Hodgkins Lymphoma
Diunggah oleh
Lefe Arvie Dela PeñaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hodgkins Lymphoma
Diunggah oleh
Lefe Arvie Dela PeñaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
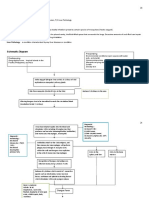
Modifiable risk factors: 1.
Diet Malnutrition Sharing food utensils
HODGKINS LYMPHOMA
Book and Net Based
Alteration on the Normal cycle of the B-cell maturation in the germinal center found on secondary lymphoid Nonmodifiable risk tissue occurs factors: 1. Age 15-35 years old Older than 55 years old
2. Environment Crowded Areas Most common in the United states, Canada and Asia
2. Genetics Can be inherited
3. Gender Male usually are affected
3. Lifestyle Kissing other partners
4. Idiopathic
Entry of EBV virus into the body either through saliva or current infection of Infectious Mononucleosis POSSIBLE EFFECTS OF EBV in HL, although no direct study is of definite to the direct effects 1. Oncogenic function to the Immune cells 2. Dysregulation of several signaling factors for B-cell 3. Reprogramming of mature B-cell which allows prolonged survival
Process on the germinal center: 1. Activated B cells function from the lymph follicle changes and begin monoclonal expansion in the environment of Folliculardendritic cells( Non-migratory) 2. After several days Somatic Hypermutation occurs. A process in which a single clone is created through normal immune- DNA mutation and type switching or
4. EBV induced protein These cells become switching occurs Decrease immune production RS cells have not undergone Not all B-cells isoof : bigger and either and normally apoptosis occurs for response renders the hypermutation, iso-switching multinucleated or those EBNA1 they immune response function body vulnerable to is who are not switched nucleated both bacterial and diminished These cells are very LMP1 viral invasion light Due to unknown visible cause upon or some Increase in growth and monoclonal LMP2 microscopy biopsy of suggests are by EBV, B-cells still rate of RS cells with help of unknown the tumor growth survives factor possibly by protein induced by and proliferates and they from Hodgkins are now called RS cells EBV
S/SX: 1. Cough 2. Fever 3. Chills 4. Sweating 5. Fatigue 6. . Painful or swollen lymph nodes 7. Skin irritations and Lesions may occur as a result of decreased immune response to any bacteria However RS cells still have B-cell They travel through the lymph vessels origins, which make it not a threat to and some are lodged and are trapped other immune cells. It attracts the in the Lymph node immune micro-environment and infiltrates local immune response Different CD molecules such as CD30 and CD 45 which are confirmatory for HL are also found in the RS since it is a B-cell in origin, many CD molecules are found in it and they serve as receptors which make them unable to be attacked and are sometimes not recognized as threats Further proliferation of RS cells and Abnormal B-cells that are oncogenic in nature Immune response is activated as a result of foreign or threat detection
Stage I. The cancer is limited to one lymph node region or a single organ.
StageStage II. In this in two III. stage, When the the cancer cancer is moves todifferent lymph lymph nodes or the cancer is the in a diaphragm, portion of tissue nodes both above and below it's or an organ and nearby lymph nodes. But the is considered stage III. Cancer may also be in cancer one still limited to a section of the body either above or portion of tissue or an organ near the lymph node Hodgkins Lymphoma can be classified in either A or B below the diaphragm. groups type. or in the spleen. Stage IV. This is the most advanced stage of A. No significant signs cells and symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer are in several cancer portions of one or more organs and tissues. Stage IV Hodgkin's lymphoma affects not only the lymph B. With significant signs and symptoms of
Complications of HL varies from its different stages however common complications are: Metastasis of cancer through several parts of the body that can be very fatal if it occurs on vital organs such as Brain, Lungs and Liver Sepsis or Viremia Severe airway compression especially if the Tumor affects the cervical lymph nodes Superior Vena cava syndrome Fatigue experience upon moving or because of References: 1. Seeleys Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 2. http://www.nlm.nih.gov 3. Hodgkins and Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma (John P. Leonard, Morton Coleman) 4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16304386
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- SLE Risk Factors and ComplicationsDokumen5 halamanSLE Risk Factors and Complicationsjoyrena ochondraBelum ada peringkat
- Outstanding 12m Bus DrivelineDokumen2 halamanOutstanding 12m Bus DrivelineArshad ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDokumen4 halamanPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoBelum ada peringkat
- Gouty Arthritissss PathophyDokumen2 halamanGouty Arthritissss Pathophybilliam123Belum ada peringkat
- GTD Case StudyDokumen9 halamanGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- Lymphoma Types, Symptoms, Stages and TreatmentDokumen20 halamanLymphoma Types, Symptoms, Stages and TreatmentChairul Adilla Ardy100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart Disease and Hydatidiform Mole CaseDokumen90 halamanRheumatic Heart Disease and Hydatidiform Mole CaseGhra CiousBelum ada peringkat
- Microbial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Dokumen82 halamanMicrobial Diseases of The Skin and Eyes (Microbiology Chapter 21)Katrina Isabel100% (1)
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDokumen3 halamanB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- PANCREATIC CANCER NURSING CAREDokumen71 halamanPANCREATIC CANCER NURSING CAREMavy CantonBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Dokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Moses Gabriel ValledorBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Breast CancerChiqui Lao DumanhugBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of Hodgkin'sDokumen10 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Hodgkin'sIvica Rae100% (1)
- Bleeding NCPDokumen13 halamanBleeding NCPBiway Regala100% (1)
- DIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)Dokumen8 halamanDIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)freyaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Castillo H MoleDokumen52 halamanCase Study Castillo H MoleGodfrey Bag-ao100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoBelum ada peringkat
- Cholecystitis Case PresDokumen103 halamanCholecystitis Case PresAnton LaurencianaBelum ada peringkat
- Abruptio PlacentaDokumen8 halamanAbruptio PlacentaNutz TolentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathways-Childrens Ministry LeaderDokumen16 halamanPathways-Childrens Ministry LeaderNeil AtwoodBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Dokumen4 halamanPathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineBelum ada peringkat
- Ductal Carcinoma Case StudyDokumen72 halamanDuctal Carcinoma Case StudyRayjundie EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of TuberculosisDokumen3 halamanPa Tho Physiology of TuberculosisFlauros Ryu JabienBelum ada peringkat
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDokumen1 halamanGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Pulmonary TuberculosisDokumen19 halamanCase Study Pulmonary TuberculosisJester GalayBelum ada peringkat
- Bsn3-2c UC-BCF CVA Case StudyDokumen49 halamanBsn3-2c UC-BCF CVA Case StudyclarheenaBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study On Colon MassDokumen29 halamanA Case Study On Colon MassDahlia D. SuelloBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJSDokumen53 halamanUnderstanding Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJSKathrina CraveBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokumen3 halamanPa Tho Physiologyaprilkow07Belum ada peringkat
- A Case Analysis OnDokumen27 halamanA Case Analysis Onbunso padillaBelum ada peringkat
- Colon Cancer Pathophysiology PDFDokumen2 halamanColon Cancer Pathophysiology PDFMaggieBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedDokumen5 halamanCancer Pathophysiology To Be EditedEyySiEffVeeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology (Risk Factors & Symptoms)Dokumen20 halamanPathophysiology (Risk Factors & Symptoms)Ann Michelle TarrobagoBelum ada peringkat
- Tetralogy of FallotDokumen3 halamanTetralogy of FallotJohn Mark PocsidioBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer of The ColonDokumen8 halamanCancer of The Colonnot your medz duranBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaDokumen3 halamanCase Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaToto RyanBelum ada peringkat
- Bladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDokumen1 halamanBladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentCarmina AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Pcap PathoDokumen2 halamanPcap PathoLardel CarayBelum ada peringkat
- H MoleDokumen2 halamanH MoleJoanna Marie Datahan EstomoBelum ada peringkat
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDokumen3 halamanPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasBelum ada peringkat
- Patho Pleural EffusionDokumen2 halamanPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Typhoid FeverDokumen1 halamanTyphoid FeverMarkChesterSaguidNagen100% (1)
- Case Studies - Tetralogy of FallotDokumen16 halamanCase Studies - Tetralogy of FallotKunwar Sidharth SaurabhBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDokumen12 halamanAcute Lymphocytic Leukemiajustin_saneBelum ada peringkat
- 4 ConceptDokumen1 halaman4 ConceptStacey GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Amoebiasis: Ingestion to ExcretionDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Amoebiasis: Ingestion to ExcretionCathy AcquiatanBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment PaperDokumen18 halamanAcute Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment Paperapi-282231236Belum ada peringkat
- Vii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmDokumen2 halamanVii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmJonna Mae TurquezaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverKenrick Randell IbanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease and FeverDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease and FeverDee SarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Colon Ca Case Study For Ring BoundDokumen66 halamanColon Ca Case Study For Ring BoundMary EnsomoBelum ada peringkat
- Personal Medical Records Document SummaryDokumen16 halamanPersonal Medical Records Document SummaryJayselle FelipeBelum ada peringkat
- PathophysiologyDokumen5 halamanPathophysiologyJessyl GirayBelum ada peringkat
- OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDokumen20 halamanOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisMikaCasimiroBalunanBelum ada peringkat
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Dokumen10 halamanSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Cervical Cancer Patho.2Dokumen2 halamanCervical Cancer Patho.2Verni Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Dokumen2 halamanPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cad NstemiDokumen2 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Cad Nstemianreilegarde100% (1)
- Pathophy NCADokumen1 halamanPathophy NCAKaren ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- HodgkinDokumen2 halamanHodgkinMRla CiriloBelum ada peringkat
- HIV Over Veiw - PPTMDokumen57 halamanHIV Over Veiw - PPTMMutegeki AdolfBelum ada peringkat
- Non Hodgkin's LymphomaDokumen27 halamanNon Hodgkin's LymphomaAnsu MaliyakalBelum ada peringkat
- ABRAMS M H The Fourth Dimension of A PoemDokumen17 halamanABRAMS M H The Fourth Dimension of A PoemFrancyne FrançaBelum ada peringkat
- EGMM - Training Partner MOUDokumen32 halamanEGMM - Training Partner MOUShaik HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits of Eating OkraDokumen4 halamanBenefits of Eating Okraama931Belum ada peringkat
- Relation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesDokumen4 halamanRelation of Jurisprudence With Other Social Sciences - LLB NotesPranjaliBawaneBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 What It Means To Be AI FirstDokumen85 halamanModule 2 What It Means To Be AI FirstSantiago Ariel Bustos YagueBelum ada peringkat
- Bonding in coordination compoundsDokumen65 halamanBonding in coordination compoundsHitesh vadherBelum ada peringkat
- Women Safety AppDokumen18 halamanWomen Safety AppVinod BawaneBelum ada peringkat
- Module 5 Communication & Change MGT - HS Planning & Policy Making ToolkitDokumen62 halamanModule 5 Communication & Change MGT - HS Planning & Policy Making ToolkitKristine De Luna TomananBelum ada peringkat
- 50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPDokumen10 halaman50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPsivananda11Belum ada peringkat
- Principal Component Analysis of Protein DynamicsDokumen5 halamanPrincipal Component Analysis of Protein DynamicsmnstnBelum ada peringkat
- Amo Plan 2014Dokumen4 halamanAmo Plan 2014kaps2385Belum ada peringkat
- Cats - CopioniDokumen64 halamanCats - CopioniINES ALIPRANDIBelum ada peringkat
- Cypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualDokumen2 halamanCypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualCarlos RodasBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2: Lesson Plan Analysis, Revision and Justification - Kaitlin Rose TrojkoDokumen9 halamanAssignment 2: Lesson Plan Analysis, Revision and Justification - Kaitlin Rose Trojkoapi-408336810Belum ada peringkat
- Experimental Investigation On The Properties of Compressed Earth Blocks Stabilised With A Liquid ChemicalDokumen7 halamanExperimental Investigation On The Properties of Compressed Earth Blocks Stabilised With A Liquid ChemicalDeb Dulal TripuraBelum ada peringkat
- Afrah Summer ProjectDokumen11 halamanAfrah Summer Projectاشفاق احمدBelum ada peringkat
- ACM JournalDokumen5 halamanACM JournalThesisBelum ada peringkat
- Rpo 1Dokumen496 halamanRpo 1Sean PrescottBelum ada peringkat
- Minimum Fees To Be Taken by CADokumen8 halamanMinimum Fees To Be Taken by CACA Sanjay BhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Destroyed Inventory Deduction ProceduresDokumen7 halamanDestroyed Inventory Deduction ProceduresCliff DaquioagBelum ada peringkat
- Beyond B2 English CourseDokumen1 halamanBeyond B2 English Coursecarlitos_coolBelum ada peringkat
- Control Systems Engineering by S C Goyal U A Bakshi PDFDokumen3 halamanControl Systems Engineering by S C Goyal U A Bakshi PDFShubham SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Thinking and Acting Outside The BoxDokumen36 halamanThinking and Acting Outside The BoxMariecris GatlabayanBelum ada peringkat
- The Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends For 2020: Tomas Huseby Executive PartnerDokumen31 halamanThe Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends For 2020: Tomas Huseby Executive PartnerCarlos Stuars Echeandia CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Team Dynamics and Behaviors for Global ExpansionDokumen15 halamanTeam Dynamics and Behaviors for Global ExpansionNguyênBelum ada peringkat
- Liu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain ClimbersDokumen2 halamanLiu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain Climberssanti.miranda.parrillaBelum ada peringkat
- Technical CommunicationDokumen35 halamanTechnical CommunicationPrecious Tinashe NyakabauBelum ada peringkat
- Costos estándar clase viernesDokumen9 halamanCostos estándar clase viernesSergio Yamil Cuevas CruzBelum ada peringkat