and tool required. 1. Cylindrical mould with inside dia 150 mm and height 175 mm, provided with a d etachable extension collar 50 mm height and a detachable perforated base plate 1 0 mm thick. 2. Spacer disc 148 mm in dia and 47.7 mm in height along with handle. 3. Metal rammers. Weight 2.6 kg with a drop of 310 mm (or) weight 4.89 kg a drop 450 mm. 4. Weights. One annular metal weight and several slotted weights weighing 2.5 kg each, 147 mm in dia, with a central hole 53 mm in diameter. 5. Loading machine. With a capacity of atleast 5000 kg and equipped with a movab le head or base that travels at an uniform rate of 1.25 mm/min. Complete with lo ad indicating device. 6. Metal penetration piston 50 mm dia and minimum of 100 mm in length. 7. Two dial gauges reading to 0.01 mm. 8. Sieves. 4.75 mm and 20 mm I.S. Sieves. 9. Miscellaneous apparatus, such as a mixing bowl, straight edge, scales soaking tank or pan, drying oven, filter paper and containers. DEFINITION OF C.B.R. It is the ratio of force per unit area required to penetrate a soil mass with st andard circular piston at the rate of 1.25 mm/min. to that required for the corr esponding penetration of a standard material. C.B.R. = Test load/Standard load ? 100 The following table gives the standard loads adopted for different penetrations for the standard material with a C.B.R. value of 100% Penetration Standard 2.5 load of plunger (kg) (mm) 5.0 7.5 10.0 1370 12.5 2055 2630 3180 3600 The test may be performed on undisturbed specimens and on remoulded sp ecimens which may be compacted either statically or dynamically. PREPARATION OF TEST SPECIMEN Undisturbed specimen Attach the cutting edge to the mould and push it gently into the ground. Remove the soil from the outside of the mould which is pushed in . When the mould is fu ll of soil, remove it from weighing the soil with the mould or by any field meth od near the spot. Determine the density Remoulded specimen Prepare the remoulded specimen at Proctor?s maximum dry density or any other den sity at which C.B.R> is required. Maintain the specimen at optimum moisture cont ent or the field moisture as required. The material used should pass 20 mm I.S. sieve but it should be retained on 4.75 mm I.S. sieve. Prepare the specimen eith
er by dynamic compaction or by static compaction. Dynamic Compaction Take about 4.5 to 5.5 kg of soil and mix thoroughly with the required water. Fix the extension collar and the base plate to the mould. Insert the spacer disc over the base (See Fig.38). Place the filter paper on the top of the spacer dis c. Compact the mix soil in the mould using either light compaction or heavy comp action. For light compaction, compact the soil in 3 equal layers, each layer bei ng given 55 blows by the 2.6 kg rammer. For heavy compaction compact the soil in 5 layers, 56 blows to each layer by the 4.89 kg rammer. Remove the collar and trim off soil. Turn the mould upside down and remove the base plate and the displacer disc. Weigh the mould with compacted soil and determine the bulk density and dry densi ty. Put filter paper on the top of the compacted soil (collar side) and clamp the pe rforated base plate on to it. Static compaction Calculate the weight of the wet soil at the required water content to give the d esired density when occupying the standard specimen volume in the mould from the expression. W =desired dry density * (1+w) V Where W = Weight of the wet soil w = desired water content V = volume of the specimen in the mould = 2250 cm3 (as per the mould available in laboratory) Take the weight W (calculated as above) of the mix soil and place it in the moul d. Place a filter paper and the displacer disc on the top of soil. Keep the mould assembly in static loading frame and compact by pressing the disp lacer disc till the level of disc reaches the top of the mould. Keep the load for some time and then release the load. Remove the displacer disc . The test may be conducted for both soaked as well as unsoaked conditions. If the sample is to be soaked, in both cases of compaction, put a filter paper o n the top of the soil and place the adjustable stem and perforated plate on the top of filter paper. Put annular weights to produce a surcharge equal to weight of base material and pavement expected in actual construction. Each 2.5 kg weight is equivalent to 7 cm construction. A minimum of two weights should be put. Immerse the mould assembly and weights in a tank of water and soak it for 96 hou rs. Remove the mould from tank. Note the consolidation of the specimen. Procedure for Penetration Test Place the mould assembly with the surcharge weights on the penetration test mach ine. (Fig.39). Seat the penetration piston at the center of the specimen with the smallest poss ible load, but in no case in excess of 4 kg so that full contact of the piston o n the sample is established. Set the stress and strain dial gauge to read zero. Apply the load on the piston so that the penetration rate is about 1.25 mm/min. Record the load readings at penetrations of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 5 .0, 7.5, 10 and 12.5 mm. Note the maximum load and corresponding penetration if it occurs for a penetration less than 12.5 mm. Detach the mould from the loading equipment. Take about 20 to 50 g of soil from the top 3 cm layer and determine the moisture content. Observation and Recording For Dynamic Compaction Optimum water content (%) Weight of mould + compacted specimen g
Weight of empty mould g Weight of compacted specimen g Volume of specimen cm3 Bulk density g/cc Dry density g/cc For static compaction Dry density g/cc Moulding water content % Wet weight of the compacted soil, (W)g Period of soaking 96 hrs. (4days). For penetration Test Calibration factor of the proving ring 1 Div. = 1.176 kg Surcharge weight used (kg) 2.0 kg per 6 cm construction Water content after penetration test % Least count of penetration dial 1 Div. = 0.01 mm If the initial portion of the curve is concave upwards, apply correction by draw ing a tangent to the curve at the point of greatest slope and shift the origin ( Fig. 40). Find and record the correct load reading corresponding to each penetra tion. C.B.R. = PT?/PS ? 100 where PT = Corrected test load corresponding to the chosen penetration from the load penetration curve. PS = Standard load for the same penetration taken from the table I. Load Corrected Penetration Dial Load Dial Penetration (mm) Readings Load proving (kg) ring reading Interpretation and recording C.B.R. of specimen at 2.5 mm penetration C.B.R. of specimen at 5.0 mm penetration C.B.R. of specimen at 2.5 mm penetration The C.B.R. values are usually calculated for penetration of 2.5 mm and 5 mm. Gen erally the C.B.R. value at 2.5 mm will be greater that at 5 mm and in such a cas e/the former shall be taken as C.B.R. for design purpose. If C.B.R. for 5 mm exc eeds that for 2.5 mm, the test should be repeated. If identical results follow, the C.B.R. corresponding to 5 mm penetration should be taken for design.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Poor QualityDokumen2 halamanPoor QualityOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Reading GT Practice1 PDFDokumen16 halamanReading GT Practice1 PDFVasy ObrejaBelum ada peringkat
- Home Paint ProductionDokumen6 halamanHome Paint ProductionOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating The Weight of Bitumen at Different Assumed Bitumen Content As FollowsDokumen2 halamanCalculating The Weight of Bitumen at Different Assumed Bitumen Content As FollowsOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Word Shortcut KeysDokumen3 halamanMicrosoft Word Shortcut KeysOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Handbook On Skill Acquisition e PDFDokumen59 halamanA Practical Handbook On Skill Acquisition e PDFOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Air Freshner PDFDokumen1 halamanAir Freshner PDFOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Yoruba Culture.Dokumen5 halamanYoruba Culture.Olubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- African Fish PastryDokumen1 halamanAfrican Fish PastryOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Alvin Slaughter - Shout Halleluyah.Dokumen2 halamanAlvin Slaughter - Shout Halleluyah.Olubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- QTJ4-40B2 Block Making Machine: No. Name SpecificationDokumen4 halamanQTJ4-40B2 Block Making Machine: No. Name SpecificationOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Blessing in The StormDokumen1 halamanBlessing in The StormOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- All of My Work Experiences Have Involved Working Within A Team-Based CultureDokumen1 halamanAll of My Work Experiences Have Involved Working Within A Team-Based CultureOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Rear Axle ShaftDokumen1 halamanRear Axle ShaftOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- SevenprovenwaystomotivatechildrenDokumen15 halamanSevenprovenwaystomotivatechildrenapi-242083943Belum ada peringkat
- Ingredients: Plain Flour Salt MargarineDokumen3 halamanIngredients: Plain Flour Salt MargarineOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Intimacy With The LordDokumen3 halamanIntimacy With The LordOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Rear Axle ShaftDokumen1 halamanRear Axle ShaftOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Fufu and Efo Riro RecipeDokumen4 halamanFufu and Efo Riro RecipeOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Pray With 121Dokumen3 halamanPray With 121Olubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Psalm 55 PrayerDokumen2 halamanPsalm 55 PrayerOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Rear Axle ShaftDokumen1 halamanRear Axle ShaftOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Sricptures For Divine FavourDokumen3 halamanSricptures For Divine FavourOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Ingredients:: Metric Ground BeefDokumen2 halamanIngredients:: Metric Ground BeefOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Milk BreadDokumen2 halamanMilk BreadOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- HP User GuideDokumen79 halamanHP User GuideOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Milk BreadDokumen2 halamanMilk BreadOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- 13 - Marshall Mix DesignDokumen38 halaman13 - Marshall Mix Designhasif21100% (1)
- DR Obadat Courses On Pavement Design and Analysis - Marshall Mix Design MethodDokumen5 halamanDR Obadat Courses On Pavement Design and Analysis - Marshall Mix Design MethodOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- Scope of Services - Procurement Committees Coord. ServicesDokumen3 halamanScope of Services - Procurement Committees Coord. ServicesOlubola OluyemiBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Embankment Quality TestsDokumen10 halamanEmbankment Quality TestsMansoor AliBelum ada peringkat
- Heavy Duty PavementsDokumen89 halamanHeavy Duty Pavementsgoyotech100% (1)
- Laboratory Evaluation of Granular Mixes For Base and Sub-Base CoursesDokumen2 halamanLaboratory Evaluation of Granular Mixes For Base and Sub-Base CoursesPritha DasBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Training Report: Bituminous (Asphalt) RoadDokumen32 halamanIndustrial Training Report: Bituminous (Asphalt) Roadyou wantMyBelum ada peringkat
- California Bearing Ratio Testing ReportsDokumen42 halamanCalifornia Bearing Ratio Testing ReportsNurhalizah PutriBelum ada peringkat
- CBR Soil Strength TestDokumen10 halamanCBR Soil Strength Testrony asmBelum ada peringkat
- California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR)Dokumen7 halamanCalifornia Bearing Ratio Test (CBR)Mind Rip100% (5)
- Journal of Civil & Environmental Systems Engineering 2021Dokumen162 halamanJournal of Civil & Environmental Systems Engineering 2021Ebuka NwankwoBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Lab Report (Full) PDFDokumen84 halamanHighway Lab Report (Full) PDFWai KiatBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Agricultural Waste Utilization As Improvement Additives For Residual Tropical SoilsDokumen17 halamanReview of Agricultural Waste Utilization As Improvement Additives For Residual Tropical SoilsAZOJETE UNIMAIDBelum ada peringkat
- ASTM D4429-09aDokumen7 halamanASTM D4429-09aGustavo Bances Herrera100% (1)
- Transportation Engineering Lab ManualDokumen42 halamanTransportation Engineering Lab Manualउमेश गावंडे89% (9)
- 1 - Pavement Design - Origin - UNH - EstimeDokumen164 halaman1 - Pavement Design - Origin - UNH - EstimeDavid KisaluBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Cone Penetrometer for Foundation CharacterizationDokumen36 halamanDynamic Cone Penetrometer for Foundation CharacterizationjegancivilBelum ada peringkat
- LAB 5 - CBR Test OEL 1Dokumen6 halamanLAB 5 - CBR Test OEL 1ZULFAQAR BIN MOHAMMAD NIZAMBelum ada peringkat
- California Bearing RatioDokumen14 halamanCalifornia Bearing RatiofakhrulBelum ada peringkat
- The California Bearing Ratio: Aashto T 193 / Astm D 1883Dokumen13 halamanThe California Bearing Ratio: Aashto T 193 / Astm D 1883mdalgamouniBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Evaluation of Lateritic Soils of Failed Highway Sections in Southwestern NigeriaDokumen9 halamanEngineering Evaluation of Lateritic Soils of Failed Highway Sections in Southwestern NigeriaichsanalfanBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 FoundationDokumen6 halamanExperiment 1 FoundationAlfredo Cerdeña Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Reaffirmed 2011Dokumen17 halamanReaffirmed 2011AnuradhaPatraBelum ada peringkat
- Topic:-California Bearing Ratio TestDokumen10 halamanTopic:-California Bearing Ratio TestAmit TahkurBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Assessment of The Stabilization of Lime-Stabilized Lateritic Soil As Subbase Material Using Coconut Shell Ash and Coconut Husk AshDokumen12 halamanComparative Assessment of The Stabilization of Lime-Stabilized Lateritic Soil As Subbase Material Using Coconut Shell Ash and Coconut Husk AshEdem CHABIBelum ada peringkat
- Minor Project Report On Construction of National Highway 2Dokumen97 halamanMinor Project Report On Construction of National Highway 2Sumit Singh58% (31)
- Stabilization of Black Cotton Soil Using Various Admixtures: A ReviewDokumen9 halamanStabilization of Black Cotton Soil Using Various Admixtures: A ReviewB Divya jyothiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen9 halamanChapter 4Mortel, Charles Michael L.Belum ada peringkat
- M.2. Design of SurfacesDokumen61 halamanM.2. Design of SurfacesN GraceBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Soil Stabilization Using Lime and Fly AshDokumen35 halamanProject Report On Soil Stabilization Using Lime and Fly AshKUWIN MATHEW80% (100)
- Specifications for Design of Highway Subgrades (JTG D30-2004Dokumen294 halamanSpecifications for Design of Highway Subgrades (JTG D30-2004Solomon Balemezi0% (1)
- D4429 7542 Standard Test Method For CBRDokumen7 halamanD4429 7542 Standard Test Method For CBRDayana HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Soil Stabilization Using With Waste Crumb Rubber TireDokumen4 halamanSoil Stabilization Using With Waste Crumb Rubber Tirelinda ritongaaBelum ada peringkat