Switchyard Final
Diunggah oleh
Pritam SamantaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Switchyard Final
Diunggah oleh
Pritam SamantaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
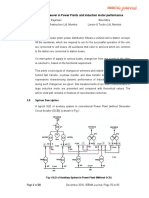
SWITCHYARD What is a Switchyard? The switchyard is a junction connecting the Transmission & Distribution system to the power plant.
It means collection of electrical equipment where high voltage electricity is switched using of various component. What is a Substation? An electrical substation is a subsidiary station of an electricity generation, transmission and distribution system where voltage is transformed from high to low or the reverse using transformers. What is the difference between Switchyard and Substation? The function of substation is to stepping up or down the voltage as per requirements. It receives electrical power via incoming transmission lines and delivers electrical power via the outgoing transmission lines. The function of Switchyards is to deliver the generated power from power plant at desired voltage level to the nearest grid. Function of switch yard The function of electrical switch yard is to deliver the generated power from power plant at desired voltage level to the nearest grid or in another way you can say simply switching the received power supply from various generating station to various location w.r.t their requirement. ELEMENTS OF A SWITHYARD 1. Galvanized steel structures for towers, gantries and equipment support 2. Bus Bar 3. Insulators 4. Lightning Arrestor 5. Circuit Breaker 6. Isolator 7. Earthing Switch 8. Current Transformer 9. Potential transformer 10.Capacitor voltage transformer 11.Wave trap and PLCC 12.Shunt reactor/Capacitor 13.Power Cables
14.Control Cables for protection and control 15.Control and Protection Panel 16.DC Battery and Charging Equipment
Description of the equipment 1. Galvanized steel structures for towers, gantries and equipment support
2. Bus Bar: Bus bar is that conductor where feeders from generating
station & feeders for different load-Centre are connected. The type of arrangement adopted depends on various factors viz. to ensure uninterrupted and reliable power supply distribution, should be economically viable, should be easy for operation and maintenance, and should be more flexible. The materials used for bus bar should have low resistivity, higher softening temperature, good mechanical properties and low cost. To accommodate more number of bays within limited space, two tire designs of conductors are followed in modern switchyards. The upper level consists of flexible bus bar arrangement of ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforcement) strung between Aframes by using string of insulators consisting of several number of disc insulators depending upon the voltage level. This arrangement requires high structures and high spacing of conductors. In MTPS four main bus systems are used: - MAIN BUS 1, MAIN BUS 2, MAIN BUS 3 & MAIN BUS 4 (main bus 1 and main bus 2 is connected by jumper to main bus 3 & 4). MAIN BUS 1 & MAIN BUS 2 are used for unit 1 to unit 4 (220 KV, 50 Hz). MAIN BUS 3 & MAIN BUS 4 are used for unit 5 & 6(220 KV, 50 Hz). Two new main buses are introduced for unit 7 and unit 8 (400 KV, 50 Hz).
3. Insulator:
The live equipments are mounted over the steel structures or suspended from gantries with sufficient insulation in between them. Porcelain insulators are most widely used. Following two types of insulators are used in switchyard: a) Pedestal b) disc
a) PEDESTAL: These are used on steel structures for rigid supporting of pipe bus bars, for holding the blade and fixed contacts of the isolators. b) DISC: These insulator units are connected to each other to form a string insulator of required length to suit the system voltage. In switchyards these insulators are for stringing of swing bus, at the dead end and as a drop down conductor. Normal system voltage, system over voltage due to switching and lighting strokes, rainfall, atmospheric pollution etc. are the important factors to be considered along with the mechanical factors such as loading, swing etc. for the selection of insulators in the switchyard.
4. Lightning Arrestor/ Surge Diverter :
In switchyard, the first and the last equipment is lightning arrestor, also called surge arrestor, as it protects the switchyard from any surges. Temporary over-voltages may be caused by a number of system events such as line to ground-fault , circuit back feeding , load rejection, ferroresonance. There may be also other internal surges known to be switching surges. A lightning arrestor resembling a safety valve of the system diverts these over voltages to ground by lowering its resistance. Use of lightning arrestor: i. ii. iii. It protects the equipment from lightning stroke. It is used to give electrostatic shielding against external field. Lightning arrester is used to provide path to unwanted excessive currents.
5. Circuit Breaker: Circuit breakers are the main switching equipment in a
switchyard. These are capable of safe interruption of normal as well as very high fault currents without causing any damage to the circuit breakers contacts. The breakers shall essentially consist of moving and fixed contacts kept within a dielectric medium. The medium in case of EHV may be compressed air, insulating oil, sulphur hexafluoride gas or high vacuum. The moving contact is connected to the external operating mechanism through insulating handle/rod capable of making it on and off with sufficient force and speed. As the contacts separate arcing between these parting contacts takes place due to high temperature, voltage gradient and multiplication of electrons present within the arc space. For successful arc interruption the function of the dielectric medium is to fulfill the following basic requirements.
Types: i. Oil Circuit breaker: Oil circuit breakers rely upon vaporization of some of the oil to blast a jet of oil through the arc. ii. Gas Circuit breaker: Gas (SF6) circuit breaker sometimes stretch the arc using magnetic field and then rely upon the dielectric strength of SF6 to quench the stretched arc. iii. Vacuum Circuit breaker: Vacuum circuit breakers have minimal arcing (as there is nothing to ionize other than the contact material), so that the arc quenches when it is stretched by a small amount(<2-3 mm).Vacuum circuit breakers are frequently used in modern medium voltage switchgear to 35000 volts. Unlike the other types they are inherently unsuitable for interrupting DC faults. iv. Air Circuit breaker: Air circuit breaker may use compressed or the magnetic force of the earth itself to elongate the earth.as the length of the sustainable earth is dependent on the available voltage the elongated earth will eventually exhaust itself. Use: Basic use of switchgear is protection which is interruption of short circuit and overload fault currents while maintaining service to unaffected circuits. Switchgear also provides isolation of circuits from power supplies. Switchgear is also used to enhance system availability by allowing more than one source to feed a load. Specification of SF6 circuit breaker: Rated voltage: 6.6 kv, Rated pressure of SF6 3.4 barabs Rated current: 800A, Motor supply voltage: 220V/DC Rated frequency:50HZ Auxiliary circuit:220 V Rated peak making current:103 KV Trip/closed coil 220V/DC Rated breaking current:40 KA, Rated short time current for 3sec:40 KA Maker: NGEF in technical collaboration with ABB SPACE Italy.
6. Isolator: It is used for no load opening or closing of circuits. They can be
operated remotely by motorized, hydraulic, pneumatic mechanisms or manually. Isolators have their positional switches at their mechanism boxes for development of a set of contacts according to ON or OFF status of the isolators.
Uses of isolator: It provides electrical isolation of the equipment, bus bar and circuit from the live parts for maintenance purpose. It is using for transfer of load from one bus to another.
7. Earthing Switch: 8. Current Transformer: Current Transformer is a series connected
transformer having single bar primary several protection cores and one metering core of respective accuracy classes. The entire transformer element is kept in porcelain case with transformer oil in sealed condition and is pressurized by nitrogen for reducing corona. Design: Uses of Current Transformer: i. Ct are used for electronic meter whose VA are very less ii. It is used for units protection such as BUS Zone, differential protection. iii. CT are used extensively for measuring current and monitoring the operation of power grid. iv. Protection devices and revenue metering may use separate CTs to provide isolation between metering and protection circuits.
9. Potential Transformer: PT is parallel connected type of instrument
transformer used for metering and protection in high voltage circuits or phasor phase shift isolation. They are designed to present negligible load to the supply being measured and to have an accurate voltage ratio to enable accurate metering. PT has only one terminal that is input terminal. 10. Capacitive voltage transformer: It is combination of capacitive voltage divider and conventional EMVT measuring a reduced proportional voltage. As CVT consists of inductance in iron core and of capacitance, it would be subjected to ferro-resonance oscillations and transient phenomenon. Hence ferro resonance suppressor device is used. CVTs are used in EHV substation both as voltage transformer as well as coupling capacitor for power line carrier application. 11. Wave trap and PLCC: Wave trap is used in power line carrier communication
(PLCC). Since the power transmission lines physically go between substations, it is used to possible to use this metallic link as a communication link without dependence on the telecom company network. The signals are primarily protection signals and in
addition, voice and data communication signals. Wave trap traps the high frequency communication signals sent on the lines from the remote substation and diverting them to the PLCC panel in the substation control room through coupling capacitor. The wave trap opposes high impedance to the high frequency communication signals(150 kHz to 500 kHz),thus obstructs the flow of these signals into the substation bus bar whereas provides a path of negligible impedance to the power frequency (50 Hz) current to substation bus bar. The wave trap looks like a drum and installed by hanging from substation line site gantry structure and connected in series with the transmission line. A coupling capacitor is connected to wave trap in one end and other to PLCC equipment through a coupling device. It is erected below the line side truss on MS structure and connected to the wave trap by ACSR conductor. The coupling capacitor acts as high impedance to power frequency while provides a very low impedance to the carrier frequency.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Overview of SubstationDokumen38 halamanOverview of SubstationHarish Pamuru100% (1)
- Technical Subjective QuestionsDokumen52 halamanTechnical Subjective QuestionsEngr AHmed Ali DallBelum ada peringkat
- Electric CalDokumen20 halamanElectric CalRisky RiyanshBelum ada peringkat
- SubstationsDokumen34 halamanSubstationsBeen Carlo De JasminBelum ada peringkat
- SwitchgearDokumen23 halamanSwitchgearAnonymous Yq9ibs100% (1)
- How To Protect Transmission LinesDokumen15 halamanHow To Protect Transmission Linesneneng beeBelum ada peringkat
- Sub Station Training ReportDokumen26 halamanSub Station Training Reportprem080990% (10)
- CEA GuidelineDokumen25 halamanCEA GuidelinepussykhanBelum ada peringkat
- Autochangeover in Power PlantsDokumen18 halamanAutochangeover in Power PlantsSukant BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Generating Station Substation ComponentsDokumen30 halaman2 Generating Station Substation ComponentsFrancheskah DuqueBelum ada peringkat
- O & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba MieDokumen31 halamanO & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba MiewaleedalzaidiBelum ada peringkat
- 01 - Power System Protection-Basics and Breakers v2 (Revised) PDFDokumen55 halaman01 - Power System Protection-Basics and Breakers v2 (Revised) PDFJawwad Sadiq Ayon100% (1)
- Structure of PowerDokumen7 halamanStructure of Powerkala6006Belum ada peringkat
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDari EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityBelum ada peringkat
- 220 KV Sub-StationDokumen17 halaman220 KV Sub-StationJaat Pankaj BurraBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Protection: Power Transformers and Power AutotransformersDokumen29 halamanTransformer Protection: Power Transformers and Power Autotransformersmoham akhBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Insulated SubstationDokumen17 halamanGas Insulated Substationsurbhijain329100% (1)
- INDIAN ELECTRICITY RULES AND INDUSTRIAL SAFETY One Point E & C PDFDokumen5 halamanINDIAN ELECTRICITY RULES AND INDUSTRIAL SAFETY One Point E & C PDFHarshal VaidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Power TransmissionDokumen40 halamanElectrical Power TransmissionSonu Lovesforu100% (1)
- 11 KV Switchgear 31.5kaDokumen32 halaman11 KV Switchgear 31.5kaSyed Moiz NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- Sub-Stations: Departmental of Electrical EngineeringDokumen41 halamanSub-Stations: Departmental of Electrical EngineeringJAYESHBelum ada peringkat
- Kelvin LawDokumen6 halamanKelvin LawAbdul AlimBelum ada peringkat
- 400kv Sub - Station Final PPT by RAVIDokumen14 halaman400kv Sub - Station Final PPT by RAVIbanwala33% (3)
- 33KV Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technical SpecificationDokumen20 halaman33KV Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technical SpecificationUma KantBelum ada peringkat
- Power Transformer DesignDokumen13 halamanPower Transformer Designswiss22100% (1)
- Introduction to Electric Power TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTIONDokumen100 halamanIntroduction to Electric Power TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTIONUmair BeygBelum ada peringkat
- Visit 400kV Alamathy Substation and Learn About Its Design and FunctionsDokumen5 halamanVisit 400kV Alamathy Substation and Learn About Its Design and FunctionsJothi PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Designing of HV Power Substation and LayoutDokumen11 halamanDesigning of HV Power Substation and LayoutSuresh UmadiBelum ada peringkat
- Starting Methods of Induction MotorsDokumen8 halamanStarting Methods of Induction MotorsChathuranga Nagasinghe100% (1)
- Motor-Control Centers SpecificationsDokumen12 halamanMotor-Control Centers SpecificationsDolyBelum ada peringkat
- Protection of SubstationDokumen21 halamanProtection of SubstationARVIND100% (2)
- Sub StationDokumen33 halamanSub StationMohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Busbar TrunkDokumen16 halamanBusbar Trunkabhi_0302Belum ada peringkat
- Comparison Between Vacuum and SF6 Circuit BreakerDokumen9 halamanComparison Between Vacuum and SF6 Circuit BreakerMohammed MadiBelum ada peringkat
- 400 KV Metal Oxide Surge Arrestor CigreDokumen12 halaman400 KV Metal Oxide Surge Arrestor CigreDilip ARBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Breakers: Presented by Ajay.S 11EE02Dokumen28 halamanCircuit Breakers: Presented by Ajay.S 11EE02Ahmad Kalbounah0% (1)
- Bus BarDokumen8 halamanBus BarAnonymous QGHbz92u100% (1)
- Protect Electrical Equipment from Over VoltagesDokumen16 halamanProtect Electrical Equipment from Over VoltagesSweqZBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter6 PDFDokumen38 halamanChapter6 PDFJaved LakanwalBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4: Substation Equipment's Details and Operations: July 2021Dokumen14 halamanModule 4: Substation Equipment's Details and Operations: July 2021Gundeboyina GopiBelum ada peringkat
- Earthing Is AbstractDokumen3 halamanEarthing Is AbstractShrikant KajaleBelum ada peringkat
- Ee208 Chapter 2 TransformersDokumen15 halamanEe208 Chapter 2 TransformersTinozivasheBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Bus-Bar Arrangement TypesDokumen8 halamanElectrical Bus-Bar Arrangement TypesAmit DebnathBelum ada peringkat
- Midway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCDokumen15 halamanMidway Report: Project Semester: Study of 220KV Substation and SLDCdamanpreet singhBelum ada peringkat
- Auxiliary TransformerDokumen47 halamanAuxiliary TransformerVsrisai Chaitanya100% (1)
- 2-Contractors and RelaysDokumen13 halaman2-Contractors and RelaysMais AlsharifBelum ada peringkat
- Paper On Automatic Reclosing Transmission Lines Applications and Its ConsiderationsDokumen8 halamanPaper On Automatic Reclosing Transmission Lines Applications and Its ConsiderationsGagan GillBelum ada peringkat
- Bus Switching Configurations in Air Insulated Substations AISDokumen5 halamanBus Switching Configurations in Air Insulated Substations AISArnel Pascual LaquindanumBelum ada peringkat
- Power and Distribution Transformers Sizing Calculations - Part Nine Electrical KnowhowDokumen11 halamanPower and Distribution Transformers Sizing Calculations - Part Nine Electrical KnowhowRodel PelimianoBelum ada peringkat
- Instructor Engr. Muhammad YaseenDokumen33 halamanInstructor Engr. Muhammad Yaseenbedilu77Belum ada peringkat
- Evaluating Motor and Transformer Inrush CurrentsDokumen4 halamanEvaluating Motor and Transformer Inrush CurrentsMind of BeautyBelum ada peringkat
- Elec 5204 Review Quizzes AnsDokumen9 halamanElec 5204 Review Quizzes Ansveljal6317Belum ada peringkat
- Intoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationDokumen3 halamanIntoduction To 400Kv Switchyard: Single Line Diagram of 400kV SubstationPratik LahaneBelum ada peringkat
- Resistance Earthed Systems: Fault CurrentsDokumen25 halamanResistance Earthed Systems: Fault CurrentsRameez Ahmed100% (1)
- Power Cable SystemsDokumen35 halamanPower Cable SystemsMohd Muzani100% (1)
- Transmission Line Capacity CalculationDokumen11 halamanTransmission Line Capacity CalculationRajesh Pillai88% (16)
- Guide for protection engineers handbookDokumen347 halamanGuide for protection engineers handbookumamaheshwarraoBelum ada peringkat
- Bus and Line ProtectionDokumen26 halamanBus and Line ProtectionYugendran KumaravelBelum ada peringkat
- Switching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsDari EverandSwitching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculam Vitae: Carrier ObjectiveDokumen2 halamanCurriculam Vitae: Carrier ObjectivePritam SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- Bat Ko Thoda Round GhumakeDokumen1 halamanBat Ko Thoda Round GhumakePritam SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- University Holiday ListDokumen2 halamanUniversity Holiday ListPritam SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- To Draw Activity NetworkDokumen1 halamanTo Draw Activity NetworkPritam SamantaBelum ada peringkat
- 8장 마찰-reDokumen93 halaman8장 마찰-reAzad DuppalaBelum ada peringkat
- RAJIV RANJAN SINHA IP 09 SR No. 09Dokumen15 halamanRAJIV RANJAN SINHA IP 09 SR No. 09rajeev ranjanBelum ada peringkat
- Current Status of FPV and TrendsDokumen10 halamanCurrent Status of FPV and TrendsKaushik DasBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 8 Series and Parallel CircuitsDokumen18 halamanLesson 8 Series and Parallel Circuits23 ZACH Benjamin Isaac IV LabayenBelum ada peringkat
- ElectroMagnetic Field Theory+ExercisesDokumen302 halamanElectroMagnetic Field Theory+Exercisesrtobary6189100% (1)
- Use of Gas Tables Permitted, Assume Suitable Value For Missing DataDokumen2 halamanUse of Gas Tables Permitted, Assume Suitable Value For Missing DataVenkitaraj K PBelum ada peringkat
- Generator Write UpDokumen14 halamanGenerator Write UpJerome B. PioBelum ada peringkat
- Sinusoidal Pulse Width ModulationDokumen8 halamanSinusoidal Pulse Width Modulationabdurrahim_t100% (1)
- Lecture 8 Engine Cycles - OttoDokumen42 halamanLecture 8 Engine Cycles - OttoMuhammad AbubakarBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferDokumen6 halaman2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferShanel100% (1)
- Case Study of The Application in A Large Industrial FacilityDokumen10 halamanCase Study of The Application in A Large Industrial FacilityAndres VergaraBelum ada peringkat
- พอฤทัย วิริยะภาค26 3.5Dokumen2 halamanพอฤทัย วิริยะภาค26 3.55.6 25 [พิงค์แพรว]นางสาวพอฤทัย วิริยะภาคBelum ada peringkat
- NEPLAN Turbine-Governor ModelsDokumen99 halamanNEPLAN Turbine-Governor ModelsRatilal M Jadav100% (1)
- GENPHY2 - Lesson - Ohm's Law and ResistanceDokumen3 halamanGENPHY2 - Lesson - Ohm's Law and ResistanceJazmaine SimbulanBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Assigned For Term I (Theory) : Biology at EaseDokumen19 halamanSyllabus Assigned For Term I (Theory) : Biology at EaseDILSHAD AYJNISHDBelum ada peringkat
- 4.1. Interaction Light-Matter 2-7-08Dokumen10 halaman4.1. Interaction Light-Matter 2-7-08mladen lakicBelum ada peringkat
- 400A Diesel Welding MachineDokumen3 halaman400A Diesel Welding MachineSuristiono WidjayaBelum ada peringkat
- Conzerv Power Energy MetersDokumen3 halamanConzerv Power Energy MetersAtchayavelBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment: Atwood Machine: ObjectivesDokumen4 halamanExperiment: Atwood Machine: ObjectivessygexBelum ada peringkat
- Speed, Distance and Time CalculationsDokumen3 halamanSpeed, Distance and Time CalculationsSameer Ali MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Emi Unit 4Dokumen2 halamanEmi Unit 4Murali KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Coulomb's Law ExplainedDokumen22 halamanCoulomb's Law ExplainedJewel EmeraldBelum ada peringkat
- Rfic Unit IIDokumen36 halamanRfic Unit IIBlessina PreethiBelum ada peringkat
- PC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Dokumen1 halamanPC1144 Summary (Chapter 37-39)Khor Shi-JieBelum ada peringkat
- Infineon-Application Note Design of A 600 W HB LLC Converter Using CoolMOS - P6-AN-v01 - 00-ENDokumen42 halamanInfineon-Application Note Design of A 600 W HB LLC Converter Using CoolMOS - P6-AN-v01 - 00-ENигорь сидоренкоBelum ada peringkat
- MIT Subthreshold OperationDokumen29 halamanMIT Subthreshold Operationsanjeevsoni64Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Report 2Dokumen4 halamanLab Report 2Mohd Azman0% (1)
- Isc Three Terminal Negative Voltage Regulator: INCHANGE Semiconductor Product SpecificationDokumen2 halamanIsc Three Terminal Negative Voltage Regulator: INCHANGE Semiconductor Product SpecificationlisbanisBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICS Variance CalculationDokumen6 halamanPHYSICS Variance CalculationLorely DelgraBelum ada peringkat
- Marineflex Yzp 0,6/1 KV: Low Voltage Power Cables 16098Dokumen2 halamanMarineflex Yzp 0,6/1 KV: Low Voltage Power Cables 16098Javier EverestBelum ada peringkat