Instrumentation
Diunggah oleh
Red David BallesterosHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Instrumentation
Diunggah oleh
Red David BallesterosHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Instrumentation
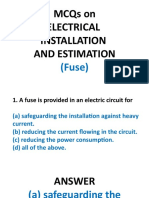
1. What is the degree of exactness of measurement when compared to the expected value of the variable being measured? A. Accuracy B. Error C. Deviation D. Precision 2. The art or process of determining the existence or knowing the magnitude of something, directly or indirectly in terms of a recognized standard. A. Measurement B. Testing C. Recording D. Evaluating 3. A procedure or sequence of operations for determining whether a component or equipment is functioning or working normally. A. Measurement B. Test C. Recording D. Evaluating 4. In measurement, what do you call the degree of exactness compared to the expected value of the variable being measured? A. precision B. accuracy C. sharpness D. correctness 5. A measure of consistency repeatability of measurements called A. precision B. accuracy C. sharpness D. correctness 6. Precision is also known as A. correctness B. accuracy or is C. sharpness D. reproducibility 7. In measurements, the sum of a set of numbers divided by the total number of pieces of data in the given set is called A. geometric mean B. algebraic mean C. arithmetic mean D. effective value 8. The deviation of a reading from the expected value A. accuracy B. precision C. error D. difference 9. Errors due to frictions of the meter movement, incorrect spring tension, improper calibration or faulty instruments: A. Observational errors B. Environmental errors C. Instrument errors D. Gross errors 10. When an instrument is subjected to harsh environments such as high temperature, strong magnetic, electrostatic or electromagnetic field, it may have detrimental effects and cause errors known as A. Observational errors B. Environmental errors C. Instrument errors D. Gross errors 11. Errors introduced by the observer or user. A. Observational errors B. Environmental errors C. Instrument errors D. Gross errors 12. Errors in analog meter reading due to your physical position with respect to the meter scale. A. parallax error B. angular error C. linear error D. deviation 13. What do you call the difference between any number within the set of numbers and the arithmetic mean of that set of numbers? A. parallax error B. angular error C. linear error D. deviation 14. An instrument or device having recognized permanent or stable value that is used as a reference. A. standard instrument/device B. reference instrument/device C. fixed instrument/device D. ideal instrument/device 15. The smallest change in a measured variable to which an instrument will respond. A. quantize value B. resolution C. minimum D. step size 16. A device or mechanism used to determine the value of a quantity under observation. A. measuring kit B. evaluator C. instrument D. sensor 17. What is the basic unit for measuring current flow? A. coulomb B. ampere C. atomic weight D. volt
18. An instrument used to detect and measure the presence of electrical current is generally called A. DArsonval meter B. electrodynamometer C. galvanometer D. potentiometer 19. What is movement? A. B. C. D. the common type of meter
24. Measurement of high dc-voltages usually done by using A. Electrostatic B. moving-coil C. dynamometer D. thermocouple
is
B. wattmeter C. watt-hour meter D. multi-meter 31. A device used to mechanically measure the output power of a motor. A. dynamometer B. Megger C. concentric-vane instrument D. radial-vane instrument 32. An indicating instrument whose movable coils rotate between two stationary coils, usually used as wattmeter. A. induction-type meter B. radial-vane instrument C. electrodynamometer D. concentric-vane instrument 33. Dynamometers are mostly used as A. voltmeter B. ammeter C. ohmmeter D. wattmeter 34. What damping method is generally used in dynamometers? A. spring B. fluid friction C. eddy-current damping D. air friction 35. Which dynamometer instrument uniform scale? A. voltmeter B. ammeter C. ohmmeter D. wattmeter has a
Fixed coil Farad DArsonval Digital
25. Measuring instrument that can be used only to measure voltages. A. electrostatic B. thermocouple C. dynamometer D. permanent-magnet moving-coil 26. This instrument measures temperatures by electric means, especially temperatures beyond the range of mercury thermometers. A. pyrometer B. electrostatic instrument C. moving-magnet instrument D. permanent-magnet moving-coil instrument 27. This instrument refers to that one, which measures the intensity of the radiation, received from any portion of the sky. A. megaohmmeter B. pyranometer C. Megger D. galvanometer 28. What is the normal indication on a megger (megohmmeter) when checking insulation? A. one B. infinity C. middle of scale D. zero 29. Resistance measuring instrument particularly used in determining the insulation resistance. A. megaohmmeter B. Megger C. galvanometer D. A or B are correct 30. An electrodynamic meter used measure power A. hook-on type voltmeter to
20. A permanent-magnet moving-coil instrument. A. induction instrument B. DArsonval meter movement C. moving-iron instrument D. moving-magnet instrument 21. An instrument which depends on current in one or more foxed-coils acting on one or more pieces of soft iron, at least one of which is movable. A. moving-magnet instrument B. moving-iron instrument C. DArsonval meter movement D. induction instrument 22. What is that device, which depends on the action of a movable permanent magnet, in aligning itself in the resultant field, produced either by a fixed permanent magnet and adjacent coil or coils carrying current, or by two or more current-carrying coils whose axes are displaced by a fixed angle? A. DArsonval meter movement B. induction instrument C. moving-magnet instrument D. moving-iron instrument 23. What ammeter is mostly used measuring high-frequency currents? A. electrostatic B. moving-coil C. dynamometer D. thermocouple in
36. For a dynamometer to be able to measure high current, a ________ should be used. A. shunt resistor B. multiplier C. CVDT D. current transformer 37. Error in voltmeter reading is due to A. insertion B. loading C. battery aging D. conversion
38. Error in ammeter reading id due to A. insertion B. loading C. battery aging D. conversion 39. Which type of meter requires its own power source? A. A voltmeter B. An ammeter C. An ohmmeter D. A wattmeter 40. Error in ohmmeter reading is due to A. insertion B. loading C. battery aging D. meter friction 41. Decreasing the value of the shunt resistor of an ammeter, its current measuring capability A. increases B. decreases C. remains constant D. none of the above 42. Increasing the value of the series resistor of a voltmeter, its voltage measuring capability A. increases B. decreases C. remains constant D. none of the above 43. A device that is used to measure current without opening the circuit A. megger test B. clamp probe C. ammeter D. multi-meter 44. Which of the ammeter below that has no insertion error? A. DArsonval meter B. clamp-meter C. micrometer D. meter with current transformer
45. To prevent damage of the multirange ammeter during selection, a/an _______ should be used. A. direct shunt B. selected shunt C. Ayrton shunt D. shunt fuse 46. For the greatest accuracy, what should be the input impedance of a VOM be? A. 1,000 ohms/V B. 50,000 ohms/V C. as large as possible D. as small as possible 47. Voltage impedance with A. B. C. D. measurement in a high circuit requires a voltmeter low input impedance high input impedance high voltage probe low voltage probe
current of 1.0 ampere, what is the value of the shunt resistor in ohms if the voltage across the meter is 9.0 volts? A. 9.0 B. 10 C. 900 D. 100 52. What is the purpose of the rheostat in ohmmeter? A. balancing resistance B. counter resistance of measured circuit C. coil resistance D. compensate aging battery of the meter 53. The zero-adjust control in an analog type ohmmeter is used to A. compensate for the differing internal battery voltage B. make sure the pointer is moving correctly C. align the infinity resistance position D. align the zero-voltage position 54. The scale of a hot wire instrument is a/an __________ function. A. linear B. squared C. log D. exponential 55. Moving iron instrument function that is A. log B. exponential C. linear D. squared have a scale
48. A meter has a full-scale current of 50A, what is its sensitivity? A. 20k/V B. 20V/ C. 50k/V D. 50A/V 49. If a meter with a full-scale current of 100A is used as an ac voltmeter with half-wave rectification, its ac sensitivity is A. 10,000 /V B. 4,500 /V C. 9,000 /V D. 100 /V 50. In order to make an accurate measurement as possible, the internal resistance of a voltmeter must be A. as high as possible B. as low as possible C. proportional to the voltage range D. proportional to the current range 51. An ammeter has a full-scale deflection current of 100mA. If the same ammeter is used to measure a full-scale
56. To increase the measuring capability of a moving-iron ac ammeter, a _______ should be used. A. shunt B. multiplier C. swamping resistors D. different number of turns of operating coil
57. Which electrical instruments below is the most sensitive? A. moving-iron B. dynamometer C. thermocouple D. PMMC 58. Basically, a PMMC instrument used only in A. ac measurements B. dc measurements C. rms measurements D. all of the above can be
64. What is(are) the force(s) acting on the pointer of an indicating instrument when it is in motion? A. controlling and deflecting torques B. damping and deflecting torques C. controlling and damping torques D. controlling, damping, deflecting torques 65. Material that is mostly used as pointer in indicating instruments. A. soft iron B. aluminum C. silver D. stainless a
and repulsion between electrically charged bodies? A. induction instrument B. electrostatic instrument C. moving-magnet instrument D. DArsonval meter movement 71. What do you call of an instrument that depends for its operation on the reaction between magnetic flux set up by currents in fixed windings and other currents set up by electromagnetic induction in movable conducting parts? A. induction instrument B. electrostatic instrument C. moving-magnet instrument D. DArsonval meter movement 72. A meter for its operation, it depends on a movable iron vane which aligns itself in the resultant field of a permanent magnet and an adjacent current carrying coil. A. induction instrument B. electrostatic instrument C. moving-magnet instrument D. permanent-magnet moving coil-instrument 73. What is the measuring instrument that uses the force of repulsion between fixed and movable magnetized iron vanes, or the force between a coil and a pivoted vane-shaped piece of soft iron to move the indicating pointer? A. pyrometer B. vane-type instrument C. electrostatic instrument D. moving-magnet instrument 74. Its an electrostatic voltmeter in which an assembly of figure 8 shaped metal plates rotates between the plates of a stationary assembly when a voltage is applied between the assemblies. The length of the arc of rotation is proportional to the electrostatic attraction and thus, to the applied voltage. A. varmeter B. variometer
59. Controlling torque in PMMC. A. spring action B. magnetic action C. electromagnetic action D. tension cable 60. What damping method is used induction type ammeters? A. air friction B. electrostatic damping C. fluid friction D. eddy current damping 61. Induction used as A. B. C. D. in
66. A Kelvin electrostatic voltmeter uses what method of damping? A. fluid friction B. spring action C. mechanical friction D. eddy-current damping 67. Shunts in meters should have _________ temperature coefficient resistance. A. positive B. negative C. very small D. very large a of
type instruments are mostly voltmeter ammeter wattmeter watt-hour meter
62. In indicating instruments, what will happen to the controlling torque if the deflection becomes greater? A. increases B. decreases C. remains unchanged D. drops to zero 63. The force(s) that is(are) acting on the pointer of an indicating instrument as it rest on its final deflected position. (Note: damping torque is 0). A. controlling torque B. deflecting torque C. damping torque D. A & B above
68. In a moving coil ammeter, a _________ is connected in series with the soil to compensate for temperature variations. A. limiting resistor B. shunt resistor C. multiplier D. swamping resistor 69. Where can A. B. C. D. we use the dynamometer? dc only ac only dc and ac peak measurement
70. What is the meter that depends for its operation on the forces of attraction
C. potentiometer D. Kelvin voltmeter 75. What is that instrument used for measuring the strength and direction of magnetic fields? A. varmeter B. potentiometer C. magnetometer D. Kelvin voltmeter 76. What do you call of that instrument used for measuring reactive power in vars? A. varmeter B. pyrometer C. reactive volt-ampere meter D. A or C is correct 77. What is this instrument or circuit that has four or more arms, by means of which one or more of the electrical constants of an unknown component may be measured? A. bridge B. Hazeltine circuit C. Loftin White circuit D. DArsonval meter movement 78. A four-arm bridge. Al arms of which are predominantly resistive; used for measuring resistance. A. bridge B. resistance bridge C. Wheatstone bridge D. B or C is correct 79. This is the method of using a Wheatstone bridge to determine the distance from the test point to a fault in a telephone or telegraph line or cable. A. Mesh B. Varley loop C. Batten system D. Cordonnier system 80. This refers to a four-arm ac bridge used for measuring inductance against a standard capacitance. A. Maxwell bridge B. slide-wire bridge
C. resistance bridge D. Wheatstone bridge 81. Refers to an ac bridge for measuring the inductance and Q of an inductor in terms of resistance, frequency and a standard capacitance. A. Hay bridge B. Maxwell bridge C. slide-wire bridge D. Wheatstone bridge 82. This is a special bridge for measuring very low resistance (0.1 or less). The arrangement of the bridge reduces the effects of contact resistance, which causes significant error when such low resistances are connected to conventional resistances bridges. A. Hay bridge B. Maxwell bridge C. Wheatstone bridge D. Kelvin double bridge 83. A type of four-arm capacitance bridge in which the unknown capacitance is compared with a standard capacitance. This bridge is frequently employed in testing electrolytic capacitors, to which a dc polarizing voltage is applied during the measurement. What is this bridge? A. Hay bridge B. Maxwell bridge C. Schering bridge D. Wheatstone bridge 84. What do you call of that frequencysensitive bridge in which two adjacent arms are resistances and the other two arms are RC combinations? A. Hay bridge B. Wein bridge C. Maxwell bridge D. Schering bridge 85. When the capacitors of a Wein bridge are replaced by inductors, the bridge becomes A. Wein-bridge filter B. variometer C. Schering bridge
D. Wein inductance bridge 86. A simplified version of the Wheatstone bridge wherein, two of the ratio arms are replaced by a 100 cm long Manganin of uniform cross-sections and provided with a slider. A. Hay bridge B. Schering bridge C. slide-wire bridge D. Wein inductance bridge 87. Bridge used to measure both inductive and capacitive impedances at higher frequencies. A. Hay bridge B. Schering bridge C. Wein bridge D. radio-frequency bridge 88. A bridge wherein all electrically identical A. balance bridge B. balance circuit C. balance line D. all of the above legs are
89. Comparison between dc and ac measuring instruments A. generally, ac instruments are less sensitive than dc instruments B. errors such as induced emfs, frequency variations, and harmonic-current components are only present in ac instruments C. in ac instruments, higher value of current is needed than in dc instruments to produce the same deflection D. all of these are correct 90. What is an electronic instrument capable of showing on screen and maybe on print, relative spacing of transmitter carriers, their sidebands and harmonics? A. Counters B. Spectrum analyzer C. Triggered oscilloscope D. Multimeter
91. An instrument capable of displaying simultaneously the amplitude of signals having different frequencies. A. oscilloscope B. spectrum analyzer C. VTVM D. Logic analyzer 92. Spectrum analyzer is A. a real-time analyzer B. a non-real time analyzer C. the same as a wave analyzer in all aspects D. an instrument not dependent on frequency 93. Indications of spectrum presented by means of A. a moving meter B. an iron vane C. a CRT D. a LED analyzer is
signals having frequencies beyond its normal capabilities? A. sampling oscilloscope B. digital storage oscilloscope C. storage oscilloscope D. delayed sweep oscilloscope 98. Generally, oscilloscope uses what type of deflection? A. magnetic deflection B. electromagnetic deflection C. static deflection D. electrostatic deflection 99. A device or instrument, which delivers signals of pre3cise frequency and amplitude, usually over a wide range. A. synthesizer B. frequency generators C. signal generators D. modulators 100. The two most common audio oscillators are A. Wein bridge and Colpitts B. Wein bridge and phase-shift C. Colpitts and Hartley D. Hartley and phase-shift 101. What are the two most popular RF oscillators A. Wein bridge and Colpitts B. Wein bridge and phase-shift C. Colpitts and Hartley D. Hartley and phase-shift 102. A device or instrument able to generate noise with accurate voltage for test purposes. A. signal generator B. synthesizer C. frequency generator D. noise generator 103. When do you need a noise generator? A. When starting an oscillators B. When evaluating noise performance of an oscillator C. When evaluating noise characteristics of an amplifier
D. When performing analysis
modulation
104. In RF or microwave system, what instrument is used to measure the incidental and reflected signals. A. oscilloscope B. reflectometer C. incident-wave meter D. spectrum analyzer 105. A type of photometer used to measure reflection. A. photodiode B. reflectometer C. incident-wave meter D. LED 106. A tunable RF instrument, which, by means of a sharp dip of an indicating meter, indicates resonance with an external circuit under test. A. reflectometer B. inclinometer C. dip meter D. Grid-dip meter 107. A type of dip meter employing a vacuum tube oscillator, whose indicating dc microammeter is in the grid circuit. A. reflectometer B. inclinometer C. dip meter D. Grid-dip meter 108. In meter movement, how do you prevent the meter from oscillation and overswing? A. by shorting B. by coupling C. by swamping D. by damping 109. When the meter is insufficiently damped, it is considered as A. underdamped B. overdamped C. critically damped D. negatively damped 110. A meter when _______ damped will become insensitive to small signals.
94. An electronic measuring device that provide instantaneous visual indication of voltage excursions. A. voltmeter B. power meter C. oscilloscope D. power line meter 95. An instrument that is capable displaying waveforms by means fluorescence in a CRT. A. oscilloscope B. wave analyzer C. spectrum analyzer D. distortion analyzer of of
96. Types of oscilloscopes that are able retain the display for a longer period for analysis. The display is retained by the use of flood gun. A. sampling oscilloscope B. digital storage oscilloscope C. storage oscilloscope D. delayed sweep oscilloscope 97. What do call an oscilloscope that uses sampling technique in processing
A. B. C. D.
underdamped overdamped critically damped negatively damped
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Measurement-And-Instrumentation Solved MCQs (Set-1)Dokumen8 halamanMeasurement-And-Instrumentation Solved MCQs (Set-1)imran pervezBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical InstrumentationDokumen12 halamanElectrical Instrumentationबृजभूषणशर्माBelum ada peringkat
- InstrumentationDokumen18 halamanInstrumentationSreejith VaneryBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1Dokumen4 halamanElectronic Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments Mcq-1chetanaBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Digital Instruments PDFDokumen10 halamanPrinciples of Digital Instruments PDFÖmKârGhorpadeBelum ada peringkat
- M&I Two Marks With Answer-All UnitsDokumen16 halamanM&I Two Marks With Answer-All UnitsVijay KM83% (6)
- MCQ Son Power ElectronicsDokumen2 halamanMCQ Son Power ElectronicsNoor AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature Gauge Calibration PDFDokumen14 halamanTemperature Gauge Calibration PDFAlaa RamadanBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Ej/En/Eq/Et/Ex 22425 Consumer Electronics (Cel) McqsDokumen30 halamanDepartment of Ej/En/Eq/Et/Ex 22425 Consumer Electronics (Cel) McqsSaquibh ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Set 6Dokumen14 halamanSet 6Pritamjit RoutBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Which of The Following Is Not Covered Under Mechanical Energy Domain?Dokumen6 halaman1-Which of The Following Is Not Covered Under Mechanical Energy Domain?pradnya sadigaleBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement Instrumentation Objective Questions Answers 01Dokumen2 halamanMeasurement Instrumentation Objective Questions Answers 01Vinayan K PBelum ada peringkat
- This Set of Instrumentation Transducers Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen18 halamanThis Set of Instrumentation Transducers Multiple Choice QuestionsJomalyn Fernando Bueser67% (6)
- Measurement and Instrumentation MCQ QNSDokumen70 halamanMeasurement and Instrumentation MCQ QNSnongdambaBelum ada peringkat
- 1040c Training2 Calibrating Meters TransducersDokumen32 halaman1040c Training2 Calibrating Meters TransducersAries dBelum ada peringkat
- MM All Units MCQDokumen38 halamanMM All Units MCQkrishnabr100% (2)
- Electrical Machines MCQDokumen13 halamanElectrical Machines MCQmahesh.m.pBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Engineering Nts Mcqs For Jobs in PakistanDokumen15 halamanElectrical Engineering Nts Mcqs For Jobs in PakistanDanish IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement and Instrumentation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDF - Preparation For EngineeringDokumen14 halamanMeasurement and Instrumentation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDF - Preparation For EngineeringMahesh sBelum ada peringkat
- Analog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsDokumen13 halamanAnalog, Digital and Power Electronics 100 Important MCQsHamdam NazarovBelum ada peringkat
- 110 TOP MOST Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions PDFDokumen34 halaman110 TOP MOST Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions PDFSIVAKAMI80% (5)
- Electrical and Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and Answers PDFDokumen4 halamanElectrical and Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and Answers PDFRameshAithagoinaBelum ada peringkat
- Engg Multiple Choice Questions - Instruments and MeasurementDokumen21 halamanEngg Multiple Choice Questions - Instruments and MeasurementVishwanath Brungi100% (1)
- 300+ TOP ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION Objective Questions and Answers PDFDokumen10 halaman300+ TOP ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION Objective Questions and Answers PDFC PazhanimuthuBelum ada peringkat
- Te Unit-2 MCQ PDFDokumen10 halamanTe Unit-2 MCQ PDFRajBelum ada peringkat
- 40 Top Circuit Theorems and Conversions Questions and Answers PDFDokumen3 halaman40 Top Circuit Theorems and Conversions Questions and Answers PDFsayedBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Electrical Installation and EstimationDokumen22 halamanMCQ Electrical Installation and Estimationdinesh majumdarBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Interview Question PDFDokumen22 halamanElectrical Interview Question PDFGopi Srikanth VegiBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Questions HVEDokumen6 halamanMCQ Questions HVEKokila ChezianBelum ada peringkat
- Last Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics KTC-1Dokumen7 halamanLast Area Day 8 - Basic Electronics KTC-1ellajanepoBelum ada peringkat
- Signal Multiplier Icc312Dokumen2 halamanSignal Multiplier Icc312supermannonBelum ada peringkat
- Emi MCQDokumen27 halamanEmi MCQgautam100% (3)
- Industrial Drives McqsDokumen19 halamanIndustrial Drives McqsBurning Sun100% (2)
- Electrical Traction - Mainte, Esti PDFDokumen33 halamanElectrical Traction - Mainte, Esti PDFSAPNA PAWARBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Engineering Questions-3Dokumen1 halamanElectrical Engineering Questions-3tutulkarBelum ada peringkat
- 100 TOP MOST Electrical Engineering MaterialsDokumen17 halaman100 TOP MOST Electrical Engineering MaterialsPrateek DevBelum ada peringkat
- Instruments and Measurement MCQsDokumen12 halamanInstruments and Measurement MCQsAshesh Tiwari50% (2)
- Objective QuestionsDokumen26 halamanObjective QuestionsAbid GandapurBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSDUCERS QUIZ ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION Practice Tests Objective Tests Free Download Many Online Tests Exams For India ExamsDokumen9 halamanTRANSDUCERS QUIZ ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION Practice Tests Objective Tests Free Download Many Online Tests Exams For India Examshemavathi114071Belum ada peringkat
- MCQsDokumen29 halamanMCQsSuhaib QaisarBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ in AC Generators Part 3 REE Board ExamDokumen21 halamanMCQ in AC Generators Part 3 REE Board ExamManuel DizonBelum ada peringkat
- 11 - 135 TOP Transformers - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDokumen15 halaman11 - 135 TOP Transformers - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsHussam Gujjar100% (2)
- Analog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFDokumen10 halamanAnalog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFPalani CBelum ada peringkat
- Questions & Answers On Motor Control by Static Power ConvertersDokumen12 halamanQuestions & Answers On Motor Control by Static Power Converterskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- 5069 User ManualDokumen8 halaman5069 User ManualSaranga JayawardanaBelum ada peringkat
- Nescom TestDokumen1 halamanNescom TestGreen SignalBelum ada peringkat
- 160 Instruments and Measurements Mcqs With AnswersDokumen19 halaman160 Instruments and Measurements Mcqs With AnswersRakeshKrBelum ada peringkat
- ES 521 Engineering Management Part 2 PDFDokumen18 halamanES 521 Engineering Management Part 2 PDFJulison ManawataoBelum ada peringkat
- Mcqs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDokumen11 halamanMcqs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsHussam Gujjar100% (1)
- MCQDokumen23 halamanMCQnandhakumarme100% (1)
- Engr. Muhammad Shafique: B) Maxwell's EquationDokumen11 halamanEngr. Muhammad Shafique: B) Maxwell's EquationAbid GandapurBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Measurements and InstrumentationDokumen47 halamanMCQ Measurements and Instrumentationeee2014.rvsBelum ada peringkat
- Heat SinkDokumen15 halamanHeat Sinknitin chauhanBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ in Philippine Electrical Code PEC Part 5 REE Board ExamDokumen19 halamanMCQ in Philippine Electrical Code PEC Part 5 REE Board ExamManuel DizonBelum ada peringkat
- ECE ReviewerDokumen17 halamanECE ReviewerKristine AbanadorBelum ada peringkat
- Group Study - Instrumentation QuestionnaireDokumen7 halamanGroup Study - Instrumentation QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoBelum ada peringkat
- Test and MeasurementsDokumen16 halamanTest and MeasurementsKimberly TaboraBelum ada peringkat
- PINOYBIX Tests and MeasurementsDokumen20 halamanPINOYBIX Tests and MeasurementsRogelio Tacugue MahilumBelum ada peringkat
- CRKT Breaker and Instruments 1Dokumen15 halamanCRKT Breaker and Instruments 1Lovely Joy MoloBelum ada peringkat
- Stem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11Dari EverandStem: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V11Belum ada peringkat
- 6 STD B31v1 - 6 E2Dokumen173 halaman6 STD B31v1 - 6 E2Giovanni SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Section 3Dokumen44 halaman4 Section 3mostafatiefa100% (1)
- Untitled 1Dokumen3 halamanUntitled 1Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- ECT SyllabusDokumen1 halamanECT SyllabusMaykel Mapute MonsendoBelum ada peringkat
- Card Main FIRSTDokumen1 halamanCard Main FIRSTjhmarques3Belum ada peringkat
- NxLink Technical Instruction ManualDokumen26 halamanNxLink Technical Instruction ManualRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Excel Review Center Solutions To Take Home Exam - Analytic Geometry 1Dokumen5 halamanExcel Review Center Solutions To Take Home Exam - Analytic Geometry 1Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Boylestad Terms and DefinitionsDokumen4 halamanBoylestad Terms and DefinitionsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4Dokumen84 halamanWeek 4Gustavo OrtizBelum ada peringkat
- Complaint Lost Affidavit-NTCDokumen1 halamanComplaint Lost Affidavit-NTCPeter John LabisBelum ada peringkat
- 1 3Dokumen9 halaman1 3buzz20090Belum ada peringkat
- Derivatives Chapter1Dokumen46 halamanDerivatives Chapter1Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- May 2013 CPA Top 10Dokumen1 halamanMay 2013 CPA Top 10abam1092Belum ada peringkat
- Resonant CircuitsDokumen51 halamanResonant CircuitsHaris Bin KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Oscillators and MultivibratorsDokumen2 halamanOscillators and MultivibratorsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- PC Gilmore Desktop Packages: PCG Office Package PCG Home PackageDokumen1 halamanPC Gilmore Desktop Packages: PCG Office Package PCG Home PackageMadelline Joy RitaritaBelum ada peringkat
- DC Electrical CircuitsDokumen4 halamanDC Electrical CircuitsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Electricity FundamentalsDokumen8 halamanElectricity FundamentalsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Devices (FET)Dokumen4 halamanSolid State Devices (FET)Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- R A 9292 PDFDokumen18 halamanR A 9292 PDFDaryl Langamon Uy CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State Devices (Diode)Dokumen10 halamanSolid State Devices (Diode)Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- AmplifiersDokumen4 halamanAmplifiersRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Battery, Electrical Machines and Power SupplyDokumen14 halamanBattery, Electrical Machines and Power SupplyRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetism FundamentalsDokumen6 halamanMagnetism FundamentalsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Noise Reduction SystemsDokumen4 halamanNoise Reduction SystemsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- ColorsDokumen5 halamanColorsRed David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Home Owners Meeting2Dokumen8 halamanHome Owners Meeting2Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Expenses Template 8.23.2012Dokumen38 halamanExpenses Template 8.23.2012Red David BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Omega Navigation System: Operating Frequency: VLF 10 To 14 KHZDokumen15 halamanOmega Navigation System: Operating Frequency: VLF 10 To 14 KHZRed David Ballesteros67% (3)
- Telnet TNA820A20 170801 EN PDFDokumen3 halamanTelnet TNA820A20 170801 EN PDFangicarBelum ada peringkat
- MSE310-2016 Lecture Notes 3.0-3.1.5 (Student) PDFDokumen63 halamanMSE310-2016 Lecture Notes 3.0-3.1.5 (Student) PDFRanaBelum ada peringkat
- Miyachi - MA-627 Program Box ManualDokumen16 halamanMiyachi - MA-627 Program Box ManualcnmengineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Arduino Based Third Eye For Blind PeopleDokumen7 halamanArduino Based Third Eye For Blind PeopleIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Eye Project - Antony JoyDokumen14 halamanElectronic Eye Project - Antony JoyratheeshbrBelum ada peringkat
- Guardmaster® Safedge™ Pressure Sensitive Safety Edge System Installation and User Manual 440FDokumen24 halamanGuardmaster® Safedge™ Pressure Sensitive Safety Edge System Installation and User Manual 440Fsuresh putBelum ada peringkat
- Tm170tig PVCDokumen9 halamanTm170tig PVCAndrea MorsianiBelum ada peringkat
- MT-028 Tutorial: Voltage-to-Frequency ConvertersDokumen7 halamanMT-028 Tutorial: Voltage-to-Frequency ConvertersShobanraj LetchumananBelum ada peringkat
- QSK45 Wiring Diagram (Tier 1, Phase 2.0 With CENSE)Dokumen2 halamanQSK45 Wiring Diagram (Tier 1, Phase 2.0 With CENSE)987226146100% (4)
- Magic TeeDokumen3 halamanMagic TeeRaghil SotoyBelum ada peringkat
- V3000Dokumen8 halamanV3000ranaway1Belum ada peringkat
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDokumen25 halamanG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- 48 Volt Battery ChargerDokumen5 halaman48 Volt Battery ChargerpradeeepgargBelum ada peringkat
- Appleton LED Luminaires Selection Guide: NEC/CEC Hazardous LocationDokumen2 halamanAppleton LED Luminaires Selection Guide: NEC/CEC Hazardous LocationDhrubajyoti BoraBelum ada peringkat
- LRB120-3 DatasheetDokumen2 halamanLRB120-3 DatasheetMatheus PadilhaBelum ada peringkat
- Current Mode Controller Design For Single Phase Grid Connected Inverter Using Proportional Resonant Control StrategyDokumen6 halamanCurrent Mode Controller Design For Single Phase Grid Connected Inverter Using Proportional Resonant Control StrategyijeteeditorBelum ada peringkat
- Nidek YC-1600 Service ManualDokumen111 halamanNidek YC-1600 Service Manualqwertyu100% (2)
- Manual For Promovec Display LCDDokumen12 halamanManual For Promovec Display LCDJason LeBelum ada peringkat
- 2.introduction Sensors TransducerDokumen15 halaman2.introduction Sensors TransducerRaunaq SinghBelum ada peringkat
- TL084 - Nte859Dokumen3 halamanTL084 - Nte859nollcaton7685Belum ada peringkat
- FP06P Data Sheet: FP06P-S1-04-32-NU-V-77A-110A-M-30Dokumen1 halamanFP06P Data Sheet: FP06P-S1-04-32-NU-V-77A-110A-M-30Ainayya alfatimahBelum ada peringkat
- 95FL - Válvula Control Proporcional (Bridada)Dokumen13 halaman95FL - Válvula Control Proporcional (Bridada)Rafael SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- PLCDokumen56 halamanPLCFelix Lee Kah NgieBelum ada peringkat
- Control Solenid Main Mod Control Circuit High P0963Dokumen4 halamanControl Solenid Main Mod Control Circuit High P0963Christian Ramos Alarcon100% (1)
- WPS-Nozzle With Reinforcement Pad (CS-CS) .Dokumen1 halamanWPS-Nozzle With Reinforcement Pad (CS-CS) .suria qaqcBelum ada peringkat
- ZS Chart - 090315 - Final PDFDokumen2 halamanZS Chart - 090315 - Final PDFRajendra Prasad ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- References Leca+Philip Stretchable 50376-2017-Philippe-UnlockedDokumen21 halamanReferences Leca+Philip Stretchable 50376-2017-Philippe-Unlockedck maitiBelum ada peringkat
- G130 - GENIE C14 MicrocontrollerDokumen1 halamanG130 - GENIE C14 MicrocontrollerAsseel FleihanBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure - ASKA Mobile Light Tower - V5Dokumen8 halamanBrochure - ASKA Mobile Light Tower - V5cool.boys4200Belum ada peringkat