STLD
Diunggah oleh
satyakar_vvkDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
STLD
Diunggah oleh
satyakar_vvkHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Code No: R22035
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (Com. to ME, AME, MM)
SET - 1
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. Explain the characteristic features of the following with examples? i) Metallic bond ii) Ionic bond iii) Covalent bond
Max. Marks: 75
2.
a) State Hume Rotherys rules for the formation of substitutional type of solid solutions. b) Write briefly about electron compounds? Draw Fe-C phase diagram and label all the phases. Describe the phase changes during solidification of Fe 0.45% C alloy. a) Explain the Malleabilizing treatment given to white cast iron? Sketch the typical microstructure of malleable cast iron. Label the phases in it. b) Write short notes on tool and die steels? a) Explain the effects of alloying elements on Fe Fe3C diagram? b) Compare the following heat treatment processes i) Annealing and normalizing ii) Carburizing and nitriding a) Discuss the physical and mechanical properties of copper. Write down the applications of pure copper. b) Name any two important brasses from alpha () brass group. Give their composition, properties and important applications. a) Compare the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of ceramics with those of metals. b) Discuss the different types of bonding in ceramics. Define and classify composite material? Explain about any three types of composite materials.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: R22035
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (Com. to ME, AME, MM)
SET - 2
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. 2. Compare and contrast metallic, covalent and ionic bonds. Give examples. Write short notes on the following i) Hume-Rotherys rules ii) Interstitial compounds
Max. Marks: 75
3.
a) What is proeutectiod ferrite? How it differs from eutectoid ferrite? b) Describe the slow cooling history of 0.4% C in Fe-Fe3C diagram and calculate the proportions of different phases at 11000C, 7270C , and at 6000C and also draw the room temperature microstructures? Explain the following: a) Hadfields manganese steel b) Tool steels c) Grey cast irons. a) Explain the various stages in an heat treatment cycle. b) Explain the following heat treatment process? i) Annealing ii) Carburizing Explain the structure and properties of Al and its alloys? Write short notes on the following: a) Abrasive materials b) Nano-materials Classify composite materials? Explain the manufacturing methods of composite materials?
4.
5.
6. 7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: R22035
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (Com. to ME, AME, MM)
SET - 3
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. 2.
Max. Marks: 75
Explain the different types of bonding in materials and illustrate them with suitable examples. a) Explain the types of solid solutions with examples?. b) Write about Hume Rotherys rules? a) What is eutectoid reaction? Explain eutectoid reaction in Fe-Fe3C diagram? b) Describe the slow cooling history of 0.8% C in Fe-Fe3C diagram from austenite to room temperature and calculate the proportions of different phases and also draw the room temperature microstructures? a) Classify steels? Explain the properties of plain carbon steels? b) Write short notes on cast irons? a) What are T-T-T diagrams? Explain the construction of TTT diagrams? b) Discuss the effect of alloying elements on the T-T-T diagram? Explain the structure and properties of Ti and its alloys? Write short notes on a) Ceramics b) Abrasive Materials Differentiate between the following: a) Particle-reinforced and fiber reinforced composite materials b) MMCs and C-Composites
3.
4.
5.
6. 7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: R22035
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE (Com. to ME, AME, MM)
SET - 4
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Max. Marks: 75
1.
Explain the origin of metallic bonding. How does it differ from ionic bonding? Explain with suitable examples. a) How are the alloys classified according to the microstructures? Explain them. b) What do you mean by intermediate alloy phase? Explain any one type of intermediate alloy phase with some examples Write short notes on: a) Miscibility gap b) Degrees of freedom c) Invariant reactions d) Segregation. a) State and describe various factors affecting the properties of cast Irons. b) Distinguish between white heart and black-heart malleable Iron. a) Draw a T-T-T diagram for 0.4% C steel and identify the microstructural phases and their hardness values? b) Write short notes on age hardening behavior? Explain about structure and properties of Cu and its alloys? a) Compare the properties of crystalline ceramics and glass ceramics. b) Why annealing and tempering operations are performed on glass? Explain Write short notes on a) Types of reinforced materials b) Manufacturing methods of composites
2.
3.
4.
5.
6. 7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: R22023
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Com. to EEE, ECE, BME, EIE, ECC)
SET - 1
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) Assume an arbitrary number system having a radix of 5 and 0, 1, 2, L and M as its independent digits. Determine: i) The decimal equivalent of (2LM.L1) ii) The octal equivalent of (21L.M2) iii) The hexagonal equivalent of (LM1.L2) iv) The total number of possible four-digit combinations in this arbitrary number system. b) What is an excess-3 BCD code? Which short coming of the 8421 BCD code is overcome in the excess-3 BCD code? Illustrate with the help of an example. (8M+7M)
2.
a) i) Simplify F ( A, B, C , D, E ) = ABC D + ABCD + ABC D + ABCDE + ABC D E + ABC DE ii) Prove that AB + C + D [D + (E + F )G ] = D (AB + C ) + D G (E + F ) b) With the help of the generalized form of the Hamming code, explain how the number of parity bits required to transmit a given number of data bits (8M+7M)
3.
a) Write a simplified max-term Boolean expression for 0, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 14 using the Karnaugh mapping method. b) Minimize the following function using the Quine-McCluskey method. Y = (1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 24, 25, 26, 28, 29, 31) (6M+9M)
4.
a) Discuss the functional principle of 4-bit ripple carry adder what is its major disadvantage? b) Draw the logic diagram of a three-digit Excess-3 adder and briefly describe its functional principle? (8M+7M)
5.
a) Design a two-level positive logic decimal-to-BCD priority encoder for decimal inputs from 0 to 4. b) Implement the following logic function using MUX with three select inputs? (8M+7M)
1 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 1
6.
a) Obtain the programming table for three-digit binary to gray code conversion using PLA b) How does a programmable logic device differ from a fixed logic device? What are the primary advantages of using programmable logic devices? (8M+7M)
7.
a) Design a synchronous counter that counts as 000, 010, 101, 110, 000, 010 Ensure that the un used states of 001, 011, 100 and 111 go to 000 on the next clock pulse. Use J-K flip-flops. b) Obtain conversion from D flip-flop to J-K flip-flop (9M+6M)
8.
Derive a circuit that realizes the FSM defined by the state assigned table below using JK flipflops PS A B C D E NS, Z X=0 X=1 B,0 E,0 E,0 D,0 D,1 A,0 C,1 E,0 B,0 D,0 (15M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Com. to EEE, ECE, BME, EIE, ECC)
SET - 2
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) Perform the following operations using r-1s complement arithmetic: i) (+43)10 (53)10. ii) (3F85)16 (1E73)16 b) Prove that16-bit 2s complement arithmetic cannot be used to add +18150 and +14618, while it can be used to add 18150 and 14618. (8M+7M) a) What do you understand by canonical and expanded forms of Boolean expressions? Illustrate with examples. b) What is the Hamming distance? Discuss with the help of examples, what is the role of the Hamming distance in deciding the error detection and correction capability of a code meant for the purpose? (8M+7M) a) i) Simplify the Boolean function given by f ( X , Y , Z ) = X .Z + X .Z for the dont care condition expressed X .Y + X .Y .Z + X .Y .Z as ii) Simplify the Boolean function given by f ( A, B, C ) = ( A + B + C ) (A + B + C ) ( A + B + C ) for the dont care condition expressed as
2.
3.
(A + B )(A + B + C )
b) Minimizing a given Boolean expression using the QuineMcCluskey tabular method yields the following prime implicants: 00, 11, 110 and 000. Draw the corresponding Karnaugh map. (9M+6M) 4. a) How can a 4-bit parallel adder (ripple carry) be converted to a parallel subtractor using XOR gates. (Hint: use two's complement subtraction.) b) Draw the logic diagram of a three-digit BCD adder and briefly describe its functional principle. (6M+9M) a) How could a 1-of-4 multiplexer plus one other gate be used for the implementation of full adder? b) Design a combinational circuit that converts a decimal digit from 2,4,2,1 code to 8, 4,-2,1code. (6M+9M)
5.
1 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 2
6.
a) Obtain the programming table for the SUM output of the full adder to implement with PLA b) What do you understand by the following as regards programmable logic devices? i) Combinational and registered outputs; ii) Configurable output logic cell; iii) reprogrammable PLD; (4M+11M)
7.
a) Obtain the count sequence of i) a MOD-10 Ring counter ii) a MOD-10 Johnson counter Determine the number of flip-flops required to construct the above counters. b) Draw and explain the operation of universal shift register a) Convert the following Mealy machine into a corresponding Moore machine? PS NS, Z X=0 X=1 A C,0 B,0 B A,1 D,0 C B,1 A,1 D D,1 C,0 b) Design the circuit for the above table?
(8M+7M)
8.
(8M+7M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 3
Time: 3 hours
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Com. to EEE, ECE, BME, EIE, ECC) Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1. a) Perform the following operations using 2s complement arithmetic: i) (+43)10 (53)10. ii) (3E91)16 (1F93)16 b) Represent the unsigned decimal numbers 351 and 986 in BCD, and then show the steps necessary to form their sum. (8M+7M)
2. a) It is proposed to construct an eight-input NAND gate using only two-input AND gates and two-input NAND gates. Draw the logic arrangement that uses the minimum number of logic gates. b) What is a parity bit? Define even and odd parity. What is the limitation of the parity code when it comes to detection and correction of bit errors? (8M+7M)
3. a) Use Karnaugh maps to show that AC + A C and A C + AC are factors of A BC D + AB C D and find a suitable third and final factor. b) Using the QuineMcCluskey tabular method, find the minimum sum of products for (1, 2, 3, 9, 13, 14 ) + (0,7, 10, 15) (8M+7M)
4. a) Draw the truth table of a full subtractor circuit. Write a min-term Boolean expression for DIFFERENCE and BORROW outputs in terms of minuend variable, subtrahend variable and BORROW-IN. Minimize the expressions and implement the min hardware. b) Briefly describe the concept of look-ahead carry generation with respect to its use in adder circuits. (8M+7M)
5. a) What is a de-multiplexer and how does it differ from a decoder? Can a decoder be used as a de-multiplexer? b) Implement the following logic function using MUX with three select inputs? F (a, b, c, d ) = a + bcd + ad + c 1 of 2 (8M+7M)
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 3
6. a) Distinguish between a programmable logic array (PLA) device and a programmable array logic (PAL) device in terms of architecture and capability to implement Boolean functions. b) Realize the following switching functions with PROM F1 (A,B,C,D) = m(0,1,3,4,5,6,7,12,13) F1 (A,B,C,D) = m(5,6,7,10,11,13,14,15) (8M+7M)
7. a) Draw the truth table and briefly describe its operation of the following types of flip-flop: i) A positive edge-triggered J-K flip-flop with active HIGH J and K inputs and active LOW PRESET and CLEAR inputs; ii) A negative edge-triggered J-K flip-flop with active LOW J and K inputs and active LOW PRESET and CLEAR inputs. b) Enumerate the differences between transition table and state table? (9M+6M)
8. a) Explain the capabilities and limitations of finite state machines b) Convert the following Mealy machine into a corresponding Moore machine. PS A B C D E NS, Z X=0 X=1 B,0 E,0 E,0 D,0 D,1 A,0 C,1 E,0 B,0 D,0 (8M+7M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 4
Time: 3 hours
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Com. to EEE, ECE, BME, EIE, ECC) Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Solve i) (AD012)16 = (X)5 ii) (5.204)10 = (X)3 b) Add the maximum positive integer to the minimum negative integer, both represented in i) 16-bit 1s complement binary notation. Express the answer in 1s complement binary ii) 16-bit 2s complement binary notation. Express the answer in 2s complement binary (8M+7M) a) Write both sum-of-products and product-of-sums Boolean expressions for i) a two-input AND gate, ii) a two-input NAND-gate, iii) a two-input EX-OR gate and iv) a two-input NOR gate from their respective truth tables. b) i) Simplify F ( A, B, C , D, E ) = ABCD + ABC D + ABCD + ABC D + ABCDE + ABC D E + ABC DE ii) Prove that [AB + C + D ] [D + (E + F )G ] = D (AB + C ) + D G (E + F ) (8M+7M)
2.
3.
A logic system has three inputs A, B and C and two outputs Y1 and Y2. The output functions Y1 and Y2 are expressed by Y1 = A BC + BC + A C + AB C + ABC and Y2 = A B + AC + ABC Determine the minimized output logic functions using the QuineMcCluskey tabular method (15M) a) Draw the circuit diagram of a 4-bit adder-subtractor and briefly describe its functional principle. b) Briefly describe the concept of look-ahead carry generation with respect to its use in adder circuits. (8M+7M) a) Draw the logic diagram and truth tables for the following: i) An eight-line to three-line priority encoder with active LOW inputs and outputs and an active LOW ENABLE input. ii) A four-line to16-line decoder with active HIGH inputs and active LOW outputs and an active LOW ENABLE input; b) Implement the three-variable Boolean function using an 8-to-1multiplexer and a 4-to1multiplexer? F ( A, B, C ) = A C + AB C + ABC (8M+7M)
4.
5.
1 of 2
Code No: R22023
R10
SET - 4
6.
a) Design four-digit Excess-3 code converter using PROM with the help of programming table b) Realize the following switching functions with PAL with the help of programming table F1 (A,B,C,D) = m(0,1,3,4,5,6,7,12,13) (6M+9M) a) How can presettable counters be used to construct counters with variable modulus? b) Obtain the count sequence of i) a MOD-10 Ring counter ii) a MOD-10 Johnson counter Determine the number of flip-flops required to construct the above counters. (7M+8M)
7.
8.
Convert the following Mealy machine into a corresponding Moore machine and realize using JK Flip-flop (15M) PS NS, Z X=0 X=1 A C,0 B,0 B A,1 D,0 C B,1 A,1 D D,1 C,0
2 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 PRINCIPLES OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE (Com. to CSE, IT)
SET - 1
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) Give the derivation and parse tree for expressions to generate the string slope * x + intercept b) List the principal phases of compilation, and describe the work performed by each. (7M+8M)
2.
a) Why does the use of dynamic scoping imply the need for run-time type checking? b) Consider the following pseudo code. Procedure P (A, B: real) X: real Procedure Q (B, C: real) Y: real ... Procedure R (A, C: real) Z: real . . . (*) ... Assuming static scope, what is the referencing environment at the location marked by (*)? (7M+8M)
3.
a) Describe in detail about evaluating attributes for the expression(1 + 3)*2 b) Describe the similarities and differences between context-free grammars and tree grammars. (7M+8M)
4.
a) Why is it generally expensive to catch all uses of uninitialized variables at run time? Why is it impossible to catch all uses of uninitialized variables at compile time? b) Describe the jump code implementation of short-circuit Boolean evaluation. (7M+8M)
1 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
SET - 1
5.
a) Explain the difference between type conversion, type coercion, and non-converting type casts. b) Discuss the significance of holes in records. Why do they arise? What problems do they cause? (7M+8M)
6.
a) What is the principal purpose of generics? In what sense do generics serve a broader purpose in C++ and Ada than they do in Java and C#? b) Describe in detail about implementing synchronization. (7M+8M)
7.
a) Summarize visibility rules of C++. How do the rules for member name visibility in Smalltalk and Objective-C differ from the rules of most other object-oriented languages? b) Explain in detail about Shared and Replicated Inheritance with examples. (7M+8M)
8.
a) Define Functional Programming Language. List the properties of Functional Programming languages and describe each of them briefly. b) Summarize Prologs facilities for database manipulation. Explain the usage of assert, retract, and clause. (7M+8M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 PRINCIPLES OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE (Com. to CSE, IT)
SET - 2
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) Describe the form in which a program is passed from the scanner to the parser; from the parser to the semantic analyzer; from the semantic analyzer to the intermediate code generator. b) Summarize the difference between LL and LR parsing. Which one of them is also called bottom-up? Top-down? Which one is also called predictive? Shift reduce? What do LL and LR stands for? (7M+8M)
2.
a) What do we mean by the scope of a name-to-object binding? Explain about the closest nested scope rule. b) Explain the distinction between decisions that are bound statically and those that are bound dynamically. What is the advantage of binding things as early as possible? What is the advantage of delaying bindings? (7M+8M)
3.
a) Why cant action routines be placed at arbitrary locations within the right hand side of productions in an LR CFG? b) Give the Attribute grammar to decorate an abstract syntax tree for the calculator language with types. (7M+8M)
4.
a) Explain the difference between prefix, infix, and postfix notation. What is Cambridge Polish notation? Name two programming languages that use postfix notation. b) Describe three different search strategies that might be employed in the implementation of a case statement, and the circumstances in which each would be desirable. (7M+8M)
1 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
SET - 2
5.
a) Summarize the ways in which one dereferences a pointer in various programming languages. b) In what ways may an enumeration type be preferable to a collection of named constants? In what ways may a sub range type be preferable to its base type? It what ways may a string be preferable to an array of characters? (7M+8M)
6.
a) Describe different parameter Modes in Ada .How do they differ from the modes of most other Algol-family languages? b) Describe the algorithm used to identify an appropriate handler when an exception is raised in a language like Ada or C++. (7M+8M)
7.
a) Compare Java final methods with C++ non-virtual methods. How are they the same? How are they different? b) What is a metaclass in Smalltalk? Explain the difference between initialization and assignment in C++ with suitable examples. (7M+8M)
8.
a) Why is the order of evaluation is essential in evaluating expressions? Explain in detail about Strictness and Lazy Evaluation and I/O Streams. b) Define Horn Clause with an example. What sorts of logical statements cannot be captured in Horn clauses? Also describe the generate-and-test programming idiom. (7M+8M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 PRINCIPLES OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE (Com. to CSE, IT)
SET - 3
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) Explain the distinction between interpretation and compilation. What are the comparative advantages and disadvantages of the two approaches? b) What does it mean for a context-free grammar to be ambiguous? (7M+8M)
2.
a) Explain the distinction between the lifetime of a name-to-object binding and its visibility. b) Why are binding rules particularly important for languages with dynamic scoping?(7M+8M)
3.
a) What does it mean for an attribute grammar to be S-attributed? L-attributed? Noncircular? What is the significance of these grammar classes? b) Describe in detail about the role of semantic analyzer. (7M+8M)
4.
a) What is a tail-recursive function? Why is tail recursion important? Write a tail-recursive function in Scheme or ML to compute n factorial n! = _1in i = 1 2 You will probably want to define a helper function) b) Discuss in detail about problems with the Fortran IV do loop. (7M+8M)
n). (Hint:
5.
a) Discuss the comparative advantages of structural and name equivalence for types. Name three languages that use each approach. b) Discuss the differences between the denotational, constructive, and abstraction-based views of types. (7M+8M)
1 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
SET - 3
6.
a) What does it mean for a generic parameter to be constrained? Explain the difference between explicit and implicit constraints. Why will C# accept int as a generic argument, but Java wont? b) What is an exception? Explain how to implement exceptions in a way that incurs no cost in the common case (when exceptions dont arise). (7M+8M)
7.
a) Explain the difference between dynamic and static method binding (i.e., between virtual and non-virtual methods). (7M+8M)
b) Explain why in-line subroutines are particularly important in object-oriented languages.
8.
a) What is a higher-order function? Give three examples of higher order functions. Also explain the concept of Currying in detail. b) What mathematical formalism underlies logic programming? Briefly describe the process of unification and resolution in logic programming. (7M+8M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 PRINCIPLES OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE (Com. to CSE, IT)
SET - 4
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1.
Max. Marks: 75
a) What is the difference between a phase and a pass of compilation? Under what circumstances does it make sense for a compiler to have multiple passes? b) What is P-code and also discuss in detail about bootstrapping? (7M+8M)
2.
a) Consider the following pseudo code, assuming nested subroutines and static scope. Procedure main g: integer Procedure B(a : integer) x: integer Procedure A(n : integer) g := n Procedure R(m : integer) write integer(x) x /:= 2 integer division if x > 1 R(m + 1) else A(m) body of B x := a a R(1) body of main B(3) write integer(g) b) What does this program print? Show the frames on the stack when A has just been called. For each frame, show the static and dynamic links. c) Explain how A finds g. (5M+5M+5M)
1 of 2
Code No: R22056
R10
SET - 4
3.
a) What is an attribute grammar? What is the difference between synthesized and inherited attributes? b) What sort of information do action routines typically keep in global variables, rather than in attributes? (7M+8M)
4.
a) Explain about Structured Alternatives to goto in detail. b) Describe three subtleties in the implementation of enumeration-controlled loops. Why do most languages not allow the bounds or increment of an enumeration controlled loop to be floating-point numbers? (7M+8M)
5.
a) What does it mean for a language to be strongly typed? Statically typed? What prevents, say, C from being strongly typed? b) Discuss the type safety problems that arise with variant records. How can these problems be addressed? (7M+8M)
6.
a) Describe in detail about the calling sequence to maintain stack layout. Explain this with a typical stack frame. b) Describe three alternative means of allocating co-routine stacks. What are their relative strengths and weaknesses? (7M+8M)
7.
a) Describe how virtual functions can be used to achieve the effect of subroutine closures. b) Describe in detail about data hiding in Euclid and Ada. (7M+8M)
8.
a) Explain in detail how Control Flow and Assignment Expressions are defined in Scheme with examples. Also discuss briefly on the concept of Program as Lists in Scheme. b) What are clauses, terms, and structures in Prolog? What are facts, rules, and queries? Give examples of each. (7M+8M)
2 of 2
Code No: R22015
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY (Civil Engineering)
SET - 1
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. What are the main and allied branches of geology? Explain them.
Max. Marks: 75
2.
Write the physical properties, occurrence, and uses of following mineral. a) Feldspars b) Calcite c) Hematite d) Clay
3.
What are the agents of metamorphism? Give their types of metamorphism based on the agents.
4.
Explain the following: a) Strike b) Dip c) Parts of faults
d) Types of unconformities with sketches and give their importance in civil engineering
5.
a) Types of aquifer, fluctuation of the water table level in unconfined aquifers. b) Types of waters under the zone of aeration and zone of saturation.
6.
Describe the classification of geophysical methods of gravity, magnetic methods with their importance in geological considerations.
7.
Write the importance of geology for constructions of Dam. What are the effects of associated geological structure for the selection of dam site with sketches
8.
Write the importance of Rock types and influence of structures for successful tunneling with sketches
1 of 1
Code No: R22015
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY (Civil Engineering)
SET - 2
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. Explain the role of importance of geology in Civil Engineering.
Max. Marks: 75
2. Write the physical properties, chemical composition, types, occurrence and uses of following minerals. a) Quartz group b) Mica group
3. Describe the structures and textures of igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks
4. What are the parts of FOLDS? Give their classification with sketches.
5. Briefly explain the classification, effects, causes and intensity of earthquakes and give their preventive manures for construction of building in earthquake prone areas.
6. Explain the principles, importance of seismic Refraction method. In civil engineering constructions.
7. What are the types and purposes of Dams. Give the influence of Rock types for successful construction at a dam site. 8. Write short notes on : a) Effects, lining of tunnels. b) Purposes of tunneling c) Over break
1 of 1
Code No: R22015
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY (Civil Engineering)
SET - 3
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. Write the following: a) Valley development and development of River. b) The importance of geological work of Rivers.
Max. Marks: 75
2. Write the physical properties, chemical composition types and uses of followings minerals. a) Augite b) Garnet c) Magnetite d) Tourmalene
3. Explain the classification of Rocks with their characters.
4. What are the parts of FAULTS. Give their mechanism, types and role of importance in Civil Engineering.
5. Explain the various geological, geophysical, hydrological methods. For ground water exploration. Techniques.
6. To emphasize the special Civil Engineering importance of the principle of Electrical resistivity method indetail.
7. Describe the importance and geological considerations in the selection of a dam site.
8. What are the purposes of tunneling? Give their importance of groundwater condition for successful tunneling.
1 of 1
Code No: R22015
R10
II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY (Civil Engineering)
SET - 4
Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. Write the following : a) What are the types of geological agents? b) Explain the detail of process of weathering of rocks
Max. Marks: 75
2. Write the physical properties, chemical composition, occurrence and types of following minerals a) Olivine b) Bauxite c) Kyanite d) Pyrite
3. Write the followings: a) Types of granites. b) Types of sand stones
4. What are the parts & types of joints and give their occurrences in Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic Rocks.
5. Define the terms porosity and permeability. Explain the classification of Rocks based on porosity & permeability, and impotance of rock types for groundwater point of view.
6. a) What are the environmental effects of mining? b) What are the environmental impacts of impounding water in a Reservoir?
7. Write the capacity, evaporation, water tightening, lithology and influence of geological structure for life of a Reservoir.
8.
Explain the importance of geological structures for successful tunneling. With sketches 1 of 1
Code No: V0422
R07
SET - 1
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What is Object Oriented Programming? Explain its features? b) How to declare one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays? Give examples? a) What is a class? How do you declare a class? How do you access class members? Explain with an example? b) Explain Method Overloading with an example? a) Explain Single and Multiple Inheritance with an example? b) What is a super keyword ? Explain its usage with suitable examples. a) What is a Package? How do you define and access Packages? b) How do you declare and extend Interfaces? a) What is an Exception? How do you handle Exceptions? b) How do you create your own Exceptions? Explain with an example? c) Define a Thread? How do you create threads by implementing runnable interface? a) What is an Event? Explain handling Mouse Events? b) Explain Graphics methods in AWT? a) What are the Layout Managers in AWT control? b) Explain Radio buttons and Check boxes? c) Explain creation of Applet and passing parameters to Applets? a) Explain about TCP/IP sockets? b) Explain FileInputStream and FileOutputStream classes? c) Write a program to read two strings and check they are equal or not? Max. Marks: 80
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: V0422
R07
SET - 2
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What are the features of java? Explain them? b) What is Byte code? Explain? 2. a) What is a Class, Object? Explain how to create reference variables? b) What is a Constructor? Explain Parameterized Constructors? 3. a) What is Method Overriding? Give example? b) What is an Abstract Class? Explain with an example? 4. a) Define a Package? Explain how to create and access Packages? b) What is a CLASS PATH? c) Define an Interface? How Classes are different from Interfaces? 5. a) What is an Exception? Explain multiple trycatch blocks? b) Explain finally keyword? c) What is a Thread? How do you create multiple threads? 6. a) What is an Event? Explain handing Keyboard Events? b) Explain creation and handling Frame Events? 7. a) Create a simple student application by using Labels, Text fields, Check boxes and Buttons? b) Explain about JButtons class? c) Explain Applet life cycle? 8. a) Explain basics of Networking? b) What is InetAddress class? Explain? c) Write a program to read a string and check it is Palindrome or not? Max. Marks: 80
1 of 1
Code No: V0422
R07
SET - 3
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What is an Object Oriented Program? Explain its features? b) Write a program to generate Fibonacci series? a) What is Method Overloading? Explain with an example? b) What are Static members and Static Methods? Explain? a) Explain Inheritance with an example? b) What is dynamic method dispatch? Explain? a) How do you create Packages? Explain how do you use the Packages with an example? b) Define an Interface? How Classes are different from Interfaces? a) What is an Exception? What are the Exception types in java? Explain? b) How do you throw your own Exceptions? Give an example? c) What is a Thread? Explain thread Synchronization? a) What is an Event? How do you create event handlers? b) Explain Colour class? c) How do you create and select a Font Object? a) Explain managing and handling of Scroll bars? b) Explain JButtons class? c) What is an Applet? How an Applet is different from an application? a) Explain URL connection in java? b) Explain about BufferedInputReader and BufferedOnputReader classes? c) Write a program to read an array of string and print them in sorted order? Max. Marks: 80
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: V0422
R07
SET - 4
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What are the various types of Operators supported by java? b) Explain break and continue statements with suitable example? a) What is a Constructor? Explain parameterized constructor and passing objects as parameters? b) What is recursion? Explain with an example?? a) What is Method Overriding? Explain with an example? b) Can you prevent method overriding? How? a) What is a Package? How do you create and use Packages? Give example? b) Define an Interface? How Classes are different from Interfaces? a) What is an Exception? Explain multiple trycatch blocks? b) What is a Thread? Explain inter thread communication? c) Explain deadlock handling with an example? a) What is an Event? Explain Event classes? b) Explain AWT Graphics class? a) Explain Check boxes and Check box groups by taking suitable example? b) Explain creation of Combo box control? c) What is an Applet? What are different types of Applets? a) Explain TCP/IP sockets in java? b) Explain FileReader and FileWriter classes? c) How do you declare Strings? Explain any 4 String handling functions? Max. Marks: 80
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
Code No: V0122
R07
SET - 1
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES (Com. to CE, EEE, ME, CSE, EIE, BME, IT, AME, BOT) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ***-*** 1. a) What is the necessity of having multidisciplinary knowledge for tackling environmental problems? b) What are the various renewable energy sources? What is their potential contribution to future energy needs? (8M+8M) a) What are the adverse effects of mineral extraction? b) Explain the role of individuals in conservation of natural resources. a) Explain consumptive use and productive use. b) Explain the structure and functioning of Stream ecosystem. a) What are the various Ex-situ conservation measures of wild life in India? b) Explain genetic species and ecosystem diversity. Max. Marks: 80
2.
(8M+8M)
3.
(8M+8M)
4.
(8M+8M)
5. a) What are the various effects of water pollution? b) What are the mitigation measures to be taken during floods? 6. a) What is sustainable development? What is the present trend of development? b) What are the functions of State Pollution Control Boards?
(8M+8M)
(8M+8M)
7.
a) What are the reasons for variation in population growth rates of developed and developing countries? b) How do you take advantage of information technology in enhancing health? (8M+8M)
8.
Write short notes on the following. a) Ozone Depletion b) Nuclear Accidents c) Conflicts over Water d) Land Slides
(4M+4M+4M+4M)
1 of 1
Code No: V0122
R07
SET - 2
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES (Com. to CE, EEE, ME, CSE, EIE, BME, IT,AME, BOT) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What is need of awareness to individuals about environmental problems? b) What are the various reasons for depletion of forests? Discuss the remedial actions? (8M+8M) a) What do you mean by overexploitation of ground water? What are the various consequences of overexploitation? b) Explain the adverse effects of dams on forest with special reference to any ongoing Project. (8M+8M) a) What do you mean by ecological succession? Describe it in brief. b) What is the main structure of a desert ecosystem? Explain its functioning. Max. Marks: 80
2.
3.
(8M+8M)
4.
5.
6.
a) What are the various endangered and endemic species of India? b) What is Habitat Loss? What are reasons for it? Suggest a few remedial actions. (8M+8M) a) What are the main causes of thermal pollution? b) What is Indoor air pollution? What are the various causes of indoor air pollution? (8M+8M) a) What is acid rain? What are main substances responsible for it? b) What are the powers and functions of Central Pollution Control Board? (8M+8M) a) Explain the role of Family Welfare Programs in the control of population explosion? b) What are the measures taken to prevent rapid spread of HIV in India? (8M+8M) Write short notes on the following a) Timber Extraction b) Human rights c) Value Education d) Climate Change
1 of 1
7.
8.
(4M+4M+4M+4M)
Code No: V0122
R07
SET - 3
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES (Com. to CE, EEE, ME, CSE, EIE, BME, IT,AME, BOT) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) How do explain the interrelated nature of environmental problems? b) What are the reasons for depletion of natural resources? Explain strategies for conservation of natural resources. (8M+8M) a) What are the reasons for overgrazing? Explain the changes caused due to overgrazing? b) Explain the various aspects of land degradation. How it can be arrested? (8M+8M) a) What are the various models of energy flow in an ecosystem? Explain them in brief. b) Explain the structure and functions of forest ecosystem. (8M+8M) a) What are the conflicts between man and wildlife? How to minimize them? b) What are the various threats for biodiversity in India? a) What are the main causes of Noise Pollution? b) What are the effects of urban solid wastes? Max. Marks: 80
2.
3.
4.
(8M+8M)
5.
(8M+8M)
6.
7.
a) What are the salient features of Forest Conservation Act? b) What are the various issues involved in the enforcement of environmental legislation? (8M+8M) a) What are the various measures needed for containing high rate of population growth in India? b) What is the relation between health and environment? Explain with suitable examples. (8M+8M)
Write short notes on the following a) Disaster Mitigation Measures b) Fertilizer and Pesticide Problem c) Interstate water disputes d) Renewable energy sources
8.
(4M+4M+4M+4M)
1 of 1
Code No: V0122
R07
SET - 4
II B.Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, April 2012 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES (Com. to CE, EEE, ME, CSE, EIE, BME, IT,AME, BOT) Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ******* 1. a) What is need of awareness to every person about environmental problems? b) What are the various disciplines of study that are useful in tackling environmental problems? Describe their role in brief. (8M+8M) 2. a) What are the various reasons for tropical deforestation? Also suggest the measures for controlling deforestation? b) What are the disparities in use of resources in a Global Contest? What do you mean by equitable use of resources? (8M+8M) 3. a) What are food chains? How they are important? b) What is the main structure of grassland ecosystems? Explain its functions. (8M+8M) 4. a) What are the efforts of India for the conservation of wild life? b) What are the various in-situ conservation methods of biodiversity practiced in India? (8M+8M) 5. a) What are the various control measures of air pollution? b) What are the mitigation measures to be taken at the time of Max. Marks: 80
Cyclones?
(8M+8M)
6. a) What is rain water harvesting? Why is it necessary? b) What are the reasons for increased consumerism in India? What are the consequences of it? (8M+8M) 7. a) What is the status of human rights in India? What are the additional measures to be taken to protect them? b) Explain the role of information technology in environment protection with special reference to our country? (8M+8M) 8. Write short notes on the following a) Marine Oil Pollution b) Fly Ash Problem c) Global Warming d) Water Logging
(4M+4M+4M+4M)
1 of 1
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 1
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2012 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Explain the collector modulation method for generating AM wave with a neat circuit diagram and waveforms. (b) An AM amplier provides an output of 106 W at 100% modulation. The internal loss is 20 W i. What is un-modulated carrier power? ii. What is the side band power? [10+6]
2. (a) Give the block diagram for coherent detection of DSB-SC modulated wave and explain the operation of it. (b) Describe the phasor representation of AM-SC signal.
N
[8+8]
3. A synchronous detection of SSB signal shows phase and frequency discrepancy. ConsiderS (t) =
i=1
cos [(c t) cos(i t + i ) sin(c t) sin(i t + i )]is an SSB signal.
The signal is multiplied by the locally generated carrier cos c t and then passed through a low-pass lter. (a) Prove that the modulating signal can be completely recovered if the cut-o frequency of the lter is fN < fo < 2fc . (b) Determine the recovered signal when the multiplying signal is cos[c + ]. (c) Determine the recovered signal when the multiplying signal is cos[( c t+ )t]. Give << i where c = 2fc , = 2 f. [16] 4. Explain demodulation of FM signal with the help of PLL. 5. Draw the noisy model of AM receiver and evaluate its noise performance. [16] [16]
6. (a) Classify radio transmitters based on the type of modulation and Service involved. (b) Explain AM transmitters with modulation at high carrier power level with the help of its block diagram. [16] 7. (a) Explain radio receiver characteristics. (b) Calculate the image rejection of a double conversion receiver which has a rst IF of 1 MHz and a second IF of 200 KHz, an RF amplier whose tuned circuit has a Q of 75 ( same as that of mixer ) and which is tuned to a 30 MHz signal. Give answer in dB. [16] 1 of 2
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 1
8. Why is cross talk present in PTM system? Explain the generation and demodulation of PDM signals with suitable diagrams. [16]
2 of 2
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 2
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2012 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) What are the main objectives of a communication system design? What are the primary resources of any communication system. (b) The RC load for a diode envelope detector consists of a 1000 pF capacitor in parallel with a 10-K resistor. Calculate the maximum modulation depth that can be handled for sinusoidal modulation at a frequency of 10 KHz if diagonal peak clipping is to be avoided. (c) A broadcast AM transmitter radiates 50 KW of carrier power. What will be the radiated power at 85 % of modulation and what is the side band power? [6+6+4] 2. (a) Consider the wave obtained by adding a non coherent carrier Ac cos (2 fc t + ) to DSB-SC wave m(t) cos (2 fc t ) where X (t) is the message waveform. This waveform is applied to an ideal envelope detector. Find the resulting detector out put. Evaluate the output for. i. = 0 and ii. = 0 and |X (t)| << Ac /2. (b) Explain the DSB-SC generation by balanced modulator using FET ampliers. [8+8] 3. (a) Explain with block diagram, the phase shift method of generating SSB modulated waves. (b) Compare AM, DSB and SSB systems. [8+8]
4. (a) Explain about FM generation using transistor reactance tube modulator. (b) Explain balanced ratio detector for detecting FM signal. 5. (a) Determine the output SNR in a PM system. (b) For a modulating signal x(t) = cos3 wm t, show PM is superior to FM by a factor of 2.25 from the output SNR point of view. [16] 6. Draw the block diagram of SSB Pilot carrier radio transmitters system and explain its operation. [16] 7. (a) Explain he working principle of a superhet receiver with the help of neat block diagram. [8+8]
1 of 2
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 2
(b) A superhet receiver has an RF amplier and an IF of 450 KHz is tuned to 15 MHz. calculate the Q values of RF and mixer input tuned circuits, both being the same, if receiver?s image rejection is to be 120. [16] 8. Why is cross talk present in PTM system? Explain the generation and demodulation of PDM signals with suitable diagrams. [16]
2 of 2
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 3
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2012 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Dene communication. Explain with block diagram the basic communication system. Write about modern communication system. (b) A carrier wave of frequency 10 MHz and peak value of 10 V is amplitude modulated by a 5 KHz sine wave of amplitude 6 V. Determine the modulation index and draw the one sided spectrum of modulated wave. [8+8] 2. (a) Consider the wave obtained by adding a non coherent carrier Ac cos (2 fc t + ) to DSB-SC wave m(t) cos (2 fc t ) where X (t) is the message waveform. This waveform is applied to an ideal envelope detector. Find the resulting detector out put. Evaluate the output for. i. = 0 and ii. = 0 and |X (t)| << Ac /2. (b) Explain the DSB-SC generation by balanced modulator using FET ampliers. [8+8] 3. Describe the time domain band-pass representation of VSB. Draw the block diagram of VSB generation corresponding to the time domain description. [16] 4. Explain demodulation of FM signal with the help of PLL. [16]
5. Explain how S/N ratio is a gure of merit incase of performance of a communication channel. [16] 6. (a) What are the carrier frequency requirements of radio transmitters. (b) What is frequency scintillation? How is it avoided. [16]
7. (a) Present the necessity of a mixer in a receiver. Give a circuit schematic and explain. (b) A superhet radio receiver is tuned to receive a 1500 KHz carrier amplitude modulated by a 5 KHz sinusoidal tone. Assuming the IF to be 455 KHz, identifythe input and output frequency components for the IF amplier. The IF bandwidth is 1 KHz. [16] 8. (a) Describe the synchronization procedure for PAM, PWM and PPM signals. (b) Discuss about the spectra of PWM and PDM signals. [16]
1 of 1
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 4
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2012 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Explain the collector modulation method for generating AM wave with a neat circuit diagram and waveforms. (b) An AM amplier provides an output of 106 W at 100% modulation. The internal loss is 20 W i. What is un-modulated carrier power? ii. What is the side band power? [10+6]
2. (a) Draw the schematic diagram of chopper type balanced modulator and explain the generation of DSB-SC. (b) Consider an incoming narrow band signal of bandwidth 10 KHz and midband frequency which may lie in the range 0.535 - 1.605 MHz. it is required to translate this signal to a xed frequency band centered at 0.455 MHz. Determine the range of tuning that must be provided in the local oscillator. [8+8] 3. A synchronous detection of SSB signal shows phase and frequency discrepancy.
N
ConsiderS (t) =
i=1
cos [(c t) cos(i t + i ) sin(c t) sin(i t + i )]is an SSB signal.
The signal is multiplied by the locally generated carrier cos c t and then passed through a low-pass lter. (a) Prove that the modulating signal can be completely recovered if the cut-o frequency of the lter is fN < fo < 2fc . (b) Determine the recovered signal when the multiplying signal is cos[c + ]. (c) Determine the recovered signal when the multiplying signal is cos[( c t+ )t]. Give << i where c = 2fc , = 2 f. [16] 4. Explain demodulation of FM signal with the help of PLL. [16]
5. (a) Prove that the gure of merit of AM system for single stone modulation with 100% modulation is 1/3. (b) An AM system with envelope detection is operating at threshold. Determine the power gain in decibels needed at the transmitter to produce (S/N )o = 30 dB for tone modulation with m = 1. [16] 6. (a) Classify radio transmitters based on the type of modulation and Service involved. 1 of 2
Code No: V0405/R05
Set No. 4
(b) Explain AM transmitters with modulation at high carrier power level with the help of its block diagram. [16] 7. (a) Briey explain the function of each of the blocks in the superheterodyne receiver. (b) Explain how the use of an RF amplier improves the signal-to-noise ratio of a supeheterdyne receiver. [16] 8. (a) What are the dierent type of Pulse Modulations? Explain? (b) Explain the method of generation and detection of PAM signals with neat schematics. [16]
2 of 2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- SCI - Learning Packet - Biology Week 5Dokumen13 halamanSCI - Learning Packet - Biology Week 5Pal, Julia HanneBelum ada peringkat
- Book 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitDokumen566 halamanBook 4: Alternating Current Electric CircuitMAT JIBRUD100% (3)
- Canal Bank Protection WorksDokumen48 halamanCanal Bank Protection WorksLandon Mitchell100% (1)
- Irrigation Methods in Fruit CropsDokumen16 halamanIrrigation Methods in Fruit CropsDr.Eswara Reddy Siddareddy75% (4)
- Chapter4 Synchronous MachinesDokumen34 halamanChapter4 Synchronous Machinessatyakar_vvk100% (1)
- MINING LAW of The PhilippinesDokumen79 halamanMINING LAW of The PhilippinesJe Re MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogue of Fungi of Colombia - 2022Dokumen514 halamanCatalogue of Fungi of Colombia - 2022Alejandro100% (1)
- EDC Q and ADokumen17 halamanEDC Q and Asatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Notes On Type of MaterialsDokumen15 halamanUnit 2 Notes On Type of Materialssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDokumen33 halamanElectronic Devices and Circuitssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Special Electrical Machines EEE 012Dokumen3 halamanSpecial Electrical Machines EEE 012satyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8 Stepper MotorsDokumen7 halamanLecture 8 Stepper MotorsRafi Andanawari Drajat100% (1)
- EDC Q and ADokumen17 halamanEDC Q and Asatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Stepper Motor Theory of OperationDokumen11 halamanStepper Motor Theory of OperationSherif EltoukhiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes ELE-B7: Ramadan El Shatshat Synchronous MachineDokumen25 halamanLecture Notes ELE-B7: Ramadan El Shatshat Synchronous Machinesatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Notebook Guide LinesDokumen184 halamanSmart Notebook Guide Linessatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Intro Stepper PDFDokumen44 halamanIntro Stepper PDFHansean WidjajaBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling of Synchronous Generators: 99% of The Electric Power Allover The World Is Generated by Synchronous GeneratorsDokumen22 halamanModeling of Synchronous Generators: 99% of The Electric Power Allover The World Is Generated by Synchronous Generatorssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Netgear Dgn1000 UmDokumen108 halamanNetgear Dgn1000 Umsatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Pspice AnalysisDokumen13 halamanPspice Analysissatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Machine 2Dokumen32 halamanElectrical Machine 2Irfan NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- AC MotorsDokumen4 halamanAC Motorssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- AC MotorsDokumen4 halamanAC Motorssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes Elec A6: Induction MachinesDokumen39 halamanLecture Notes Elec A6: Induction MachinesRam PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- PS-1 Question PapersDokumen98 halamanPS-1 Question Paperssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Single Phase Induction MotorDokumen27 halamanLecture Single Phase Induction Motorsatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Induction Motor BasicsDokumen48 halamanInduction Motor BasicsIjabiBelum ada peringkat
- Em-Ii 12Dokumen1 halamanEm-Ii 12satyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Em IiDokumen77 halamanEm Iisatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus of EM-IIDokumen2 halamanSyllabus of EM-IIsatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- PDC Question PapersDokumen56 halamanPDC Question Paperssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- ECA-II Question PapersDokumen86 halamanECA-II Question Paperssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- Control Systems Question PapersDokumen76 halamanControl Systems Question Paperssatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
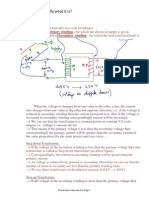
- Transformer-Basically What It IsDokumen2 halamanTransformer-Basically What It Issatyakar_vvkBelum ada peringkat
- FireflyDokumen2 halamanFireflyMerylle BejerBelum ada peringkat
- M Kps Tree Planting ProjectDokumen9 halamanM Kps Tree Planting ProjectTerriah AlonarBelum ada peringkat
- Eia - Construction and Operation Period of Stationary Sea-Bohr PlattformDokumen259 halamanEia - Construction and Operation Period of Stationary Sea-Bohr PlattformEzzadin BabanBelum ada peringkat
- Placement: BROCHURE 2018-20Dokumen24 halamanPlacement: BROCHURE 2018-20Salil PantBelum ada peringkat
- Module 8 Exercising Efficient and Effective Sustainable Practices in The WorkplaceDokumen45 halamanModule 8 Exercising Efficient and Effective Sustainable Practices in The WorkplaceJa Castañeda Paggao100% (1)
- Interseal 670 HS EN O-FDokumen4 halamanInterseal 670 HS EN O-Fapde06Belum ada peringkat
- Carbayo & Marques - 2011Dokumen2 halamanCarbayo & Marques - 2011Leonardo CottsBelum ada peringkat
- Examples in Chile of Sustainable Buildings: Holland, 2000Dokumen28 halamanExamples in Chile of Sustainable Buildings: Holland, 2000Naz FreedomBelum ada peringkat
- Spring 2005 Kansas Native Plant SocietyDokumen10 halamanSpring 2005 Kansas Native Plant SocietyKansas Native Plant SocietyBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Science 6Dokumen11 halamanSmart Science 6april light50% (2)
- Hardtop Smartpack Technical Data SheetDokumen5 halamanHardtop Smartpack Technical Data SheetGurdeep Sungh AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Working Paper Series 2009-10Dokumen86 halamanWorking Paper Series 2009-10Equitable Tourism Options (EQUATIONS)Belum ada peringkat
- Env 203-2man & Env Issues - FALL - 13Dokumen61 halamanEnv 203-2man & Env Issues - FALL - 13Nayeem FerdousBelum ada peringkat
- Map Showing Prioritization For Artificial Recharge Distict:-Aurangabad, Taluka: - Paithan, Village: - KatpurDokumen1 halamanMap Showing Prioritization For Artificial Recharge Distict:-Aurangabad, Taluka: - Paithan, Village: - KatpurHanuman KakdeBelum ada peringkat
- Green Roof Details and Design For ArchitectureDokumen15 halamanGreen Roof Details and Design For ArchitectureGen Lamsis AlmoraBelum ada peringkat
- EcotourismDokumen184 halamanEcotourismLe NhungBelum ada peringkat
- Climate Change Affecting AnimalsDokumen4 halamanClimate Change Affecting Animalsapi-582829020Belum ada peringkat
- List of Postage Stamps of India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDokumen57 halamanList of Postage Stamps of India - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFSelvaraj VillyBelum ada peringkat
- (D) Food Security (E) Rural DevelopmentDokumen26 halaman(D) Food Security (E) Rural DevelopmentAslam MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Executive Summary Srak Helmeted HornbillDokumen16 halamanExecutive Summary Srak Helmeted HornbillLailan Syahri RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Impact Assessment - Pulau Banyak Main Green Turtle Rookery in Western IndonesiaDokumen45 halamanRapid Impact Assessment - Pulau Banyak Main Green Turtle Rookery in Western IndonesiaMonica KuhonBelum ada peringkat
- Lantau Tomorrow PlanDokumen2 halamanLantau Tomorrow PlanHKFPBelum ada peringkat
- Chandigarh College of ArchitectureDokumen19 halamanChandigarh College of ArchitectureAkshay Singh AhlawatBelum ada peringkat
- Site Analysis DrawingsDokumen25 halamanSite Analysis Drawingsapi-3728723Belum ada peringkat
- PISCO Fish Training Overview UCSB-2017Dokumen59 halamanPISCO Fish Training Overview UCSB-2017Victoria VerdugoBelum ada peringkat