WK VII Wiki
Diunggah oleh
api-174496267Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
WK VII Wiki
Diunggah oleh
api-174496267Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
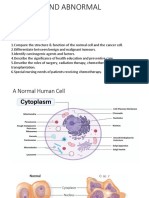
Amanuel Negussie DOS 531 Week VII Benign: Hemangioma Histology: Cutaneous hemangiomas are identified as raised lesions
that are benign neoplastic proliferation of vascular endothelial cells.1 Simplistic classification schema of hemangioma:1,2 Capillary hemangiomas also known as superficial hemangiomas - small vessel Cavernous hemangiomas also known as deep hemangiomas large vessel Mixed hemangiomas
Refined classification schema of hemangioma:2 Capillary hemangioma, including juvenile Cavernous hemangioma Venous hemangioma Arteriovenous hemangioma Epithelioid hemangioma Hemangioma of granulation tissue Miscellaneous hemangioma of deep soft tissue [including synovial and intramuscular hemangiomas] Lymph node drainage: No lymph node drainage2 Benign: Hetrotopic Bone Histology: Hetrotropic ossifications are classified as:3 Neurogenic hetrotropic ossification Traumatic myositis ossification Fibrodsyplasia ossificans progressiva [Muchmeyers disease]
Histology subtypes:3 Mature fatty bone marrow Mature trebucular bone
Figure 2. Retrieved from Orthobullets.3
Lymph node drainage: Since hetrotropic bone dose not metastasize to other sites, there is no lymph node drainage.
Gynecomastia Histology: *Histology is independent of cause4 Early phase4 Intraductal epithelial proliferation Both epithelial or myepithelial May be micropapillary or cribriform May show squamous metaplasia May be atypical
Periductal stroma typically edematous
Late phase4 Less epithelial proliferation Periductal fibrosis
Lobule formation infrequently seen
Lymph node drainage Lymphatic drainage of male breast is similar to that of the female breast. It includes axillary, internal mammary, and supraclavicular/infraclavicular nodes.5
Figure 2. Retrieved from American Cancer Society.5
Basal Cell Histology: There is no specific generally accepted classification of basal cell carcinoma. Most classifications are based on growth pattern of the tumor. The most basic histological types are :6 Nodular type [solid] in 30-75% of all BCC Superficial type [multicentric, multifocal] 10-15% of all BCC Infiltrative 10% of all BCC
Lymph node drainage: It is very rare for basal cell carcinoma to spread to lymph nodes.7 The drainage sites depend on the location of the original diagnosis.
Squamous Cell Histology: Histologically, squamous cell carcinomas of the skin demonstrate dermal invasion, pleomorphism of tumor cells, and presence of karatinization (may be absent in poorly differentiated type).8 Histologic subtype include:9 Keratoacanthoma Acantholytic spindle cell verrucous clear cell papillary signet ring pigmented desmoplastic
Lymph node drainage: Although still rare, squamous cell carcinomas spread more to lymph nodes than basal cell carcinoma.10 The drainage sites depend on the location of the original diagnosis. Melanoma Histology: Histologic subtypes of melanoma include:11 Superficial spreading melanoma [75% of all melanomas] Epidermal malanocytes [ Intraepidermal melaocytes [commonly large cells] Nodular melanoma [most common in middle aged adults] Lentigo maligna and maligna melanoma [seen on sun damaged head and neck of elderly people] Acral lentiginous melanoma [rare and found on acral surfaces] Mucosal lentiginous melanomas
Lymph node drainage: When melanomas progress beyond stage II, they spread to nearby lymph nodes.12 References 1. Wirth FA, Lowitt MH. Diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous vascular lesions. http://www.aafp.org/afp/1998/0215/p765.html. Accessed July 8, 2013. 2. Kistler BJ, Gellman H. Orthopedic surgery for hemangioma workup. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1255694-workup#a0723. Accessed July 8, 2013. 3. Woon C. Hetrotropic ossification. http://www.orthobullets.com/pathology/8044/heterotopic-ossification. Accessed July 8, 2013. 4. Gynecomastia. Stanford school of medicine. http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/gynecomastia/. Accessed July 8, 2013. 5. Breast cancer in male. American cancer society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/breastcancerinmen/detailedguide/breast-cancer-in-menwhat-is-breast-cancer-in-men. Accessed July8, 2013. 6. Vantuchova Y, Curik R. Histological types of basal cell carcinoma. http://www.med.muni.cz/biomedjournal/pdf/2006/05/261_270.pdf. Accessed June 8, 2013. 7. Skin Cancer: Basal and Squamous cell. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/skincancer-basalandsquamouscell/detailedguide/skincancer-basal-and-squamous-cell-what-is-basal-and-squamous-cell. Accessed July 8, 2013. 8. Squamous cell carcinoma. http://www.mrcophth.com/pathology/skin/squamouscellcarcinoma.html. Accessed July 8, 2013. 9. Rinker MH, Fenske NA, Scalf LA, et al. Histologic variants of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/409063. Accessed July 8, 2013. 10. Skin Cancer: Basal and Squamous cell. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/skincancer-basalandsquamouscell/detailedguide/skincancer-basal-and-squamous-cell-what-is-basal-and-squamous-cell. Accessed July 8, 2013.
11. Smoller BR. Histologic criteria for diagnosing primary cutaneous malignant melanoma. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v19/n2s/full/3800508a.html. Accessed July 9, 2013. 12. Lymph node involvement. Skin cancer foundation. http://www.skincancer.org/skincancer-information/melanoma/the-stages-of-melanoma/lymph-node-involvement. Accessed 9, 2013.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Black Soldier Fly Larvae ManualDokumen14 halamanBlack Soldier Fly Larvae ManualLeonardo Shibata100% (1)
- Register Environmental ImpactsDokumen7 halamanRegister Environmental ImpactsArmand LiviuBelum ada peringkat
- Herbal Abortifacient Drugs A ReviewDokumen6 halamanHerbal Abortifacient Drugs A Reviewyogesh ushirBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conservation: in Different ScenariosDokumen15 halamanEnergy Conservation: in Different ScenariosAnonymous DcdleqMEBelum ada peringkat
- Pyrogen and Endotoxins GuideDokumen13 halamanPyrogen and Endotoxins GuideAnil Kumar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen193 halamanUntitledurosBelum ada peringkat
- Current management of hemangiomas and vascular malformationsDokumen18 halamanCurrent management of hemangiomas and vascular malformationsRini RahmawulandariBelum ada peringkat
- EVA and MVADokumen19 halamanEVA and MVATanveer Ahmad100% (1)
- Cooling & Heating: ShellmaxDokumen3 halamanCooling & Heating: Shellmaxvijaysirsat2007Belum ada peringkat
- Neoplasia 1Dokumen14 halamanNeoplasia 1Omar MaanBelum ada peringkat
- Case Report Reference Article (Published)Dokumen3 halamanCase Report Reference Article (Published)manojananthappanBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacy 2 Pathology Lecture 10Dokumen10 halamanPharmacy 2 Pathology Lecture 10Mohamad saeedBelum ada peringkat
- Canine Liposarcoma Case Report - ABVPDokumen54 halamanCanine Liposarcoma Case Report - ABVPRodrigo RosaBelum ada peringkat
- Solid - Cystic Hidradenoma: A Case ReportDokumen5 halamanSolid - Cystic Hidradenoma: A Case ReportIOSRjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Bone TumorsDokumen29 halamanBone TumorsmatameaBelum ada peringkat
- Malignant Oral Cavity Conditions GuideDokumen64 halamanMalignant Oral Cavity Conditions GuideYug KathuriaBelum ada peringkat
- J Aorn 2010 06 012Dokumen17 halamanJ Aorn 2010 06 012Mark Andres MasarateBelum ada peringkat
- 200 Important Points of Special Pathology - DR NotesDokumen17 halaman200 Important Points of Special Pathology - DR NotesDr NotesBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Lymphangioma Rare CasesDokumen3 halamanAdult Lymphangioma Rare CasesRini RahmawulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Oncology New AdultDokumen13 halamanOncology New Adultرافت العواضيBelum ada peringkat
- Aisha Tabassum EtalDokumen4 halamanAisha Tabassum EtaleditorijmrhsBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Tmu - JD - 039 PDFDokumen4 halaman1 Tmu - JD - 039 PDFKristina SabuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Tmu - JD - 039Dokumen4 halaman1 Tmu - JD - 039Hasan BlackBelum ada peringkat
- UrineDokumen4 halamanUrineVidhya MuruganBelum ada peringkat
- PathologyDokumen15 halamanPathologySaba SaqerBelum ada peringkat
- (Fig. 17.3, A) : 3. Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequence Evolves From Pre-Existing Adenomas, Referred To AsDokumen31 halaman(Fig. 17.3, A) : 3. Adenoma-Carcinoma Sequence Evolves From Pre-Existing Adenomas, Referred To AsdystoBelum ada peringkat
- Review Article: Hemangiomas and Vascular Malformations: Current Theory and ManagementDokumen11 halamanReview Article: Hemangiomas and Vascular Malformations: Current Theory and ManagementDewi AngrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Soft Tissue TumorDokumen67 halamanSoft Tissue TumorVincentius Michael WilliantoBelum ada peringkat
- Basal Cell AdenomawDokumen3 halamanBasal Cell AdenomawDrRobin SabharwalBelum ada peringkat
- Tu GloDokumen5 halamanTu GloJandira SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Slide 15 Diseases of Salivary Glands IIDokumen64 halamanSlide 15 Diseases of Salivary Glands IIJustDen09100% (1)
- Soft Tissues PathologyDokumen53 halamanSoft Tissues PathologyWz bel DfBelum ada peringkat
- CNS Flash PointsDokumen3 halamanCNS Flash PointsAbdul MannanBelum ada peringkat
- NeoplasiaDokumen9 halamanNeoplasiaRinaldo GintingBelum ada peringkat
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokumen3 halamanInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourBelum ada peringkat
- Smooth Muscle Tumor of Vulva With Uncertain Malignant PotentialDokumen4 halamanSmooth Muscle Tumor of Vulva With Uncertain Malignant PotentialmajoBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Case CAPDokumen82 halamanClinical Case CAPIna GargBelum ada peringkat
- Cystic HygromaDokumen5 halamanCystic HygromaAde Triansyah EmsilBelum ada peringkat
- A Case of Primary Myxoid Liposarcoma of The Heart Masquerading As Massive Pericardial Effusion - A Case ReportDokumen5 halamanA Case of Primary Myxoid Liposarcoma of The Heart Masquerading As Massive Pericardial Effusion - A Case ReportEditor ERWEJBelum ada peringkat
- Cancers and Abnormal GrowthsDokumen37 halamanCancers and Abnormal GrowthsNABAKOOZA ELIZABETHBelum ada peringkat
- OncologyDokumen23 halamanOncologyEslam NassarBelum ada peringkat
- TumorsDokumen50 halamanTumorsdrshailaBelum ada peringkat
- Low Grade Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma: A Case ReportDokumen3 halamanLow Grade Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma: A Case ReportNazia BhatBelum ada peringkat
- Fibrosarcoma: Continuing Education ActivityDokumen5 halamanFibrosarcoma: Continuing Education ActivityDiana Tarisa Putri0% (1)
- Neoplasia 2Dokumen57 halamanNeoplasia 2Dyvanal ArifinBelum ada peringkat
- Articulo de Serie de CasoDokumen8 halamanArticulo de Serie de CasoJairo Lino BBelum ada peringkat
- Rare Tumour - Sebaceous Carcinoma of The ScalpDokumen2 halamanRare Tumour - Sebaceous Carcinoma of The ScalpInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Belum ada peringkat
- Nonsquamous Cell Malignant Tumours of The Oral Cavity: An OverviewDokumen6 halamanNonsquamous Cell Malignant Tumours of The Oral Cavity: An OverviewranggadrBelum ada peringkat
- 2 NeoplasiaDokumen48 halaman2 Neoplasiayadetakebede53Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding the Pathophysiology and Presentation of Multiple MyelomaDokumen21 halamanUnderstanding the Pathophysiology and Presentation of Multiple MyelomaPampirBolongBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 112 Guide to Caring for Patients with CancerDokumen15 halamanNCM 112 Guide to Caring for Patients with CancerShiena Mae PelagioBelum ada peringkat
- Neoplasia (II) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDokumen138 halamanNeoplasia (II) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityleyreaBelum ada peringkat
- Progressive Dyspnea in Patient With Large Mediastinal Mass: Casereport Open AccessDokumen5 halamanProgressive Dyspnea in Patient With Large Mediastinal Mass: Casereport Open AccessFendry KolondamBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Bedah - QuwDokumen14 halamanReferat Bedah - QuwSaniaty TuankottaBelum ada peringkat
- Glomus TumorDokumen14 halamanGlomus Tumorhardrocker_2007Belum ada peringkat
- MCQS CNS PathologyDokumen14 halamanMCQS CNS PathologyFourth YearBelum ada peringkat
- Cervicofacial Vascular Anomalies. I. Hemangiomas and Other Benign Vascular TumorsDokumen9 halamanCervicofacial Vascular Anomalies. I. Hemangiomas and Other Benign Vascular TumorsBikash ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- PBC 23124 PDFDokumen7 halamanPBC 23124 PDFBalaguer RodolfoBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDokumen56 halamanRenal Cell CarcinomaBONG AIKCHINGBelum ada peringkat
- Article - Cytological Features of The Warthin-Like Variant of Salivary Mucoepidermoid CarcinomaDokumen5 halamanArticle - Cytological Features of The Warthin-Like Variant of Salivary Mucoepidermoid CarcinomaCandeBelum ada peringkat
- Low Grade Gliomas: DR Arnab BoseDokumen48 halamanLow Grade Gliomas: DR Arnab BoseandriBelum ada peringkat
- Neoplasia - AkDokumen45 halamanNeoplasia - Aksunday danielBelum ada peringkat
- Neoplasma Otak: FK UisuDokumen32 halamanNeoplasma Otak: FK UisuRifaMaisarohBelum ada peringkat
- (Botelho M.C. y Col. 2014) .Dokumen17 halaman(Botelho M.C. y Col. 2014) .Mericia Guadalupe Sandoval ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- Pleural Tumors: January 2005Dokumen3 halamanPleural Tumors: January 2005zanggut merahBelum ada peringkat
- 32 A 57Dokumen6 halaman32 A 57Eldimson BermudoBelum ada peringkat
- Angiosacaaroma 1Dokumen15 halamanAngiosacaaroma 1Francisco ZurgaBelum ada peringkat
- V 13 RtsummaryonsitetrainingworkshopfamanuelnegussieDokumen1 halamanV 13 Rtsummaryonsitetrainingworkshopfamanuelnegussieapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Amanuel Negussie: Certificate of AttendanceDokumen1 halamanAmanuel Negussie: Certificate of Attendanceapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ResumeDokumen2 halamanResumeapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Ec 102 Eclipseinverseplanningimrtandrapidarcv 13 CamanuelnegussieDokumen1 halamanEc 102 Eclipseinverseplanningimrtandrapidarcv 13 Camanuelnegussieapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Joe RTDokumen1 halamanJoe RTapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Fall EvalsDokumen6 halamanFall Evalsapi-212894050Belum ada peringkat
- PhotonDokumen3 halamanPhotonapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ImrtDokumen3 halamanImrtapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Fall EvalsDokumen6 halamanFall Evalsapi-212894050Belum ada peringkat
- Amanuel Final 5 1 14Dokumen19 halamanAmanuel Final 5 1 14api-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- BrachytherapyDokumen3 halamanBrachytherapyapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ElectronDokumen2 halamanElectronapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Fall EvalsDokumen6 halamanFall Evalsapi-212894050Belum ada peringkat
- Case Log FallDokumen2 halamanCase Log Fallapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- For E-PortfolioDokumen14 halamanFor E-Portfolioapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Monthly EvalDokumen2 halamanMonthly Evalapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- August Citation AssignmentDokumen2 halamanAugust Citation Assignmentapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ConferenceDokumen7 halamanConferenceapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Case Study - AnDokumen31 halamanComprehensive Case Study - Anapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ComptotalsDokumen3 halamanComptotalsapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Tally 1Dokumen2 halamanTally 1api-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Conference LogsDokumen1 halamanConference Logsapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- PT Case LogsDokumen2 halamanPT Case Logsapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- ConferencesDokumen4 halamanConferencesapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Case Study Final - AdjustedDokumen17 halamanComprehensive Case Study Final - Adjustedapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- September Case StudyDokumen20 halamanSeptember Case Studyapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- October Case StudyDokumen15 halamanOctober Case Studyapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- May EvalDokumen6 halamanMay Evalapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- July Case StudyDokumen18 halamanJuly Case Studyapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- 2nd Rotation PallDokumen3 halaman2nd Rotation Pallapi-174496267Belum ada peringkat
- RL Procedure Hard Natural Rubber PT - SURYA SAKTI SUKSESDokumen7 halamanRL Procedure Hard Natural Rubber PT - SURYA SAKTI SUKSESMuhammad ZakiBelum ada peringkat
- Ramdump Modem 2023-05-13 21-52-06 PropsDokumen21 halamanRamdump Modem 2023-05-13 21-52-06 PropsNanda TampanBelum ada peringkat
- The International Research Congress On Integrative Medicine and Health 2014Dokumen159 halamanThe International Research Congress On Integrative Medicine and Health 2014Sergio Jesús Huapaya GálvezBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Project-Polymerase Chain ReactionDokumen21 halamanBio Project-Polymerase Chain ReactionS.AbiniveshBelum ada peringkat
- LENZE E84AVxCx - 8400 StateLine-HighLine-TopLine 0.25-45kW - v9-0 - ENDokumen291 halamanLENZE E84AVxCx - 8400 StateLine-HighLine-TopLine 0.25-45kW - v9-0 - ENClaudioBelum ada peringkat
- B Cell Cytokine SDokumen11 halamanB Cell Cytokine Smthorn1348Belum ada peringkat
- BOM Eligibility CriterionDokumen5 halamanBOM Eligibility CriterionDisara WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- AP000100 EngDokumen9 halamanAP000100 EngLucas WrightBelum ada peringkat
- (L-2) - Cell - Mar 03, 2020Dokumen52 halaman(L-2) - Cell - Mar 03, 2020puneetlokwani04Belum ada peringkat
- 22Dokumen22 halaman22vanhau24Belum ada peringkat
- Badhabits 2022Dokumen53 halamanBadhabits 2022Sajad KhaldounBelum ada peringkat
- Quality and Functionality of Excipients-Art (Alumnos-S) PDFDokumen14 halamanQuality and Functionality of Excipients-Art (Alumnos-S) PDFLaura PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Finding the Right Pharmacy for Your NeedsDokumen4 halamanFinding the Right Pharmacy for Your Needsprabakar VBelum ada peringkat
- ApiDokumen4 halamanApiMahmoud Alwasif100% (1)
- ERAS DR - TESAR SP - AnDokumen26 halamanERAS DR - TESAR SP - AnAhmad Rifai R ABelum ada peringkat
- B Fire BehaviorDokumen39 halamanB Fire BehaviorDon VitoBelum ada peringkat
- The Payment of Bonus Act 1965 PDFDokumen30 halamanThe Payment of Bonus Act 1965 PDFappu kunda100% (1)
- Councillor Danny Thorpe: Leader, Royal Borough of GreenwichDokumen2 halamanCouncillor Danny Thorpe: Leader, Royal Borough of GreenwichDr-Syed Ali TarekBelum ada peringkat
- Young-Hwa: (Model No.: Yhass)Dokumen8 halamanYoung-Hwa: (Model No.: Yhass)Diki NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- An Interview - ExercisesDokumen3 halamanAn Interview - ExercisesCarmen GloriaBelum ada peringkat
- NECC Sri Lanka May 2017 An Open Appeal To UN and International Community PDFDokumen18 halamanNECC Sri Lanka May 2017 An Open Appeal To UN and International Community PDFThavam RatnaBelum ada peringkat
- Marathon Electric Motors Price List for Motors and Fans Effective March 15, 2019Dokumen24 halamanMarathon Electric Motors Price List for Motors and Fans Effective March 15, 2019Mohan BabuBelum ada peringkat