American Colonial Architecture
Diunggah oleh
Cam DeteraHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
American Colonial Architecture
Diunggah oleh
Cam DeteraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
AMERICAN COLONIAL ARCHITECTURE (1898-1942, 1945-1946} > American colonial regime embarked on projects in the fields of: * Education
A. Priority was given to educate the Filipinos B. Focus of education 1. The spread of democracy and formation of good citizens, including the rights and responsibilities of the people 2. Reading and writing C. Allowed the Americnns o spread or share their culture, particularly the English languge D. Religion was not included in the curriculum of the schools E. Gave everyone the hance to study introduction of Public School Buildings 1. Child from age 7 was required to register in schools located in their own town or province and were given free school materials 2. 3 levels of education A.Elementary level 4 primary yrs and 3 intermediate yrs B. Secondary or hih school level 4 yrs; C. Third level college or tertiary level F. Volunteer Filipino soldiers 1st techersof the Filipinos. 1. Part of their mission was to build classrooms in every place where they were assigned. 2> Stopped teaching when a group of teachers from the U.S came to the Philipines in June 1901 3. August 1901, 600 teachers called Thomasites arrived. Their name from the ship they traveled on S.S. Thomas. G. Elementary and secondary schools were opened in cities and provinces. H. There were also colleges during the American period: 1. Philippine Normal School in 1901 ( now a university ) 2. National University ( 1901) ; 3. University of the Philippines was also founded in 1908
4. University of Manila ( 1914 ) 5. Philippine Women University ( 1919 ); and 6. Far Eastern University I. Attention was given to vocational and health practice J. Normal, vocational, agricultural, and business schools were also opened: 1. Philippine Nautical School 2. Philippine School of Arts and Trades 3. Central Luzon Agriculture School K. Students who excelled academically sent to the U.S to continue their studies and become expert in desired fields or professions called scholars. In return, they were to teach or work in government offices after they finished. Successful Filipino Scholars Judge Jose Abad Santos, Francisco Benitez, Dr. Honoria Sison and Francisci Delgado. L. Formal education was also provided to those who were of age. M. Schools were also built in non-Catholic areas like Sulu, Mindanao, and Mountain Provinces. * Health and Sanitation A. Construction of Public toilets and baths B. Health services * Public works * Communication * Transportation * Resources development * Conservation > The American Governors started to organized the structure of government. From the local municipalities to provincial governments and offices > American Architects A. Daniel H. Burnham Grand plan for Manila and Baguio
B. William E. Parsons ( 1904- 1914 ) 1. Burnhams plan for Manila, Baguio, prepared city plans for Cebu and Zamboanga 2. Major Buildings PGH, Normal School, Manila Hotel, Army and Navy, Elks Club, YMCA, provincial and government buildings, and schools C. George Fenhagen D. Ralph Harrington Doane ( 1916- 1918 ) Post Office, Dept. of Foreign Affairs E. Wilton Becket Jai Alai Bldg F. Richard Kisling Rizal Monument in 1905 > William Cameron Forbes American Commissioner, Organizer and promoter A. City of Baguio and construction of Mansion House ( Governor Generals Palace ) > Corp of Army Engineers in charge of the construction of ordinary buildings and other infrastructure > Division of Architecture in the Bureau under the Jones Law was created were American and Filipino architects were employed > Filipino pensionado architects studied architecture in America and Europe > Design in concrete and mortar beton brut William Parsons A. Prefabrication bldg. coponents such as walls section, floors, slabs, columns, beams are produced in factory, transported and assembld. B. Precast Cement ornaments and fixtures classical capitals, friees and reliefs for pediments. > Following Burnhams Dictum, Spanish colonial architecture should be the basis of the new style. A. Parsons made use of arches,, plain walls, and capiz windows > Materials Precast cement mouldings and relief. Glass blocks exterior and interior. Stained glass used in churches were used in domestic architecture. > Architectural Styles adopted. Government builders favored neoclassical style. New York design influence is strongly reflected. Art deco and Art nouveau style were introduced in 1930. * Revivalist Architecture A. historical fever revived other styles of architecture B. Classical tradition of the Romans and Greek dominated the 19th c
C. Romanticism movement was popularized. D. Gothic, Romanesque and Byzantine E. Also included are non-western styles Egyptians, Moorish, Indians, etc. F. Neoclassicism 1. Preferred sober dignity to the excesses of baroque 2. Advocated a break from post-renaissance that led to the revival of ancient Greek architecture pure honest and simple. 3. exact classic proportions and ornamented surfaces with correctly rendered pilasters, massed either singly or pairs under semi-circular or triangular pediments. 4. great impact to the Architects trained in the U.S under the Ecole de Beaux Arts as seen in our Government buildings. * New Art (French, Art Nouveau) A. Known as judendstil, bandwurmstil or tapeworm style, English style or stile liberty, modernimo, sezession B. Negative form of revolt against Eclecticism C. organic and dynamic forms D. curving designs E. whiplash lines * Art deco (French, art decorative) A. Originated from the 1925 Paris Exposition Internationale des Arts Decoratifs et Industriels Modernes rise of Modernistic architecture 1. The exhibit covered a wide range of work, such as glass, ceramic and metal objects for domestic use, jewelry, textile, furniture, etc. B. Form and styles matters over function C. Introduction in the Philippines marked the end of neoclassic dominance. > EARLY FILIPINO ARCHITECTS * Arcadio De Guzman Arellano A. Studied at Escuela de Artes y Oficios Maestro de obras (Master builder) in 1895
B. Captain of Engineering Corps of Emilio Aguinaldos revolutionary army supervised repair of Barasoain Church. C. 1st Filipino employed in 1901 by Gov. Taft as consulting architect D. Set up the first architectural and surveying office E. Worked in revivalist style F. Designed the Gota de Leche and Casino Espanyol * Carlos A. Baretto A. 1st employed by Division of Architecture formerly a Bureau of Architecture in 1901 and Division of Building Construction and Repair in 1905 B. Government pensionado send to Drexel Institute, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania C. 1st Filipino with academic title D. Worked in 1908 1913 * Antonio Manalac Toledo A. Finished architectural studies at Cornell University in 1910 B. employed at the Bureau of Public Works under William Parsons C. 1st professor at the Mapua Institute of Technology D. UP campus Plans, and Buildings UP Padre Faura complex, other UP buildings, Leyte Capitol, Department of Tourism and Finance city Hall of Manila E. Adheres to to neoclassical style * Tomas Bautista Mapua A. Graduate from Cornell University B. Worked in the Bureau of Public Works in 1911 1927 C. Founded Mapua Institute of Technology D. First board of Examiners for Architects in the Philippines E. Building De La Salle College, Centro Escolar University, Nurses Home PGH,, and others * Juan De Guzman Arellano A. Architect and Painter
B. Graduate from Drexel University and took post graduate work in Architecture at the University of Pennsylvania and attended the Beaux Arts School in New York C. Buildings Gota de Leche, Casino Espanyol, Legislative Bldg., Post Office, Metropolitan Theater, Villamor Hall UP, other government buildings D. Neoclassic, art deco and later nativist phases > 2ND GENERATION FILIPINO ARCHITECTS * Andres Luna de San Pedro A. Architect and painter B. Son of the painter Juan Luna C. Enrolled at the Ecole de Beaux Arts, France D. Served as architect of the City of Manila then went to private practice E. Revivalist, art deco and modern style F. Legarda Elementary School, Crystal Palace, Zobel Houses, Perez Samanillo Bldg, St. Cecilia Hall, St. Scholasticas College, etc. * Pablo Sebrero Antonio A. Worked in the Bureau of Public Works while attending high school at night B. Took correspondence school in architecture and structural engineering at the Mapua Institute of Technology C. Far Eastern University, Philippine National Bank, Manila Railroad Co., Manila Polo Club, Galaxy Theater D. National Artist in Architecture * Fernando Hizon Ocampo A. Civil Engineer graduate at UST, and architecture degree from the University of Pennsylvania in 1921. Took advance studies at the American Academy in Rome B. Worked in US Architectural firm and worked in the architecture division, Bureau of Public Works C. Formed a partnership with Tomas Arguelles D. One of the founders of the UST School of Architecture and Fine Arts established in 1930 E. Paterno Bldg, Mc. Arthur Bridge, UST Central Seminary Bldg., etc
F. Traditionalist with art deco style * Juan Felipe De Jesus Nakpil A. National Artist B. Took engineering at UP and University of Kansas C. Studied in France and obtained a diploma in architecture from the Fountainebleau Sool of fine arts D. Worked in the Bureau of Public Works and became partner of Andres Luna de San Pedro E. Quezon Institute Administration bldg., Manila Jockey Club, Avenue Hotel and Theater, Quiapo Church, etc. > BUILDING TYPES * GOVERNMENT OFFICE BUILDINGS A. Classification 1. National legislative, executive and judicial branches, depts. and bureaus under and other government institution such as banks 2. Provincial Kapitolyo (capitol) houses the governors office, provincial boards, courts and other offices 3. City or municipal city halls or municipality halls which houses the city or municipal government, mayors office, city or town council and local courts B. Local government buildings include post office, police station and fire stations C. Designed and constructed in line with the policy of preparing the Filipino people for democratic self government D. Provincial capitols were built in the 2nd decade of the 20th c. E. Symmetrical in plan, formal in massing with rooms along corridors or around courtyard F. Landscaping projects included the plazas in front of the provincial capital and parks G. Provincial capitols were located away from the town center and were set on spacious grounds. Some built on elevated areas or near seashore H. Monuments were focal points in the plaza I. Pre WWW II buildings were in neo classic style
** EXAMPLES** 1. LEGISLATIVE BUIDING (NATIONAL MUSEUM), Manila A. Started in 1918, by Archts. Ralph Doane, Antonio Toledo and Juan Arellano, completed in 1926 B. Originally designed as public library C. Congress of the Philippines, Executive Houses, Senate D. 4 storey rectangular building with 2 interior courts E. Appearance of 3 storey set on a podium formed by ramp and stairways F. Four column portico of Corinthian order with a triangular pediments, and both ends of the faade two column portico complimenting the central portico G. Neo-classic Greek revival H. Superb massing, siting and handling of the main approach. I. Faithfully reconstructed after WW II 2. Laguna Provincial Capitol ( 1912) 3. Bacolod Provincial Capitol Building 4. Lingayen Capitol, Pangasinan ( 1918 ) 5. Cebu Provincial Capitol 6. Batangas Capitol 7. Bulacan Provincial Capitol 8. Tagbilaran Capitol Building 9. Dumaguete Capitol building 10. CAGAYAN PROVINCIAL CAPITAL A. Completed in 1950 B. Sited on a large tract of land, approached via long vista of maintained garden C. Two-storey building made of concrete D. Symmetrical in plan E. Central portion of the faade with tall square columns supporting the rectangular pediment and bordered parapet termination main feature 11. Urdaneta Municipal Building, Pangasinan 12. Lemery Municipal Building, Batangas 13. Compostela Presidencia, Cebu 14. Lopez Municipal Building, Tayabas ( 1928 ) 15. Camalig Municipal Building, Albay 16. Alang-Alang Public School, Leyte 17. Romblon Municipal Building, Romblon * PUBLIC SCHOOL AND COLLEGES A. When the government started to function smoothly the Americans brought in teachers to educate the young and offered later professions to Filipinos B. Spanish government built around 1,000 school buildings in the Philippines, 39 located in Manila
C. Americans while setting up the public school system used in the buildings as well as ermitas (chapels), rented private homes and set up temporary structures paid for by the municipal funds. D. GABALDON SCHOOLHOUSES 1. Named after Isauro Gabaldon who promulgated the Gabaldon law under Philippine Commossion Act 1801 and augmented by act 2029 of the Philippines Assembly in 1908 A. allocated 1 million pesos made available for 4 yrs. For the construction of elementary buildings in municipalities in the country 2. William Parsons as consulting architect of the Bureau of Public Works designed in 15 different types 3. Well drained square site was considered ideal and built away from the street with open areas for playfield, gardens and alks 4. Concrete foundation and walls and Galvanized iron roofs 5. 1 storey elevated by 1 m to keep the wooden floor safely above humid grounds with clssrooms on the sides of an open gallery 6. Floor to ceiling of about 4 m to allow hot air to rise 7. Features derived from bahay kubo and bahay na bato A. Hip and steep roof with wide overhangs B. Tall but narrow windown swung outwards with transom made of wood and capiz shells C. Prefabricated for short construction time 8. Some elementary and high school buildings especially in urban centers are more elaborate than the quick-build type have two to three floors 9. High school buildings followed a longitudinal plan and may have porticos in renaissance style with arches resting on columns or arches without columns ** EXAMPLES ** 1. ZAMBOANGA EAST AND WEST CENTRAL SCHOOLS A. Renamed after Prv. Albert L. Burleigh, 2nd Infantry Div. to honor his achievements in Jolo B. Patterned after the one storey Prairie style of American schools C. Listed in the Patrimonial Properties of Zamboanga City as the oldest school building during the American regime 2. Provincial High School, Guinobatan, Albay and Sorsogon 3. Baguio Central School
4. Hinundayan Central School, Leyte 5. Pasig Provincial High School, Rizal 6. PHILIPPINE NORMAL COLLEGE, Taft Avenue A. Manila Normal School B. 1st bldg. designed by W. Parsons C. Retained the traditional Spanish tile roof, interrupted by 3 California gables on either side which marked the entrances of the 3-storey building D. Built of reinforced concrete E. Glazed tile wall ornamentation 7. LEGARDA ELEMENTARY SCHOOL, Manila A. Andres Luna de San Pedro, Ecole des Beaux-Arts B. Built in 1920 8. SILIMAN HALL, City of Dumaguete, Negros Oriental A. 1st bldg.. of the Siliman Institute planned by Dr. David S. Hibbard in 1901 and constructed by the students B. 1st bldg. that used cast iron for structural purposes C. GI sheets breakthrough roofing material D. Spacious verandas maximizing the east and south views of the sea E. Capiz windows and spaces reminiscent of the bahay na bato but Victorian inspired details F. Tropical architecture G. Embossed metal ceiling panels manufactured in England H. Interior wrought iron column and decorative capital salvaged by Charles Glung, US secretary of the Army and Navy, from the debris if the theater in US. I.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Architecture of The Philippines, Traditions and Changing Expressions) Arkitekturang Filipino Spaces and Places in HistoryDokumen4 halamanThe Architecture of The Philippines, Traditions and Changing Expressions) Arkitekturang Filipino Spaces and Places in HistoryAndrew Dionaldo100% (1)
- The Ifugao Hut - EditedDokumen8 halamanThe Ifugao Hut - EditedArvee VillamorBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptive Reuse Examples in The PhilippinesDokumen3 halamanAdaptive Reuse Examples in The PhilippinescbgwnkimBelum ada peringkat
- Design 6 Major Plate No.1 ARCHITECTURALDokumen4 halamanDesign 6 Major Plate No.1 ARCHITECTURALJayson PobarBelum ada peringkat
- Design # Title: Hernando, Anna Pauline B. Architectural Design 8 BS Architecture 4-1Dokumen1 halamanDesign # Title: Hernando, Anna Pauline B. Architectural Design 8 BS Architecture 4-1Charlene Ordoñez Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Early Shelter To Spanish ColonialDokumen96 halamanEarly Shelter To Spanish ColonialTricia Infante100% (1)
- History of Philippine ArchitectureDokumen245 halamanHistory of Philippine ArchitectureMikee PBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 11 UCSPDokumen29 halamanDaily Lesson Log Grade 11 UCSPDonald Montano Dela Torre100% (14)
- Philipines Paint ManufacturersDokumen11 halamanPhilipines Paint ManufacturersThiwakkaran Muagan67% (3)
- BP 344 Accessibility Law With IllustrationsDokumen30 halamanBP 344 Accessibility Law With IllustrationsEmmanuel Linguaje Managbanag II100% (1)
- Week No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityDokumen12 halamanWeek No. 1: Rizal Technological UniversityStephany JulaoBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Tapp Pinoy PDFDokumen28 halaman04 Tapp Pinoy PDFMelannie OcampoBelum ada peringkat
- American Colonial Architecture in The Philippines Notes Part 1 PDFDokumen8 halamanAmerican Colonial Architecture in The Philippines Notes Part 1 PDFNino Ylagan100% (1)
- Module - 4 - Post-World War Ii EraDokumen218 halamanModule - 4 - Post-World War Ii EraAlexBelum ada peringkat
- Marcosian ContemporaryDokumen45 halamanMarcosian ContemporaryTricia InfanteBelum ada peringkat
- American Colonial Architecture in the Philippines Part 2: City Beautiful Movement and Tropical ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanAmerican Colonial Architecture in the Philippines Part 2: City Beautiful Movement and Tropical ArchitectureNino Ylagan0% (1)
- A Brief History of Philippine ArchitectureDokumen8 halamanA Brief History of Philippine ArchitecturecarloBelum ada peringkat
- Philippines Insurance Adjusters License List 2016-2018Dokumen8 halamanPhilippines Insurance Adjusters License List 2016-2018Evan Calusayan100% (1)
- Module - 2 - Spanish Colonial Era PDFDokumen362 halamanModule - 2 - Spanish Colonial Era PDFAlex100% (1)
- Philippine Architecture PDFDokumen15 halamanPhilippine Architecture PDFMa Teresita Millano100% (2)
- Specialized Allied ServicesDokumen30 halamanSpecialized Allied ServicesJesi ViloriaBelum ada peringkat
- Modular BuildingsDokumen20 halamanModular BuildingsCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Filipino ArchitectureDokumen57 halamanFilipino ArchitectureZarah Candido100% (6)
- Pre ColonialDokumen11 halamanPre Colonialkathyrin100% (2)
- Hoa 4Dokumen8 halamanHoa 4namika marbaBelum ada peringkat
- Who Are Some Famous Architects From The PhilippinesDokumen54 halamanWho Are Some Famous Architects From The PhilippinesMark Joseph Caadiang NaralBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Generation ArchitectsDokumen9 halaman1st Generation ArchitectsBenjie LatrizBelum ada peringkat
- Hoa 4 - American Colonial PeriodDokumen27 halamanHoa 4 - American Colonial Periodcrono6680% (5)
- Hoa Module 4 P1Dokumen94 halamanHoa Module 4 P1cyril delfin100% (2)
- Bahay Na Bato FinalDokumen8 halamanBahay Na Bato FinalSeff JABelum ada peringkat
- Filipino Architects - Arcadio Arellano and Antonio ToledoDokumen2 halamanFilipino Architects - Arcadio Arellano and Antonio ToledoEmmanuel InocencioBelum ada peringkat
- Module - 3 - American Colonial EraDokumen434 halamanModule - 3 - American Colonial EraAlex100% (1)
- Years and Have Built Massive Rice Terraces That Would Be A Symbol of The Province in Later TimeDokumen4 halamanYears and Have Built Massive Rice Terraces That Would Be A Symbol of The Province in Later TimeFrance CortezanoBelum ada peringkat
- Spanish Colonial EraDokumen5 halamanSpanish Colonial EraAlexBelum ada peringkat
- IB History Internal Assessment - Treatment of Chinese FilipinosDokumen14 halamanIB History Internal Assessment - Treatment of Chinese FilipinosEscalusBelum ada peringkat
- 1st & 2nd Generation Arch'TsDokumen5 halaman1st & 2nd Generation Arch'TsBenjie Latriz100% (1)
- Philippine Architecture Timeline and Other InformationDokumen9 halamanPhilippine Architecture Timeline and Other InformationJay Clark Bermudez100% (2)
- History of Philippine architecture in 40 charactersDokumen10 halamanHistory of Philippine architecture in 40 charactersCistron ExonBelum ada peringkat
- Arkitekturang Filipino 4 - Imperial Imaginings - American A...Dokumen2 halamanArkitekturang Filipino 4 - Imperial Imaginings - American A...ISABELLE MAXINE MANTO67% (3)
- Notice of School Assignment Civil Service Exam Professional October 23 2016 PDFDokumen441 halamanNotice of School Assignment Civil Service Exam Professional October 23 2016 PDFPhilBoardResultsBelum ada peringkat
- Module - 5 - Late Twentieth Century & The New MillenniumDokumen181 halamanModule - 5 - Late Twentieth Century & The New MillenniumAlex100% (1)
- Post War ArchitectureDokumen12 halamanPost War ArchitectureANNA PATRICIA REYNOSOBelum ada peringkat
- Architecture of The PhilippinesDokumen9 halamanArchitecture of The PhilippinesShin Hye ParkBelum ada peringkat
- Prewar Modern InfluenceDokumen9 halamanPrewar Modern InfluenceErica PagsBelum ada peringkat
- Post World War 2 ArchitectureDokumen11 halamanPost World War 2 ArchitectureMartina Jeunesse FlorendoBelum ada peringkat
- HOA 4 Module 2Dokumen5 halamanHOA 4 Module 2AlexBelum ada peringkat
- Historical Significance of Quiapo Church and Plaza MirandaDokumen16 halamanHistorical Significance of Quiapo Church and Plaza MirandaCynthiaFeliciano100% (1)
- Filipino StyleDokumen20 halamanFilipino StyleRon AndayaBelum ada peringkat
- YapDokumen4 halamanYapDenise Michaela YapBelum ada peringkat
- HOA 4 GROUP 2 HANDOUTS Spanish Colonial Architecture Part 2.edited 1Dokumen13 halamanHOA 4 GROUP 2 HANDOUTS Spanish Colonial Architecture Part 2.edited 1Moa Alyanna Trinidad0% (1)
- San Miguel Corporation: Architect: Franciso "Bobby" ManosaDokumen26 halamanSan Miguel Corporation: Architect: Franciso "Bobby" ManosaHazel Joy CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- History of Architecture - PhilippinesDokumen13 halamanHistory of Architecture - PhilippinesJyzel NacuBelum ada peringkat
- Post World War Ii EraDokumen7 halamanPost World War Ii EraAlexBelum ada peringkat
- HOA 1 SummaryDokumen10 halamanHOA 1 SummaryNicole Osuna Dichoso100% (1)
- Philippine Architecture Pre-Spanish PeriodDokumen7 halamanPhilippine Architecture Pre-Spanish PeriodDash AssxEzioBelum ada peringkat
- FRANCISCO Manosa (TheoryDokumen19 halamanFRANCISCO Manosa (TheoryShaira Reyes100% (10)
- Pre-Colonial Architecture Lecture1Dokumen4 halamanPre-Colonial Architecture Lecture1ace leeBelum ada peringkat
- Postcolonial Modernity in Philippine Architecture 1946-1960sDokumen23 halamanPostcolonial Modernity in Philippine Architecture 1946-1960sKristee Marie O. LagamonBelum ada peringkat
- ARH 304 Group 4 BONTOC HOUSE Philippine Vernacular ArchitectureDokumen11 halamanARH 304 Group 4 BONTOC HOUSE Philippine Vernacular ArchitectureSarah Grace BelañoBelum ada peringkat
- Hoa ReviewerDokumen3 halamanHoa ReviewerRachel Mae BahoyBelum ada peringkat
- Arch 18 - Reflection Paper About Asian ArchitectureDokumen2 halamanArch 18 - Reflection Paper About Asian ArchitectureKevin Throy Corpuz ElpedesBelum ada peringkat
- HOA RenaissanceDokumen6 halamanHOA RenaissanceLyke Cris Toriaga MateoBelum ada peringkat
- Vernacular TermsDokumen1 halamanVernacular TermsLara KayeBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy: Francisco "Bobby" MañosaDokumen6 halamanPhilosophy: Francisco "Bobby" MañosaJohnDominicMoralesBelum ada peringkat
- American Colonial ArchitectureDokumen2 halamanAmerican Colonial ArchitectureJella DulatreBelum ada peringkat
- History Architectural Education PhilippinesDokumen1 halamanHistory Architectural Education PhilippinesMatel SumatraBelum ada peringkat
- Juan Marcos Arellano y de GuzmánDokumen11 halamanJuan Marcos Arellano y de GuzmánCedie Aviles Serafica100% (2)
- Architecture in The Philippines American To Martial LawDokumen35 halamanArchitecture in The Philippines American To Martial LawMartin loreñaBelum ada peringkat
- Hoa ReviewerDokumen5 halamanHoa ReviewerGraezelBelum ada peringkat
- NBC Building Restrictions for Natividad Boulevard 2000Dokumen24 halamanNBC Building Restrictions for Natividad Boulevard 2000Cam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- NBC Building Restrictions for Natividad Boulevard 2000Dokumen24 halamanNBC Building Restrictions for Natividad Boulevard 2000Cam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On The Efficiency Measure of PNRDokumen30 halamanA Study On The Efficiency Measure of PNRCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Dew HarvestingDokumen16 halamanDew HarvestingCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Paper # 3: Business Suits vs. Designers: Why Architectural Practice Is Going Down The GurglerDokumen6 halamanReaction Paper # 3: Business Suits vs. Designers: Why Architectural Practice Is Going Down The GurglerCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Ho1 Concept of State and Etc.Dokumen3 halamanHo1 Concept of State and Etc.Cam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Database on Unit Costs and Work Accomplishments for Structural WorksDokumen2 halamanDatabase on Unit Costs and Work Accomplishments for Structural WorksCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- BuildoffsiteglossaryV1.3revised July06Dokumen39 halamanBuildoffsiteglossaryV1.3revised July06Cam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- R7 GANTCHART SCURVE 3b PDFDokumen1 halamanR7 GANTCHART SCURVE 3b PDFCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- Masterformat: Advantages and DisadvantagesDokumen3 halamanMasterformat: Advantages and DisadvantagesCam DeteraBelum ada peringkat
- ADU - ECE Laws and EthicsDokumen15 halamanADU - ECE Laws and EthicsJoel TaglinaoBelum ada peringkat
- High Schools in Metro Manila (As of 2008)Dokumen150 halamanHigh Schools in Metro Manila (As of 2008)Paul Immanuel LaderaBelum ada peringkat
- CHED-RIPH Required ReadingsDokumen4 halamanCHED-RIPH Required ReadingsMakrocen SantillanBelum ada peringkat
- E-11 JRNL, Cert, RCRDS of Chain of CustodyDokumen3 halamanE-11 JRNL, Cert, RCRDS of Chain of CustodyERGIE WANAWAN (PCPT WANAWAN. ERGIE T.)Belum ada peringkat
- Economics For Business 7Th Edition by John Sloman Full ChapterDokumen22 halamanEconomics For Business 7Th Edition by John Sloman Full Chapterralph.belville615100% (52)
- Soul Boat (Abrera)Dokumen15 halamanSoul Boat (Abrera)MBelum ada peringkat
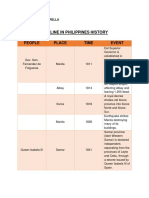
- Key events and figures in early Philippine historyDokumen2 halamanKey events and figures in early Philippine historyJenella Mika EstrellaBelum ada peringkat
- Idea1 MDC Conzace BOTO 2023 AllocationDokumen20 halamanIdea1 MDC Conzace BOTO 2023 Allocationbadeth.bandejasBelum ada peringkat
- The Cagayan Railway Extension ProjectDokumen8 halamanThe Cagayan Railway Extension ProjectDeus NobiscumBelum ada peringkat
- Progress Check - MarikinaDokumen9 halamanProgress Check - MarikinaJean TroncoBelum ada peringkat
- Ofw ClinicsDokumen19 halamanOfw Clinicsnum_lock_erBelum ada peringkat
- Week 5: Science, Technology and Nation BuildingDokumen8 halamanWeek 5: Science, Technology and Nation BuildingjkhkasdgskfkBelum ada peringkat
- City of Manila v. ColetDokumen31 halamanCity of Manila v. Coletevelyn b t.Belum ada peringkat
- Top 130 Schools and Universities in The Philippines With The Most Board PassersDokumen4 halamanTop 130 Schools and Universities in The Philippines With The Most Board PassersmarkiejnBelum ada peringkat
- QC Annual Report 2019 2020Dokumen72 halamanQC Annual Report 2019 2020John Steven GanitanoBelum ada peringkat
- Science and The Spanish Colonial StateDokumen3 halamanScience and The Spanish Colonial StatePrincess DimayacyacBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 Governance in The PhilippinesDokumen12 halaman2018 Governance in The Philippinesoy dyBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 7. Case StudyDokumen2 halamanActivity 7. Case StudyBernadette AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Tle0814 MlaDokumen207 halamanTle0814 MlaCoolbuster.NetBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Contemporary Art Overview: Minding The Gaps (2012)Dokumen8 halamanPhilippine Contemporary Art Overview: Minding The Gaps (2012)Joy UyBelum ada peringkat
- Personal History FormDokumen4 halamanPersonal History FormKim1412Belum ada peringkat
- Water Factsheet CisternsDokumen3 halamanWater Factsheet CisternsRejoice SamboBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Gned04 BSP 1 7Dokumen10 halamanSyllabus Gned04 BSP 1 7Mayeyean TaguibalosBelum ada peringkat