Competency Appraisal Worksheet Guide (Final)
Diunggah oleh
Shan JanoloHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Competency Appraisal Worksheet Guide (Final)
Diunggah oleh
Shan JanoloHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
COMPETENCY APPRAISAL WORKSHEET GUIDE.
Submitted by: Shanna Mariz I. Janolo
Submitted to: Mr. Gaudymer Lopez RN.,MAN.
I.
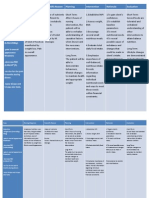
Fill the table with appropriate nursing interventions: patient Noemi undergoing adrenalectomy. Five interventions each phase. INTRAOPERATIVE INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE 1. The patient 1. So, the patient should be should be informed about aware on the IV infusions , contraptions hymodynamic given. monitoring techniques, nasogastric suctioning. 2. Monitor vital 2. For baseline signs. data. 3. Protect client 3. It will cause from exposure further to infectious complications microorganism to the client. 4. Employ 4. As a universal careful hand precautios. washing technique before contact with the patient. 5. To prevent 5. Protect client client from from falls and injury accident. POSTOPERATIVE INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE 1. Intake and 1. To maintain output must be baseline data. measured accurately and must measure frequently. 2. Be alert in any 2. It can cause signs of adrenal client further insufficiency. complications.
PREOPERATIVE INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE 1. Explain the 1. To inform the client about client about the procedure. procedure. 2. To prevent 2. Assess BP hypotension. and fluid volume frequently. 3. Provide a nutritional support in promoting physical stamina. 3. To withstand the rigors of surgery and improve wound healing postoperativel y.
3. Encourage client to eat high in protein and carbohydrate. 4. Avoid client prolonged fasting.
3. For client nutrition.
4. Fasting can precipitate hypoglycemic episodes. 5. Client should have a sufficient rest periods along with comfort measures.
4. Instruct client postoperative coughing, deep breathing and turning.
4. It gives the patient confidence and promotes complications
5. Anticipate stressful situations for the patient and prevent.
5. Explain that diet high in protein and and vitamins are helpful
5. Since glucocorticoid exceeds produces a state of catabolism.
6. Diff. nursing responsibilities of the patient undergoing radioactive therapy. Keep the skin dry. Should remove ink marks. Avoid using powders, lotion, creams, alcohol, and deodorant. Wear loose fitting clothes. Protect skin from direct sunlight, chlorine and extreme temp.
7. Nursing diagnosis and nursing interventions for patient Shane (dse. Graves disease.)
A. Less than body requirements r/t accelerated metabolic rate. Provide client with well balanced, high calorie diet. Encourage client to eat foods that are nutritious and contain ample amounts of protein, carbohydrates, fats, and minerals. Clients should weight daily and weight losses of more than 4.4lb should be reported B. Activity intolerance r/t exhaustion secondary to accelerated metabolic rate. Provide client with environment that is restful. Promote rest. Prevent them from disturbing.
C. Hyperthermia r/t increase metabolic rate. Provide client with cool environment. Use only a lightweight sheet for the top cover and give them light loose pajamas. If the client is diaphoretic, may need to change the bed sheets and clothes frequently.
8. Signs of escalating anxiety for shielas behavior. Increasingly withdrawn Agitated Irritable Management: CATEGORIZE. Distraction. Fighting back Isolation Attempts to feel better Help-seeking
9. Diagnosis and Interventions for shiela who has expects of having schizophrenia. 3 DIAGNOSES: Disturbed thought process r/t presence of persecutory delusions. Self-care deficit r/t poor personal hygiene. Ineffective coping r/t fear.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
INTERVENTIONS Monitor for physical discomfort such as pain and physical illness. Remove clients from or avoid situation know to cause agitation. Decrease stimulants such as caffeine, bright lights and load noise and music. Avoid criticism and do not argue. Avoid display of anger, discouragement, or frustrations when interacting with them.
RATIONALE 1. Close observation to client will prevent it from self harm. 2. To prevent client for further injury. 3. It may help the client to relief from stress. 4. Client can think that may cause them hurt themselves. 5. So, they cannot disappointment them.
REFERENCE: Stuart, Gail W. et al, 2005, Principles and Practice of Psychiatric Nursing 8th edition, pp. 414-415 Black, Joyce M., et al, 1993, Saunders Company, Luckmann and Sorensens Medical- Surgical Nursing A Psychophysiologic Approach, 4th edition pp.1818-1847
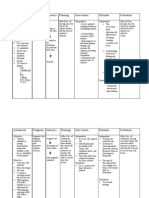
Shanna Mariz I. Janolo N4E NURSING CARE PLAN FOR RISK FOR INJURY ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING Subjective: Risk for injury After hours of nursing intervention client will Increased muscle related to increased muscle be able to: weakness. weakness. Difficulty Short term: climbing the Free from stairs to another incidence of Easy fatigability fall, patients safety will be Objective: ensured. Protruding abdomen and Long term: buttocks Demonstrate Round face behaviors, Presence of lifestyle edema changes to Obvious facial reduce risk hair factors and Numerous protect self bruises in the from injury skin BP: 160/90 Ca: 4.3 mEq/L
INTERVENTION INDEPENDENT: Assess the person for factors known to increase fall risk such as history of falls, mental status changes and sensory deficits Assess patients environment for factors known to increase fall risk such as unfamiliar setting and inadequate lighting
RATIONALE
Evidence indicates that a person who has sustained Short term: one or more Free from falls in the incidence of past year is fall, patients more likely to safety will be fall again ensured. Long term: Patients who Demonstrate are not behaviors, familiar with lifestyle the placement changes to of furniture reduce risk and factors and equipment in protect self the room are from injury more likely to experience a fall.
EVALUATION After hours of nursing intervention client was able to:
Place items used by the patient within
Stretching to get items from bedside
easy reach
Use side rails on beds as needed.
Encourage the patient to participate in a program of regular exercise
tables that are out of reach can disrupt the patients balance and contribute to falls Patients who are disoriented or confused have been known to climb over siderails and fall Evidence suggests that people who engage in regular exercise and activity will strengthen muscles
DEPENDENT: Encourage the patient to wear shoes or slippers with nonskid soles
Nonskid footwear provides sure footing for the patient
when ambulating
Orient the patient to the layout of the room.
Provide the patient with a chair that has a firm seat and arms on both sides
with diminished foot and toe lift when walking The more familiar the patient is with the layout of the room, the less likely the patient is to trip over furniture This chair style is easier to get out of especially when the patient experiences weakness and impaired balance when transferring from bed to chair Incorrect use or improper maintenance of canes,
Educate the patient and family caregivers
about the correct use and maintenance of mobility assisted devices COLLABORATIVE: Refer the person for diagnostic musculoskeleta l evaluation
walkers and wheelchairs can increase the risk for falls
Collaborate with other health care team members to evaluate the patients medications that contribute to falling
Physical therapy evaluation can identify problems with balance and gait that can increase a persons fall risk A review of the patients medication by the prescribing health care provider and the pharmacist can identify side effects and drug interaction
Refer the family to community resources for assistance in making home safety modifications
Many community service organizations provide financial assistance to help older alults make safety improvement s
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NCP Knowledge Deficit (FINAL)Dokumen8 halamanNCP Knowledge Deficit (FINAL)Nikki Ricafrente89% (9)
- ATI CompDokumen9 halamanATI CompTee Wood100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen48 halamanNursing Care PlansJuliantiMamangkey86% (7)
- Wolverhampton NHS Interview QuestionsDokumen10 halamanWolverhampton NHS Interview QuestionsChristiana OnyinyeBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Diagnosis For CataractDokumen3 halamanNursing Diagnosis For CataractZainul HazwanBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Orems Theory To NSG PracticeDokumen26 halamanApplication of Orems Theory To NSG PracticeLorde Sungcad Ricafrente100% (3)
- NCPs For ParotidectomyDokumen12 halamanNCPs For ParotidectomyCarla Manaloto50% (2)
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsDokumen1 halamanGordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsTracy100% (37)
- HEMORRHOID (Case Study)Dokumen45 halamanHEMORRHOID (Case Study)enny92% (24)
- Fire Alarm SymbolsDokumen6 halamanFire Alarm Symbolscarlos vasquezBelum ada peringkat
- 2006 SM600Dokumen2 halaman2006 SM600Ioryogi KunBelum ada peringkat
- Patient SafetyDokumen102 halamanPatient SafetyAlain CheryBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0000.Dokumen34 halamanWa0000.Abdelrahman AbdouBelum ada peringkat
- FocusDokumen15 halamanFocusSergio Rivas100% (3)
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJose Benit DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- DocxDokumen7 halamanDocxShannon GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Health Teaching PlanDokumen5 halamanHealth Teaching PlanLester Dalanon100% (1)
- Gnur 405 SuzyDokumen6 halamanGnur 405 SuzySeth MensahBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Perinatal FinalsDokumen6 halamanNCP - Perinatal FinalsJanette L. Ortega0% (1)
- Case Study StabDokumen7 halamanCase Study StabMari Jasmeen Estrada Noveda100% (1)
- NCP IsoDokumen4 halamanNCP IsoBriccio Calingin IIIBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen17 halamanNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDokumen21 halamanGuillain Barre Syndromebasinang_jangilBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Map - Abby !Dokumen3 halamanConcept Map - Abby !Franklin A. Salaum III0% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Patient Centered Collaborative Care Ignatavicius 6th Edition Test BankDokumen24 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing Patient Centered Collaborative Care Ignatavicius 6th Edition Test BankLukeYoungxfpyj100% (32)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen6 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Semester Three ME113Dokumen36 halamanSemester Three ME113Cheng XinvennBelum ada peringkat
- Operating RoomDokumen81 halamanOperating Roomjaypee01100% (3)
- NCPDokumen6 halamanNCPAngelaTrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- NCPs For ParotidectomyDokumen8 halamanNCPs For ParotidectomyAcohCChao100% (1)
- NCP Icu-CcuDokumen6 halamanNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Patient in Acute Biologic CrisisDokumen58 halamanCare of Patient in Acute Biologic CrisisVon LarenaBelum ada peringkat
- Errors in NursingDokumen59 halamanErrors in NursingCzerwin JualesBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental EAQDokumen20 halamanFundamental EAQDean WinchesterBelum ada peringkat
- Care PlansDokumen24 halamanCare PlansKeiChaBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Nursing 1st CompressedDokumen45 halamanPrinciples of Nursing 1st Compressedlovi.ortiz.auBelum ada peringkat
- Care PlanDokumen4 halamanCare Planapi-217086261Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen4 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusBelum ada peringkat
- NUR403 Assiginment 2Dokumen8 halamanNUR403 Assiginment 2KwanNingYuBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Patient 3 Cervical CADokumen8 halamanNCP Patient 3 Cervical CAFatima LabaoBelum ada peringkat
- Objectives of The Case StudyDokumen5 halamanObjectives of The Case StudyChristian TayagBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen12 halamanNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- GERDDokumen5 halamanGERDSteve Randolph67% (3)
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPannamargie07Belum ada peringkat
- IITR Healthcare Interview Preparation GuideDokumen8 halamanIITR Healthcare Interview Preparation GuideReshma Zera100% (1)
- Nursing Care For Patients With Multiple SclerosisDokumen1 halamanNursing Care For Patients With Multiple Sclerosis4gen_2Belum ada peringkat
- NCP TonsilitisDokumen11 halamanNCP TonsilitisGra Cie50% (6)
- NCP For OsteomyleitisDokumen5 halamanNCP For OsteomyleitisAyaBasilioBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPLouis RoderosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FinalDokumen7 halamanNCP FinalRuss RussBelum ada peringkat
- NRSG 117 Care Plan-B - 1Dokumen6 halamanNRSG 117 Care Plan-B - 1Jill McKeeman GillespieBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses Roles in Radiation TherapyDokumen12 halamanNurses Roles in Radiation Therapy30 Rozina TamangBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Prioritization and NCP (Bataan)Dokumen7 halamanNursing Prioritization and NCP (Bataan)Rudy Mark ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- NSG 1405 Care PlansDokumen3 halamanNSG 1405 Care PlansAshley CyriacBelum ada peringkat
- Uworld Study-Guide 2020Dokumen1.007 halamanUworld Study-Guide 2020Ramnath Rajbanshi100% (1)
- IPSGDokumen4 halamanIPSGmohsinaBelum ada peringkat
- IPSGDokumen4 halamanIPSGmohsinaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP StrokeDokumen7 halamanNCP StrokeMonica Gagarin Cortez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans: Desired Outcome Interventions Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plans: Desired Outcome Interventions Impaired Physical MobilityNaomi MasudaBelum ada peringkat
- CARE PLANS Part 2Dokumen8 halamanCARE PLANS Part 2Mhee FaustinaBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyDari EverandMastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyBelum ada peringkat
- The COAT & Review Approach: How to recognise and manage unwell patientsDari EverandThe COAT & Review Approach: How to recognise and manage unwell patientsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Notes Receivable - ProblemsDokumen2 halamanNotes Receivable - ProblemsShan Janolo67% (3)
- Bolivia, JanoloDokumen9 halamanBolivia, JanoloShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: University of The EastDokumen4 halamanRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: University of The EastShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Economics AnalysisDokumen1 halamanEconomics AnalysisShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Check 2Dokumen1 halamanCheck 2Shan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Bolivia, JanoloDokumen9 halamanBolivia, JanoloShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- ThedddddyDokumen1 halamanThedddddyShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Business Letter - EnGLISHDokumen27 halamanBusiness Letter - EnGLISHShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Socialization ProgramDokumen1 halamanSocialization ProgramShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter IDokumen6 halamanChapter IShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Human Relations and Social Orientation Program INTRODUCTION - The Social Skills of An Individual Is The Main Topic of The Course ThroughDokumen3 halamanHuman Relations and Social Orientation Program INTRODUCTION - The Social Skills of An Individual Is The Main Topic of The Course ThroughShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Conceptual FrameworkDokumen1 halamanConceptual FrameworkShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen40 halamanDrug Studyapi-374468390% (61)
- FluimucilDokumen2 halamanFluimucilianecunar86% (7)
- B6 FormDokumen3 halamanB6 FormShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Clubfoot or Talipes EquinovarusDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Clubfoot or Talipes Equinovarusderic100% (4)
- ApocalyptoDokumen5 halamanApocalyptoShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- B6 FormDokumen3 halamanB6 FormShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Anc ArticleDokumen9 halamanAnc ArticleShan JanoloBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer ProDokumen25 halamanPolymer ProJeerisuda KingklangBelum ada peringkat
- School Administration and Supervision MAED 605Dokumen24 halamanSchool Administration and Supervision MAED 605Jaynie Ann TapdasanBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Shrink CoatingDokumen5 halamanHeat Shrink CoatingMekhmanBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal RustamDokumen15 halamanJurnal RustamRustamBelum ada peringkat
- Robodrill 01Dokumen298 halamanRobodrill 01vuchinhvdcBelum ada peringkat
- (Template) The World in 2050 Will and Wont Reading Comprehension Exercises Writing Creative W 88793Dokumen2 halaman(Template) The World in 2050 Will and Wont Reading Comprehension Exercises Writing Creative W 88793ZulfiyaBelum ada peringkat
- PU-133AB - 規格GMXa spc 2022Dokumen5 halamanPU-133AB - 規格GMXa spc 2022Ý TrầnBelum ada peringkat
- Banco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileDokumen1 halamanBanco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileGwen CaldonaBelum ada peringkat
- Vishaka GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanVishaka GuidelinesAakashKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Critique PaperDokumen1 halamanCritique PapernicolealerBelum ada peringkat
- Genomics and Crop ImprovementDokumen56 halamanGenomics and Crop Improvementsenguvelan100% (6)
- Eaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enDokumen4 halamanEaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enEsteban Fernando Meza IbacetaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Over Hauser Enhancement (NOE)Dokumen18 halamanNuclear Over Hauser Enhancement (NOE)Fatima AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Jan Precious Mille BDokumen1 halamanJan Precious Mille BJebjeb C. BrañaBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial RemediesDokumen13 halamanOrganic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial Remediesapi-271179911Belum ada peringkat
- Steel Scrap Recycling Policy 06.11.2019 PDFDokumen31 halamanSteel Scrap Recycling Policy 06.11.2019 PDFAnshul SableBelum ada peringkat
- AIR Modeller 78 2018Dokumen68 halamanAIR Modeller 78 2018StefanoBelum ada peringkat
- YuzurtDokumen2 halamanYuzurtFranco Ascari100% (1)
- 084 - ME8073, ME6004 Unconventional Machining Processes - NotesDokumen39 halaman084 - ME8073, ME6004 Unconventional Machining Processes - NotesA. AKASH 4001-UCE-TKBelum ada peringkat
- BS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctDokumen60 halamanBS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctRamiAl-fuqahaBelum ada peringkat
- Hand-Pallet Truck - NewDokumen2 halamanHand-Pallet Truck - NewAkhilBelum ada peringkat
- SubstationsDokumen39 halamanSubstationspBelum ada peringkat
- (Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFDokumen441 halaman(Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFMuhammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Form Apr 22 2022Dokumen4 halamanForm Apr 22 2022api-589628245Belum ada peringkat
- P3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter (Higher) Mark SchemeDokumen3 halamanP3 Chapter 2 End-Of-Chapter (Higher) Mark SchemePaul LloydBelum ada peringkat
- Carapace DigitalDokumen15 halamanCarapace DigitalVillain ChatBelum ada peringkat
- Facebow Tech Spec Gen LRDokumen1 halamanFacebow Tech Spec Gen LRrojBelum ada peringkat
- Clack 2983 WS1EE Twin Valve LDokumen2 halamanClack 2983 WS1EE Twin Valve Lmohamed boufasBelum ada peringkat