Orientation and Seminar On Service Vehicles
Diunggah oleh
Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Orientation and Seminar On Service Vehicles
Diunggah oleh
Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
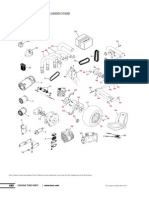
SERVICE VEHICLES OPERATING COMPONENTS AND SYSTEMS ENGINE: Gasoline and Diesel 1.
Fuel distribution Injection Pump or Carburetor or Fuel Injection is fuel delivery system. Proper delivery means proper idling up to smooth and powerful torque. Diesel needs no electricity to burn fuel due to compression burning. Gasoline needs electricity to burn fuel due to combustion burning. Fuel filter is needed to prevent sediments from entering fuel delivery system and needs replacing every 500 hrs. Things to feel for: Sudden loss of power, choking, hesitation, etc. 2. Lubrication Engine uses Oil to proper lubricate mechanical parts and prolong life and prevent premature wear and damage to engine. 30 weight for gasoline engine 40 weight for diesel engine 2 cycle oil for 2 stroke engines Oil and filter for water-cooled engine must be replaced every 80 to 100 hrs. Oil for air-cooled engine must be replaced every 30 to 50 hrs. Oil for all vehicles must be replaced every 5,000 hrs or 3 months. 2 cycle oil ratio is at 20:1 (gasoline : 2 cycle oil) Things to look for: Colour (very dark), oil thickness, level, leaks in the engine. 3. Cooling system Engine uses Water or air to bring down and control engines running temperatures. Ratio of water to coolant can vary from 30 : 70 coolant to water ratio up to 50 : 50 ratio. Coolant helps bring up boiling temperature and conditions radiators, hoses and water pumps. Too much can also be harmful to the engine. Coolant must be replaced every 2 years for all types of engines. Air cooled engines are cooled down by high circulating air within the engine block by driven by fans attached to the flywheel. Air-cooled engines also run at a higher temperature than water-cooled engines. Things to look for: water level, rust, oil, bubbling, overflowing, leaks (in the hose fittings and radiators), hose (cracking, hardening) 4. Clutch, transmission and differential system Most service vehicles utilizes a clutch to couple the engine to the transmission and differential to send power to wheels that drives the vehicle either in a forward or reverse mode. Clutches usually last for up to 3 years or 40,000 kms in Philippine condition. The life varies depending on the driver, terrain, traffic condition etc. Things to look for: Chattering, slipping, hardening of the clutch pedal, brake fluid (colour and level), leaks in the brake calipers and drums.
Transmission provides different gear ratios to the engine for low end up to top end for both fuel efficiency and less stress on the engine. They either come in manual or automatic. Both transmissions need a clutch to help engage the engine to the desired gear every time there is a gear change. Transmission uses a transmission fluid to help keep the mechanical part lubricated and prolong the life. Must be replaced every 1 to 2 years depending on the operating condition. Things to look for: Difficulty in engaging gears, grinding noise, transmission fluid level if dipstick is available, gear shifter and rod linkages. Differential helps distribute power from the transmission to the wheels. The speed delivered to the wheels depends on what gear the transmission is in coupled with the engine revolution. Differential uses a gear oil of either 90 or 140 depending on the vehicle and manufacturers specifications. Gear oil must be replaced every 1 to 2 years depending on the operating condition. Gear oil helps to reduce friction and prolong the life of the differential. Things to look for: Grinding noise, humming noise, leaks. 5. Brake system All vehicles use brakes to assist the vehicle in stopping. They come in either disc or drum brake. They work very similar to a hydraulic system by using brake fluid available in DOT 3 or DOT 4. Fluids must not be mixed. Replace fluid and flush system every 1 to 2 years depending on operating condition. Things to look for: Brake fade and weakening, squealing noise, pulling uneven braking especially under sudden hard braking, leaks, brake pad wear (disc brakes only), vibration on the steering wheel during braking (shimmy). 6. Suspension Suspension assist the vehicle to absorb any uneven bumps on the surface and keeps the vehicle to stay stable on high speeds and cornering. This consists of coil or leaf springs coupled with shock absorbers, ball joints and bushings. Maintenance is very minimal with only greasing of some ball joints and bushings. Things to look for: Jolting, noise, uneven tire wear, extreme body roll, bottoming out. 7. Power Steering - Hydraulic System Power Steering is hydraulic driven by either engine or electric motor. They work on a system where a hydraulic pump is driven by the engine, thereby generating pressure in the system. The pressure from the pump forces the hydraulic fluid to circulate and drive the steering box to assist steering. Hydraulic fluid should be replaced every 2 years or 40,000 kms. Since the system is sealed from air and water, contamination comes from the moisture in the air. Hydraulic fluid draws water from the air causing the fluid to loose its viscosity that leads to premature wear in the hydraulic components.
Things to look for: Grinding noise, humming noise, leaks, discoloration (milky white), worn hydraulic hoses due to continuous rubbing, worn oil seals, worn orings in the fittings, etc. 8. Tires Tires provide both the traction and steering for all equipments. Since most turf equipments are without suspension such as leaf springs, coils and shock absorbers, they are designed to travel slowly. All turf tires are not meant for highway use. It is very important to inflate tires properly in order to prevent blow- outs or uneven wearing either inside or outside. An under inflated tires will prematurely wear the outside part of the tire and will overheat and blow under heavy load. Over inflated tires will prematurely wear in the middle part of the tire and will can also cause tire blow-out. Tires come in tubeless and tubular type. Things to look for: Under or over inflated tire, leaks, uneven wearing as indicator of inflation, nails, cuts on the side walls. 9. Batteries Battery is a standby power source needed to drive electrical components while the engine is either running or not. A good example of an electrical component needed while the engine is not running is the starter and fuel shut off solenoid. The battery is also needed as the initial supplier of power while the engine is already running. Some examples of components are lighting, fuel shut off solenoid, fuel pumps, hydraulic solenoids, computer boxes, etc. The principle is when power is needed by any electrical component, the battery then supplies the power. Once the charge of the battery runs low, then the regulator senses this and supplies power to the battery from the alternator until full charge is restored in the battery. Things to look for: For ordinary batteries, always check water level using only distilled water. Make sure that the terminals are properly mounted making sure that the polarities are correct. Make sure that the terminals are tightened. Loose terminals will lead to non charging and low power supply of the battery. Use the correct size battery for each unit.
ATTENDANCE LIST Date:_________________ 1._________________________________________ 2._________________________________________ 3._________________________________________ 4._________________________________________ 5._________________________________________ 6._________________________________________ 7._________________________________________ 8._________________________________________ 9._________________________________________ 10.________________________________________ 11.________________________________________ 12.________________________________________ 13.________________________________________ 14.________________________________________ 15.________________________________________ 16.________________________________________ 17.________________________________________ 18.________________________________________
19.________________________________________ 20.________________________________________
21.________________________________________ 22.________________________________________ 23.________________________________________ 24.________________________________________ 25.________________________________________ 26.________________________________________ 28.________________________________________ 29.________________________________________ 30.________________________________________ 31.________________________________________ 32.________________________________________ 33.________________________________________ 34.________________________________________ 35.________________________________________ 36.________________________________________ 37.________________________________________ 38.________________________________________ 39.________________________________________ 40.________________________________________
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- JRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 1-11Dokumen11 halamanJRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 1-11Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates HD - Brochure - Small Micro BeltsDokumen8 halamanGates HD - Brochure - Small Micro BeltsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- JRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 30-40Dokumen11 halamanJRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 30-40Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- JRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 12-21Dokumen10 halamanJRM Inc 2010 CatalogPricing 12-21Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Draftguard Anti-Rotation DeviceDokumen2 halamanGates Draftguard Anti-Rotation DeviceMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates PowerGrip - GT2GT3 BeltsDokumen1 halamanGates PowerGrip - GT2GT3 BeltsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 Accuproducts CatalogDokumen24 halaman2012 Accuproducts CatalogMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- JRM Inc 2010 - Catalog22-2941210Dokumen8 halamanJRM Inc 2010 - Catalog22-2941210Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Broyhill Sprayer ProductsDokumen52 halamanBroyhill Sprayer ProductsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Original Timing Belt ADDokumen1 halamanGates Original Timing Belt ADMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Quad Power III BeltsDokumen6 halamanGates Quad Power III BeltsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 Accuproducts CatalogDokumen24 halaman2012 Accuproducts CatalogMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Vulco - Power BeltsDokumen1 halamanGates Vulco - Power BeltsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- GAtes Predator Drive Belts SystemDokumen4 halamanGAtes Predator Drive Belts SystemMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates Original Timing Belt ADDokumen1 halamanGates Original Timing Belt ADMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates MectrolDokumen1 halamanGates MectrolMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Parts Cat Ride RMDokumen50 halaman2011 Parts Cat Ride RMMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Facer 1000 - (ENG)Dokumen18 halamanRapid Facer 1000 - (ENG)Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Maxiforce 2009 CatalogDokumen228 halamanMaxiforce 2009 CatalogMotokoy Sprekitik Takoykoy100% (1)
- WC Product PricelistDokumen84 halamanWC Product PricelistMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Gates EPDM Micro V Ad BeltsDokumen1 halamanGates EPDM Micro V Ad BeltsMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Proposal PackageDokumen6 halamanMaintenance Proposal PackageMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- PTP Bedknives HOCDokumen2 halamanPTP Bedknives HOCMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Make An OfferDokumen2 halamanMake An OfferMotokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Barrel PonicsDokumen101 halamanBarrel Ponicsparaypan100% (1)
- Itunes DiagnosticsDokumen3 halamanItunes DiagnosticsKalyan ChakravarthyBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Steps To Setting Up Your Arowana TankDokumen6 halaman5 Steps To Setting Up Your Arowana TankedwinhlcBelum ada peringkat
- Full Disk Fighter 2012Dokumen3 halamanFull Disk Fighter 2012Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Full Disk Fighter 2012Dokumen3 halamanFull Disk Fighter 2012Motokoy Sprekitik TakoykoyBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- QDD301,601T (EN) BrochureDokumen4 halamanQDD301,601T (EN) Brochurenaquib uddin sarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Hyosung 125 GV Uso ManutenzioneDokumen43 halamanHyosung 125 GV Uso ManutenzioneMatteoBelum ada peringkat
- Mower ManualDokumen68 halamanMower ManualLarry PotterBelum ada peringkat
- Study and Analysis of Tire Changing Machine Components: - Now A Days in Automobile Field New FeaturesDokumen6 halamanStudy and Analysis of Tire Changing Machine Components: - Now A Days in Automobile Field New FeaturesHarshal PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Final Report Canadian Circular Economy For RubberDokumen141 halamanFinal Report Canadian Circular Economy For Rubberratz23695Belum ada peringkat
- Hitachi Lx70 7Dokumen5 halamanHitachi Lx70 7Tuấn AnhBelum ada peringkat
- Test Method OthersDokumen15 halamanTest Method OthersEnd End100% (1)
- McCormick MTX135 Tractor Operator Manual PDFDokumen22 halamanMcCormick MTX135 Tractor Operator Manual PDFfjjsjekdmmeBelum ada peringkat
- Result Preview 2QFY19Dokumen156 halamanResult Preview 2QFY19Sachin SikkaBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan HitachiDokumen44 halamanKumpulan HitachiMunajat Nursaputra100% (1)
- NTRC Axle Load Survey Pakistan Highway NetworkDokumen10 halamanNTRC Axle Load Survey Pakistan Highway NetworkFayaz RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Accessories and Consumables Catalogue: Edition 2 - 2015Dokumen108 halamanAccessories and Consumables Catalogue: Edition 2 - 2015Achmad Bahrul UlumBelum ada peringkat
- The String Method of Wheel AlignmentDokumen5 halamanThe String Method of Wheel Alignmentrb4069100% (1)
- Piaggio X7 250 I.E - WorkshopDokumen320 halamanPiaggio X7 250 I.E - WorkshopZoilo DominguezBelum ada peringkat
- Grove RT 540 e Manuel TechniqueDokumen16 halamanGrove RT 540 e Manuel TechniqueMohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Hitachi ZX 210W-3, 220W-3Dokumen596 halamanHitachi ZX 210W-3, 220W-3Anonymous yjK3peI784% (31)
- Engine Output: 103 kW/141 HP/2.200 RPM Bucket Sizes: 2.0-2.4 M Operating Weight: 12.7 TonDokumen4 halamanEngine Output: 103 kW/141 HP/2.200 RPM Bucket Sizes: 2.0-2.4 M Operating Weight: 12.7 Tonsaka dewaBelum ada peringkat
- HSE HAZARD RISK ASSESSMENT Rev 2Dokumen43 halamanHSE HAZARD RISK ASSESSMENT Rev 2TarekBelum ada peringkat
- 25854224Dokumen5 halaman25854224Fajar SodiqBelum ada peringkat
- Taller - Benelli - Tornado - 899TREKDokumen352 halamanTaller - Benelli - Tornado - 899TREKManuelmpg MotosBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Rubberdam PDFDokumen33 halamanPresentation Rubberdam PDFAbhishek RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Ordnance Corps Vehicles ManualDokumen294 halamanOrdnance Corps Vehicles ManualValeriy ValkovetsBelum ada peringkat
- 385 - 95R25 MICHELIN X-CRANE+ 170F TL - HeuverDokumen4 halaman385 - 95R25 MICHELIN X-CRANE+ 170F TL - Heuversteven.sun.auBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Dokumen136 halaman2005 Harley Davidson Sportster 883 66418Josef Bruno SchlittenbauerBelum ada peringkat
- Nanoindentation DmaDokumen8 halamanNanoindentation DmaDildeep PallipadBelum ada peringkat
- 1F4 Catalog0808Dokumen12 halaman1F4 Catalog0808Edwin Ng0% (1)
- Honda CRF250L Owners Manual EngDokumen114 halamanHonda CRF250L Owners Manual EngWhiskey TangoFoxtrotBelum ada peringkat
- Flexi Tech 60rg DataDokumen2 halamanFlexi Tech 60rg DatadogankkuBelum ada peringkat
- Check List Van PDFDokumen1 halamanCheck List Van PDFScribdTranslationsBelum ada peringkat