27 Gaussian Beams
Diunggah oleh
Serge Mandhev SwamotzDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
27 Gaussian Beams
Diunggah oleh
Serge Mandhev SwamotzHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
27. 27.
Gaussian Gaussian Beam Beam
Gaussian beam
: Gaussian function
How to determine - Beam size W at z - beam waist - beam radius - divergence angle
Now, lets start with the wave equation in free-space
Wave Equation
( wavenumber )
: Helmholtz equation
The wave equation for monochromatic waves
Paraxial Paraxial Helmholtz Helmholtz equation equation
: Helmholtz equation : Consider a plane wave propagating in z-direction
: Slowly varying approximation
2 2 2 T 2 + 2 x y
Slowly varying envelope approximation of the Helmholtz equation Paraxial Helmholtz equation.
A paraxial wave is a plane wave e-jkz modulated
by a complex envelope A(r) that is a slowly varying function of position:
The complex envelope A(r) must satisfy the paraxial Helmholtz equation
One simple solution to the paraxial Helmholtz equation : paraboloidal waves
Another solution of the paraxial Helmholtz equation : Gaussian beams
Gaussian Gaussian beam beam
where, W0 : beam waist z0 : Rayleigh range
Gaussian beam
2 = z W0 0
Gaussian Gaussian beam beam
Intensity Intensity of of Gaussian Gaussian beam beam
The intensity is a Gaussian function of the radial distance . This is why the wave is called a Gaussian beam. On the beam axis ( = 0)
At z = z0 , I = Io/2
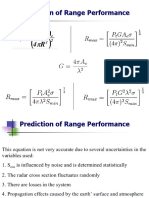
Gaussian Gaussian beam beam :: Power Power
The result is independent of z, as expected. The beam power is one-half the peak intensity times the beam area.
The ratio of the power carried within a circle of radius in the transverse plane at position z to the total power is
Power ratio clipped by aperture
( 0 = a )
Beam Beam radius radius
At the Beam waist : Waist radius = W0 Spot size = 2W0
(far-field)
(divergence angle)
Depth Depth of of Focus Focus
The axial distance within which the beam radius lies within a factor root(2) of its minimum value (i.e., its area lies within a factor of 2 of its minimum) is known as the depth of focus or confocal parameter
beam area at waist
A small spot size and a long depth of focus cannot be obtained simultaneously !
Depth of focus, Rayleigh range, and Beam waist
Gaussian Gaussian parameters parameters :: Relationships Relationships between between parameters parameters
Phase Phase of of the the Gaussian Gaussian beam beam
kz : the phase of a plane wave. : a phase retardation ranging from - /2 to - /2 . : This phase retardation corresponds to an excess delay of the wavefront in comparison with a plane wave or a spherical wave
The total accumulated excess retardation as the wave travels from
Guoy effect
Wavefront Wavefront -- bending bending
Wavefronts (= surfaces of constant phase) :
Wavefronts Wavefronts near near the the focus focus
Wave fronts:
/2 phase shift relative to spherical wave
TRANSMISSION TRANSMISSIONTHROUGH THROUGHOPTICAL OPTICALCOMPONENTS COMPONENTS
A. Transmission Through a Thin Lens
Gaussian beam relaying
Gaussian beam Focusing
If a lens is placed at the waist of a Gaussian beam,
If (2 z0 ) >> f ,
Other Beams Other Beams higher order beams
higher order beams
Hermite-Gaussian
Bessel Beams
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterDari EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterBelum ada peringkat
- Paraxial Wave EquationDokumen15 halamanParaxial Wave EquationSamantha ToBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian Beam DeriveDokumen30 halamanGaussian Beam DeriveVandana SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian Beam PropagationWEBDokumen5 halamanGaussian Beam PropagationWEBCelesCastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian Beam OpticsDokumen16 halamanGaussian Beam OpticsModyKing99Belum ada peringkat
- Propagation of Gaussian Beam OpticsDokumen6 halamanPropagation of Gaussian Beam OpticsMohamed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian Beam OpticsDokumen12 halamanGaussian Beam OpticsHanh MaiBelum ada peringkat
- Knife EdgeDokumen6 halamanKnife EdgeJulian David Henao EscobarBelum ada peringkat
- Maxwell'S Equations: V in The Positive X-Direction, GX T BG Af yDokumen13 halamanMaxwell'S Equations: V in The Positive X-Direction, GX T BG Af yp_k_soni_iit_physicsBelum ada peringkat
- MellesGriot Gaussian Beam OpticsDokumen14 halamanMellesGriot Gaussian Beam OpticsKurt PatzikBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4: Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (Continued) and The Shallow Water TheoryDokumen11 halamanLecture 4: Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (Continued) and The Shallow Water Theoryవేలుసామి లింగాసామిBelum ada peringkat
- Spatial Proflle of A Laser BeamDokumen6 halamanSpatial Proflle of A Laser Beamalireza.p1983Belum ada peringkat
- 0207 1Dokumen29 halaman0207 1Sveti JeronimBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen61 halamanUnit 1SEHARABANU MULLABelum ada peringkat
- Optical Resonators: Michael KossinDokumen5 halamanOptical Resonators: Michael KossinMichael KossinBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6 Wave Motion - UptoDokumen47 halamanLecture 6 Wave Motion - UptoAryan MahmudBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Iii: Laser Beam Properties ECE 476 I. PurposeDokumen7 halamanLab Iii: Laser Beam Properties ECE 476 I. PurposeVinayak SavarkarBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 - Wang Et Al. - Near-Field Properties of Diffraction Through A Circular Subwavelength-Size Aperture - Chinese Physics BDokumen12 halaman2012 - Wang Et Al. - Near-Field Properties of Diffraction Through A Circular Subwavelength-Size Aperture - Chinese Physics BClaudio BiaginiBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Equation For DummiesDokumen6 halamanWave Equation For DummiesagonzalezfBelum ada peringkat
- First Helmholtz Vortex TheoremDokumen2 halamanFirst Helmholtz Vortex TheoremJason RossBelum ada peringkat
- Photonics: Principles and Practices: Instructor's Power Point For Optoelectronics and Second EditionDokumen51 halamanPhotonics: Principles and Practices: Instructor's Power Point For Optoelectronics and Second EditionBalaji Raja RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Design of EM DevicesDokumen162 halamanDesign of EM Deviceswickedness100% (1)
- Chapter 2. Griffiths-Electrostatics-2.1 2.2Dokumen12 halamanChapter 2. Griffiths-Electrostatics-2.1 2.2Hazem TawfikBelum ada peringkat
- Gaussian BeamsDokumen58 halamanGaussian BeamsDaniel Humberto Martinez SBelum ada peringkat
- Fibre PPT 3Dokumen20 halamanFibre PPT 3Miraj SheikhBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Longitudinal Modes of A Laser Cavity: Adrian Down May 01, 2006Dokumen7 halaman1 Longitudinal Modes of A Laser Cavity: Adrian Down May 01, 2006Joshua WhitneyBelum ada peringkat
- Bessel Beams: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Dokumen12 halamanBessel Beams: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Jojo KawayBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics in Vacuum - 1673699222Dokumen73 halamanElectrostatics in Vacuum - 1673699222Jigyarth SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Equation - Wikipedia PDFDokumen79 halamanWave Equation - Wikipedia PDFelvianadiyahBelum ada peringkat
- Laser Beam Profile, Spot Size and Beam Divergence: Ravitej UppuDokumen3 halamanLaser Beam Profile, Spot Size and Beam Divergence: Ravitej UppuReena SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- MG GaussianBeamsDokumen18 halamanMG GaussianBeamsPamela Aimée SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Fiber ModesDokumen45 halamanOptical Fiber Modesnavyasanuj1Belum ada peringkat
- Handout09 A2 UsefulDokumen5 halamanHandout09 A2 UsefulJoyee BasuBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture10 ScatteringLengthResonanceScatteringBeritWignerFormula2019Dokumen23 halamanLecture10 ScatteringLengthResonanceScatteringBeritWignerFormula2019Sagar RawalBelum ada peringkat
- L.N. Pyatnitsky - A Concept of TurbulenceDokumen8 halamanL.N. Pyatnitsky - A Concept of TurbulenceWhiteLighteBelum ada peringkat
- Problem 1: Gaussian Beams To The Moon: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 1 Due 5PM 18 AprilDokumen2 halamanProblem 1: Gaussian Beams To The Moon: EE 231, Lasers Spring 2007 Problem Set 1 Due 5PM 18 AprilHusam Abduldaem MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- The Ricker Wavelet and The Lambert W Function: Yanghua WangDokumen5 halamanThe Ricker Wavelet and The Lambert W Function: Yanghua WangLeidy OsorioBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Radiation Emitted An Ultrarelativistic Particle Crossing A Curved Interface Between MediaDokumen4 halamanTransition Radiation Emitted An Ultrarelativistic Particle Crossing A Curved Interface Between MediarijurahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Ps 1Dokumen2 halamanPs 1Chashan DeepBelum ada peringkat
- Brief Review of Vector Calculus: GradientDokumen32 halamanBrief Review of Vector Calculus: GradientSukhmander SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Kendriya Vidayalaya AlmoraDokumen11 halamanKendriya Vidayalaya AlmoraLol hole GamerBelum ada peringkat
- Gauss Proof and ProblemsDokumen18 halamanGauss Proof and Problemsabhishek secretBelum ada peringkat
- Wiki Landau QuantizationDokumen4 halamanWiki Landau QuantizationAnup DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Scattering and Born ApproximationDokumen6 halamanScattering and Born ApproximationManu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrostatics: Dr. Entesar GanashDokumen55 halamanElectrostatics: Dr. Entesar GanashMalik HammadBelum ada peringkat
- Evanescent WaveDokumen5 halamanEvanescent WaveRahul RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iv ClassnotesDokumen65 halamanUnit Iv ClassnotesKokila PadviBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2: (Gauss's Law and Its Applications)Dokumen24 halamanChapter-2: (Gauss's Law and Its Applications)JwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Theory Techniques and ApplicationsDokumen57 halamanQuantum Theory Techniques and ApplicationsJaidriel Meg CabandingBelum ada peringkat
- (Edit Source - Edit) : Is The Differential Vector Element of Path Length Tangential To The Path/curve, As WellDokumen2 halaman(Edit Source - Edit) : Is The Differential Vector Element of Path Length Tangential To The Path/curve, As WellsenthilanviewBelum ada peringkat
- Kovak2007 PDFDokumen15 halamanKovak2007 PDFNimal J. PereraBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency and The Redshift Factor: Notes For GR-I - CCDDokumen4 halamanFrequency and The Redshift Factor: Notes For GR-I - CCDahmedsarwarBelum ada peringkat
- 1401 1687v1 PDFDokumen20 halaman1401 1687v1 PDFCristian CustodioBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2Dokumen16 halamanCH 2Kashif AmjadBelum ada peringkat
- Microwave and Radar Systems: 1. Write A Short Note About Rectangular Waveguides..Dokumen33 halamanMicrowave and Radar Systems: 1. Write A Short Note About Rectangular Waveguides..selvaBelum ada peringkat
- Standing Wave Ratio: Relationship To The Reflection CoefficientDokumen5 halamanStanding Wave Ratio: Relationship To The Reflection Coefficientpreethy.wilsBelum ada peringkat
- Wave GuidesDokumen141 halamanWave GuidesVamshi Krishna100% (1)
- Tremaine 1997 0407Dokumen41 halamanTremaine 1997 0407Particle Beam Physics LabBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 23Dokumen18 halamanChapter 23daniaathar786Belum ada peringkat
- UNIT 1 CHEMISTRyDokumen101 halamanUNIT 1 CHEMISTRyRishabh KothariBelum ada peringkat
- PNCinterview QuestionsDokumen6 halamanPNCinterview QuestionsSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 10 Prelab Report1Dokumen4 halamanLab 10 Prelab Report1Serge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Boeing Interview PreparationDokumen5 halamanBoeing Interview PreparationSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- ENEE 498R Formula SheetDokumen3 halamanENEE 498R Formula SheetSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Exam - SolutionDokumen6 halamanMidterm Exam - SolutionSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- FPGAsDokumen55 halamanFPGAsSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Cover LetterDokumen1 halamanCover LetterSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- QuizDokumen11 halamanQuizSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Derivation of Ideal Diode EquationDokumen14 halamanDerivation of Ideal Diode EquationSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electric Circuit Theory - A One-Semester Text by I. D. Mayergoyz - Wes LawsonDokumen39 halamanBasic Electric Circuit Theory - A One-Semester Text by I. D. Mayergoyz - Wes Lawsonmerrink100% (2)
- Magnetostatics Part2Dokumen15 halamanMagnetostatics Part2Serge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- #Include Void Populate - A (Int A (10), Int B (10) ) Void Swap - B (Int A (10) )Dokumen2 halaman#Include Void Populate - A (Int A (10), Int B (10) ) Void Swap - B (Int A (10) )Serge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Enee 460Dokumen1 halamanEnee 460Serge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric OpticsDokumen8 halamanGeometric OpticsSerge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- ENEE 322 Due in Discussion Week of Feb. 4, 2013 Homework 01Dokumen2 halamanENEE 322 Due in Discussion Week of Feb. 4, 2013 Homework 01Serge Mandhev SwamotzBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 4 Test - Paper 2Dokumen3 halamanTopic 4 Test - Paper 2IB BaddiesBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Efficient Focused Surface Acoustic Wave Devices For Potential Microfluidic Applications.Dokumen18 halamanDesign of Efficient Focused Surface Acoustic Wave Devices For Potential Microfluidic Applications.Tiffany RusBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic RadiationDokumen22 halamanElectromagnetic RadiationSelva Kumar0% (1)
- Check Out This File: Engg Physics MCQs - Unit 1 - PolarizationDokumen10 halamanCheck Out This File: Engg Physics MCQs - Unit 1 - PolarizationNikhil SatbhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Herschel ProjectDokumen14 halamanHerschel Projectapi-285213466Belum ada peringkat
- Manual Macherey Nagel - COTDokumen121 halamanManual Macherey Nagel - COTcrononimeBelum ada peringkat
- C008 - Quiet Revolution Noise Statement 20100803v1Dokumen15 halamanC008 - Quiet Revolution Noise Statement 20100803v1Roland PetersBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 9.3 - Interference - AHLDokumen35 halamanTopic 9.3 - Interference - AHLPaul Amezquita50% (2)
- EITN90 Radar and Remote Sensing Lecture 11: Fundamentals of Pulse Compression WaveformsDokumen60 halamanEITN90 Radar and Remote Sensing Lecture 11: Fundamentals of Pulse Compression Waveformswire010Belum ada peringkat
- EM Wave Propagation and PolarisationDokumen13 halamanEM Wave Propagation and PolarisationSurya Prakash Singh100% (1)
- Q3 ACTIVITY 3.6 Let's Make Waves!Dokumen5 halamanQ3 ACTIVITY 3.6 Let's Make Waves!MarilynTorreCameroBelum ada peringkat
- Types of FiberDokumen24 halamanTypes of FiberAmit SwarBelum ada peringkat
- Teoría Electromagnética y OndasDokumen9 halamanTeoría Electromagnética y OndasciroBelum ada peringkat
- Science - G8 - Q1 - Week 4Dokumen48 halamanScience - G8 - Q1 - Week 4Angelito MadesBelum ada peringkat
- Large Index of Refraction With EITDokumen4 halamanLarge Index of Refraction With EITAsi EilamBelum ada peringkat
- Hsslive Xii Physics Chapter 10 SeemaDokumen16 halamanHsslive Xii Physics Chapter 10 Seemamr.xxyyzz00Belum ada peringkat
- MP EM Ass 24: Electromagnetic WavesDokumen13 halamanMP EM Ass 24: Electromagnetic WavesBlueAstro100% (2)
- Acoustics For Underwater Applications: Dr. G. A. Ramadass Ramadass@niot - Res.in Niot ChennaiDokumen96 halamanAcoustics For Underwater Applications: Dr. G. A. Ramadass Ramadass@niot - Res.in Niot Chennaishijunavarch30100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum WorksheetDokumen2 halamanElectromagnetic Spectrum WorksheetLucas KazemBelum ada peringkat
- Scan-Antenna UHF 5GDokumen3 halamanScan-Antenna UHF 5GGhislain DutilhBelum ada peringkat
- Hecht - Chapter 1Dokumen16 halamanHecht - Chapter 1JunHyoung KimBelum ada peringkat
- CST Microwave StudioDokumen28 halamanCST Microwave StudiodheifibraheemBelum ada peringkat
- Comsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsDokumen3 halamanComsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsNicolasMaregaBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 101-110Dokumen10 halamanFundamentals of Ultrasonic Phased Arrays - 101-110Kevin HuangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter04 ExercisesDokumen7 halamanChapter04 ExercisesiaessackjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Audio - And.speech - Processing.part 1.prof - Muralikrishna.hDokumen15 halamanAudio - And.speech - Processing.part 1.prof - Muralikrishna.hWilly MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Lattice Vibrations, Part I: Solid State Physics 355Dokumen22 halamanLattice Vibrations, Part I: Solid State Physics 355Anonymous 9rJe2lOskxBelum ada peringkat
- Radiometric Corrections 3Dokumen50 halamanRadiometric Corrections 3Tomi Frans PBelum ada peringkat
- CMAX-DMW60X1-43I53 Product SpecificationsDokumen2 halamanCMAX-DMW60X1-43I53 Product SpecificationsAhmad AlshaerBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: BranderhoterDokumen3 halamanThis Study Resource Was: BranderhoterCarmen BallestaBelum ada peringkat