Performance Management
Diunggah oleh
kiranaishaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Performance Management
Diunggah oleh
kiranaishaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
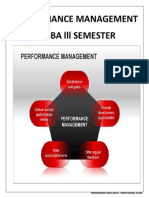
Introduction Without employee performance management, most organizations would operate under chaotic conditions.
Employee performance management is a set of guidelines for improving productivity, managing workplace behaviour, training and developing staff and providing constructive feedback on a regular and consistent basis. An employee performance management system consists of elements that help employers simultaneously achieve business goals and maintain employee satisfaction. Definition Employee performance management is a process that companies use to ensure their employees are contributing to producing a high quality product or service. Employee performance management encourages the employee to get involved in the planning for the company, and therefore anticipates by having a role in the process the employee will be motivated to perform at a high level. Significance of Employee Performance Employee performance is important for an organization, because it keeps the employees on track in terms of work projects. It is common that employees are asked to help out in different departments or on projects with a tight deadline. If this happens too often, the employee might not finish the tasks she was hired to do. Employee performance reviews ensure that the workers are focused on their jobs and work toward reaching the company's overall goals and satisfying the organization's mission statement. Why Is Employee Performance Management Important? Managing employee performance is beneficial to both the employee and manager. If done properly, it is an opportunity for two-way communication, and the information acquired can be useful. The frequency of performance management may be determined by company policy, the size of the team and the complexity of team tasks. 1. Employee Motivation: For most employees, knowing how their work contributes to the company's success can be motivating. Performance management can tell employees how they are doing in this regard. 2. Concerns: Regular employee performance management can address performance or behaviour concerns before they become serious problems.
3. New Skills: Acquiring new or different skills benefits both the employee and company. This can lead to shared responsibilities in team tasks, among other benefits. 4. Career Direction: Developing existing skills or learning new ones lets an employee plan for the next career move. The performance management process can create a plan to bridge gaps between current skills and future needs. 5. Communication: Performance management can make the employer aware of general employee satisfaction and needs. Employee Performance Management Tools Employee performance management is a core human resources discipline that facilitates an agency in meeting its overall mission. Management and employee participation in the performance management process improves organizational effectiveness, stimulates communication and provides clarity.
Planning Performance planning is the first step in the performance management process. Setting clear performance expectations and communicating them is essential to achieving and sustaining a high-performance culture. Collaborative two-way planning meetings held at the beginning of each rating cycle allow management to develop measurable performance goals with employee input. Active participation is vital to the success of the planning process.
Monitoring Progress reviews enable management and employees to address performance strengths and/or weaknesses prior to the end of the rating cycle. Conducting progress reviews keeps the line of communication open, thereby facilitating coaching and feedback. Progress towards meeting expectations should be discussed throughout the rating cycle. Employees should also inform managers of additional resource needs or roadblocks to meeting expectations. Since performance plans can be modified prior to the end of the rating cycle, unrealistic goals can be replaced or removed. Monitoring performance continually ensures there are no surprises at the end of the rating cycle.
Development Employee development enhances performance and introduces new skills. Providing the proper tools and technology needed to meet performance expectations helps an employee go above and beyond the acceptable level of competence. Receiving the training required to develop job skills is also good for employee morale. If an employee's performance does fall below the level necessary to meet expectations, a performance improvement plan should be developed and administered to address the issue.
Rating Employees must receive annual ratings each performance appraisal period. Evaluating an employee's performance against the standards developed in the performance plan summarizes the employee's accomplishments. Employees are encouraged to provide input by sending managers positive feedback from peers, management and/or customers. Ratings that are above the level of acceptable competence can lead to increases in salary or monetary awards. Performance that remains below the level of acceptable competence, after a performance improvement plan, can lead to disciplinary action.
Rewarding To retain the agency's top talent it is important to provide well-timed incentives. Performance awards are given to employees in recognition of contributions toward the organization's strategic goals. Rewarding excellent performance demonstrates appreciation and increases employee morale. Employees also value management communication of a job well done.
How to Monitor Employee Performance Great employee performance is a key to your business's success. Employees are the first line of many businesses' offense and their performance makes a direct impression on your customers. Customers are the primary source of your business's income and normally factor
their overall experience at your establishment into whether they may return or become a regular customer. This is why monitoring your employee's performance is invaluable. Instructions 1 Plan employee's job tasks in advance. This gives the employee both direction and an overall idea of the performance standards you expect her to meet. 2 Consistently supervise and evaluate your employee's performance. Provide feedback by administering monthly or annual progress reviews and give positive suggestions to better help her strengthen her performance. 3 Administer monthly or annual trainings to your employee that focus on improving positive work flow, time management, and introducing new skills and responsibilities. This keeps your employee(s) versatile and able to adapt to new working conditions quicker. 4 Identify your best employee and use her as a model for current and future employees. Identifying your best employee validates your expectations for employee performance and serves as proof that your expectations are realistic and reasonable. 5 Reward your employee. Rewarding your employee makes her feel appreciated and gives her a sense of value. Rewarding your employee also gives her motivation to keep up her level of performance. Activities Involved in Monitoring Employee Performance Performance management is essential in ensuring that a company's workforce is motivated, productive and committed to their jobs. Traditionally, managers monitor their employees' performance through quarterly or annual performance reviews. These sessions allow managers and employees to discuss the employee's strengths and weaknesses exemplified over the course of the review period. However, other activities are required to monitor employees' performance.
Goal Setting: Have employees start each new review session by setting future, measurable goals. Goal development is important in the business world because, according to
"Entrepreneur," effective goal-setting activities are directly associated with higher employee satisfaction and performance. Having clearly defined goals motivates employees to work toward their expected achievements. In turn, employees are evaluated by managers based on completion of goals throughout the year.
Regular Supervision: Provide regular supervision for subordinates. According to the U.S. Office of Personnel Management, regular supervision acts as continuous monitoring. At this time, supervisors should compare employees' work performance against the standards and expectations. Supervision sessions also allow employees to express concerns and ask questions as things come up, rather than having to wait all year to touch base at their annual review. By being available to connect with employees, managers monitor performance on a more consistent basis. In turn, they detect concerns and resolve performance issues more promptly.
Feedback: Offering employees feedback on their work is an effective way of monitoring their progress and letting employees know how well they performed a particular task or project. Furnishing employees with constructive notes makes them feel like their work is valued and appreciated, without having to meet in a formal setting.
Formal Reviews: Formal performance reviews are individual meetings between supervisors and their employees. Prior to the meeting, the supervisor fills out an evaluation form that scores the employee's performance based on professionalism, quality of work, organizational skills, timeliness and productivity. When the supervisor meets with employees, the results of the evaluation are shared and the supervisor summarizes what the employee's strengths are, as well as which areas need to be improved.
Reward Systems: Reward systems should be built into performance monitoring. When employees are recognized for their hard work, they feel more appreciated and therefore more motivated to continue doing a good job. The U.S. Office of Personnel Management explains
that rewards can be as simple as a certificate of appreciation or they can be more grandiose, such as giving employees cash benefits or extra days off from work. Types of Monitoring & Evaluation Performance management enables managers to monitor and evaluate how well employees are performing. Monitoring and evaluation systems are useful tools that let managers know whether employees are deserving of raises, promotions or, in some cases, termination. Managers may use one or a variety of monitoring and evaluation tactics to assess their employees. Live Observations Live observation is form of monitoring and evaluation that requires the manager or a consultant to observe an employee carrying out his job duties. In a school environment, this may mean that the school administrator sits in the teacher's classroom for a day while the teacher educates her students. In an office environment, this could mean that a manager shadows the employee during meetings and at his desk. Live observations give supervisors the chance to see employees in action and take notes about the things that employees do well or need to improve upon.
Performance Appraisals A performance appraisal is an evaluation meeting between an employee and his manager, similar to the structure of an interview. According to the October 2005 article in Entrepreneur Magazine, "Appraising Employee Performance," performance appraisals serve as feedback sessions in which the manager and employee discuss key issues that are relative to the employee's performance that the manager observes. For instance, an appraisal evaluation may indicate that an employee needs to improve the quality of his work or needs to learn how to be better organized around his desk. Performance appraisals should be constructive. They are not intended to bash or belittle an employee. Peer Reviews Peer reviews are monitoring and evaluation activities that involve coworkers scoring one another on how well they carry out their jobs. During a peer review, each employee is
responsible for monitoring and evaluating one other employee. Monitoring and evaluation tools are often used for employees to capture information and prompt them on what factors to look for. For instance, an employee may be asked to rate her peer's customer service skills. Managers collect peer reviews and assess them to see how everyone on the team scored. The review scores may be used by the manager to make changes in team assignments or to fuel a performance appraisal for individual employees. Secret Shopper Secret shoppers are activities that many companies use to find out how well employees perform. In this activity, someone from the company -- or hired by the company -- pretends to be a customer or client and interacts with the employee. The employee does not know that he is being monitored and evaluated by the customer or client. The secret shopper's experience with the employee is scored and given to a company manager for review. Self-Evaluation Self-evaluation is an evaluation process in which the employee scores herself on her performance. Self-evaluations are used to give employees a fair chance to analyze their strengths and weaknesses. Managers use self-evaluations to formulate performance appraisals.
How to Assess Employee Performance Instructions 1 Consult the employee's official job description. Align the organization's goals with the job's objective. Note any discrepancies and brainstorm ways to bring the discrepancies back in line.
2 Communicate management's expectations to the employee. A common understanding must exist between management and the employee regarding the work expectations, the nature of work to be accomplished and the standards by which the work is evaluated.
3 Offer the employee feedback concerning his performance and it's relationship to the expectations set forth by management. Be constructive instead of destructive with your comments while being honest about your appraisal.
4 Coach the employee. Provide the resources required for her to meet and exceed management's expectations. Coaching needs to be a constant and consistent effort made by management in order to clarify and modify performance before it is too late.
5 Assess the employee's strengths and weaknesses. Do this by using a narrative form, a checklist, peer and self evaluations, or by using ranking charts. The employee needs to understand why you have come to your conclusions so he is able to correct any problems.
6 Decide what type of career development or continuing education might be beneficial to assisting the employee in developing her skills and improving her performance. Be open to all options.
Factors That Affect Employee Performance in a Organization Employees don't perform in a vacuum. There are a variety of factors, personal, companybased and external that affects their performance. Identifying these factors can help improve recruitment, retention and organizational results. 1. Job Fit Employees must be qualified to perform a job in order to meet expectations. The best fit for a job is identified by skills, knowledge and attitude towards the work. If an employee is in the wrong job for any of these reasons, results will suffer. 2. Technical Training Employees can bring skills to a position but there are likely to be internal, company- or industry-specific activities that will require additional training. If a process requires a new
software package it's unrealistic to expect employees to just figure it out; they should receive adequate training. 3. Clear Goals and Expectations When everyone understands the targets and expected outcomes, it is easier to take steps to get there and measure performance along the way. Organizations without clear goals are more likely to spend time on tasks that do not impact results. 4. Tools and Equipment Just as a driver needs a vehicle in operating condition, employees must have the tools and equipment necessary for their specific jobs. This includes physical tools, supplies, software and information. Outdated equipment or none at all, has a detrimental effect on the bottom line. 5. Morale and Company Culture Morale and company culture are both difficult to define but employees will be able to report when they are poor or positive. Poor morale exists when there is significant whining, complaining and people just don't want to come to work. On the positive end, the workplace is energized by a sense of purpose and teams that genuinely want to work together.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Benefits of Performance ManagementDokumen13 halamanBenefits of Performance ManagementGopalakrishnan KuppuswamyBelum ada peringkat
- WEEK-6-Performance-Management-and-EvaluationDokumen95 halamanWEEK-6-Performance-Management-and-Evaluationgaboferlyn4Belum ada peringkat
- PMS-CHP 2Dokumen18 halamanPMS-CHP 2Soyed Mohammed Zaber HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Performance AppraisalDokumen20 halamanPerformance AppraisalGODBARBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Performance Management The Complete GuideDokumen7 halamanWhat Is Performance Management The Complete GuideCata MBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management Material II MBADokumen53 halamanPerformance Management Material II MBAJERINBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource ManagementDokumen15 halamanHuman Resource ManagementAditiBelum ada peringkat
- PM & CM Unit 1Dokumen5 halamanPM & CM Unit 1De SaravananBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 Performance MGMTDokumen19 halamanModule 3 Performance MGMTAnonymous uxd1ydBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management GuideDokumen8 halamanPerformance Management GuideKJuneBelum ada peringkat
- Performance AppraisalDokumen8 halamanPerformance AppraisalsidrasharieffBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation ReportDokumen11 halamanPresentation ReportShreyasi SBelum ada peringkat
- INTRODUCTION of Performance ManagementDokumen17 halamanINTRODUCTION of Performance Managementspavankumar141Belum ada peringkat
- Performance appraisal benefits and challengesDokumen49 halamanPerformance appraisal benefits and challengesSai PrintersBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management ProcessDokumen13 halamanPerformance Management ProcessRishabh VijayBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen19 halamanAssignmentshohelrn29Belum ada peringkat
- Best Performance Management Practices For TodayDokumen8 halamanBest Performance Management Practices For TodayMISHRA SRINIVASBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1Dokumen19 halamanModule 1prasannanayak7019Belum ada peringkat
- Performance management system at TCS analyzedDokumen6 halamanPerformance management system at TCS analyzedRIA VINCENT RCBSBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management ProcessDokumen4 halamanPerformance Management Processsiska tifanyBelum ada peringkat
- Q.5 Prepare A Performance Appraisal System and A Proper Compensation Management System For Lower To Upper Management Level Employees of The CompanyDokumen10 halamanQ.5 Prepare A Performance Appraisal System and A Proper Compensation Management System For Lower To Upper Management Level Employees of The CompanyT.v. SurendraBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Performance and EvaluationDokumen21 halamanEmployee Performance and EvaluationJessica KlingBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Performance ApprisalDokumen50 halamanEmployee Performance Apprisalshaik karishmaBelum ada peringkat
- MpobDokumen18 halamanMpobRohit AggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Performance AppraisalDokumen3 halamanPerformance AppraisalMohd Fariq0% (1)
- Executive Summary: Planning Work and Setting Expectations, Continually Monitoring PerformanceDokumen9 halamanExecutive Summary: Planning Work and Setting Expectations, Continually Monitoring Performancenyi naingBelum ada peringkat
- DraftDokumen35 halamanDraftPubg MobileBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management ObjectivesDokumen8 halamanPerformance Management ObjectivesMUHAMMED YASIRBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection Paper 2Dokumen2 halamanReflection Paper 2Alwin Glen PapaBelum ada peringkat
- Sir Gabion Human NatureDokumen30 halamanSir Gabion Human NatureGEREON DE LA CRUZBelum ada peringkat
- Report On Square LTDDokumen12 halamanReport On Square LTDNazmulHasanBelum ada peringkat
- HR Performance ManagementDokumen2 halamanHR Performance ManagementShantaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management - A Powerful Tool for Improving Organizational PerformanceDokumen15 halamanPerformance Management - A Powerful Tool for Improving Organizational Performancemegha shreeBelum ada peringkat
- Performance ManagementMBA NOTESDokumen53 halamanPerformance ManagementMBA NOTESVikash ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- HRM Course Work 1 Performance MGT & Appraisal Group 9Dokumen14 halamanHRM Course Work 1 Performance MGT & Appraisal Group 9collin85Belum ada peringkat
- A Study On Performance Appraisal Strategy of Ultratech CementDokumen102 halamanA Study On Performance Appraisal Strategy of Ultratech CementPrashanth PB100% (11)
- Performance Management - Role of HRDokumen9 halamanPerformance Management - Role of HRDeepak NagwanshiBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management Training ProgramDokumen11 halamanPerformance Management Training ProgramBitoy AlarconBelum ada peringkat
- PM - Practice Question Performance Management Question PaperDokumen5 halamanPM - Practice Question Performance Management Question Paperhareesh0% (1)
- Importance of Performance ManagementDokumen2 halamanImportance of Performance ManagementLynka Dlo OlbBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment: I M S, U B, Q, BBS M B 2018-2020Dokumen7 halamanAssignment: I M S, U B, Q, BBS M B 2018-2020Riaz Baloch NotezaiBelum ada peringkat
- Performance ManagementDokumen47 halamanPerformance ManagementPremendra SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Ii Rewarding Performance-Pay For Performance - Challenges - Meeting The Challenges For Pay - For - Performance SystemsDokumen25 halamanUnit Ii Rewarding Performance-Pay For Performance - Challenges - Meeting The Challenges For Pay - For - Performance SystemsmanojBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 12Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 12peter t. castillo100% (1)
- HRM6 Performance Appraisal and EvaluationDokumen10 halamanHRM6 Performance Appraisal and EvaluationarantonizhaBelum ada peringkat
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester IVDokumen7 halamanMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester IVroshreshBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management System GuideDokumen15 halamanPerformance Management System GuideDanielle Angel MalanaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management System Key ElementsDokumen10 halamanPerformance Management System Key ElementsParidhi SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management Is The Current Buzzword and Is The Need in The Current Times of Cut Throat Competition and The Organizational Battle For LeadershipDokumen4 halamanPerformance Management Is The Current Buzzword and Is The Need in The Current Times of Cut Throat Competition and The Organizational Battle For LeadershipZainab BukhariBelum ada peringkat
- Performance AppraisalDokumen7 halamanPerformance Appraisalanon_138935818Belum ada peringkat
- Meaning of ControllingDokumen12 halamanMeaning of Controllingfernando tamayoBelum ada peringkat
- Performance MGTDokumen6 halamanPerformance MGTTanya AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3Dokumen47 halamanUnit 3anushka jainBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment 4. Ramirez Ria Jane JDokumen4 halamanAssessment 4. Ramirez Ria Jane JRiajane RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- PM 3 PDFDokumen5 halamanPM 3 PDFSijo Joseph ChakolaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Performance ManagementDokumen13 halamanChapter 1 Performance ManagementLuna ValeriaBelum ada peringkat
- How to Improve Performance through the Balanced ScorecardDari EverandHow to Improve Performance through the Balanced ScorecardPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (3)
- Continual Process Improvement - An Essential Discipline of Successful ClubsDari EverandContinual Process Improvement - An Essential Discipline of Successful ClubsBelum ada peringkat
- Adv& DisadvDokumen6 halamanAdv& DisadvkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Intellectual Property RightsDokumen11 halamanIntellectual Property RightskiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive AdvantageDokumen27 halamanCompetitive Advantagekiranaisha100% (1)
- MaslowDokumen10 halamanMaslowkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- COMPENSATIONDokumen4 halamanCOMPENSATIONkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Competitor AnalysisDokumen12 halamanCompetitor AnalysiskiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Global MarketingDokumen7 halamanGlobal MarketingkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance ManagementDokumen9 halamanPerformance ManagementkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Optimum Appointees ProcessDokumen25 halamanOptimum Appointees ProcesskiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- A Systematic Approach in Achieving A High Level of Effectiveness and Efficiency Would Be Through A Selection and Recruitment ProcessDokumen46 halamanA Systematic Approach in Achieving A High Level of Effectiveness and Efficiency Would Be Through A Selection and Recruitment ProcesskiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- RecruitmentDokumen20 halamanRecruitmentkiranaisha100% (1)
- Strategic Alliances: The Right Way To Compete in The 21St CenturyDokumen5 halamanStrategic Alliances: The Right Way To Compete in The 21St Centuryjeet_singh_deepBelum ada peringkat
- Topic: What Is The Purpose of Planning? Analyse The Key Factors That Influence The HRP Processes?Dokumen11 halamanTopic: What Is The Purpose of Planning? Analyse The Key Factors That Influence The HRP Processes?kiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Lewin's Three-Stage Model of Change ExplainedDokumen7 halamanLewin's Three-Stage Model of Change ExplainedkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- NewDokumen1 halamanNewkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Employee 1Dokumen100 halamanEmployee 1sulthan1987Belum ada peringkat
- People ManagementDokumen18 halamanPeople ManagementkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Rewmansymprpt 0705Dokumen22 halamanRewmansymprpt 0705kiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Information SystemDokumen19 halamanManaging Information SystemkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Cloud ComputingDokumen25 halamanCloud ComputingkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- CorporateDokumen23 halamanCorporatekiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Assumptions Underlying The Concept of Comparative AdvantageDokumen7 halamanAssumptions Underlying The Concept of Comparative AdvantagekiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDokumen120 halamanStrategic Human Resource ManagementMostafijurRahmanNahid100% (4)
- Review of The HeckscherDokumen6 halamanReview of The HeckscherkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Burning PlatformDokumen4 halamanBurning PlatformkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Job Evaluation and Job RotationDokumen3 halamanJob Evaluation and Job RotationMinal WahurwaghBelum ada peringkat
- Models of Change ManagementDokumen12 halamanModels of Change ManagementkiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- CorporateDokumen23 halamanCorporatekiranaishaBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Planning Is A Very Essential Tool For Business and The First Step TowardsDokumen11 halamanMarketing Planning Is A Very Essential Tool For Business and The First Step TowardskiranaishaBelum ada peringkat