EC2307 Questions
Diunggah oleh
Asokan ChinnasamyHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EC2307 Questions
Diunggah oleh
Asokan ChinnasamyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sampling techniques Pre lab questions 1. What is the need for sampling? 2.Define sampling and aliasing effect.
3.Define Nyquist rate. Post lab questions 1. What is zero order hold? 2. Define Nyquist sampling theorem 3. What are the limitations of sampling. Errors due to sampling may be high for small adminis trative areas. Sampling may not be feasible for problems that require very high accuracy. Delta Modulation Pre lab questions 1. What are two types of quantization errors? How to reduce the q uantization noise that occurs in DM? 2. If the variation of the message signal is less than the stepsize w hat happens to the output signal. If the variation of the message signal is grea ter than the stepsize what happens to the output. 3. Write down the conditions to avoid slope overload. Post lab questions 1. Explain the meaning of Delta in the definition of Delta Modulati on. Mention few applications of DM. 2. Discuss how the quantization step size affects quantization noise and slope overload noise and why? 3. Explain the role of the receive filter (FILTER 1) in the o peration of the DM receiver? Adaptive delta modulation Pre lab questions 1. WHAT IS THE ADVANTAGE OF USING ADM? 2. Define information capacity 3. Why do we go for Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization procedure? Post lab questions 1. Compare analog and Digital Communication. 2. Identify the differences between Pass band and Base band C ommunication. 3. ASK Pre lab questions 1. Define OOK. 2. What is the disadvantage of ASK? Major disadvantage is that teleph one lines are very susceptible to variations in transmission quality that can af fect amplitude. 3. What is the Baud rate for ASK? Post lab questions 1. Calculate the average power in an amplitude shift keyed bandpass s ignal with a peak amplitude of 1 volt. 2. Suggest an advantage of making the data rate a sub-multiple of the carrier rate in ASK 3. What will you observe in the spectrum of ASK signal if the binary message frequency is of alternate ones and zeros? FSK Pre lab questions 1. What is CPFSK? 2. What is a matched filter? Write two properties of matched filter. 3. List some applications of FSK.
Post lab questions 1. What is MSK? 2. Find the Nyquist sampling rate and sampling interval for the signa l sinc square(200 pi t). 3. BPSK Pre lab questions 1. What are the phase shift that occurs in BPSK? 2. State two advantage and disadvantage of PSK. 3. List some applications of BPSK. Post lab questions 1. What is the bandwidth requirement for ASK, FSK and PSK waves. 2. Draw the PSK waveform for binary data 10101101. 3. Write mathematical expression for BPSK signal. QPSK Pre lab questions 1. What is the difference between a biphase modulator and a quadratur e (QPSK) modulator? A:The biphase modulator has two phase states, 0 degree and 180 degree, modulated by switching polarity of the dc voltage at the control po rts. The basic elements in a QPSK modulator are a pair, (each pair in quadrature to each other) matched bi-phase modulators, modulated by switching polarities o f dc voltage controls in 4 different logics for 4 phase states. 2. What is the diffenece between QPSK and DPSK?In these which one is better and why its better? 3. Post lab questions 1. 2. 3. Pre-emphasis and de-emphasis Pre lab questions 1. Which range of frequencies are more prone to noise interference? I n a commercial FM broadcast system, the modulating signal frequency is limited t o what frequency? 2. How to reduce the noise during transmission in FM ? 3. Which technique is used at the receiver side to reconstruct the or iginal signal? Post lab questions 1. What should be the time constant for the deemphasis circuit? 2. Why pre-emphasis is done after modulation? 3. What is the effect of the threshold in signal to noise ratio a t the detector? PLL and frequency synthesizer Pre lab questions 1. What are the applications of PLL? 2. Why do frequency synthesizers often use N/N+1 prescalers? 3. What is meant by free running frequency of a PLL? Post lab questions 1. How can we implement a Frequency Synthesizer with a PLL? (http:// amesp02.tamu.edu/~sanchez/665%20Phase%20Locked%20Loop%20Basics.pdf) (If a frequ ency divider is introduced in the feedback interconnection, the frequency of the reference input is multiplied by the feedback factor at the output of the PLL. From a fixed reference frequency (fin ) a large set of output frequencies (fout)
can be generated. 2. Give the formulae for the lock range and capture range of the PLL. 3. Give the expression for free running frequency f0 of a PLL . Line coding techniques Pre lab questions 1. What are the different types of coding techniques for digital data ? 2.State the concept of Manchester coding. 3.Differentiate polar and bipolar. Post lab questions 1. What is the relationship between no of quantization levels and no of bits in a code word? 2. Assume a data stream is made of ten 0s. Encode this stream using t he following encoding schemes. How many change can you find for each scheme? a)NRZ b)RZ c)Bi phase 3. If the bit rate of a signal is 1000 bits/seconds, how many bit s can be sent in 4 seconds? How many bits in 1/5 seconds? How many in 100 milli seconds?
Related questions http://blog.oureducation.in/digital-communication-technique/ 1. what is communication ? 2. what is white noise ? where is it encountered ? Define code efficiency ? Define code redundancy ? What is scrambling ? What is QPSK ? What is Carrier Recovery ? Difference between BPSK and DPSK. What is need of signaling in a PCM system? What is Shannon s Theorem? What is the mean of Capacity of a Gaussian Channel? What is pulse Width Modulation(PWM) and describe it ? Write short notes on multiplexer, regenerative repeater, linear equalizer, timin g extraction, timing jitter http://share.pdfonline.com/ca5a91c19b1b4779b10a0a99fe7fcdab/viva%20questions_new .htm 1)Define pulse code modulation (PCM) 2)Define delta modulation. 3)Define adaptive delta modulation. 4)Distinguish between DM and ADM. 5)Define ASK, PSK and FSK. 6)Differentiate ASK and FSK. 7)What are the advantages of digital transmission? 8)What is meant by line coding? 9)Define polar encoding.
10) What is PCM draw the block diagram of a typical PCM system? 11)What is delta modulation (DM)? 12)Explain the different types of errors in DM . 13)Compare the different types of DM techniques. 14) Represent the folowing binary data 1011 in 1 Polar, 2. Bipolar 3 Unipolar, 4 . Manchester coded and 5. Differential coded forms. 15).Define bipolar encoding. 16)Define unipolar encoding. 17)Define Manchester encoding 18)Explain about error detection and error correction. 19)Purpose of error control coding 20)Differentiate between coherent and noncoherent modulation technique. 21)What is QAM. 22)State and explain sampling theorem 23)Compare BER of ASK, FSK & PSK modulation techniques 24)Explain noncoherent AS K & FSK demodulation. 25)What is QAM? 26)What is Nyquist rate of sampling. 27)What is aliasing. How it is minimized practically. 28)State and explain samli ng theorem 29)What is Nyquist rate of sampling? 30)What is aliasing? How is it minimized pracically? 31)What should be the minimum sampling rate for a voice signal in the range 300 3400 Hz? 32)What are the advantages of digital communication? 33)What are the disadvantag es of dig hal communication? 34)How can an analog voice signal be digitized? 35) What is quantization? How is this error rrinimized? 36)Explain sampling theorem for a band pass signal? 37)A message signal is band limited to a frequency range of 70 12 kHz, find the m inimum sampling frequency? 38) How messages signal is reconstucted from the sampled values? 39)How is bandwidth rneasure in the case of AM, DSBSC, SSB and Digital Modulatio n? 40)For a given sinusoidal input siqnal write PAM, PWM and PPM signals. 41)What are the advantages of PPM signals? 42)Explain different types of digital modulation techniques.
43)For the binary data 101 draw ASK, FSK and PSK modulated waveforms. 44)Comment on the bandwidth requirement of the various digital modulation techniques. 45)Explain the need for M ary modulation.
46)What is QPSK modulation? 47)What is signal space representation? 48)Write the signal space representation for the following signals a) ASK, D) FS K and c) PSK. 49)Differentiate between matched filter and correlative filter. 50) What is bit error rate and probability of error in digital modulation? 51)Explain a DPSK modulator and demodulator 52) Differentiate between coherent & non coherent demodulation techniques 53)ln a PCM system the minimum SNR required is 40dB, how many bits of quantizati on is required. Adaptive delta modulation http://www.answers.com/topic/delta-modulation#Adaptive_delta_modulation Adaptive delta modulation (ADM) or continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD) is a modification of DM in which the step size is not fixed. Rather, when several consecutive bits have the same direction value, the encoder and decoder assume that slope overload is occurring, and the step size becomes progressivel y larger. Otherwise, the step size becomes gradually smaller over time. ADM redu ces slope error,at the expense of increasing quantizing error.This error can be reduced by using a low pass filter. ADM provides robust performance in the presence of bit errors meaning error dete ction and correction are not typically used in an ADM radio design, this allows for a reduction in host processor workload (allowing a low-cost processor to be used).[2]adaptive delta modulation http://blog.oureducation.in/digital-modulation/ WHAT IS COMPANDING? EXPLAIN ARQ? DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PCM & PAM? WHAT IS ENTROPY? CONVERSION OF ANALOG SIGNAL TO DIGITAL WHY WE USE AMPLIFIER IN CASE OF LONG DISTANCE COMMUNICATION? WHAT IS REDUNDANT BIT? WHY WE USE THIS BIT? http://www.neduet.edu.pk/electronics/Telecommunication/Telecom%20Data/Lab%20Mann uals/BE/DCIT%20manual%202011.pdf 1. Draw the waveform of ASK when the input signal is 11010101 using carrier frequen cy 5 KHz. 2. What are the disadvantages of ASK over FSK and PSK? 3. State three applications of ASK 4. What will you observe in the spectrum of ASK signal if the binary message freque
ncy is of alternate ones and zeros? 5. Write a mathematical expression for an ASK wave. 6. Explain the circuits that can be used for the generation and detection of ASK wa ve. 7. Explain coherent and non coherent detection. 8. How does the frequency of the carrier compare with the bit rate of the data? http://www.scribd.com/doc/75100221/38/PRE-EMPHASIS-AND-DE-EMPHASIS 1. What is the need for pre-emphasis?2. Explain the operation of pre-emphasis c ircuit.3. Pre emphasis operation is similar to high pass filter with gain in pas s band explainhow?4. De emphasis operation is similar to low pass filter with attenuation in stop ban d,Justify?5. What is de-emphasis?6. Draw the frequency response of a pre-emphasi s circuit.7. Draw the frequency response of a de-emphasis circuit.8. Give the fo rmula for the cutoff frequency of the pre-emphasis circuit.9. What is the signif icance of the 3dB bandwidth. 1. Define AM and draw its spectrum?2. Draw the phasor representation of an ampl itude modulated wave?3. Give the significance of modulation index.4. What are th e different degrees of modulation?5. What are the limitations of square law modu lator?6. Compare linear and nonlinear modulators.7. Compare base modulation and emitter modulation.8. Explain how AM wave is detected.9. Define detection proces s.10. What are the different types of distortions that occur in an envelope dete ctor? Howcan they be eliminated?11. What is the modulation used in radio broad c asting.12. What is IF frequency range in AM receiver?13. What is meant by super heterodyne? What are the advantages?14. Differences between TRF and super hetero dyne receiver.15. What are the characteristics of receiver? 1. Define AM?2. Define DSB-SC system?3. What is the working of Balanced Modulator?4. Define Modulator and Demodulator?5. Define coherent detector?6. What are the different detectors used ina) Critical modulation b) Under modulati on c) Over modulation7. What are the advantages and disadvantages of DSB-SC modu lation?8. What is a squelch circuit?9. What are the different types of fading an d solution?10. Why SSB is not used for video broad casting. 1. Define spectrum analyzer. 2. Define AM and draw its spectrum.3. Draw the phasor representation of an ampli tude modulated wave.4. Give the significance of modulation index of AM and FM.5. What are the different degrees of modulation?6. Define DSB-SC.7. Give the signi ficance of bandwidth of AM &FM.8. Difference between time domain signal and freq uency domain signal.9. What is PSD?10. Why 5KH Z in television as BW of modulation signal. 1. Define frequency modulation.2. Mention the advantages of indirect method of FM generation.3. Define modulation index and frequency deviation of FM.4. What a
re the advantages of FM?5. What is narrow band FM?6. Compare narrow band FM and wide band FM.7. Differentiate FM and AM.8. How FM wave can be converted into PM wave?9. State the principle of reactance tube modulator.10. What is the bandwidt h of FM system?11. What is the function of FM discriminator?12. How does ratio d etector differ from fosterseely discriminator?13. What is meant by linear detect or?14. What are the drawbacks of slope detector?15. Explain the circuit operatio n? 1. State the Shannon s sampling theorem.2. What is Nyquist rate?3. What is meant by Aliasing?4. What are the effects of Aliasing?5. How to avoid Aliasing effect?6. What are the various Sampling techniques?7. Explain various sampling circuits?8. Why you need a hold circuit? What is a PLL? 3. What is a VCO? 4. Define the lock range of a PLL. 5. Define the capture range of PLL. Compare NRZ-I and NRZ- L . 2. Compare NRZ and biphase encoding . What is codec? 5.Explain Line coding.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- History of Semi-Conductor DevicesDokumen6 halamanHistory of Semi-Conductor DevicesJulio SternBelum ada peringkat
- 200 Part 2 Transistor CircuitsDokumen37 halaman200 Part 2 Transistor CircuitsNeeraj SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- DigSilent TechRef - RelDispolyDokumen50 halamanDigSilent TechRef - RelDispolyАлишер ГалиевBelum ada peringkat
- US Navy Course NAVEDTRA 14029 - Aviation Electronics Technician-IntermediateDokumen538 halamanUS Navy Course NAVEDTRA 14029 - Aviation Electronics Technician-IntermediateGeorges100% (3)
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDari EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDokumen11 halamanAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics & Communication EngineeringDokumen41 halamanElectronics & Communication EngineeringKrishna Chaitanya TBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware Hacker 4Dokumen91 halamanHardware Hacker 4mictesterBelum ada peringkat
- General Digital Design Questions: How Do You Size NMOS and PMOS Transistors To Increase The Threshold Voltage?Dokumen22 halamanGeneral Digital Design Questions: How Do You Size NMOS and PMOS Transistors To Increase The Threshold Voltage?Rahul VaddelliBelum ada peringkat
- RECEIVERSDokumen41 halamanRECEIVERSAK 1Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet 4Dokumen7 halamanTutorial Sheet 4sibti007Belum ada peringkat
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDokumen9 halamanAnalog and Digital CommunicationManish MahasethBelum ada peringkat
- Principle of Communication Long Answer Question BankDokumen5 halamanPrinciple of Communication Long Answer Question BankAman yadavBelum ada peringkat
- BEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsDokumen3 halamanBEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsSiam hasanBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communications: Lab Manual (Student Copy)Dokumen78 halamanDigital Communications: Lab Manual (Student Copy)dhileepan DilipBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Dokumen5 halamanUnit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Marks - 1 UnitDokumen5 halaman2 Marks - 1 UnitSivaselva GanabathiBelum ada peringkat
- Answers To CT303 Part 1Dokumen3 halamanAnswers To CT303 Part 1RAMOLIYA HARSH MADHUKANTBHAIBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1Dokumen1 halamanAssignment 1Sabir SankhlaBelum ada peringkat
- Viva Questions Advanced Communication LabDokumen5 halamanViva Questions Advanced Communication LabDimple BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Isro, Barc Interview QuestionsDokumen7 halamanIsro, Barc Interview QuestionspuppykBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Poc PDFDokumen3 halamanQuestion Bank Poc PDFPranjul RastogiBelum ada peringkat
- Filters Classification GuideDokumen9 halamanFilters Classification GuideMichell RobinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank For Wireless CommunicationDokumen10 halamanQuestion Bank For Wireless CommunicationPRIYA RAJI100% (2)
- Digital Communication Systems Model QuestionsDokumen3 halamanDigital Communication Systems Model Questionsbku14677Belum ada peringkat
- Cseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.InDokumen23 halamanCseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.IndeepikaBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Question Bank Code: CS-303 (Computer Networks) 8 Semester, Electrical EngineeringDokumen15 halamanDepartment of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Question Bank Code: CS-303 (Computer Networks) 8 Semester, Electrical EngineeringGopikrishnan Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Iii Part A BDokumen115 halamanIii Part A BDivya SreeBelum ada peringkat
- EC2301 Digital Communications SyllabusDokumen28 halamanEC2301 Digital Communications SyllabusYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyBelum ada peringkat
- radar module 1Dokumen2 halamanradar module 1Nikhil NagarajuBelum ada peringkat
- AC Lab Viva QuestionsDokumen8 halamanAC Lab Viva Questionsvaishnavi khilariBelum ada peringkat
- Drdo - QuestionsDokumen13 halamanDrdo - Questionssaroj4studyBelum ada peringkat
- Question BankDokumen3 halamanQuestion Bankshafignits_123Belum ada peringkat
- EC6801 Question Bank on Wireless CommunicationDokumen10 halamanEC6801 Question Bank on Wireless CommunicationEASACOLLEGEBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0002Dokumen4 halamanWa0002nitish debbarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Objective of The AssignmentDokumen7 halamanObjective of The AssignmentVelvizhi MohanrajBelum ada peringkat
- DC Lab ManualDokumen24 halamanDC Lab Manualvidyae100% (2)
- Digital Communication: Subject Name:Digital Communication Prepared by:S.Sathiya Priya AP/ECEDokumen25 halamanDigital Communication: Subject Name:Digital Communication Prepared by:S.Sathiya Priya AP/ECESathiyapriya ShanmugasundaramBelum ada peringkat
- DC Manual Final PDFDokumen25 halamanDC Manual Final PDFAsma FirdouseBelum ada peringkat
- EC6801 IT Wireless CommunicationDokumen10 halamanEC6801 IT Wireless CommunicationAnbu ArasanBelum ada peringkat
- Communication Systems Ii - LabmanualDokumen12 halamanCommunication Systems Ii - LabmanualpramodBelum ada peringkat
- FinalDokumen38 halamanFinalAbdullah MdBelum ada peringkat
- CNS-ST3.1Dokumen17 halamanCNS-ST3.1Achilles AldaveBelum ada peringkat
- Ec 2301 - Digital CommunicationDokumen10 halamanEc 2301 - Digital CommunicationAadhithya PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen42 halamanReportShakiraBelum ada peringkat
- Signals and Systems Unit 1: o CanDokumen6 halamanSignals and Systems Unit 1: o CanGaurav SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- 1155dBTE 504Dokumen13 halaman1155dBTE 504Shubham AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- Dds IntroDokumen6 halamanDds IntroYermakov Vadim IvanovichBelum ada peringkat
- ECE 203 Lab Course DescriptionDokumen32 halamanECE 203 Lab Course DescriptionrajeshadktBelum ada peringkat
- C C C C !!Dokumen7 halamanC C C C !!guruvigneshwaranBelum ada peringkat
- Kasraian ECET375 Week2Dokumen42 halamanKasraian ECET375 Week2Raul PerdomoBelum ada peringkat
- Adc Cia-2 QBDokumen2 halamanAdc Cia-2 QBLOKESH KUMAR LBelum ada peringkat
- ch3 TotDokumen2 halamanch3 Tot190148sandipBelum ada peringkat
- DC Question BankDokumen6 halamanDC Question BankBha RathBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Communication Lab Manual PDFDokumen61 halamanAdvanced Communication Lab Manual PDFRachel BartonBelum ada peringkat
- 18TEL67 CTSDokumen5 halaman18TEL67 CTSChandu ChittiBelum ada peringkat
- 2103 & 2104 (WL)Dokumen48 halaman2103 & 2104 (WL)bhoopsharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 10 14.modulation FormatsDokumen72 halaman10 14.modulation FormatsJoel ManuelBelum ada peringkat
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDokumen8 halamanCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweBelum ada peringkat
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDari EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondDari EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondBelum ada peringkat
- Enabling Technologies for High Spectral-efficiency Coherent Optical Communication NetworksDari EverandEnabling Technologies for High Spectral-efficiency Coherent Optical Communication NetworksBelum ada peringkat
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversDari EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversBelum ada peringkat
- E3S1ESTEC3101-AC23112013 12pmDokumen21 halamanE3S1ESTEC3101-AC23112013 12pmAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- IES E & T Topic wise Questions Communication System YEAR 1999 MCQ 1-38Dokumen62 halamanIES E & T Topic wise Questions Communication System YEAR 1999 MCQ 1-38Girish NairBelum ada peringkat
- Guide to Short DocumentsDokumen2 halamanGuide to Short DocumentsAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Communication SystemDokumen41 halamanCommunication SystemWesley Moses SamdossBelum ada peringkat
- Title With Picture Layout: SubtitleDokumen12 halamanTitle With Picture Layout: SubtitleAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communications QBDokumen3 halamanDigital Communications QBwizardvenkat100% (1)
- CS2204 2011 Nov DecDokumen2 halamanCS2204 2011 Nov DecAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication Question BankDokumen1 halamanDigital Communication Question BankAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Digital CommunicationDokumen1 halamanDigital CommunicationAsokan ChinnasamyBelum ada peringkat
- 442 - N Englisch 1.0Dokumen10 halaman442 - N Englisch 1.0Rodrigo LinoBelum ada peringkat
- (Chapter 6-10) Tomasi Communications Systems Terms (41-70)Dokumen30 halaman(Chapter 6-10) Tomasi Communications Systems Terms (41-70)Kyle Ivan CasindacBelum ada peringkat
- TBA120 Demodulator Circuit IcDokumen3 halamanTBA120 Demodulator Circuit IcEleonor CamargoBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearDokumen24 halamanIEEE Guide For Partial Discharge Measurement in Power SwitchgearHafiziAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Marconi Synth NDokumen6 halamanMarconi Synth NsdspigBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PLLDokumen40 halamanIntroduction To PLLPrateek MudgilBelum ada peringkat
- Human Values and Professional Ethics Textbook ChaptersDokumen28 halamanHuman Values and Professional Ethics Textbook ChaptersK.G. Venkata Krishna KrUBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and programming guide for alarm control panelDokumen28 halamanInstallation and programming guide for alarm control panelewie52Belum ada peringkat
- Ev Mc3301e1Dokumen149 halamanEv Mc3301e1Md. Ameer HamjaBelum ada peringkat
- No. 2D314-013E: Toshiba Corporation 2002 All Rights ReservedDokumen37 halamanNo. 2D314-013E: Toshiba Corporation 2002 All Rights ReservedRashid Kh100% (1)
- 1973 Fairchild Linear Integrated Circuits Data CatalogDokumen548 halaman1973 Fairchild Linear Integrated Circuits Data Catalogdr_ardenBelum ada peringkat
- PLL Performance Simulation and Design 3rd EditionDokumen249 halamanPLL Performance Simulation and Design 3rd EditionfirststudentBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual: HF Marine TransceiverDokumen71 halamanService Manual: HF Marine TransceiverJalalludin RahmatBelum ada peringkat
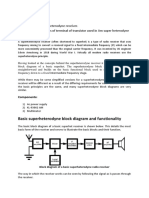
- Basic Superheterodyne Block Diagram and FunctionalityDokumen4 halamanBasic Superheterodyne Block Diagram and FunctionalityibrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Stamford MX321 ManualDokumen3 halamanStamford MX321 ManualDiego CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus: For The Post of SCT PC It&CDokumen3 halamanSyllabus: For The Post of SCT PC It&CRaaz BangaramBelum ada peringkat
- Aiwa Csd-A110, Csd-A170 PDFDokumen28 halamanAiwa Csd-A110, Csd-A170 PDFRodrigo NegrelliBelum ada peringkat
- 814180-G-EnG - IQ3 Metal Detector User GuideDokumen81 halaman814180-G-EnG - IQ3 Metal Detector User GuideEricferreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review On Mobile Phone DetectorDokumen4 halamanLiterature Review On Mobile Phone Detectorzyfepyfej0p2100% (1)
- Elements of An Optical Fiber Transmission LinkDokumen2 halamanElements of An Optical Fiber Transmission LinkranjithBelum ada peringkat
- Monogram Mgp-450 ServiceDokumen24 halamanMonogram Mgp-450 Servicehc1ycBelum ada peringkat
- EC6512 Communication System Lab ManualDokumen52 halamanEC6512 Communication System Lab ManualSalai Kishwar JahanBelum ada peringkat
- ModulationDokumen666 halamanModulationRoshdy AbdelRassoul100% (2)
- Model 777-A Leak Detector: Pin-Point Underground Leaks With Industry's Most Accurate and Proven Leak DetectorDokumen2 halamanModel 777-A Leak Detector: Pin-Point Underground Leaks With Industry's Most Accurate and Proven Leak DetectorJavier HuarcaBelum ada peringkat