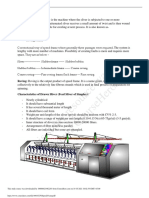
Ring Spinning Machine
Diunggah oleh
Pradip GuptaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ring Spinning Machine
Diunggah oleh
Pradip GuptaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Ring spinning Machine
The ring spinning machine was first invented in 1828 by the American Thorp. In 1830, another American scientist, Jenk, contributed the traveler rotating on the ring. There have been many development has done in ring spinning machine for the last years but the basic concept remained unchanged.
Some other modern spinning systems:
a) b) c) d) Open end rotor spinning system Air Jet spinning system Friction spinning system Wrap spinning system
Advantage of Ring spinning system:
i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Any type of material (fibre) can be spun Wide range of count can be processed It delivers a yarn with optimum characteristics. Idealized twisting system It is uncomplicated and easy to operate Higher yarn strength can be achieved
Disadvantages:
i) ii) Low production Machine generates more heat
Limitations: In ring spinning machine twisting and winding are done simultaneously.
Thats why the power consumption is higher.
Major manufacturer of ring frame:
a) b) c) d) e) Lakshmi Machinery Works Limited, India Toyoda Textile Machinery , Japan Rieter Machine Works Limited, Switzerland Suessen Gmbh, Germany China Textile Machinery Group co. Limited, china
Operations involved in ring frame:
i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi) Creeling Drafting Twisting Winding Building Doffing
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Function of ring frame:
a) Draft the roving until the required fineness is achieved b) Twist the drafted strand to form yarn of required count and strength c) Winding the twisted yarn on to the bobbin for suitable storage, transportation and further processing.
Drafting system:
A) Regular drafting without apron- i) Conventional 3 over 3 drafting system ii) Improved drafting system B) Apron drafting i) Single Apron- a. Saco Lowel Drafting b. Improved system ii) Double apron- a. Casablancas drafting system b. SKF drafting system
Some important models of SKF drafting system:
SKF PK-211 SKF PK-220 SKF PK-225 SKF PK-235 SKF PK-255 SKF PK-265 SKF PK-2025
Types of drafting system: There are commonly two types of drafting system are used
in ring frame: 1) Spring loaded drafting system or Pendulum arm. example: SKF PK 2025 or Texparts 2035 2) Pneumatic drafting system: SKF PK 3025
Difference between pneumatic and pendulum arm drafting system:
Pneumatic drafting system 1. Loaded by pneumatic pressure i.e. compressed air 2. Uniform pressure is applied to all drafting rollers 3. Consistent yarn quality is achieved 4. Modern drafting system Pendulum arm 1. Loaded by spring 2. Applied pressure in all drafting zones is not uniform 3. Consistent yarn quality is not achieved 4. conventional system
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Various components of Ring Frame
Thread guide:
It is a yarn guide made by bending a wire named snail wire. Snail wire may be different in types like p-shaped wire Functions: a) Its main function is to guide the yarn thus maintain the security of the yarn. b) It prevents yarn collision with adjacent yarns. c) It surface should be smooth to prevent rubbing of yarn. Rubbing creates yarn hairiness. Spindle: The spindle is the main part of a ring frame which helps in twisting, winding simultaneously. Sometimes, spindle referred as heart of spinning. It hold the bobbin, somewhat loosely but tight enough to prevent slippage.
Functions of spindle: a) Twisting and winding is performed by spindle. b) It holds the bobbin. c) The capacity of ring frame is mainly determine by the number of spindle.
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Different parts of spindle: The parts of spindle are given below: Spindle blade Wharve Bolster Lock Bearing Bolster cage The last three parts help the spindle to fix at the right place and work properly. Ring: The ring are made of low carbon steel i.e. soft steel or ceramic in the form of a bar which modeled into ring shaped either by bending and welding or by pressing by means of dies and then the stock is given the desired projection term as ring flange. Function: There are some important functions of ring. These are given below:a) Ring guides the circular run of the traveler. b) It also helps in twisting by means of running of the traveler. c) It also acts as a track of traveler.
Figure: Ring cups
Classification of ring: A) According to origin or element:- i. Metallic ring ii. Ceramic ring B) According to number of flange:- i. Single flange ring
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
ii. Double flange ring Relation between bobbin dia and Ring dia: B= 0.39R Where B= Bear bobbin dia and R= Ring dia. Flange: The path of traveler on the ring is called flange. It may be single or double. Flange width: The term flange width express the difference the outer diameter and inner diameter of a ring. Flange width is expressed in flange no. Flange width= (Flange no. + 3)/32 inch Flange no. 1 1.5 2 Flange width (mm) 3.2 3.6 4
Traveller: Traveler is the most tinny and simple mechanical element in ring frame which carries the most important function like simultaneous twisting, winding, thread guide etc. Function of traveller:- Traveller does some important in ring frame. These are mentioned below:a) Twisting on the drafted strand of fibre. b) Winding of the yarn on the bobbin. c) Maintain winding tension of the yarn by the frictional resistance between the ring and the traveler. d) It acts as a guide for yarn on the way to be wound on the bobbin.
Figure: Travellers
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Traveler speed and its effects: Traveller does not have a drive of its own. It drags
along behind the spindle. Since the spindle rotates at a high speed, a high contact pressure is generated between the ring and traveler during winding, mainly due to centrifugal force. The pressure introduces strong frictional forces which in turn lead to significant generation of heat. It is the important problem of ring/traveler. The front roller delivers a certain length of yarn. Thats why length wound up must corresponds to the difference in peripheral speed of traveler and spindle. The speed difference is due to lagging of the traveler relative to the spindle. Parts of traveller: There are three parts of a traveller. They are given below: Bow Horn Flange Type of traveller: Travelers can be classified into following two ways:A) According to shape: C traveller Elliptical traveller B) According to the X-section of wire: Round traveller Flat traveller Semi-circular traveller
Specification of traveller: A ring traveler is specified by the followingsa) b) c) d) Traveller no.: 1, 2, 3, 1/0, 2/0, 3/0 etc. Cross section of the wire and shape Flange no. Surface finish- Stainless steel made, Carbon finish, Nicle finish etc. e) Type of materials etc. Notation of traveller: A traveller can be notified as follows3/0 MS/hF 5/0 MS/FF 7/0 HI-NI/ hf Here, 3/0- Traveller number MS- Mild steel Hf- Half flange FF- Full flange HI-NI- High Nicle Finish
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Traveller Number or size of traveller: Here, if the weight of 10 traveller is 10
grains then the number of those traveller is 1 and so on. Recommended traveler no. for various yarn counts: Count (Ne) 16 20 30 40 50 60 80 100 Traveller No. 2 1-2/0 3/0-4/0 6/0-8/0 10/0-12/0 13/0-15/0 16/0-19/0 19/0-20/0
Force acting on traveler:
i) ii) iii) iv) v) Apron: Rubber Apron is made of synthetic rubber material, with excellent wearresistance/oil-resistance/ageing-resistance and smooth surface. In addition, it is of good stability, flexibility & wide application. It is used in drafting system of ring frame and some other modern drafting system in spinning machine. It contains cradle for guiding its direction of length. Traveller weight Frictional force between ring and traveler Centrifugal force Balloon tension Winding tension
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Figure: Rubber apron Rubber cot: It is one type of synthetic rubber material which is used in top rollers of ring frame drafting system. The rubber cots also used on drawing frames, combing machines & spinning frames. Its hardness can be varied. The hardness of rubber cots is expressed by degree. Generally harder cots are used in the back rollers and softer rollers are used in front rollers. Hardness ranges are given belowSoft: 60 to 70 Shore Medium: 70 to 90 shore Hard: above 90 shore 80 to 85 shore are mostly used at the back roller and 63 to 65 shore at front roller.
Figure: Rubber cots
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Yarn realization: It is the term used to denote the percentage of yarn produced from given weight of raw cotton. It depends on waste extraction. Yarn realization% = (92-Z), for carded yarn = (95-Z)(1-C/100)-3, for combed yarn Where, Z = trash extracted (%) in process stages C= comber noil%
Factors considered for selection of a traveler:
a) Yarn count: Higher the yarn count, lower will be the traveler weight. b) Spindle Speed: If the spindle speed is high, then the yarn tension will be high. So lighter traveler should be used to minimize tension. c) Ring dia: For same spindle speed and count, with the increase of ring diameter yarn tension as well as frictional area increases. So traveler should be lighter. d) Empty bobbin dia: When empty bobbin dia decreases, winding angle decreases resulting a higher yarn tension. So a light traveler should be used. e) Lift of bobbin: If the lift of bobbin increases yarn tension will be higher. So traveler weight should be less. f) Cross section of traveler: We know, if frictional area increases, lighter traveler should be light. For flat frictional area increases, traveler weight decreases. For semi circular, frictional area decreases, traveler weight increases. For circular, frictional area decreases, traveler weight increases.
Some important information:
1. 2. 3. 4. Usually used ring diameter: 33, 36, 38, 40, 42, 45 mm Ring cup diameter: Empty bobbin dia. = 2:1 or 2.5:1 bobbin length = 5 x Ring Diameter Bobbin lift = Bobbin length 20mm
Draft ranges in ring spinning: Higher draft usually causes the reduction in yarn
quality. The following draft limits have been established for practical. Carded yarn (Cotton) : up to 35 Carded blended: up to 40 Combed cotton and blended yarns Of medium fineness: up to 40 Of fine yarn: up to 45 Synthetic fibres: up to 45 (~50).
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Break draft: Total draft of a ring frame is limited. Since the main draft should not exceed its limit, a additional draft is implied in the back zone (between back and middle roller). This draft facilitates the main draft and known as break draft. Normally twisted roving and total drafts up to 40: break draft should be 1.1-1.4 Strongly twisted roving: break draft should be 1.3-1.5 When total draft exceeds 40, break draft: 1.4-2.
Recent development of ring frame:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. Improved drafting system Higher no. of spindle (up to 1008) Auto doffing Auto piecing Higher draft range (more than 100) Grooved T-in cylinder Inverter motor device Gearing in oil bath Tangential belt drive Data collection system (Ring Data) Roving stop motion etc.
Count and TM:
Count (Ne) Woven yarn 10-20 20-40 40-60 60-80 Above 80 Knitted Yarn: TM (Twist Multiplier) 4.6-4.8 4.4-4.6 4.2-4.4 3.8-4.2 3.6-3.7 3.6-3.8 (generally)
We know, TPI = TM count (for indirect system) TPM = TM/count (for direct system)
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Yarn manufacturing-II with lab
Why actual production always less then calculated production:
Reasons are: 1. Electrical and mechanical problem 2. Creeling problem 3. Roving breakage 4. Doffing problem 5. Piecing problem 6. Power failure 7. Worker negligence etc.
Different types of wastages of spinning mill:
There are various types of wastages which are found in spinning mill during the processing of raw cotton. About 12-13% wastages are produced for card process and 2530% wastage are produced for combed process. The names of different wastages are given below: 1. Blow room (waste= 3%) i. Dropings-2 ii. Lap waste etc. 2. Carding (waste= 4%) i. Dropings-1 ii. Sliver waste iii. Vacuum waste 3. Draw frame (waste= 0.5%)i. sliver waste 4. Lap former (waste=0.5%) i. lap waste ii. Sliver waste iii. Vacuum waste 5. Comber (waste= 12-18%) i. Noils ii. lap waste iii. Sliver waste 6. Simplex (waste= 0.5%) i. Roving waste ii. Sliver waste 7. Ring Frame (waste= 2-3%) i. Pneumafil ii. Hard waste ii. Sweeping iv. Vacuum waste 8. Winding section(waste=1%) i. Hard waste
Break in / running in: If we use metal ring we cannot go to the production directly. To
make the ring ready for production its surface should must be smooth and for this reason we have to run the machine and change the traveler in interval of time. The initial running of traveler on ring to make it smooth is called break in or running in.
Prepared by: Alamgir Hossain, Lecturer, Dept. of TE, DIU
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ring Spinning MachineDokumen55 halamanRing Spinning MachineAyaz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Vortex Spinning 2Dokumen6 halamanVortex Spinning 2Salome KyatuheireBelum ada peringkat
- Draw FrameDokumen50 halamanDraw FrameDev Narayan KushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn-1, Report On Mill VisitDokumen11 halamanYarn-1, Report On Mill VisitBoier Sesh Pata100% (2)
- Textile Technology Internship ReportDokumen24 halamanTextile Technology Internship Reportgunashekarkalluri100% (1)
- Practical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningDokumen5 halamanPractical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningTalha saeedBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn AssignmentDokumen10 halamanYarn AssignmentHIMASHA SAMARANAYAKABelum ada peringkat
- Rotor PrincipleDokumen12 halamanRotor PrincipleAnkit Balotia100% (1)
- Friction SpinningDokumen39 halamanFriction SpinningPåñdît ẞhyãmãñtãk MãñîBelum ada peringkat
- Cardingmachine 140324082245 Phpapp01Dokumen33 halamanCardingmachine 140324082245 Phpapp01SantoshBelum ada peringkat
- Compact Yarn: S.M. Farhana Iqbal Associate Prof. ButexDokumen22 halamanCompact Yarn: S.M. Farhana Iqbal Associate Prof. ButexSadia TabassumBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On: Different Parts of Ring FrameDokumen15 halamanPresentation On: Different Parts of Ring FrameTowfic Aziz Kanon100% (3)
- Melange YarnDokumen11 halamanMelange YarnMd Ariful IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly learning objectives for blow room machinesDokumen24 halamanWeekly learning objectives for blow room machinesTalha saeedBelum ada peringkat
- Solved QP of Knit Tech April 2023Dokumen4 halamanSolved QP of Knit Tech April 2023RajendrakumarBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: Speed FrameDokumen9 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Speed FrameRatul HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Cleaning Point of Uniclean Machine in Blow Room On Cleaning Efficiency and Yarn QualityDokumen21 halamanEffect of Cleaning Point of Uniclean Machine in Blow Room On Cleaning Efficiency and Yarn QualitySantoshBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn Manufacturing Tandem CardingDokumen5 halamanYarn Manufacturing Tandem CardingIndrajit BoseBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture ComberDokumen20 halamanLecture ComberMD. Sharifuzzaman Joy100% (1)
- Open End SpinningDokumen8 halamanOpen End SpinningAmir Shahzad75% (4)
- The Heart of Spinning: Understanding the Key Operating Principles and Tasks of Carding MachinesDokumen101 halamanThe Heart of Spinning: Understanding the Key Operating Principles and Tasks of Carding MachinesUmår F ÃfriDiBelum ada peringkat
- Roving FrameDokumen99 halamanRoving Frameirfanfakhar2Belum ada peringkat
- Elements of Circular KnittingDokumen5 halamanElements of Circular KnittingSanika JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Weft Knitting PrincipleDokumen11 halamanWeft Knitting PrincipleTamanna AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- 1.all Drafting System. All Parts of DraftingDokumen3 halaman1.all Drafting System. All Parts of DraftingRatul Hasan0% (1)
- Air Jet Spinning: Principles and Production of Fasciated YarnDokumen7 halamanAir Jet Spinning: Principles and Production of Fasciated YarnAbi NikilBelum ada peringkat
- 1ci3pqr1q 814635Dokumen5 halaman1ci3pqr1q 814635Santosh50% (2)
- Combing FAQ's: Everything You Need to KnowDokumen16 halamanCombing FAQ's: Everything You Need to KnowNasir Sarwar100% (2)
- Blowroom Blending Methods for Fiber MixturesDokumen3 halamanBlowroom Blending Methods for Fiber Mixturesmoosking100% (1)
- Course: Yarn Manufacturing 2Dokumen24 halamanCourse: Yarn Manufacturing 2fekadeBelum ada peringkat
- Rotor Spinning Mill PlanDokumen35 halamanRotor Spinning Mill Planstylish eagleBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenDokumen14 halamanManufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenKareena KallaBelum ada peringkat
- Improving productivity of ring framesDokumen8 halamanImproving productivity of ring framesAmrit virkBelum ada peringkat
- Ring Frame - Technological AspectsDokumen43 halamanRing Frame - Technological AspectsAliAhmad50% (2)
- Rotor SpinningDokumen4 halamanRotor SpinningJasmeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Different Types of Card Clothing Used in Carding MachineDokumen6 halamanStudy On Different Types of Card Clothing Used in Carding MachineAbhishek BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- Weft Fork Motion BasicsDokumen10 halamanWeft Fork Motion Basicssukanya prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn Lab ReportDokumen6 halamanYarn Lab ReportYeasin ArafatBelum ada peringkat
- Blowroom: Basic Operations in The BlowroomDokumen3 halamanBlowroom: Basic Operations in The BlowroomIndu VikasiniBelum ada peringkat
- Raymond UCO DenimDokumen25 halamanRaymond UCO DenimChaitanya Gajbhiye100% (1)
- Compact SpinningDokumen15 halamanCompact SpinningCẩm TúBelum ada peringkat
- Description of Warping MachineDokumen11 halamanDescription of Warping MachineAlhajAliBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Yarn StrengthDokumen11 halamanFactors Affecting Yarn StrengthAbhishek ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Working Procedure of Comber MachineDokumen3 halamanWorking Procedure of Comber MachineRatul HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Jute Spinning Methods and ProcessesDokumen20 halamanJute Spinning Methods and ProcessesAbdus Salam Ratan100% (1)
- Inspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Dokumen3 halamanInspection of Waste Extracted by Different Machines of Spinning Department.Ammar Naeem BhattiBelum ada peringkat
- Patterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafDokumen33 halamanPatterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafHifza khalidBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn Manufacturing - IIDokumen3 halamanYarn Manufacturing - IITextile Department Help Desk.Diu100% (1)
- Guideline For Writing A Lab Report: Title PageDokumen66 halamanGuideline For Writing A Lab Report: Title PageAshiqur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn Manufacturing - I Carding ProcessDokumen31 halamanYarn Manufacturing - I Carding ProcessSantoshBelum ada peringkat
- TappetDokumen10 halamanTappetoronno5Belum ada peringkat
- Ring FrameDokumen13 halamanRing FrameAnkit Kumar0% (1)
- Drafting Waves of SliversDokumen4 halamanDrafting Waves of Sliversnalaka.sampathBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn Numbering System Yarn Count Direct Count System Indirect Count SystemDokumen3 halamanYarn Numbering System Yarn Count Direct Count System Indirect Count SystemTanmay JagetiaBelum ada peringkat
- Spin Plan Bengal ThesisDokumen149 halamanSpin Plan Bengal Thesisstylish eagleBelum ada peringkat
- Carr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDari EverandCarr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDavid J. TylerPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Isit437 L02Dokumen15 halamanIsit437 L02Pradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
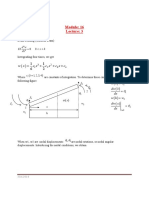
- Approximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Dokumen7 halamanApproximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Pradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- AI Skills Taxonomy JuneDokumen6 halamanAI Skills Taxonomy JunePradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Econometrics SampleDokumen2 halamanEconometrics SamplePradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m15l38 PDFDokumen3 halamanm15l38 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulleys and ForceDokumen8 halamanPulleys and ForceBegin Bahrum SianturiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 PDFDokumen8 halamanChapter 2 PDFPradip Gupta100% (1)
- E-commerce Security Lecturer DetailsDokumen8 halamanE-commerce Security Lecturer DetailsPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Total DerivativeDokumen8 halamanTotal DerivativePradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Torque and Power PDFDokumen9 halamanTorque and Power PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Drive System User Guide v1bDokumen20 halaman2011 Drive System User Guide v1bPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- WX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXDokumen6 halamanWX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Design Process in Competition Robotics - PAPER.20091204 PDFDokumen29 halamanEngineering Design Process in Competition Robotics - PAPER.20091204 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 2007CON Drive Systems CopioliDokumen56 halaman2007CON Drive Systems CopioliДалибор МарковићBelum ada peringkat
- Pulley Drive SysDokumen16 halamanPulley Drive SysrameshdesignBelum ada peringkat
- m16l41 PDFDokumen4 halamanm16l41 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m16l41 PDFDokumen4 halamanm16l41 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m15l37 PDFDokumen5 halamanm15l37 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Approximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Dokumen7 halamanApproximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Pradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- WX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXDokumen6 halamanWX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m16l40 PDFDokumen5 halamanm16l40 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Fig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsDokumen4 halamanFig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m16l40 PDFDokumen5 halamanm16l40 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m15l38 PDFDokumen3 halamanm15l38 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Fig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsDokumen4 halamanFig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m15l37 PDFDokumen5 halamanm15l37 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m14l35 PDFDokumen3 halamanm14l35 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 5Dokumen5 halamanModule 5AmanNanda0% (1)
- Two Mass Spring System MotionDokumen4 halamanTwo Mass Spring System MotionPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- m14l32 PDFDokumen3 halamanm14l32 PDFPradip GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Control of CountDokumen13 halamanControl of CountsagarkanzarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Woven Fabric DefectsDokumen28 halamanWoven Fabric DefectsGreeshma75% (4)
- Australian WoolDokumen14 halamanAustralian WoolP. PaarthBelum ada peringkat
- Spinning Packing DensityDokumen14 halamanSpinning Packing DensityVenkat PrasannaBelum ada peringkat
- Spinnovation No. 21 English Web PDFDokumen36 halamanSpinnovation No. 21 English Web PDFMd. Humayun KabirBelum ada peringkat
- Wool Carbonising: Learning ObjectivesDokumen10 halamanWool Carbonising: Learning ObjectivesAbel TayeBelum ada peringkat
- Combed Yarn For KnittingDokumen7 halamanCombed Yarn For KnittingAnmol JainBelum ada peringkat
- At Asu Menberu Tesfaw Intern ReportDokumen94 halamanAt Asu Menberu Tesfaw Intern ReportChristianBelum ada peringkat
- Jute Yarn SpinningDokumen15 halamanJute Yarn SpinningDebasish GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn manufacturing I: Cotton grading and blowroom processesDokumen219 halamanYarn manufacturing I: Cotton grading and blowroom processesfekadeBelum ada peringkat
- Carding (Jute)Dokumen12 halamanCarding (Jute)ইসলামিক টিভি100% (2)
- Process Control and Yarn Quality in SpinningDokumen7 halamanProcess Control and Yarn Quality in Spinningjack_hero_56Belum ada peringkat
- Drafting SystemDokumen11 halamanDrafting SystemRatul HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Process ControlDokumen30 halamanProcess ControlhaishpithadiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of High Temperature Drying Prior to GinningDokumen11 halamanEffects of High Temperature Drying Prior to GinningNessre ZeineBelum ada peringkat
- YARNDokumen31 halamanYARNamanBelum ada peringkat
- 2010-3-38-Effect of The Draft Ratio On The Properties of Vortex Spun Yarn PDFDokumen5 halaman2010-3-38-Effect of The Draft Ratio On The Properties of Vortex Spun Yarn PDFSubba RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Introd TextileDokumen25 halamanIntrod TextileNila Kumar SinghaBelum ada peringkat
- Key factors to control Cloth BarrenessDokumen19 halamanKey factors to control Cloth Barrenesskamal kantBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Attachment of Shohagpur Textile Mills Ltd.Dokumen88 halamanIndustrial Attachment of Shohagpur Textile Mills Ltd.Anonymous ZH6tcBQBelum ada peringkat
- RPS Olympiad VII Question PaperDokumen8 halamanRPS Olympiad VII Question PaperShivam ZakhmiBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Wool Spinning ProcessesDokumen68 halamanPrinciples of Wool Spinning ProcessesCẩm Tú100% (1)
- Spin Plan 3Dokumen209 halamanSpin Plan 3Harsimran SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study On Ring, Rotor and Air-Jet Spun Yarn: Sharif AhmedDokumen14 halamanComparative Study On Ring, Rotor and Air-Jet Spun Yarn: Sharif AhmedBithy PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Ymt 2 ManualDokumen32 halamanYmt 2 ManualRahul Patel100% (1)
- Textile InternshipDokumen62 halamanTextile InternshipSaaks00186% (7)
- Textile Industry Internship ReportDokumen6 halamanTextile Industry Internship ReportPiyush PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Arvind Textiles Internship Report PDFDokumen107 halamanArvind Textiles Internship Report PDFOmkar Jadhav100% (1)
- Nonwoven CombinedDokumen106 halamanNonwoven CombinedTarun Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter - I Introduction and Design of StudyDokumen57 halamanChapter - I Introduction and Design of Studyஸ்ரீ கற்குவேல் அய்யனார் துணைBelum ada peringkat