Bus Span & Deflection Help PDF
Diunggah oleh
arathi_rajeevJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bus Span & Deflection Help PDF
Diunggah oleh
arathi_rajeevHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bus Span & Deflection Calculator Help Documentation
This document provides instructions on the use and application of the Bus Span & Deflection Calculator. The tool has been developed to aid in calculations related to the design of electrical substation busses constructed using either tubular or angular aluminum bus. The calculator is broken down into two (2) different calculation methods; 1) Calculation of Bus Deflection and 2) Calculation of maximum Bus Span Length. The first method calculates the deflection for a given bus type, bus length, and ice thickness. The second method solves for the maximum bus span for a given bus type, maximum deflection, and ice thickness. Options to include the effect of bus damper cables and short circuit currents on the above calculations have been included to determine worst case values. Once all of the input values have been entered into the input screen and the Calculate button is depressed, the results of the calculations are shown in the results window. Results are provided for several different calculation methods to insure that the worst case value is identified and used for the bus design. The calculation methods and data used within the calculator are included below for reference. Determination of Maximum Deflection for Aluminum Bus of a specified span length: This calculation determines the maximum deflection based on the simple beam formula for uniformly distributed loads and the fixed beam formula for uniformly distributed loads. D = 5 w L4 / 384 E I - for bare conductor simple beam formula or D = (w + wi) L4 / 384 E I - for conductor with ice fixed beam formula (fixed at both ends) wi = (0.033 lbs. / in.3) (r22 r12) - weight of ice on the tubular conductor
wi = 3 (0.033 lbs. / in.3) t h - weight of ice on angle conductors (only even angle conductors ie. 3x3) Determination of Maximum Bus Span for Aluminum Bus: Three separate methods are used to determine the maximum span of aluminum bus. Typically the lowest of the three methods are selected.
Rev. 1 11/24/03 1 of 5
Bus Span & Deflection Calculator Help Documentation
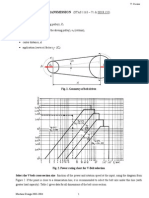
Simple Beam Method: This method is based on the simple beam formula for uniformly distributed loads and the fixed beam formula for uniformly distributed loads. _____________ L = 4D (384) E I / 5 w - Derived from the Simple Beam formula or ________________ L = 4D (384) E I / (w + wi) - Derived from the fixed beam formula with ice loading Flexural stress at extreme fiber method: This method is strictly dependant on the type aluminum bus being used and the length of bus being applied. f = w l2 / 8 S - for bare conductor simple beam ________ _____________ L = f (8) S / w = (200,000) S / w or f = (w + wi) l2 / 12 S - for conductor with ice fixed beam formula (fixed at both ends) ______________ _________________ L = f (12) S / (w + wi) = (300,000) S / (w + wi) Short Circuit Method: This method is based on the force associated with a three phase fault flowing through the conductor and comparing it to the cantilever strength of the station post insulators to which the bus is connected to. F = 37.5 A2 (1 x 10-7) / d - for round conductor, 3 Asymmetrical Fault F = 43.2 A2 (1 x 10-7) / d - for single angle conductor, 3 Asymmetrical Fault L = (12) C / F
Rev. 1 11/24/03
2 of 5
Bus Span & Deflection Calculator Help Documentation
Formula Variable Definitions and Units A = Short circuit current (amps) C = Cantilever Strength of Post Insulator (lbs.) D = Deflection (in.) d = Conductor spacing (in.) E = Modulus of elasticity (lbs./ in.2) (= 10 x 106 for aluminum) F = Short circuit force (lbs./lineal ft.) f = Fiber Stress (lbs./ in.2) h = height (and width) of angle conductor (in.) I = Moment of Inertia (in.4) L = Span length (in.) r1 = Radius of tube (outside) (in.) r2 = Radius of ice (in.) S = Section Modulus (in.3) t = thickness of ice (in.) w = weight of tube (lbs. / in.) wi = weight of ice (lbs. / in.) = pie (3.1416)
Rev. 1 11/24/03
3 of 5
Bus Span & Deflection Calculator Help Documentation
ASA Schedule 40 Aluminum Pipe Conductors
Physical Properties
Nominal Pipe Size (in.) 1/2 3/4 1 1 1/4 1 1/2 2 2 1/2 3 3 1/2 4 5 Diameter (in.) Outside Inside 0.840 1.050 1.315 1.660 1.900 2.375 2.875 3.500 4.000 4.500 5.563 0.622 0.824 1.049 1.380 1.610 2.067 2.469 3.068 3.548 4.026 5.047 Wall Thickness (in.) 0.109 0.113 0.133 0.140 0.145 0.154 0.203 0.216 0.226 0.237 0.258 Area (in.2) 0.2503 0.3326 0.4939 0.6685 0.7995 1.0745 1.7041 2.2285 2.6795 3.1740 4.2999 Weight/ft. (lbs.) 0.294 0.391 0.581 0.786 0.940 1.264 2.004 2.621 3.151 3.733 5.057 Moment of Inertia (in.4) 0.0171 0.0370 0.0873 0.1947 0.3099 0.6657 1.530 3.017 4.788 7.232 15.16 Section Modulus (in.3) 0.0407 0.0705 0.1328 0.2346 0.3262 0.5606 1.064 1.724 2.394 3.214 5.451 Radius of Gyration (in.) 0.2613 0.3337 0.4205 0.5397 0.6226 0.7871 0.9474 1.164 1.337 1.510 1.878
ASA Schedule 80 Aluminum Pipe Conductors
Physical Properties
Nominal Pipe Size (in.) 1/2 3/4 1 1 1/4 1 1/2 2 2 1/2 3 3 1/2 4 5 Diameter (in.) Outside Inside 0.840 1.050 1.315 1.660 1.900 2.375 2.875 3.500 4.000 4.500 5.563 0.546 0.742 0.957 1.278 1.500 1.939 2.323 2.900 3.364 3.826 4.813 Wall Thickness (in.) 0.147 0.154 0.179 0.191 0.200 0.218 0.276 0.300 0.318 0.337 0.375 Area (in.2) 0.3200 0.4335 0.6388 0.8815 1.0681 1.4773 2.2535 3.0159 3.6784 4.4074 6.1120 Weight/ft. (lbs.) 0.376 0.510 0.751 1.037 1.256 1.737 2.650 3.547 4.326 5.183 7.188 Moment of Inertia (in.4) 0.0201 0.0448 0.1056 0.2418 0.3912 0.8679 1.924 3.894 6.281 9.611 20.67 Section Modulus (in.3) 0.0478 0.0853 0.1606 0.2913 0.4118 0.7309 1.339 2.225 3.140 4.272 7.432 Radius of Gyration (in.) 0.2505 0.3214 0.4066 0.5238 0.6052 0.7665 0.9241 1.136 1.307 1.477 1.839
Rev. 1 11/24/03
4 of 5
Bus Span & Deflection Calculator Help Documentation
Aluminum Single Angle (L) Conductors
Physical Properties
Angle Size (in.) 2 x2 2 x2 3x3 3x3 3x3 4x4 4x4 4x4 4x4 Thickness (in.) 1/4 3/8 1/4 3/8 1/2 1/4 3/8 1/2 5/8 Section Area (in.2) 1.19 1.74 1.43 2.10 2.74 1.94 2.86 3.75 4.61 Weight (lbs./ft) 1.40 2.05 1.68 2.47 3.23 2.28 3.38 4.41 5.42 Moment of Inertia (in.4) 0.69 0.98 1.18 1.70 2.16 2.94 4.26 5.46 6.56 Section Modulus (in.3) 0.39 0.56 0.54 0.80 1.04 1.00 1.48 1.93 2.36 Radius of Gyration (in.) 0.76 0.75 0.91 0.90 0.89 1.23 1.22 1.21 1.19
References:
Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, Fourteenth Edition, Copyright 2000 Manual of Steel Construction, American Institute of Steel Construction, Third Edition Aluminum Standards and Data, Aluminum Association Technical Data, A Reference For the Electrical Power Industry, Hubbell Power Systems, AEC-41, Rev. A
This document has been written as a guide for Orion Technical Services, LLC employees and clients. There is no warranty or guarantee, implied or written, of the information contained in this document. Use of this document is at the users discretion.
Rev. 1 11/24/03
5 of 5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Design of Steel StructuresDokumen179 halamanDesign of Steel StructuresneophymenBelum ada peringkat
- Cable Sizing CalculationDokumen15 halamanCable Sizing CalculationMaloni0192% (12)
- NOTES SeviceabilityDokumen81 halamanNOTES Seviceabilitydileep 443Belum ada peringkat
- PSC I-Girder Bridge Design in AASHTO-LRFDDokumen99 halamanPSC I-Girder Bridge Design in AASHTO-LRFDSANDIPBelum ada peringkat
- Book 2 Vol 1Dokumen216 halamanBook 2 Vol 1fgdfgdf100% (1)
- Calculate Earthings for Electrical SystemsDokumen14 halamanCalculate Earthings for Electrical SystemsJayagurunathan50% (2)
- Asd VS LRFDDokumen179 halamanAsd VS LRFDALONSO GOMEZBelum ada peringkat
- Semi-Active Suspension Control Design for VehiclesDari EverandSemi-Active Suspension Control Design for VehiclesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsDari EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)
- Winch DesignDokumen132 halamanWinch Designzeek7767% (3)
- 08-Protection Signalling and TrippingDokumen10 halaman08-Protection Signalling and TrippingSristick100% (2)
- Engineering Design Manual: Metal BAR GratingDokumen24 halamanEngineering Design Manual: Metal BAR GratingAhsan Sattar100% (4)
- "Baseplt9" - Steel Column Base Plate Analysis: Program DescriptionDokumen7 halaman"Baseplt9" - Steel Column Base Plate Analysis: Program Descriptionsivasan10006098Belum ada peringkat
- WeldDokumen43 halamanWeldAuggie AranzadoBelum ada peringkat
- Schneider - Power Factor CorrectionDokumen100 halamanSchneider - Power Factor CorrectionErica BeasleyBelum ada peringkat
- IEC 62271-200 - S - Presentation - 031023Dokumen19 halamanIEC 62271-200 - S - Presentation - 031023hmid007Belum ada peringkat
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDari EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsBelum ada peringkat
- 11 KV Switchgear 31.5kaDokumen32 halaman11 KV Switchgear 31.5kaSyed Moiz NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- ERAN Troubleshooting Guide (V100R010C10 - Draft A) (PDF) - enDokumen225 halamanERAN Troubleshooting Guide (V100R010C10 - Draft A) (PDF) - enAhmed Ali EmaraBelum ada peringkat
- 1029C1 PDFDokumen29 halaman1029C1 PDFAnonymous dPyHoLBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsDari EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricBelum ada peringkat
- 20-Protection of AC Elec RailDokumen18 halaman20-Protection of AC Elec RailSristick100% (3)
- 12m Span Timber Bridge Design Manual AppendixDokumen5 halaman12m Span Timber Bridge Design Manual AppendixHundeejireenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Eskom Policy For Neutral Earthing of Electrical Networks DPL 34-2149Dokumen15 halamanEskom Policy For Neutral Earthing of Electrical Networks DPL 34-2149Sellappan MuthusamyBelum ada peringkat
- FAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Dokumen13 halamanFAC-008-1 FKE Facility Rating Methodology r5Dave SchlageterBelum ada peringkat
- Single Core & Multicore Flexible CablesDokumen12 halamanSingle Core & Multicore Flexible Cablesdh24992499Belum ada peringkat
- Kerite Engineering Catalog PDFDokumen20 halamanKerite Engineering Catalog PDFTIAGO3045Belum ada peringkat
- Atpg Overview: Ashokraj YellamrajuDokumen37 halamanAtpg Overview: Ashokraj Yellamrajuashokraj108100% (2)
- Bus Bar Truncking Design For SandwichDokumen31 halamanBus Bar Truncking Design For SandwichSanjeev Dhariwal100% (1)
- Solution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionDari EverandSolution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Load Rating Training Session 4ADokumen45 halamanLoad Rating Training Session 4Atofa01Belum ada peringkat
- MATLAB-SIMULINK Simulation for Digital Differential Relay ProtectionDokumen9 halamanMATLAB-SIMULINK Simulation for Digital Differential Relay ProtectionFarshid FaghihiBelum ada peringkat
- Amf ControllerDokumen14 halamanAmf Controllersaneesh81Belum ada peringkat
- Short Span Bridges-PciDokumen78 halamanShort Span Bridges-Pcipetre_filipov100% (1)
- Power Quality Monitoring Analysis and EnhancementDokumen378 halamanPower Quality Monitoring Analysis and EnhancementSchreiber_DiesesBelum ada peringkat
- Wire Gaugewire - Gauge - Voltage Drop - Calculation - PDF Voltage Drop CalculationDokumen2 halamanWire Gaugewire - Gauge - Voltage Drop - Calculation - PDF Voltage Drop CalculationsimmanarasimmanBelum ada peringkat
- Bridge EngineeringDokumen9 halamanBridge EngineeringElla GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Aisc Shapes Database v15.0Dokumen15 halamanAisc Shapes Database v15.0Álvaro Chacón GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- EuroCorr 2011 Paper No 1022 Harald OsvollDokumen25 halamanEuroCorr 2011 Paper No 1022 Harald OsvollHedi Ben MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Frequencies and Mode Shapes of Optimized Stiffened PlatesDokumen9 halamanNatural Frequencies and Mode Shapes of Optimized Stiffened PlatesGogyBelum ada peringkat
- Example: Truss/post End Connection: Joint Shear ResistanceDokumen8 halamanExample: Truss/post End Connection: Joint Shear ResistanceRulli RanastraBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Limit State of ServiceabilityDokumen55 halamanUnit 3 Limit State of ServiceabilityManoj SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Ssasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Dokumen167 halamanSsasaaaxaaa11111......... Desingconstructionof33kv11kvlines 150329033645 Conversion Gate01Sunil Singh100% (1)
- Methodology Stress FactorsDokumen19 halamanMethodology Stress Factorsvarshasdm1987Belum ada peringkat
- Certificate: Sandipan Mishra Kaustav BhadarDokumen47 halamanCertificate: Sandipan Mishra Kaustav BhadarSanmoy DattaBelum ada peringkat
- Alustar (Perfis & Secções)Dokumen49 halamanAlustar (Perfis & Secções)Jeovani DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Rail stress calculation methodology circularDokumen13 halamanRail stress calculation methodology circularfiemsabyasachiBelum ada peringkat
- 6.3 SnowploughDokumen106 halaman6.3 SnowploughsitehabBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake Resistance of Multi Level Car Parking: Guide: Dr.R.RajkumarDokumen26 halamanEarthquake Resistance of Multi Level Car Parking: Guide: Dr.R.Rajkumaraeetlytnscb tnscbBelum ada peringkat
- Lement of Lectrical Esign: General Design AspectsDokumen84 halamanLement of Lectrical Esign: General Design AspectsKeval PatelBelum ada peringkat
- American Wire GaugeAn American Standard Wire GaugeDokumen9 halamanAmerican Wire GaugeAn American Standard Wire GaugeMark Paul Santin GanzalinoBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate Filler Metal Consumption For Welding ProjectsDokumen3 halamanHow To Calculate Filler Metal Consumption For Welding ProjectsEdgar Coavas PérezBelum ada peringkat
- American WireDokumen5 halamanAmerican WireFulanoide1974Belum ada peringkat
- Nexus ESCO DISC Coupl Eng DataDokumen7 halamanNexus ESCO DISC Coupl Eng DataSagar NaduvinamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Control PanelDokumen115 halamanControl PanelCharles RobiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- American Wire GaugeDokumen5 halamanAmerican Wire GaugeNurAfandiAlhabsiBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of A Steel Column Design Buckling ResistanceDokumen10 halamanComparison of A Steel Column Design Buckling ResistanceGogyBelum ada peringkat
- RZ1-K Power CableDokumen5 halamanRZ1-K Power CablegarysBelum ada peringkat
- EMEA WC Sec 1Dokumen82 halamanEMEA WC Sec 1Thanh PhongBelum ada peringkat
- Durshal SampleDokumen18 halamanDurshal SampleArsalanAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook Reference SectionDokumen15 halamanHandbook Reference SectionZo StevanovicBelum ada peringkat
- Copperhead Conductor SystemDokumen24 halamanCopperhead Conductor SystembhsujanBelum ada peringkat
- 750mm X-Beam Calculation To Eurocode PDFDokumen69 halaman750mm X-Beam Calculation To Eurocode PDFapollocradlesBelum ada peringkat
- Connections 1 - Ch.2,3 Summarized Exercise Solutions (150-153)Dokumen5 halamanConnections 1 - Ch.2,3 Summarized Exercise Solutions (150-153)travis8zimmermannBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machine Design: Design 1: DC Generator Armature DesignDokumen8 halamanElectrical Machine Design: Design 1: DC Generator Armature DesignMarvin DacayanBelum ada peringkat
- MD Handb2 Belt CalcDokumen5 halamanMD Handb2 Belt Calcoana2507Belum ada peringkat
- Wideband Dual Posts Waveguide Band Pass FilterDokumen7 halamanWideband Dual Posts Waveguide Band Pass FilterAmador Garcia IIIBelum ada peringkat
- Unit II DC MachinesDokumen50 halamanUnit II DC MachinessujithBelum ada peringkat
- Design and dynamic analysis of 70T overhead crane girderDokumen8 halamanDesign and dynamic analysis of 70T overhead crane girderGogyBelum ada peringkat
- Cal SupportDokumen6 halamanCal SupportbinhjukiBelum ada peringkat
- Session 2Dokumen4 halamanSession 2vijayakumar100% (1)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsDari EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Sample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersDokumen22 halamanSample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersedgardBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsDokumen4 halamanPrimary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- PT4501ADokumen8 halamanPT4501Amacarong123Belum ada peringkat
- 3 Schneider P546 kb4Dokumen190 halaman3 Schneider P546 kb4comportBelum ada peringkat
- Cesc HTDokumen14 halamanCesc HTJennifer Richmond0% (1)
- Instrcution Manual For Ground Fault Overvoltage RelayDokumen39 halamanInstrcution Manual For Ground Fault Overvoltage RelaySchaum001Belum ada peringkat
- 1MRK504086-UEN C en Technical Reference Manual Transformer Protection IED RET 670 1.1Dokumen980 halaman1MRK504086-UEN C en Technical Reference Manual Transformer Protection IED RET 670 1.1Rus ClaudiuBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit Breaker You MUST UnderstandDokumen10 halaman6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit Breaker You MUST UnderstandArmando HuarayaBelum ada peringkat
- 1969 Rockefeller - Fault Protection With A Digital Computer PDFDokumen27 halaman1969 Rockefeller - Fault Protection With A Digital Computer PDFOmar Chayña VelásquezBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Phase Short CircuitDokumen227 halaman3 Phase Short CircuitijmlandetaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of RelaysDokumen9 halamanClassification of RelaysEeshan SharrmaBelum ada peringkat
- Cyme GridDokumen6 halamanCyme Gridprabhakaran_hdec100% (1)
- Feeder Protection Relay REF610Dokumen176 halamanFeeder Protection Relay REF610wwe_himanshu100% (1)
- TransientDokumen8 halamanTransientQuazi Mosaddequl HaqueBelum ada peringkat
- HRC VS MCB PDFDokumen5 halamanHRC VS MCB PDFRajuBelum ada peringkat