Urea Market in Brazil PDF
Diunggah oleh
gabydel74Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Urea Market in Brazil PDF
Diunggah oleh
gabydel74Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Urea Market in Brazil
With fertile land, extensive and favorable climate for agriculture, Brazil is a leading producer and worldwide supplier of food. Brazil stands out in the production of crops like soybeans, corn, rice, beans and sugar cane. Rice and beans are primarily for domestic consumption, Corn is primarily used for animal feed and production of animal protein.
Crops Summary of the total planted areas in Brasil
C ro p s Soybe an C o rn S u g ar ca n e C o tto n C o ffe e C i t ru s D ry b e a n R ice W he at T ri t i c a l e Rye B a rle y
2008 000 h 21.272 14.385 8.219 1.062 2.222 825 3.769 2.858 2.417 74 4 74
2009 000 h 21.736 13.791 8.604 808 2.371 833 4.149 2.888 2.433 69 4 78
2010 000 h 23.404 12.883 8.837 819 2.292 842 3.525 2.702 2.141 60 3 85
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Planted Areas (000 h)
2.702 3.525 842 2.292 819 8.837 23.404 Sugar cane Cotton Coffee Citrus Dry bean 12.883 Rice Wheat 2.141 60 3 85 Soybean Corn
Source: IBGE Brazilian Institute of Geography
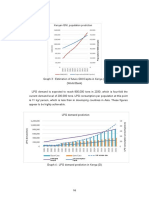
In 2009, Brazil demanded the total of 3,7MMt of Urea, in which 2,9MMt was applied in agriculture as Fertilizer. The main urea consumer crops in the country are Corn, Coffee and Sugar Cane which together sum up over 70% of the countrys urea consumption. Cotton, Potato, Beans and Wheat together sum 20%, and around 10% are consumed by other cultures. Majority of Urea consumption is designated to the Center West , South East and South regions of the country. A smaller quantity is demanded in the North East. The consumption of Urea in the country has grown around 4% every year so it is expected that 5MMt consumption could be a possible number in the next 5-6 years. Currently, Urea is imported from the main available sources in the world through the main traders and suppliers in the international market. The figure below, show the origins and its percentage of relevance to Brazilian market.
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
UREA Cunsumption 2009 (t/year) Import National Pruduction Export Installed Installed Capacity 2009 (t/year) Petrobras FAFEN BA Petrobras FAFEN SE Vale PR
UREA in Brazil 2009 3.706.642 Applications % 1.940.844 Fertilizers 1.134.600 Intermediate Chemical 15.358 Animal Feed
Chemical Process
78,9 16,9 2,9 1,3
1.782.000 495.000 657.000 630.000
Source: ABIQUIM National Association of Chemical Industry
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
As shown above, Brazil is highly dependent on importation of Urea. The same situation is extended to all NPK fertilizer consumption which around 60% of the consumption is imported. The actual scenario is influencing Brazilian government and the national industry to move towards expanding the national capacity in order to diminish the dependence of imported products, therefore, Petrobras and the national government are currently working on the following projects of Urea and Ammonia production: Urea Capacity t/year 1.210.000 665.000 0 Ammonia Capacity t/year 761.000 400.000 519.000 Gas Consumption (approx.) 1.7Mm3/day 1Mm3/day 1.2Mm3/day Start up date July 2014 Dec 2015 Dec 2014 Cost (Approx.) USD 2,0Bi USD 1,0Bi USD 1,3Bi Gas Source Bolivia Bolivia Bolivia
Petrobras Projects UFN III - Trs Lagoas MS UFN IV - Linhares ES UFN V - Uberaba MG
Impact in Brazil Production Capacity Increase Production Capacity Increase Ammonia Self-sufficiency
There are also other discussions of Urea plant projects in the Southern state Paran. The project of the consortium Azoto led by the Cooperatives of Parana State (CONAPAR-COONAGRO) is currently under negotiation with Petrobras and National Government to determine the gas availability and price. In this project, the Japanese company Toyo is competing with the Chinese Chengda to be the technology provider. There are a few other national investors prepared to participate on this venture. Please find details below: Urea Capacity Ammonia t/year Capacity t year 190.000 Gas Consumption (approx.) 600Km3/day Start up date Dec 2013 Cost (Approx.) USD 400MM
Project
Impact in Brazil Parana Self Sufficiency
Gas Source Petrobras (Bolivia)
Consrcio Azoto (Conapar) PR 330.000
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Logistics Alternatives Railroad in operation: Between Santa Cruz and Corumba is operating a railroad rail system called Bolivian Red Oriental (formerly Railroad Brazil - Bolivia), with gauge of 1.00 m and 643 km long, recently privatized. Reportedly, there is no mutual traffic between these two railroads, it is necessary to transfer the goods from one train to another, passing through customs. After customs, there is a line with 1,00 m gauge (old EFNOB - Northwest Railroad of Brazil), linking Corumb (MT), Campo Grande (MS) and Bauru (SP), and a branch line between Campo Grande and Ponta Pora (border with Paraguay), a total of 1,621 km of track. The distance by rail between Corumb and Bauru is 1299 km and between Corumb and Campo Grande 459 km. This railroad was privatized in 1996 and currently administrated by ALL. Bauru connects to the mesh of Ferroban (formerly FEPASA), which gives access to the port of Santos, in the same vein, by extension Mairinque. To reach out to the ports of Sepetiba and Rio de Janeiro, you need a transfer or Sao Paulo in Bauru, to gauge trains of 1.60 m.
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
For reference, please see the whole operation of ALL (Amrica Latina Transportes)
Railroad transport cost and transshipping at border could not be calculated by ALL. For this study, it would be necessary to analyze a co-investment on wagons with ALL as their capacity is limited to their present operations. Usually, rail transportation costs in Brazil are similar to road transportation, but due to the need of investment on equipment and transshipments (Gauge changes on the route) the costs could be higher.
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Road Alternative, Bolvia-Brazil In Bolivia, from the border town of Puerto Suarez, the highway is in poor condition. From Bolivia Border to Campo Grande (MS) to there are 432km of paved roads. From Campo Grande all regions of Brasil can be reached but distances from 500km to 1500km will be the basis for national distribution.
Transport Cost Estimate:
Inland Road transport estimative Bolivia-Brazil - Truck load 25Mt each Cochabamba to Rondonpolis (MT) or Maring (PR) - Cost R$ 340/Mt (Approx. USD 212/Mt); Santa Cruz to Rondonpolis (MT) or Maring (PR) Cost R$ 244/Mt (Approx. USD 152/Mt); Clearance, transshipment and fees Cost (approx.) R$ 60/Mt (Approx USD 37);
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Important Information - Custom clearance is necessary at Border, the material will be unloaded at Bonded Warehouse, Cleared and then transshipped to the trucks that will do the Brazilian part of the journey. This makes unitization of the cargo necessary, preferably into Big Bags (1Mt) as there is no infrastructure for Bulk transshipping which makes bulk shipments unviable for road transportation from Bolvia to Brazil. Inland Road transport Brazil The estimative below is based on transportation from the main Fertilizer Port in Brazil, Paranagu Port to two of the most important delivery regions in the country. The routes below are currently practiced by Brazilian market and can be used for comparison with Bolivian import cost. Port Paranagu (PR) to Rondonpolis (MT) 1.600Km - Cost R$ 110/Mt (Approx. USD 68/Mt)
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Port Paranagu to Maring (Paran) 530Km- Cost R$ 65/Mt (Approx. USD 40/Mt)
Note: The exchange rate used on this report were based on USD 1 = R$ 1.60
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Distribution Distribution in Brazil is mainly done by truck (25MT load each), the logistics is challenging as there is limited availability of vehicles and the roads are not in good conditions although they are mostly pavemented. Clients locations are spread around the huge agricultural area of Brasil, most of the blending facilities of the Fertilizer industry are based near the ports of Paranagu, Santos, Vitria and Rio Grande. ADM and Bunge also have blending facilities based in Cuiab and Rondonpolis, both situated in Mato Grosso State. For distribution it interesting to considering hiring Warehouses in Key cities such as Cuiab or Rondonpolis (Mato Grosso state) and Maring (Parana state), this way we can provide FOB Warehouse base sales, enabling our clients to pick up the material at their own cost if the sales are broken into smaller quantities. Distribution scheme should be submitted to a deeper analysis as it could be driven by the commercial agreement with our clients. Main Clients current Import Forecast The list below shows import forecast for 2011 of some of the main potential clients in Brazilian Market. There are many others to be included for a complete list, but these concentrate majority of the quantity commercialized in the country. Total Demand (KMt/y) 300 400 450 73
Customer ADM BUNGE HERINGER COABRA
Brazil Urea Prices National Vs Imported
10
Brasil
SPLCHM, April 2011
Forecast of Gas Prices (2004-2012)
11
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Celestial AgricultureDokumen10 halamanThe Celestial AgricultureGus TijerinaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management - Final Report 12Dokumen72 halamanStrategic Management - Final Report 12Aryan Smarty67% (3)
- Watermelon FertigationDokumen2 halamanWatermelon FertigationJose Ramon Ruiz Ledezma100% (1)
- Sugarcane Is An Important Industrial Crop of Tropical and Subtropical Regions and Is CultivatedDokumen7 halamanSugarcane Is An Important Industrial Crop of Tropical and Subtropical Regions and Is CultivatedJanaksinh SolankiBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil: Date: GAIN Report NumberDokumen3 halamanBrazil: Date: GAIN Report Numberapi-109061352Belum ada peringkat
- CH 12 (Brazil) FDokumen4 halamanCH 12 (Brazil) FXain RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Institutional Presentation: March 2012Dokumen46 halamanInstitutional Presentation: March 2012Klabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil Investment Opportunities - KSA EmbassyDokumen6 halamanBrazil Investment Opportunities - KSA EmbassyYassin AdnaneBelum ada peringkat
- The Sugarcane Industry and The Global Economic CrisisDokumen24 halamanThe Sugarcane Industry and The Global Economic CrisisHimanshu MogheBelum ada peringkat
- A Model of Location of Transshipment Terminals v3Dokumen31 halamanA Model of Location of Transshipment Terminals v3newtonrochaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceresana - Brochure Market Study AmmoniaDokumen7 halamanCeresana - Brochure Market Study AmmoniaSyukri ShahBelum ada peringkat
- The Vanishing LNG Market in Brazil: April 2017Dokumen7 halamanThe Vanishing LNG Market in Brazil: April 2017Amy MiBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Latin America One On One Conference: December 2011Dokumen49 halaman3 Latin America One On One Conference: December 2011Klabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Executive Summary ProjectDokumen13 halamanExecutive Summary ProjectJose PerezBelum ada peringkat
- 0 ArtigopublicadoDokumen7 halaman0 ArtigopublicadoMaisa Tobias IIBelum ada peringkat
- Institutional PresentationDokumen45 halamanInstitutional PresentationKlabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Plano de Negócios 2010-2014Dokumen8 halamanPlano de Negócios 2010-2014stfanuBelum ada peringkat
- IBP1482 - 19 Pipeline Crude Oil and Petroleum Products Theft in BrazilDokumen8 halamanIBP1482 - 19 Pipeline Crude Oil and Petroleum Products Theft in BrazilMarcelo Varejão CasarinBelum ada peringkat
- Newsletter EnglishDokumen12 halamanNewsletter EnglishAmanda Noemí NuñezBelum ada peringkat
- IBP1062 - 19 South America and Possibilities For BrazilDokumen6 halamanIBP1062 - 19 South America and Possibilities For BrazilMarcelo Varejão CasarinBelum ada peringkat
- Ceresana - Brochure Market Study UreaDokumen7 halamanCeresana - Brochure Market Study UreaSyukri ShahBelum ada peringkat
- KPresentation2009 1Q IngDokumen34 halamanKPresentation2009 1Q IngKlabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Ethanol Global MarketDokumen25 halamanEthanol Global MarketddribBelum ada peringkat
- Case-Studies Miguel Paraguay PDFDokumen3 halamanCase-Studies Miguel Paraguay PDFTamara StojanovicBelum ada peringkat
- BHP Billiton Operational Review For The Year Ended 30 June 2016Dokumen19 halamanBHP Billiton Operational Review For The Year Ended 30 June 2016julianajulianaBelum ada peringkat
- National Sugar Master Plan - A Road Map For Local Sugar Production by Alh. Ahmed SongDokumen17 halamanNational Sugar Master Plan - A Road Map For Local Sugar Production by Alh. Ahmed SongUmar Bala UmarBelum ada peringkat
- CD4855 - Ammonia - Urea - Markets - in - Latin - America - January - 2009 - (UPDATED - 9th - Jan) - Final BRITISH 02 PDFDokumen60 halamanCD4855 - Ammonia - Urea - Markets - in - Latin - America - January - 2009 - (UPDATED - 9th - Jan) - Final BRITISH 02 PDFgabydel74Belum ada peringkat
- Institutional Presentation: July 2012Dokumen44 halamanInstitutional Presentation: July 2012Klabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Apresentao APIMECV03 INGDokumen39 halamanApresentao APIMECV03 INGKlabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Special Report: Fao/Wfp Crop and Food Security Assessment Mission To MozambiqueDokumen36 halamanSpecial Report: Fao/Wfp Crop and Food Security Assessment Mission To MozambiqueNguyễn Yến TịnhBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of The FSRU and The LNG Market OutlookDokumen13 halamanRise of The FSRU and The LNG Market OutlookThanos PitatzisBelum ada peringkat
- 09july19 F.O.licht International Sugar Sweetener ReportDokumen48 halaman09july19 F.O.licht International Sugar Sweetener ReportAhmad Bilal100% (2)
- Argus FMB Potash Market NewsDokumen8 halamanArgus FMB Potash Market NewsAlphatrackerBelum ada peringkat
- MECAS (12) 05 - Outlook of Sugar and Ethanol Production in Brazil - EnglishDokumen50 halamanMECAS (12) 05 - Outlook of Sugar and Ethanol Production in Brazil - EnglishJaymin PatelBelum ada peringkat
- LogisticaDokumen15 halamanLogisticaDANIELBelum ada peringkat
- Juice Extraction SystemsDokumen19 halamanJuice Extraction SystemsFanilo RazafindralamboBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Presentation (May)Dokumen24 halamanCorporate Presentation (May)FibriaRIBelum ada peringkat
- Policy Note Amazon June 2011 FinalDokumen12 halamanPolicy Note Amazon June 2011 Finalbi2458Belum ada peringkat
- Jam MarmaladeDokumen28 halamanJam MarmaladeShishir Kumar Singh100% (1)
- KPresentation2009 2Q IngDokumen36 halamanKPresentation2009 2Q IngKlabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Pages From Toyota Tsusho Corporation Study On Kenya LPG Import Terminal 2019Dokumen2 halamanPages From Toyota Tsusho Corporation Study On Kenya LPG Import Terminal 2019AtieBelum ada peringkat
- BOLIVIA-BRAZIL GAS PIPELINE ReportDokumen6 halamanBOLIVIA-BRAZIL GAS PIPELINE ReportnelsonmcamachoBelum ada peringkat
- Colombia A Country With Energy DiversityDokumen8 halamanColombia A Country With Energy DiversityJoBelum ada peringkat
- Dairy FarmDokumen14 halamanDairy FarmTESFALEWATEHEBelum ada peringkat
- Country Analysis Brief: Brazil: Last Updated: November 21, 2017Dokumen17 halamanCountry Analysis Brief: Brazil: Last Updated: November 21, 2017Anonymous HJZffHvTBelum ada peringkat
- Klabin Institutional Presentation 2 Q11Dokumen35 halamanKlabin Institutional Presentation 2 Q11Klabin_RIBelum ada peringkat
- Cold Room ServiceDokumen6 halamanCold Room ServiceAbdulkaderBelum ada peringkat
- PRGE Living Working BrazilDokumen7 halamanPRGE Living Working BrazilAndreea FloreaBelum ada peringkat
- Greenwood Management: Phase 2 Project Engineering Report EucalyptusDokumen31 halamanGreenwood Management: Phase 2 Project Engineering Report EucalyptusGreenwood Management ApSBelum ada peringkat
- BTG Pactual London 2011 - Latin Opportunities ConferenceDokumen40 halamanBTG Pactual London 2011 - Latin Opportunities ConferenceMillsRIBelum ada peringkat
- Position Paper - Supply Chain of Rice in The PhilippinesDokumen5 halamanPosition Paper - Supply Chain of Rice in The PhilippinesLiby Santos100% (5)
- Automotive Opportunities in Brazil: Sector BriefingDokumen5 halamanAutomotive Opportunities in Brazil: Sector BriefingZain U Din BurzaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp Mill Expansion in Brazil Discussion DocumentDokumen10 halamanPulp Mill Expansion in Brazil Discussion DocumentHarvey SpecterBelum ada peringkat
- A. SzwarcDokumen32 halamanA. Szwarcrafa7410Belum ada peringkat
- Feasibility Study For Development of Cashew-Based Farming Operations in VichadaDokumen15 halamanFeasibility Study For Development of Cashew-Based Farming Operations in VichadaBj Palay BermudezBelum ada peringkat
- Asphalt Market and Research Challenges in Colombia: April 2012Dokumen11 halamanAsphalt Market and Research Challenges in Colombia: April 2012joselarBelum ada peringkat
- 11 PetrobrasDokumen6 halaman11 PetrobrasbshriBelum ada peringkat
- Brazilian Biofuels ExperienceDokumen31 halamanBrazilian Biofuels ExperienceANDRE LIMA DE ALVARENGABelum ada peringkat
- 04+Volkswagen+South+America+Market+With+Perspective 44 SlidesDokumen44 halaman04+Volkswagen+South+America+Market+With+Perspective 44 SlidesAntonio C S LeitaoBelum ada peringkat
- Cold Room ServiceDokumen5 halamanCold Room ServiceAbdulkaderBelum ada peringkat
- International Business (IB) Project Report On Sugar Facor in BrazilDokumen34 halamanInternational Business (IB) Project Report On Sugar Facor in BrazilkeyurchhedaBelum ada peringkat
- The future role of biofuels in the new energy transition: Lessons and perspectives of biofuels in BrazilDari EverandThe future role of biofuels in the new energy transition: Lessons and perspectives of biofuels in BrazilBelum ada peringkat
- Food Outlook: Biannual Report on Global Food Markets May 2019Dari EverandFood Outlook: Biannual Report on Global Food Markets May 2019Belum ada peringkat
- FertilizerDokumen14 halamanFertilizerJonard Opamen73% (11)
- Curriculum VitaeDokumen4 halamanCurriculum VitaemkmikmiBelum ada peringkat
- De Thi Giua HK2 Tieng Anh 12 He 7 Nam de 2Dokumen4 halamanDe Thi Giua HK2 Tieng Anh 12 He 7 Nam de 2Rosie NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- 036 Diammonium PhosphateDokumen3 halaman036 Diammonium Phosphateeng20072007Belum ada peringkat
- Agriculture in Motion: Oklahoma Academic Standards Oklahoma Ag in The ClassroomDokumen8 halamanAgriculture in Motion: Oklahoma Academic Standards Oklahoma Ag in The ClassroomMuhamad EdwardBelum ada peringkat
- Gravimetric Determination of Phosphorus in Fertilizer SamplesDokumen5 halamanGravimetric Determination of Phosphorus in Fertilizer SamplesCatherine PascuaBelum ada peringkat
- #5 - Learning From YARADokumen48 halaman#5 - Learning From YARARiki MuladiBelum ada peringkat
- CIO ListDokumen30 halamanCIO ListShivam GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Post Patent ResultsDokumen2 halamanPost Patent ResultsDharmendra B MistryBelum ada peringkat
- Schedulewise List of CpsesDokumen4 halamanSchedulewise List of CpsesSoundar RajBelum ada peringkat
- SPSS: Analysis of Experimental DataDokumen4 halamanSPSS: Analysis of Experimental DataMuhammad Naeem IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- II-6 Agronomy 1-23Dokumen24 halamanII-6 Agronomy 1-23SannyBombeoJomocBelum ada peringkat
- Fertilizer Subsidieswhich Way Forward 2-21-2017Dokumen49 halamanFertilizer Subsidieswhich Way Forward 2-21-2017Shounak DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Spec Raven FlowcontrolsDokumen2 halamanSpec Raven FlowcontrolsaritmeticsBelum ada peringkat
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 QuestionsDokumen8 halamanImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 QuestionsSHAURYA VARDHANBelum ada peringkat
- CAT 1990 QuestionsDokumen32 halamanCAT 1990 QuestionsSahil GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- JUNKKARI OY - Brosura Cu Semanatori PDFDokumen16 halamanJUNKKARI OY - Brosura Cu Semanatori PDFDinyBelum ada peringkat
- Zero Liquid DischargeDokumen9 halamanZero Liquid DischargeAhmad MuzammilBelum ada peringkat
- Icis Fert Map 2018 Sponsors-Ilovepdf-CompressedDokumen1 halamanIcis Fert Map 2018 Sponsors-Ilovepdf-CompressedHugoBelum ada peringkat
- Biological N FixationDokumen9 halamanBiological N Fixationtri cutBelum ada peringkat
- Lapford Lookout - February 2016Dokumen16 halamanLapford Lookout - February 2016StephenWensleyBelum ada peringkat
- MTO Catalog 2017Dokumen39 halamanMTO Catalog 2017dougzelenkaBelum ada peringkat
- DPR On Jaggery Manufacture in IndiaDokumen4 halamanDPR On Jaggery Manufacture in IndiaMohan PBelum ada peringkat
- GAP Coconut - 3rd Working Draft - PCMDokumen37 halamanGAP Coconut - 3rd Working Draft - PCMJaymie GoseBelum ada peringkat
- The Corn Growers Field Guide For Evaluating Crop Damage and Replant OptionsDokumen16 halamanThe Corn Growers Field Guide For Evaluating Crop Damage and Replant Optionsrobert_tignerBelum ada peringkat
- Achievement Chart: Technical Education and Skills Development AuthorityDokumen7 halamanAchievement Chart: Technical Education and Skills Development Authorityjames lacanilao100% (1)
- Overview - Clay Mineral Applications: Haydn H. MurrayDokumen17 halamanOverview - Clay Mineral Applications: Haydn H. Murraykhosrofattahi2Belum ada peringkat