1 Comments & Whitespace: 2.1 Keywords
Diunggah oleh
qabalamuraliDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1 Comments & Whitespace: 2.1 Keywords
Diunggah oleh
qabalamuraliHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CSCI 150 Fall 2011
Java Syntax #1
The following notes are meant to be a quick cheat sheet for Java. It is not meant to be a means on its own to learn Java or this course. For that you should look at your textbook and the sample code from class. Furthermore, this is not an exhaustive listing of all of Javas capabilities, as we still have many a fundamental concept to cover in this course, and in other courses down the road. These notes will be updated as we learn more syntax. Enjoy!
Comments & Whitespace
blanks and tabs ignored by Java compiler 2 types of comments: a) // This is a comment b) /* This is also a comment */ /* /* I can be nested */ */ /* And I can span multiple lines */
2
2.1
Tokens
Keywords
These are words reserved in Java for special use, so you cannot use them as your own identiers (variable, method, & class names). They are listed on p17 of your text, but a sampling is: boolean, char, class, const, double, else, final, float, for, if, import, int, long, new, public, return, static, throws, void, while
2.2
Identiers
is a name for a variable/class/method, i.e. myVar, booYA, IHateArtichokesAndOlives,. . . must begin with a letter, underscore (_), or currency symbol ($) may contain any number of digits, letters, underscores, or currency symbols after the rst character, i.e. _83yy$z Java is case-sensitive, i.e. IHateArtichokes is dierent from ihateartichokes must not use the keywords as they already have special meaning convention: class names should begin with an uppercase letter, as in MyClass. Variable and method names should begin with a lowercase letter, as in main. Class constants should be all uppercase, as in WIDTH.
CSCI 150 Java Syntax #1
2.3
Primitive Data Types
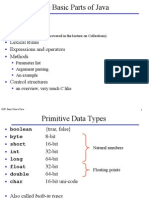
there are eight primitive types: boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float, double we typically use boolean, int, double, char boolean: true, false (no 0s and 1s allowed) char: a, b, c, . . . (any 16-bit unicode character) can convert chars to ints, and vice-versa ex. char whatAmI = 97; // This is the characters a! Ooooo use actual character, i.e. char = X; or, use escape characters: \t (tab), \n (newline), \" (), \ (), \\ ( \) int: 32 bits. Ranges from -2147483648 to 2147483647 double 64 bits. use decimal point i.e., .10, 1.0, 1.0
2.4
Operators
increment / decrement ex. x = x+1 could be written as x++ or ++x ex. artichoke = 1; baloney = artichoke++; baloney gets the current value of artichoke (i.e. 1), then artichoke increments to 2 modulus (%) (the remainder operator) ex. 24 % 5 gives 4 integer division ex. 10/4 gives 2, not 2.5
2.5
Punctuation
use ( ) for expressions and methods use ; for ending statements use { } for blocks of statements
Statements
block: any collection of statements inside { } expression: assignments, increment / decrement, method calls, object creation declaration: must tell Java about a variable before using it
CSCI 150 Java Syntax #1 ex. int a; // Declaring the variable a to be an int a = 5; // Using the variable a assignment: to store a value in a variable method call for-loops ex. for( int i=1; i < 10; i ++ ) { System.out.println( i ); }
Methods
syntax: public static <return-type> <method-name>( arguments ) { <statements> } ex. public int squareMe( int i ) { return (i * i); } return type can be void (returns no value), or any type. arguments are of the form <type> <varname>, <type> <varname>, ..., or no arguments at all if the method parameters are primitive types then the value of the actual parameter is copied into the formal parameter, that is, the method cannot change the value of an actual parameter overloading: writing multiple methods with the same name but dierent signature (i.e. dierent order of arguments, types of arguments, number of arguments, or any combination of the three)
Strings and Characters
strings are reference types (use String class) string literal: "yodelayheehoo" is an instance of class String empty string: "" concatenation is easy: ex. "you make me complete" + "ly miserable" "you make me completely miserable" even concatenating non-strings is easy: ex. "mumbo number " + 5 "mumbo number 5" must put String on one line. One!
CSCI 150 Java Syntax #1
6
6.1
Useful Classes
The Math Class
contains functions like abs, sqrt, pow, sin... contains constants like Math.PI, Math.E,...
6.2
The Random Class
need to add import java.util.*; at top of le methods functions like nextInt(n),...
6.3
The Scanner Class
need to add import java.util.*; at top o le can construct for the console or from a File, or even from a String ex. Scanner input = new Scanner( new File( "input.txt" ) ); Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); Scanner console = new Scanner( "its just string" ); method nextLine(), nextInt(), nextDouble(),...
6.4
The File Class
need to add import java.io.*; at top of le
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Unit 4 - Java Basics & Usage of Classes, Objects & InheritanceDokumen149 halamanUnit 4 - Java Basics & Usage of Classes, Objects & InheritanceAsmatullah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Java R19 - Unit-1Dokumen45 halamanJava R19 - Unit-1Lalit GautamBelum ada peringkat
- Python Notes PDFDokumen7 halamanPython Notes PDFhectorcflores1100% (1)
- Java BasicsDokumen85 halamanJava Basicsvedicsoft100% (19)
- BAP - Lec2Data Types and VariableDokumen51 halamanBAP - Lec2Data Types and VariableEdward MulondoBelum ada peringkat
- Lec4-Identifiers and VariablesDokumen33 halamanLec4-Identifiers and Variablesin time chanalBelum ada peringkat
- Datatypes and Variables JavaDokumen28 halamanDatatypes and Variables JavaGolmei ShaheamBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Java Language and OOP Part IDokumen47 halaman01 Java Language and OOP Part IHariChristianBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 1Dokumen32 halamanCHP 1Umarfarooque MursalBelum ada peringkat
- JavaDokumen131 halamanJavaAnish GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- JDK & Simple ProgramDokumen14 halamanJDK & Simple ProgramkarthikeyanBelum ada peringkat
- Session02-Learning The Java LanguageDokumen45 halamanSession02-Learning The Java Languagetuan nguyen anhBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 10 - Javascript Basics 2Dokumen21 halamanLecture 10 - Javascript Basics 2ahsangulzar009Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Starting JavaProgrammingDokumen69 halaman2 Starting JavaProgrammingSurya Dinuz EskomBelum ada peringkat
- Java TokensDokumen20 halamanJava TokensDiya Dey0% (1)
- Tutorial 2 - Syntax & Grammar: Lexical StructureDokumen8 halamanTutorial 2 - Syntax & Grammar: Lexical Structurejanesan_14Belum ada peringkat
- Unit-Ii Programming ConstructsDokumen70 halamanUnit-Ii Programming ConstructsAnna University ExamBelum ada peringkat
- Java Syntax - Guide To Java Basics: What Does Syntax Mean?Dokumen34 halamanJava Syntax - Guide To Java Basics: What Does Syntax Mean?Sofia RehanBelum ada peringkat
- Object-Oriented Programming: Computer Science Year IIDokumen34 halamanObject-Oriented Programming: Computer Science Year IIGebreigziabher M. AbBelum ada peringkat
- Progamming With Java - Lecture NotesDokumen170 halamanProgamming With Java - Lecture NotesAbdulai SualisuBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Fundementals - Numeric DataDokumen45 halaman03 Fundementals - Numeric DataflwahalmBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 OOPDokumen70 halamanChapter 2 OOPeyob getachewBelum ada peringkat
- JAVA 2nd UNIt (Chapter-1)Dokumen37 halamanJAVA 2nd UNIt (Chapter-1)TAภaу ЎALLaмᎥlliBelum ada peringkat
- SCJP Model and TipsDokumen2 halamanSCJP Model and Tipsseenu100% (2)
- ch02 PDFDokumen119 halamanch02 PDFoucht79Belum ada peringkat
- 1: Control Structures: Lab 02 Control Structures and Java Class Libraries ObjectivesDokumen10 halaman1: Control Structures: Lab 02 Control Structures and Java Class Libraries ObjectivesSonu SachdevBelum ada peringkat
- Java Programming Language Notes Set 1Dokumen42 halamanJava Programming Language Notes Set 1Brian MurithiBelum ada peringkat
- Part7 IntroductiontoJavaDokumen57 halamanPart7 IntroductiontoJavaChu ChilliesBelum ada peringkat
- The Basic Parts of Java: Data TypesDokumen48 halamanThe Basic Parts of Java: Data TypesShaswata TripathyBelum ada peringkat
- COMP1AL Final NotesDokumen4 halamanCOMP1AL Final NotesJoyce DacanayBelum ada peringkat
- Veena Antony Asst - Professor Bca Ct&Ism ST - Teresa's College (Autonomous)Dokumen18 halamanVeena Antony Asst - Professor Bca Ct&Ism ST - Teresa's College (Autonomous)DanaaSanaaBelum ada peringkat
- CPE402 Chapter3 Programming Language Fundamentals - FinalDokumen68 halamanCPE402 Chapter3 Programming Language Fundamentals - FinalFrancis Marc AlcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- Java Unit 1Dokumen47 halamanJava Unit 1Seetharam RBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To JAVA: - Platform Independent - SecuredDokumen29 halamanIntroduction To JAVA: - Platform Independent - SecuredHarinath Reddy NBelum ada peringkat
- JavaDokumen265 halamanJavaOptimus PrimeBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Java Programming: Week 2Dokumen56 halamanIntroduction To Java Programming: Week 2Shabana TahirBelum ada peringkat
- Java Programming Unit-IIDokumen29 halamanJava Programming Unit-IIwimir16623Belum ada peringkat
- STS Cat-1Dokumen490 halamanSTS Cat-1Sri AdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 3 - Numerical - DataAndExpression-part1Dokumen80 halamanWeek 3 - Numerical - DataAndExpression-part1苦労Belum ada peringkat
- Week 1Dokumen18 halamanWeek 1AlexeiBelum ada peringkat
- C Programming Tutorial - Part I: CS 537 - Introduction To Operating SystemsDokumen28 halamanC Programming Tutorial - Part I: CS 537 - Introduction To Operating SystemsVanathi PriyadharshiniBelum ada peringkat
- JAVADokumen6 halamanJAVAKeshav PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Week 011 - 012-Presentation Java ArchitectureDokumen24 halamanWeek 011 - 012-Presentation Java ArchitecturePachi PlumsBelum ada peringkat
- Java FundamentalsDokumen28 halamanJava FundamentalsRaymund TarragoBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Programming Structures in JavaDokumen23 halamanFundamental Programming Structures in JavaVinayKumarSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Java Tutorial: Write Once, Run AnywhereDokumen76 halamanJava Tutorial: Write Once, Run AnywhereJay SanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To JavaDokumen91 halamanIntroduction To JavaCiberaj PalaniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- Oops Using JavaDokumen436 halamanOops Using Java727821TUIT010 ARAVIND.SBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 11Dokumen41 halamanLecture 11myturtle game01Belum ada peringkat
- C and OOPsDokumen220 halamanC and OOPsTeodor RotaruBelum ada peringkat
- Java LectureDokumen55 halamanJava LectureJoshua SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Lect 3 - 4 - 5Dokumen62 halamanLect 3 - 4 - 5yonas asratBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Java PP1Dokumen26 halamanIntroduction To Java PP1Yosef ViniskyBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Python ProgrammingDokumen135 halamanFundamentals of Python ProgrammingVenu GadadasuBelum ada peringkat
- Bsaic JavaDokumen10 halamanBsaic Javayugal jhaBelum ada peringkat
- Java NotesDokumen138 halamanJava NotesRam Deepak100% (1)
- Unit-1 OopsDokumen67 halamanUnit-1 OopsSantanu AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Java: Best Practices to Programming Code with Java: Java Computer Programming, #3Dari EverandJava: Best Practices to Programming Code with Java: Java Computer Programming, #3Belum ada peringkat
- Agile Automation DetailedDokumen24 halamanAgile Automation DetailedqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- Software Testing Estimation TechniquesDokumen6 halamanSoftware Testing Estimation TechniquesqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- Junit Suite TestDokumen3 halamanJunit Suite TestqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- SQL Joins and ViewsDokumen9 halamanSQL Joins and ViewsChinna100% (2)
- Improving Software QualityDokumen6 halamanImproving Software QualityqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE829 Test Plan Format SampleDokumen17 halamanIEEE829 Test Plan Format Samplealakh400Belum ada peringkat
- Integration-And System Testing: O O S CDokumen32 halamanIntegration-And System Testing: O O S CqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- SQLDokumen58 halamanSQLqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- The Product Quality Measures:: 1. Customer Satisfaction IndexDokumen5 halamanThe Product Quality Measures:: 1. Customer Satisfaction IndexqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- What Is BVTDokumen2 halamanWhat Is BVTqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- BI Testing Tutorial V1.0Dokumen29 halamanBI Testing Tutorial V1.0qabalamurali100% (1)
- The Different Stages in Software Test Life CycleDokumen4 halamanThe Different Stages in Software Test Life CycleqabalamuraliBelum ada peringkat
- ASCII Stands For American Standard Code For Information InterchangeDokumen3 halamanASCII Stands For American Standard Code For Information Interchangebad_zurbicBelum ada peringkat
- GPS Tracker Communication - Protocol V1 (1) .51Dokumen36 halamanGPS Tracker Communication - Protocol V1 (1) .51alaska112Belum ada peringkat
- CX ONE V2.0 FuncionesDokumen5 halamanCX ONE V2.0 FuncionesOmar CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics by Tarik Al ShemmeriDokumen23 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics by Tarik Al ShemmerivijayaraghavnBelum ada peringkat
- Java SE 8 Fundamentals: Edition 1.0 June 2014 D87051Dokumen102 halamanJava SE 8 Fundamentals: Edition 1.0 June 2014 D87051mehmet göçerBelum ada peringkat
- CCS108 Week 2 Laboratory ExerciseDokumen3 halamanCCS108 Week 2 Laboratory ExerciseRey Grimaldo RongavillaBelum ada peringkat
- Atlanta Dynamo User Group Excel ExampleDokumen15 halamanAtlanta Dynamo User Group Excel ExampleWandersonBelum ada peringkat
- Data DictionaryDokumen35 halamanData DictionaryArchana AshokBelum ada peringkat
- Moto - GSI.SDK Manual PublicDokumen72 halamanMoto - GSI.SDK Manual PublicMihail AvramovBelum ada peringkat
- Compare Strings (C# Programming Guide)Dokumen5 halamanCompare Strings (C# Programming Guide)Kyle DalyBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Fsa To NLPDokumen21 halamanApplication of Fsa To NLPAnimesh ShawBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter No - 1: Overview of Python and Data Structures: Faculty Name: Vishal Parikh, Alpa RupalaDokumen6 halamanChapter No - 1: Overview of Python and Data Structures: Faculty Name: Vishal Parikh, Alpa RupalafesfBelum ada peringkat
- Apostila Crystal 2Dokumen482 halamanApostila Crystal 2MaurynhoBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment4 SolutionDokumen3 halamanAssignment4 SolutionzarrarBelum ada peringkat
- Global Location Number (GLN) Implementation Guide: Executive SummaryDokumen13 halamanGlobal Location Number (GLN) Implementation Guide: Executive SummaryGreg AdriaanseBelum ada peringkat
- Rave Dev Guide 5Dokumen320 halamanRave Dev Guide 5sandrolp_15Belum ada peringkat
- 01 Strings FdsfdsDokumen73 halaman01 Strings FdsfdsgfdgfdvbcBelum ada peringkat
- SDK Manual For ZK Devices VB C PDFDokumen92 halamanSDK Manual For ZK Devices VB C PDFJose Luis Rodriguez100% (1)
- Competitive Programming Network - 2nd ActivityDokumen15 halamanCompetitive Programming Network - 2nd ActivityMarice Sinisterra Institucion EducativaBelum ada peringkat
- Ab Initio Training Part 2Dokumen105 halamanAb Initio Training Part 2abhinavakBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Powerful Python One-Liners You Should Know: 1-Typecasting of All Items in A ListDokumen3 halaman5 Powerful Python One-Liners You Should Know: 1-Typecasting of All Items in A ListMaithili KarandeBelum ada peringkat
- Honeywell Vista 21ip Programming GuideDokumen24 halamanHoneywell Vista 21ip Programming GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions For Class 12 Computer Science (Python) - Review of PythonDokumen31 halamanImportant Questions For Class 12 Computer Science (Python) - Review of PythonHelloBelum ada peringkat
- Strlcpy SlidesDokumen14 halamanStrlcpy SlidespostscriptBelum ada peringkat
- Regex Cheat SheetDokumen9 halamanRegex Cheat SheetDennis HuigenBelum ada peringkat
- ProblemSet LoopStatementsDokumen11 halamanProblemSet LoopStatementsRana ZuhaibBelum ada peringkat
- Use The Following Array When Answering Questions 1 Through 4Dokumen5 halamanUse The Following Array When Answering Questions 1 Through 4nooraBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questions of Pointers and Strings: PointerDokumen2 halamanPractice Questions of Pointers and Strings: PointerManishaBelum ada peringkat
- TSM 1.0 - User Manual - Excerpt TERRANOVA Smart Metering LibrariesDokumen37 halamanTSM 1.0 - User Manual - Excerpt TERRANOVA Smart Metering LibrariesKingkulkBelum ada peringkat
- Akai Z4/Z8 and MPC 400 Sysex SpecificationsDokumen58 halamanAkai Z4/Z8 and MPC 400 Sysex SpecificationsSaverio PaiellaBelum ada peringkat