Agronomy To Baco
Diunggah oleh
Prasanth YellaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Agronomy To Baco
Diunggah oleh
Prasanth YellaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
TOBACCO PRODUCTION AND PROTECTION TECHNOLOGIES FOR IMPROVING THE PRODUCTIVITY & QUALITY (AGRONOMIC PRACTICES) 9 Tobacco is an important
commercial crop cultivated in an area of 0.4 million ha producing annually around 700 million kg of cured leaf out of which 260 M kg is Flue-Cured Virginia tobacco (cigarette type). India is the 3rd largest producer of tobacco in the world after China and Brazil. Majority of the states in the Indian union territory grow one type or the other to a greater or lesser extent, significantly influencing the economy and prosperity of the farming community. Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV), Bidi, Hookah and Chewing, Cigar filler, Cigar Wrapper, Cheroot, Burley, Oriental, HDBRG, Lanka etc., are the different types of tobacco grown in the country. Tobacco is consumed in the form of cigarettes, cigars, cheroots, bidis, pipe and hookah. It is chewed in the form of Surti, Zarda, Qiwamquid, Masheri, Kharamasala. Also, tobacco is inhaled in the form of snuff. The crop provides employment to about 36 million people directly or indirectly including 6 million farmers in the country. India ranks 5th largest exporter of tobacco in the world after Brazil, USA, Malawi and Turkey. The crop fetches annually around Rs.1,713 crores as foreign exchange through exports and over Rs. 9,100 crores as excise revenue. An estimated ~250 million people in the country use tobacco in different forms.
Flue-cured Virginia tobacco:
In Andhra Pradesh, Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco is grown in an area of 1,25,000 ha in East Godavari, West Godavari, Khammam, Krishna, Guntur, Prakasam , Nellore, Karimnagar and warangal districts with a total production of 170 M kg of leaf. While in Karnataka, FCV tobacco is cultivated in 85,000 ha of area with a production of 87 M kg leaf. It is also grown in a smaller area in the states of Maharastra and Orissa. The recommended production technologies for FCV tobacco cultivation in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are presented in Table 1
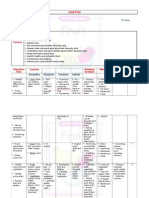
Table 1: Crop production practices for FCV tobacco in India Cultural Practice Variety Andhra Pradesh Traditional Northern Light Black Soils Soils Gauthami, Hema Kanchan VT-1158, Hemadri and Siri Karnataka Karnataka Light Soils Kanchan, Thrupthi, Rathna Swarna, Bhavya, Deep ploughing in March and April
Southern Light Soils Gauthami, Hema, VT1158 and Kanthi Deep ploughing between July and September
Preparatory Cultivation
Deep ploughing in summer, 2-3 ploughings between July and September
Deep ploughing and Discing with tractor with the onset of monsoon
Organic manures (tonnes/ ha)
FYM @7.5
Date of planting
Mid October to mid November
Sunnhemp green manuring or application of FYM or FPC @10-12 or sheep or cattle penning Mid-Sept. to midOct. in upper NLS and mid-Oct. to mid-Nov. in lower NLS 100 x 60 cm Furrow planting followed by ridging on 40 th day Dollop 115:60:120
FYM @ 5
FYM @ 810
Mid October to Mid. November
1st week of May to middle of June
Spacing Planting method
70 x 50 cm Flat planting
70 x 50 cm Flat planting followed by ridging / earthing up Plant rowplough furrow 60:60:60 60:60:80 (Podili) One life saving irrigation @ 40-45 days of planting 2 or 3 times before 40 days
Method of fertilization Fertiliser dose (N: P2O5: K2O kg/ha) Irrigations
Plant rowplough furrow 45:0:0 50:50:50 (Bhadrachalam) Crop is grown on conserved soil moisture Two at 20th & 40th day after planting Judicious topping at first flower opening Decanol or Royalten 4%
100 x 60 cm Flat planting followed by ridging Dollop 60:40:120
8-10
Intercultural operations
Level of topping
2 or 3 times up to 40 days and ridging on 40 th day Topping at flower bud initiation at 24 leaves Decanol or Royalten 4% followed by hand desuckering Priming mature leaves Flue-curing Plant position grading
Bud topping
Grown in S-W monsoon conditions 2 or 3 times before 40 days Bud topping
Sucker control
Decanol or Royalten 4%
Decanol or Royalten 4% Priming mature leaves Flue-curing Plant position grading
Harvesting
Priming mature leaves Flue-curing Farm grading
Curing method Grading
Priming mature leaves Flue-curing Farm grading
Bidi and Pikka tobacco: Bidi tobacco is cultivated in Gujarat and Karnataka in 1.15 lakh ha area while Pikka tobacco is an important tobacco cultivated in Orissa for chewing and cheroot purposes. Important production technologies recommended for Bidi tobacco cultivation in Gujarat and Karnataka and for Pikka tobacco in Orissa are furnished in Table 2. Table 2: Crop production practices for Bidi and Pikka tobacco in India Cultural Practice Variety Bidi Tobacco Gujarat Karnataka Anand119, Anand 2, GT- A-119, 4, GT-5,GT-7,GT-9,GTH- NPN 190, Spoorthy 1, GTH-1 (MR) Bhavya Sree NBD-43 Deep Ploughing in summer Green manuring or FYM @12.5 or poultry manure or Azolla August 90 x 60 cm Flat planting Plant row - plough furrow method 160:0:0 Deep Ploughing in summer FYM @10 10-25th August 100 x 75 cm Flat planting Deep placement before planting 125:60:40 Pikka Tobacco Orissa Pyruvithanam, J.P.1, NG-74, II1327
Preparatory Cultivation Organic Manures (tonnes/ha) Date of planting Spacing Planting method Method of fertilization Fertiliser dose (N: P2O5: K2O kg/ha) Irrigations Intercultural operations Level of topping Sucker control Harvesting
Deep Ploughing in summer FYM @10
2nd Fortnight of August 75 x 50 cm Flat planting & ridging Band placement 80:40:40
As and when required As and when required 18-24 leaves Decanol 4-6% & hand removal When leaves develop spangles Sun - curing Bukha, Geran, Galia, Lankada
3-4 irrigations 2-3 times 16-20 leaves Khudaband 4-6% or Stomp 1.5% When maximum no. of leaves develop spangles Sun - curing I sort, II sort etc.
Nil Two hoeings & hand weeding 10-12 leaves Decanol 4% & hand removal Stalk cut method
Curing method Grading
Sun - curing ----
Burley, Natu and Lanka tobaccos: In Andhra Pradesh, Burley, Natu and Lanka tobaccos are cultivated to an extent of 45,000 ha. The Important recommended production technologies for these tobaccos are given in Table 3.
Table 3: Crop production practices for Burley, Natu and Lanka tobaccos in Andhra Pradesh. Cultural Burley Irrigated Natu Rainfed Natu Lanka Practice Lanka Spl. Variety Burley-21 and Kommugudem, Tokaku, Banket A1 Peddavithanam, Viswanath, Pyruvithanam, Natu Spl., Rangapuram Prabhat, WAF, Bhairavi Preparatory Cultivation Organic manures (tonnes/ha) Date of planting Deep Ploughing in summer FYM @ 10 Deep ploughing in summer FYM @ 10 12 or green manuring Deep ploughing in summer FYM @ 15 Deep ploughing in summer FYM @10
Mid-July to mid-August 90 x 45 cm Ridge planting
Second to last week of October 60 x 60 cm Flat planting followed by ridging Dollop
Spacing Planting method
Mid-Oct. to 1st week of November 90 x 90 cm Flat planting
Method of fertilization Fertiliser dose (N: P2O5: K2O kg/ha) Irrigations Interculture Level of topping Sucker control Harvesting
Dollop
Plough furrow
Last week of Oct. to 15th Nov. 60 x 60 cm Flat planting followed by ridging Dollop
125:50:50
350:50:100
80:50:50
300:50:50
Monsoon crop 2 3 times No topping ---Priming
6-8 2 3 times 14-16 leaves Decanol 6% Stalk cut (katta) or priming (Thoranam method) Air-curing Melmi & Gulla
Rainfed 2-4 times 14-16 leaves Decanol 6% Priming
3-4 3-4 times 12-14 leaves Decanol 6% Stalk cut
Curing method Grading
Air-curing Flyings, bottom, middle and top
Air-curing Bright, brown, dark brown, green and perished leaf
Air-curing Kotaku, Baraku Mattasam and Gulla
Cigar & Cheroot, Chewing, Hookah and HDBRG Tobaccos: Chewing, cigar and cheroot tobaccos are the major types grown in Tamil Nadu. Chewing tobacco is mainly grown in West Bengal, Bihar, U.P. & Assam, while hookah tobacco is cultivated in U.P.,
Bihar, Gujarat, Haryana and Assam. HDBRG tobacco is mainly cultivated in black soils of Guntur district in Andhra Pradesh with 3 4 irriagations which is used in cigarette blending. Table 4: Crop production practices for in Cigar & Cheroot, Chewing, Hookah and HDBRG Tobaccos in India Cultural Practice Cigar & Cheroot Tamil Nadu O-K.1, Bhavani Spl., Olor-10, I-737, Sangami ChewingBihar, Tamil Nadu & West Bengal Bihar : Vaishali Spl., Sona, PT76, Lichchavi West Bengal: Podali, Chama Tamil Nadu: Bhagyalakshmi, Meenakshi, Abirami, Kaviri, Meenakshi (CR) Deep ploughing in summer FYM @ 25 HookahWest Bengal DD-437 and Dharla SonarMotihari, Manasi HDBRGAndhra Pradesh HDBRG
Variety
Preparatory Cultivation Organic manures (tonnes/ha) Date of planting
4-6 ploughings in Kharif FYM @ 25 or sheep penning Mid-Oct., to Mid-Nov.
Deep ploughing in summer FYM @ 20
Deep ploughing in summer FYM @ 10 1st week of Oct., 1st week of November
Spacing
Planting method
Cigar: 70 x 50 cm Cheroot: 60 x 45 cm Ridge planting
Bihar & Bengal: Mid Sept. to mid Oct. T.N. Last week of Oct. to end of Nov. Bihar: 90 X 75cm Bengal: 90 x 45 cm T.N. 65 x 65cm Ridge planting
Mid-Oct. to 1st week of November
Method of fertilization Fertiliser dose (N: P2O5: K2O kg/ha) Irrigations
Dollop 100:50:100
Dollop Bihar:250:60:60 Bengal: 120:50:75 T.N:100:50:0 Bihar :3 Bengal: 2 Tamil Nadu: 22
Jati: 90 x 90 cm Motihari: 60 x 45 cm Flat planting followed by ridging Pocketing 120:50:75
80 x 50 cm
Flat planting
PRPF 100:50:50
20
2-3
Intercultural operations Level of topping
2 3 times 14-16 leaves
2 3 times Bihar: 14 16 leaves Bengal: 8-10 leaves Tamil Nadu: 10 leaves Decanol or Royalten 6% Stalk - cut Sun-curing Bihar:1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th grades T.N: Rasi & Kruz
4 - 5 times 8 10 leaves
2-3 times 20 leaves
Sucker control Harvesting Curing method Grading
Decanol or Royalten 6% Stalk - cut Sun-curing Plant position (Rasi & Kruz)
Decanol or Royalten 6% Priming Air-curing Panpatta No.1, Niras &Jalapatta
Decanol or Royalten6% Priming Sun-curing Bottom, middle &top primings
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Lose Fat and Gain Muscle FundamentalsDokumen19 halamanLose Fat and Gain Muscle FundamentalsMuntele StraniuBelum ada peringkat
- Bee sting reactions and treatments explained in depthDokumen9 halamanBee sting reactions and treatments explained in depthPrasanth YellaBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Survey STATISTICAL Appendix 2012-13Dokumen130 halamanEconomic Survey STATISTICAL Appendix 2012-13pavan6754Belum ada peringkat
- Classical Biological Control of Papaya Mealy BugDokumen4 halamanClassical Biological Control of Papaya Mealy BugPrasanth YellaBelum ada peringkat
- Tobacco 109Dokumen18 halamanTobacco 109Prasanth YellaBelum ada peringkat
- English NDA 2009Dokumen24 halamanEnglish NDA 2009rubsuraBelum ada peringkat
- DiapauseDokumen1 halamanDiapausePrasanth YellaBelum ada peringkat
- Agri StatDokumen23 halamanAgri StatPrasanth YellaBelum ada peringkat
- BOPIS Recipe: Filipino Pork Heart and Lungs DishDokumen4 halamanBOPIS Recipe: Filipino Pork Heart and Lungs DishDessa Ruth ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Panic at the Diner: A Cooperative Game of Fulfilling Orders Against the ClockDokumen4 halamanPanic at the Diner: A Cooperative Game of Fulfilling Orders Against the ClockSara DragicevicBelum ada peringkat
- Danh Tư Số Ít-NhiềuDokumen9 halamanDanh Tư Số Ít-Nhiềudien.nguyen.bbs19Belum ada peringkat
- A PositionDokumen10 halamanA PositionFernanda DiasBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates Protein FatsDokumen18 halamanCarbohydrates Protein Fatskristinealborte123Belum ada peringkat
- Grocery list essentialsDokumen38 halamanGrocery list essentialsElizabeth Sánchez LeónBelum ada peringkat
- Trad 2Dokumen1 halamanTrad 2Irina StoicaBelum ada peringkat
- Snap Factsheet Pennsylvania - From Center On Budget and Policy PrioritiesDokumen2 halamanSnap Factsheet Pennsylvania - From Center On Budget and Policy PrioritiesMichelle Rotuno-JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Cropping Pattern of North East India: An Appraisal: November 2014Dokumen12 halamanCropping Pattern of North East India: An Appraisal: November 2014Biraj GogoiBelum ada peringkat
- Free Meal PlanDokumen9 halamanFree Meal PlanBernadett KáluczBelum ada peringkat
- Label ReadingDokumen4 halamanLabel ReadingemysamehBelum ada peringkat
- Food Groups: Your Options To Choose FromDokumen1 halamanFood Groups: Your Options To Choose FromJupaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Make A Cup of Coffee: Materials and IngredientsDokumen1 halamanHow To Make A Cup of Coffee: Materials and IngredientsmayaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 - Pastry Doughs - Puff Pastry and PhylloDokumen4 halamanTopic 3 - Pastry Doughs - Puff Pastry and PhylloRosedel BarlongayBelum ada peringkat
- Laziness Is The Main Cause of ObesityDokumen2 halamanLaziness Is The Main Cause of Obesitychamomile222100% (1)
- Tasty Bites eatables ltd- India's largest prepared Indian food brandDokumen3 halamanTasty Bites eatables ltd- India's largest prepared Indian food brandCOOK EAT REPEATBelum ada peringkat
- Meniu Limba EnglezaDokumen4 halamanMeniu Limba EnglezaDiana BotaBelum ada peringkat
- Cagayan Valley's Five Provinces ExploredDokumen15 halamanCagayan Valley's Five Provinces ExploredJhandy BolandoBelum ada peringkat
- Food - Lesson Plan (Can Do)Dokumen5 halamanFood - Lesson Plan (Can Do)claudiamonteirodt5eBelum ada peringkat
- Inggris Abg DavinDokumen6 halamanInggris Abg Davinnoni noniBelum ada peringkat
- Complete The Sentences With The Correct Forms of The Verbs in BracketsDokumen2 halamanComplete The Sentences With The Correct Forms of The Verbs in BracketsCarlos Merchant100% (1)
- MNT 1 DM Case Study Due 11 29 2016Dokumen3 halamanMNT 1 DM Case Study Due 11 29 2016api-340581896Belum ada peringkat
- Opera (Cake Project)Dokumen9 halamanOpera (Cake Project)Shashank ShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Menu Tanjung Food Hub LabuanDokumen36 halamanMenu Tanjung Food Hub LabuanAqilahBelum ada peringkat
- Pds Sunflower Oil High Oleic Tx008082Dokumen3 halamanPds Sunflower Oil High Oleic Tx008082khairil_amrieBelum ada peringkat
- S45262 Sep 10Dokumen4 halamanS45262 Sep 10Vishnu Vardhan PadidalaBelum ada peringkat
- Easy IdliDokumen7 halamanEasy IdlijunkyardBelum ada peringkat
- Lumpiang Sariwa: Ingredients: FillingDokumen17 halamanLumpiang Sariwa: Ingredients: FillingKathie De Leon VerceluzBelum ada peringkat
- Tanjore Marathi RecipesDokumen10 halamanTanjore Marathi RecipessathyavasuBelum ada peringkat