Bio Paper 1 Mid Term 2011
Diunggah oleh
Hilmi DinHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bio Paper 1 Mid Term 2011
Diunggah oleh
Hilmi DinHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
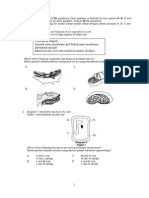
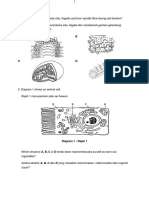
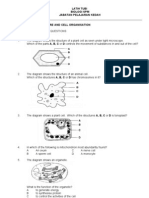
SECTION A 1. Figure 1 shows a cross-section of a plant cell.
FIGURE 1
Which organelle is involved in cellular respiration? A B P Q C D R S
2. A scientist carries out investigations on bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi and algae. What is his field of study in biology? A virology B bacteriology C entomology D microbiology
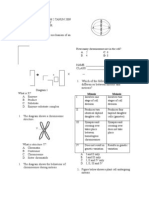
3.
Figure 2 shows part of a DNA molecule.
FIGURE 2
Which of the following represents Q, R and S? Pentose sugar A B C D Q Q S S Nitrogenous base R S R Q Phosphate group S R Q R
4. Which of the following are functions of water? I II Component of cell membrane. Solvent for solutes, provides an aqueous medium for biochemical reactions. III Turgid cells give support to herbaceous plants. IV As a reactant in photosynthesis.
A I and II only B I, III and IV only C II, III and IV only D I, II, III and IV 5. The Figure 3 shows a stage during mitosis in a plant cell.
FIGURE 3 What is the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell after completing the cell division? A B C D 2 4 8 16
6. Figure 4 shows different phases of a cell cycle. Phase X is an interphase and phase Y is a mitotic phase.
FIGURE 4 What are represented by P, Q, R, U and V? P A B Mitosis Growth gap Q Cytokinesis Cell growth DNA replication Cell growth R DNA replication DNA replication Growth gap Growth gap U Cell growth Cytokinesis Mitosis Mitosis V Growth gap Mitosis Cytokinesis Cytokinesis
C Cell growth D DNA replication
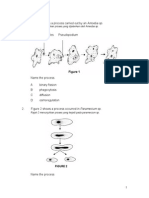
7. The diagram shows various stages in a cell division.
I A IV II IIII B I IV II III C II IV III I D II IIII IV
II
III
IV
Arrange the diagram to show the correct sequence of a cell division.
8. Figure 5 shows several stages in meiosis.
FIGURE 5 Which of the following is not true about P? A Homologous chromosomes separate and move to the opposite poles. B The spindle fibres pull the chromosomes away from one another. C Stage P is called Anaphase I. D Four chromosomes move towards each pole.
9. G1, G2, M and S in the diagram show the phases of a cell cycle.
DNA synthesis is represented by. A G1 C M B G2 D S
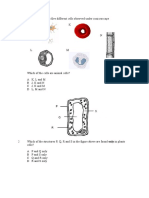
10. Figure 6 shows cells P and Q undergoing cell division.
FIGURE 6
Which of the following statement is true about K and L? K A B It carries genetic information. Each daughter cell of P contains half the number of K. C Haploid number in each daughter cell. D Crossing over occurs. It pulls the chromosomes to the opposite poles. It still exists in the daughter cells. L It begins to form during prophase. It is attached to the centromere.
11.
Figure 7 shows one stage of a meiotic cell division.
FIGURE 7 The possible chromosomes in each daughter cell are I P and Q II R and S III Q and R IV P and S A B C D I and II only III and IV only I, II and III only I,II, III and IV
12.
Figure 8 shows a mitotic cell division.
FIGURE 8
What are represented by P, Q, R and S?
P A B C D Chromatid Centriole Chromatid Centromere
Q Centriole Chromatid Centromere Spindle fibre
R Centromere Spindle fibre Centriole Chromatid
S Spindle fibre Centromere Spindle fibre Centriole
13
. Figure 9 shows a mitotic division of an animal cell.
FIGURE 9 The processes that occur before and after this stage are
Before A B C D Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase
After Cytokinesis Metaphase Telophase Prophase
14. Figure 10 shows a mitotic division during Prophase I in an anther of a flowering plant.
FIGURE 10
How many chromosomes are found in a pollen grain? A B C D 1 2 4 16
15. Which of the following stage of mitosis is shown in the Figure 11 below?
FIGURE 11 A B C D Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
16. Figure 12 shows a cell division of an animal cell.
FIGURE 12 How many chromosomes are found in the heart cell? A B C D 2 4 8 16
17. Figure 13 shows a cell division during Telophase II of an animal cell.
FIGURE 13 How many chromosomes are found in its skin cell? A 2 B 4 C 8 D 6 18. Which of the following statements are not true about the Figure 14 below?
FIGURE 14 I The cell is undergoing an interphase stage. II The chromosomes are long and threadlike. III A new combination of genes occurs on a chromosome . IV This stage exists at the apical meristem of a plant.
A B C D
I and II only II and III only III and IV only II, III and IV only
19. Figure 15 shows a cell division.
FIGURE 15 What is the stage of cell division and how many chromosomes are found in each daughter cell? Stage A B C D Metaphase Prophase Anaphase II Metaphase I Number of chromosomes 4 4 2 2
20. Which of the following is true about the Figure 16 below?
FIGURE 16 A. The cell division occurs at an ovule cell. B. Each daughter cell consists of two pairs of chromosomes. C. When the cell division is completed, 2 daughter cells are produced. D. All the chromosomes are identical.
21. Rearrange the phases of cell division shown in Figure 17 in the correct order.
FIGURE 17
A C
PSQR RQSP
B D
RSQP SQPR
22. Which of the following is produced from a meiotic division? A. B.
C.
D.
23. Which of the following shows the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis I II III IV Cell divides once Daughter cell is diploid Parent cell is diploid Four daughter cells are formed
Meiosis Cell divides twice Daughter cell is haploid. Parent cell is haploid Two daughter cells are formed.
A B C D
I and II only II and III only III and IV only II, III and IV only
24. Which of the followings are not true about cloning a sheep. I A heart cell and an egg cell are used. II The heart cell is fused with a fertilized egg. III The organisms produced have different genetic content from the parent. IV Clones can be produced in larger numbers but in a longer time. A I and II only B III and IV only C I, II and III only D II, III and IV only 25. Figure 18 shows the procedure to carry out a food test.
FIGURE 18 Identify the food sample being tested. A. Protein. B. Lipid. C. Starch. D. Sucrose.
26. Figure 19 shows the longitudinal section of a stomach.
FIGURE 19
Which of the following is the function of the ring of muscle X? A. Regulates the flow of enzyme into the stomach. B. Controls the amount of acid released in the stomach. C. Stops the food from flowing into the duodenum. D. Regulates the release of food from the stomach to the duodenum. 27. Figure 20 shows the apparatus set-up used in determining the energy value in a cashew nut.
FIGURE 20 The following reading were obtained from the experiment. Mass of cashew nut Volume of water used Initial temperature of water Final temperature 4.2 J g -1 oC -1]. A. 5.6 kJ. C. 5600 kJ. B. 13.0 kJ. D. 1333 kJ. 0.6 g 20.0 ml 40o C 80o C
Calculate the energy value of the cashew nut per gram. [ Specific heat capacity of water =
28. Figure 21 shows one of the systems in a human.
FIGURE 21
Which of the following is the function of the system shown? A. B. C. D. Converts complex molecules to simple molecules. Controls the body temperature. Fights infection. For reproduction.
29. Figure 22 shows the right proportion for the various classes of food in a food pyramid.
FIGURE 22 Which of the following shows the correct classes of food in the pyramid? 1 A Fats 2 Proteins 3 Carbohydrates 4 Vitamins and minerals B Carbohydrates Vitamins and minerals C Proteins Carbohydrates Fats Vitamins and minerals D Carbohydrates Fats Vitamins and minerals Proteins Proteins Fats
30. Figure 23 shows the apparatus used to test for the presence of starch in green leaf.
FIGURE 23
What is the purpose of heating the leaf in ethanol? A. To soften the leaf. B. To kill the bacteria on the leaf. C. To kill the cell and break down the cell wall. D. To dissolve and remove chlorophyll from the leaf.
31. Figure 24 shows an experiment carried out to determine the concentration of vitamin C in pineapple juice.
FIGURE 24 The data obtained were as shown above. If 2.5 ml of the pineapple juice was required to decolourise 1 ml of DCPIP, calculate the concentration of vitamin C in 100 ml of the juice. A. 2.5 mg / 100 ml. B. 4.0 mg / 100 ml. C. 40 mg / 100 ml. D. 250 mg / 100 ml.
32. Figure 25 shows the apparatus set-up to study the effects of macronutrient deficiencies in plant.
FIGURE 25 What is the purpose of connecting the apparatus to the air pump?
A. To eliminate the carbon dioxide in the glass jar. B. To provide aeration to the roots so that respiration can take place. C. To pump out excessive culture solution in the glass jar. D. To eliminate any insoluble particles in the solution.
33. Figure 26 shows the structure of a villus.
FIGURE 26 Which of the following are the nutrients found in P and Q? P A Fatty acids, glycerol and minerals B C Glucose and amino acids Mineral ions, glucose, amino acids and Vitamins B and C. D Glucose, amino acids and vitamins A, D, E and K Mineral ions and fat droplets Fatty acids, glycerol and vitamins A, D, E and K Fatty acids, glycerol and vitamins B and C. Q Glucose and amino acids
34.
Figure 27 shows a model of the small intestine.
FIGURE 27
After 30 minutes, the water in the beaker will show the presence of
A Glucose only. B Starch only. C Both glucose and starch. D Neither glucose nor starch.
35.
Figure 28 shows a series of enzyme action on a substrate.
FIGURE 28 What are T, U, V, W and X? T A B C D Enzyme Substrate Complex Products U Substrate Enzyme Substrate Enzyme V Complex Complex Products Substrate W Enzyme Enzyme Enzyme Complex X Products Products Enzyme Enzyme
36.
Figure 29 shows the set-up of the apparatus used in an experiment to determine the energy content in the cashew nut. At the start the boiling tube was filled with 20 ml of water at a temperature of 30 oC.
FIGURE 29 Using the data from the experiment, calculate the energy content of the cashew nut per gram. . [ Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g -1 oC -1].
A 149.0 J/g. B 218.4 J/g. C 6825 J/g. D 5420 J/g. 37. Figure 30 shows the effect of aquatic plants on the universal indicator in two different conditions. Both the tubes X and Y are exposed to the light.
FIGURE 30 What are the processes taking in tubes X and Y? Tube X Photosynthesis A B C D X X Respiration X X X Tube Y Photosynthesis Respiration X X
38.
Figure 31 shows an investigation to study a factor necessary for photosynthesis. A plant with variegated leaf of green and yellow part is used.
FIGURE 31 After being exposed to sunlight for half an hour, the leaf is tested for starch. The results is as shown in the figure above. What factor is being investigated?
A. B. C. D.
Water. Chlorophyll. Carbon dioxide. Sunlight.
39.
Figure 32 shows the structure of a chloroplast.
FIGURE 32 In which of the following structures does the light reaction occur during photosynthesis? A. B. C. D. 40. P Q R S
Figure 33 shows the effect of pH on the rate of activity.
FIGURE 33 The activity is catalysed by enzyme A. B. C. D. tripsin. amylase pepsin lipase
41.
Figure 34 shows part of the nephrone structure in the kidney.
FIGURE 34 What is the process at X? A Filtration B Ultrafiltration C Microfiltration D Macrofiltration
42.
Figure 35 shows the structure of a human nephron.
FIGURE 35 Which labelled parts show positive tests for the presence of chloride ions, proteins and reducing sugar? Chloride ions A B C D III IV V III Proteins II I I IV Reducing sugar I II IV I
43.
P is a gas, Q is a form of energy and R is a liquid absorbed by the plant shown in the Figure 19 below for photosynthesis. What are P, Q and R?
Figure 19
FIGURE 36 P A B C D Oxygen Carbon dioxide Nitrogen Oxygen Q Lightning Sunlight Lightning Sunlight R Alcohol Water Alcohol Water
44.
Figure 37 below shows a section through a leaf of a plant.
FIGURE 37 What plant is it likely to be? A. B. C. D. Cactus Hydrilla sp. Hibiscus Water lily
45 Anaerobic respiration occurs in A. cytoplasm of the cell. B. the nucleus. C. the mitochondrion. D. the golgi apparatus.
46. What are the products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells? I. Lactic acid.
II. Energy (38 ATP released. for each glucose). III. Carbon dioxide. IV. Ethanol. A. I and ll only. B. III and IV only. C. I, II and IV only. D. I, II, III and IV. 47 Which of the following are not the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Aerobic respiration I. II. III. Uses oxygen. Large amount of energy released. In plants and yeast, glucose Anaerobic respiration Does not use oxygen. Small amount of energy released. is No alcohol and carbon dioxide are
converted to alcohol and carbon produced in plants and yeast. dioxide. IV. Glucose is converted to lactic acid. No lactic acid is produced.
A. I and II only. B. III and IV only. C. I, II and IV only. D. I, II, III and IV.
48. Which of the following processes does not occur during inhalation? A. The diaphragm contracts and flattens. B. The ribcage is pulled upwards and outwards. C. Volume of thoracic cavity increases and air enters into the lungs. D. Internal intercostal muscles contract, external intercostal muscles relax. 49. In plants, mitotic division occurs actively in the. A meristematic tissue B epidermal tissue C parenchyma tissue D collenchymas tissue
50. Which of the following is the phase mitosis during which chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate from one another? A prophase B anaphase C metaphase D telophase
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Trial SPM Bio-P1 2018Dokumen21 halamanTrial SPM Bio-P1 2018CHIENG LEH ZING -Belum ada peringkat
- Q Bio 2012Dokumen24 halamanQ Bio 2012Visva VisvamBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Biologi Tingkatan 4Dokumen16 halamanSoalan Biologi Tingkatan 4Dekfa Miefa0% (1)
- Bio SPM 2003 P1Dokumen13 halamanBio SPM 2003 P1SeanBelum ada peringkat
- Biology: AnalysisDokumen24 halamanBiology: AnalysisChua HcBelum ada peringkat
- Biology SPM Modul A: Chapter 2, 3 & 4 (Form 4) GROUP IDokumen9 halamanBiology SPM Modul A: Chapter 2, 3 & 4 (Form 4) GROUP INorshamsiah SamsudinBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Question CompilationDokumen18 halamanBio Question CompilationGranpaXBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Mid Year Exam (Paper 1) With AnswersDokumen23 halamanBiology Mid Year Exam (Paper 1) With Answersayip_tajul100% (2)
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k1 BerjawapanDokumen11 halamanSPM 4551 2006 Biology k1 Berjawapanpss smk selandarBelum ada peringkat
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersDokumen21 halamanBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi Ting 4 Kertas 1Dokumen15 halamanBiologi Ting 4 Kertas 1Siti HajarBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 07 Midyear K1 (Asrama Penuh)Dokumen20 halamanBio 07 Midyear K1 (Asrama Penuh)Ferguson TehBelum ada peringkat
- Biology: AnalysisDokumen38 halamanBiology: AnalysisYiLingTengBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Bio f5 Sem 1 2015 Paper 1Dokumen19 halamanFinal Exam Bio f5 Sem 1 2015 Paper 1hmBelum ada peringkat
- Ujian Prestasi 2 / 2015 Biologi Tingkatan 4Dokumen16 halamanUjian Prestasi 2 / 2015 Biologi Tingkatan 4Fadhliana UzalliBelum ada peringkat
- Cylindrical Shaped Smooth Outer Membrane and Folded Inner MembraneDokumen26 halamanCylindrical Shaped Smooth Outer Membrane and Folded Inner MembranerhimalinyBelum ada peringkat
- Cape BIO Multiple Choice Unit IDokumen9 halamanCape BIO Multiple Choice Unit IRhondene WintBelum ada peringkat
- Percubaan Biologi Kertas 1 Melaka 2016Dokumen29 halamanPercubaan Biologi Kertas 1 Melaka 2016Siti Norliana JohariBelum ada peringkat
- Figure 1 Shows A Process Carried Out by An Amoeba SP.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Proses Yang Dijalankan Oleh Ameoba SPDokumen16 halamanFigure 1 Shows A Process Carried Out by An Amoeba SP.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Proses Yang Dijalankan Oleh Ameoba SPBrandi WebbBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bio P1Dokumen14 halamanQuestion Bio P1Rohana PaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 2Dokumen15 halamanBiology 2AlexanderGramtBelum ada peringkat
- Final Bio Form 4 LatestDokumen13 halamanFinal Bio Form 4 LatestdonkeykongusaBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi Modul 1 (P1 & P2)Dokumen175 halamanBiologi Modul 1 (P1 & P2)shazy7Belum ada peringkat
- Biologi Ting 4 ModulDokumen20 halamanBiologi Ting 4 ModulNoine AiniBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 Biology Form 5Dokumen11 halamanPaper 1 Biology Form 5GerlJerlBelum ada peringkat
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Pahang STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (1A4E8B7F) - 1 PDFDokumen0 halaman(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Pahang STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (1A4E8B7F) - 1 PDFChai Kah ChunBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Higher Biology TestDokumen46 halamanAdvanced Higher Biology TestcacaBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi SkemaDokumen38 halamanBiologi SkemaSanthiya MadhavanBelum ada peringkat
- Staar Biology Preparation Packet (Wo-Coversheet)Dokumen18 halamanStaar Biology Preparation Packet (Wo-Coversheet)api-262368188Belum ada peringkat
- Biology Paper 1 November 2003Dokumen15 halamanBiology Paper 1 November 2003Emmanuel MukweshaBelum ada peringkat
- Set 1 STPM Biology 2022 Kelantan (Soalan)Dokumen9 halamanSet 1 STPM Biology 2022 Kelantan (Soalan)Dharani RavindranBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Form 4 Paper 1Dokumen23 halamanBiology Form 4 Paper 1unieezz100% (2)
- Grade 11 Revision QuestionsDokumen12 halamanGrade 11 Revision QuestionsSaheed AbdulkarimBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi Kertas 1Dokumen29 halamanBiologi Kertas 1ain_senseiBelum ada peringkat
- Ulangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Dokumen99 halamanUlangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Norizan DarawiBelum ada peringkat
- Module Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2Dokumen9 halamanModule Trial STPM Biology Term 1 2022 Set 2RuoQi LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 Biology STPMDokumen11 halamanPaper 1 Biology STPMmiadiBelum ada peringkat
- SMK Batu Muda, 51100 KL Ujian 1 Tahun 2011 Biologi Tingkatan 4 Nama: . Tingkatan: . Answer All Questions in Section A, B and C. Section ADokumen9 halamanSMK Batu Muda, 51100 KL Ujian 1 Tahun 2011 Biologi Tingkatan 4 Nama: . Tingkatan: . Answer All Questions in Section A, B and C. Section Anurliyana_samsudinBelum ada peringkat
- SPM 4551 2005 Biology k1Dokumen10 halamanSPM 4551 2005 Biology k1pss smk selandarBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1Dokumen13 halamanScience Form 1Aziah Husain67% (3)
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Dokumen10 halamanBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockBelum ada peringkat
- Kertas 1Dokumen28 halamanKertas 1E-one Saw-dBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Biologi Kertas 1 2017Dokumen25 halamanBahan Biologi Kertas 1 2017nizampermaiBelum ada peringkat
- Up2 Sains 2015Dokumen16 halamanUp2 Sains 2015Fadhliana UzalliBelum ada peringkat
- Biology STPM Trials 2010 GombakDokumen43 halamanBiology STPM Trials 2010 GombakJarrett Jady Yap100% (3)
- (667209331) Question-Paper-1-Final-F4-Sbp-2011Dokumen39 halaman(667209331) Question-Paper-1-Final-F4-Sbp-2011Fadhliana UzalliBelum ada peringkat
- Penilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009Dokumen6 halamanPenilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009yantraksBelum ada peringkat
- Biology End-Of-Course Practice ExamDokumen23 halamanBiology End-Of-Course Practice ExamMacner JobeBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi Ting 4 Kertas 1 2013Dokumen12 halamanBiologi Ting 4 Kertas 1 2013Nurwahidah ZolkifleeBelum ada peringkat
- AH Biology All 2009Dokumen26 halamanAH Biology All 2009Xinyee XpBelum ada peringkat
- M.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)Dokumen11 halamanM.C Activity For 01,02 & 03 (Qurrat)sumizulfi786Belum ada peringkat
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualDari EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualBelum ada peringkat
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesDari EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Bioprocessing for Cell-Based TherapiesDari EverandBioprocessing for Cell-Based TherapiesChe J. ConnonBelum ada peringkat
- Zika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyDari EverandZika Virus and Diseases: From Molecular Biology to EpidemiologyBelum ada peringkat
- Bio - Cell Structure and Function QuizDokumen2 halamanBio - Cell Structure and Function QuizAditi AGRAWALBelum ada peringkat
- Plantgdb: A Resource For Comparative Plant GenomicsDokumen7 halamanPlantgdb: A Resource For Comparative Plant GenomicsCarlton KingBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Bank PDFDokumen202 halamanMCQ Bank PDFPublic Interest100% (1)
- Marocmolecule Review Worksheet - Answer KeyDokumen3 halamanMarocmolecule Review Worksheet - Answer KeyBecka RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- GST Gene Fusion System HandbookDokumen132 halamanGST Gene Fusion System HandbookDaniela Gonzalez CaceresBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Quiz MSDokumen30 halamanRevision Quiz MSPreya ShahBelum ada peringkat
- WO2015169811A2Dokumen141 halamanWO2015169811A2Muhamad Alif Bin Che NordinBelum ada peringkat
- Ligand ProteinDokumen4 halamanLigand ProteinOscar George LuBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Activity Worksheets Science 9 q1 Week 7Dokumen4 halamanLearning Activity Worksheets Science 9 q1 Week 7GINALYNROSE ROSIQUEBelum ada peringkat
- Class 12 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Mind MapDokumen1 halamanClass 12 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Mind Mapupgratesleet704Belum ada peringkat
- Hyprt Doc 214Dokumen3 halamanHyprt Doc 214api-490638499Belum ada peringkat
- Perspectives: Overcoming Challenges and Dogmas To Understand The Functions of PseudogenesDokumen11 halamanPerspectives: Overcoming Challenges and Dogmas To Understand The Functions of Pseudogenesİzem DevecioğluBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 - Lecture 3-CanvasDokumen42 halaman2018 - Lecture 3-CanvasAdam Bryant PoonawalaBelum ada peringkat
- Gene Therapy - PresentationDokumen19 halamanGene Therapy - PresentationElectRon ShajalBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Science 6th Edition Freeman Solutions Manual DownloadDokumen16 halamanBiological Science 6th Edition Freeman Solutions Manual DownloadAlyce Vargas100% (24)
- MuhjDokumen10 halamanMuhjtstBelum ada peringkat
- 106生物Dokumen16 halaman106生物德瑞克Belum ada peringkat
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced Studies College Department Gec StsDokumen4 halamanAsia Pacific College of Advanced Studies College Department Gec StsKen lopez100% (1)
- Inborn Errors of Protein MetabolismDokumen48 halamanInborn Errors of Protein MetabolismChudasama DhruvrajsinhBelum ada peringkat
- Physiological Stress in BroilersDokumen10 halamanPhysiological Stress in BroilersDr Manju PattanashettiBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 1.1 Cell OrganelleDokumen2 halamanWorksheet 1.1 Cell OrganelleCyndel TindoyBelum ada peringkat
- Bigdye Terminator V3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit: ProtocolDokumen72 halamanBigdye Terminator V3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit: Protocoliis faridahBelum ada peringkat
- Teknik Menjawab Soalan BiologiDokumen30 halamanTeknik Menjawab Soalan BiologiFaezah KamaluddinBelum ada peringkat
- Glycogen Storage Capacity and de Novo Iipogenesis During Massive Carbohydrate Overfeeding in ManDokumen9 halamanGlycogen Storage Capacity and de Novo Iipogenesis During Massive Carbohydrate Overfeeding in ManSalvio EspositoBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses: Viruses Are Entities ThatDokumen4 halamanViruses: Viruses Are Entities ThatMudit MisraBelum ada peringkat
- Science Grade 9Dokumen41 halamanScience Grade 9Neil Janas100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet - WK7Dokumen6 halamanCell Organelles Worksheet - WK7wobbleshopeBelum ada peringkat
- 5e5f1afd-ba20-4315-aa34-cba1006821f5Dokumen17 halaman5e5f1afd-ba20-4315-aa34-cba1006821f5layanhaliloBelum ada peringkat
- (Prof. Dr. Klaus Wolf (Auth.) ) Nonconventional Yea (B-Ok - Xyz)Dokumen630 halaman(Prof. Dr. Klaus Wolf (Auth.) ) Nonconventional Yea (B-Ok - Xyz)Muhammad HusseinBelum ada peringkat
- Ingram JME09 LCT EthiopiaDokumen11 halamanIngram JME09 LCT EthiopiaJosue BarralBelum ada peringkat