Exam 2097 2005
Diunggah oleh
Kashka IraniJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Exam 2097 2005
Diunggah oleh
Kashka IraniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
MID YEAR EXAMINATION 2005
PORTFOLIO: SCHOOL OF: COURSE CODE: COURSE TITLE: DATE: TIME: DURATION OF EXAMINATION: Reading: Working: EXAMINATION PAPER DETAILS:
Science, Engineering & Technology Electrical and Computer Engineering EEET 2097 Electronic Circuits 14 June 2005 1:45pm 5:00pm
15 minutes 3 hours
Number of pages (including cover sheet): Number of questions: Number of questions to be attempted: Total points available: INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
All working must be done in this exam book. Use of any electronic calculator is permitted. Text books, notes, assignments are allowed. If necessary write on the back the page. This exam contributes 50% to the overall subject assessment. Before submitting this paper please complete the following box:
13 6 6 100
Candidates Family Name:
Candidates Given Name:
Candidates Address:
Candidates Student No.:
Candidates signature:
Question no.
Total
Marks
Document: EEET2097_05/CC Save Date: 13-05-2005 Page: 1/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Question 1 (5+4+6+3 points): A) If RE=9.4 k, Vcc=10 V, VEE=10 V (-VEE=-10V), and Vbe for both transistors is equal to 0.6 V, calculate emitter current for each transistor. What is the bias voltage at emitter (VE) and base (VB) of each transistor? B) If Rc1=Rc2=10 k, what is collector voltage? What is the maximum voltage swing in output (neglect the saturation voltage)? C) Calculate the differential mode and common mode gains, if h fe==200 for each transistor. Consider VT=25 mV. D) If vin1 = 10cos(t) mV and vin2 = 10cos(t) mV, find an expression for vout.
Vcc
Rc1
Rc2
Vout
Vin11 +
1
Vin22
RE -VEE
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 2/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 3/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
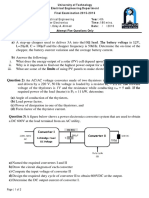
Question 2 (4+2+4+6 points): A regulated power supply is shown below. The Zener diode voltage is V z= 4.3 V. A) if RA=RB=10 k calculate the output Voltage (Vout) B) RL=10 . Calculate the load current. If of the transistor Q1, is 100 calculate its base current IB. C) Assume zener diode current is 10 mA and Vinput is 20 V. Calculate the value of R. D) By choosing a proper RB (a variable resistor (RV)+ a constant resistor (RC), RV+RC=RB) make a variable voltage regulator that can change from 6V to 15 V. Calculate RV and RC. RA=10 k.
Q1 + R RA +
Vinput
Vout RL
Zener Diode
RB
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 4/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 5/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Question 3 (8+8 points): A) Calculate the bias point for the circuit shown. Determine voltages at all nodes and currents (label the nodes and currents in the circuit below) through the device (Vt=1 V, kn(W/L)=0.2 mA/V2, RG=5 G, RD=2 k and VDD=5 V). The coupling capacitor is large. B) Draw the small signal equivalent circuit. Calculate devices trans-conductance (gm) and the amplifiers voltage gain.
VDD=10 V
RG=5G
RD=5 k
+
Vou
t
Vin
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 6/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 7/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Question 4 (3+3+4+4 points): For the step-up (boost) switching power supply circuit shown find: A) The steady state output voltage (Vout). B) If the average output current is 0.5 A calculate the load resistance R L. C) Calculate the peak-to-peak change in the inductor current as well as the minimum and maximum currents in the inductor. D) If the capacitor is 1000 F calculate the peakto-peak value of the output voltage ripple. T1=20 sec, T= 40 sec, Vin=10 V, L= 2 mH.
VSW
L=2 mH
Diode
T1
T2 T
Vout RL
Vin=10 V
VSW
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 8/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 9/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Question 5 (2+3+3+5+2+4 points): For a pn junction diode with the following parameters: NA=1017/cm3, ND=1016/cm3 ni= 1010 /cm3, VT=25mV A=0.010.01 cm2=10-4 cm2 (diodes cross section) Dp= 10 cm2/V, Dn= 20 cm2/V Lp= 210-3 cm, Ln=10-3 cm A) Calculate the diode forward bias voltage (barrier voltage). B) Calculate the saturation current, IS. C) If the relation between the electron current and the hole current is In=0.1195IP and IF (diodes forward current) is equal to 0.1 mA, calculate In and IP. D) Calculate n and p and then from In and IP calculate T. E) Calculate the diffusion capacitance (Cd) F) If for the circuit shown, the forward bias voltage is V 0=0.895 V (instead of 0.7 V for normal silicon type diodes), and if the junction capacitance is 10 pF calculate the delay time needed to switch on the diode. Input voltage (V in) is changing from -10 V to 10 V and the diode has been in the switch-off mode for a long time. Rs=1 k.
RS
Vin
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 10/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 11/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Question 6 (12+5 points): A) The Figures below show a simple class-A power amplifier and the corresponding load current (iC). i) Find the dc bias current of the transistor. ii) Find the amplitude of the signal current through the load. iii) Find the conversion efficiency of the amplifier. iv) What is the theoretical maximum efficiency that can be obtained from this circuit? Why is the calculated efficiency in iii) far less than the theoretical maximum?
Rload 100
iC iC
100mA
Large
200mA
time
B) A VBE multiplier is used to bias a class-AB push-pull power output stage as shown. Find the bias current I. Assume is large and |VBE| = 0.7V when ON. You do not need other component values.
I 3k 1k 1 1 I
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 12/13
RMIT University 2005
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Document: EEET2097_05/CC
Save Date: 13-05-2005
Page: 13/13
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ECE 1231 Sem 1 04/05Dokumen6 halamanECE 1231 Sem 1 04/05Ikram RazakBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Electronics Lab Manual-10esl67Dokumen61 halamanAnalog Electronics Lab Manual-10esl67manojmanojsarmaBelum ada peringkat
- Convertidores DC DCDokumen4 halamanConvertidores DC DCDawn OsborneBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 3Dokumen2 halamanSheet 3Nano GomeshBelum ada peringkat
- Hyuga SimulationDokumen8 halamanHyuga SimulationJimmy MachariaBelum ada peringkat
- EEE - 3207 - IA - Mid - 203 - For Elms - 2Dokumen1 halamanEEE - 3207 - IA - Mid - 203 - For Elms - 2Jobayer AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- NIT Rourkela ECE Dept B.Tech 1st Sem Basic Electronics Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDokumen3 halamanNIT Rourkela ECE Dept B.Tech 1st Sem Basic Electronics Mid-Term Exam QuestionsYASHBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Dokumen9 halamanFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Fatihah Aina100% (1)
- Engineering Department: RESIT FINAL ASSIGNMENT: Semester-2, 2019-20 EEPW2251: Electrical Power TechnologyDokumen3 halamanEngineering Department: RESIT FINAL ASSIGNMENT: Semester-2, 2019-20 EEPW2251: Electrical Power TechnologyFarooq KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics II Final Exam QuestionsDokumen26 halamanElectronics II Final Exam QuestionsRazan AlyahyaBelum ada peringkat
- ECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDokumen20 halamanECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineeringsenpai_mendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Bee4223 - Power Electronics & Drives SysDokumen9 halamanBee4223 - Power Electronics & Drives Sysdinie90Belum ada peringkat
- AE 1 EQ by Faiz SirDokumen16 halamanAE 1 EQ by Faiz SirFaiz RangariBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Electronics First Exam Fall 2023Dokumen14 halamanDigital Electronics First Exam Fall 2023Faizan alamBelum ada peringkat
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDokumen7 halamanENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Circuits & Logic Design Lab ManualDokumen83 halamanElectronic Circuits & Logic Design Lab ManualsunandaalurBelum ada peringkat
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Dokumen9 halamanFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaBelum ada peringkat
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Dokumen28 halamanIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyBelum ada peringkat
- 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Final ExaminationDokumen13 halaman6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits: Final ExaminationhelpsatyaBelum ada peringkat
- Graphic Era University: Switchgear & Protection. of Pwr. Sys. Lectures BookDokumen108 halamanGraphic Era University: Switchgear & Protection. of Pwr. Sys. Lectures BookdoggaraviBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics Circuit Design LabDokumen34 halamanElectronics Circuit Design Labsrvdhar100% (1)
- ESE122Dokumen12 halamanESE122Shahrul Shafiz HaridanBelum ada peringkat
- ExercisesDokumen2 halamanExercisesAnalyn ZuluetaBelum ada peringkat
- 06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabDokumen70 halaman06ESL37 - Analog Electronics LabqwertyjklfghBelum ada peringkat
- Review 1 ManuvalDokumen25 halamanReview 1 ManuvalvikasBelum ada peringkat
- ELEG 220 01 and 02 SP15 Final ExamDokumen18 halamanELEG 220 01 and 02 SP15 Final ExamSaied Aly SalamahBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic System Design Practical JournalDokumen48 halamanElectronic System Design Practical JournalSushant SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALDokumen70 halaman06ESL37 Analog Electronics Lab MANUALSan AngadiBelum ada peringkat
- Edc 8Dokumen9 halamanEdc 829viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- Lab 1a Performance of A Half Wave and Single Bridge RectifierDokumen6 halamanLab 1a Performance of A Half Wave and Single Bridge RectifierMujtaba FarrukhBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Integrated Circuits (Lic'S) Laboratory Manual: Iii / Iv B.E (Ece), I - SemesterDokumen52 halamanLinear Integrated Circuits (Lic'S) Laboratory Manual: Iii / Iv B.E (Ece), I - SemesterArun JyothiBelum ada peringkat
- COMM 471 - F14 - Midterm - Makeup - Solutions PDFDokumen5 halamanCOMM 471 - F14 - Midterm - Makeup - Solutions PDFSandy ZakariaBelum ada peringkat
- ch02 AnalogMultiplierDokumen32 halamanch02 AnalogMultipliergamaladdiniBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Exam ECE 1312 Question S2 1011Dokumen11 halamanMid Exam ECE 1312 Question S2 1011Fatihah AinaBelum ada peringkat
- ELEG 220 (Fall 2014) Final Exam: Title: Electric Circuits Score: / 140 /35Dokumen18 halamanELEG 220 (Fall 2014) Final Exam: Title: Electric Circuits Score: / 140 /35Saied Aly SalamahBelum ada peringkat
- Phy PPDokumen5 halamanPhy PPKelvin BrianBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Devices and Integrated Circuits - Operational Amplifier - SOLVED PROBLEMS - Safari Books OnlineDokumen34 halamanElectronic Devices and Integrated Circuits - Operational Amplifier - SOLVED PROBLEMS - Safari Books Onlinemuhaned190100% (1)
- Os PB1 Ee QuestionnaireDokumen16 halamanOs PB1 Ee Questionnairejohnmichaelpilota51Belum ada peringkat
- Ac Lab CompleteDokumen50 halamanAc Lab CompletePraveen ChittiBelum ada peringkat
- Objective Type Question and AnsDokumen13 halamanObjective Type Question and AnsAl FathahBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electronics by BakshiDokumen226 halamanBasic Electronics by Bakshiniju86% (7)
- DMRC Junior Engineer Electrical Question Papers 2012 Sample PaperDokumen4 halamanDMRC Junior Engineer Electrical Question Papers 2012 Sample PaperParamjeet Singh50% (2)
- Electrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFDokumen7 halamanElectrical-Engineering-Examination Syllabus PDFJoseph JoeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Engineering Examination PDFDokumen7 halamanElectrical Engineering Examination PDFJustine James AdonaBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of A 9V Power SupplyDokumen7 halamanConstruction of A 9V Power SupplyCarroll SarmejeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialDokumen26 halamanLecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialGaffar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2352484722009854 MainDokumen8 halaman1 s2.0 S2352484722009854 Mainmasum.sBelum ada peringkat
- RC Differentiator & IntegratorDokumen6 halamanRC Differentiator & IntegratorMatt Imri100% (1)
- Electronics Engineering DepartmentDokumen4 halamanElectronics Engineering DepartmentRainwin TamayoBelum ada peringkat
- AEC LabManualDokumen30 halamanAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalBelum ada peringkat
- ED REPORT (GRP 3)Dokumen9 halamanED REPORT (GRP 3)Shreyas MarudwarBelum ada peringkat
- ECD Lab EEC 752Dokumen17 halamanECD Lab EEC 752juhi99360% (5)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDari EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisDari EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisBelum ada peringkat
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysDari EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to DisplaysBelum ada peringkat
- Wideband Dipole Antenna With Inter-Digital CapacitorDokumen4 halamanWideband Dipole Antenna With Inter-Digital CapacitorKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Confirmation of Candidature RequirementsDokumen2 halamanConfirmation of Candidature RequirementsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Table of ContentsDokumen1 halamanTable of ContentsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- EEET2097 Lecture 11 2013Dokumen0 halamanEEET2097 Lecture 11 2013Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis PresentationsDokumen112 halamanThesis PresentationsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Vostro-3700 Service Manual En-UsDokumen77 halamanVostro-3700 Service Manual En-UsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Table of ContentsDokumen1 halamanTable of ContentsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Vostro-3700 Service Manual En-UsDokumen77 halamanVostro-3700 Service Manual En-UsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- 2.4 GHZ Plaster Antennas For Health MonitoringDokumen5 halaman2.4 GHZ Plaster Antennas For Health MonitoringKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- MOS BJT ComparisonDokumen2 halamanMOS BJT ComparisonKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- EEET2334 35 Sample MST 2013Dokumen8 halamanEEET2334 35 Sample MST 2013Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- VA From SimulationDokumen1 halamanVA From SimulationKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Fig. 6.2 Different Modes of Operation of The Differential Pair: (A) The Differential Pair With A Common-Mode Input Signal VDokumen23 halamanFig. 6.2 Different Modes of Operation of The Differential Pair: (A) The Differential Pair With A Common-Mode Input Signal VKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- 3.4 - BJT Differential Amplifiers: ObjectiveDokumen14 halaman3.4 - BJT Differential Amplifiers: ObjectiveVanessa HensleyBelum ada peringkat
- QNX Neutrino Rtos FaqsDokumen6 halamanQNX Neutrino Rtos FaqsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 8 PDFDokumen27 halamanLecture 8 PDFKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6Dokumen39 halamanLecture 6Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Install LogDokumen25 halamanInstall LogKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- VAC From Simulation VDC 400Dokumen1 halamanVAC From Simulation VDC 400Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- 07-28-13 Solidworks Pins 5Dokumen1 halaman07-28-13 Solidworks Pins 5Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- EEET 2097 - Current Sources & MirrorsDokumen4 halamanEEET 2097 - Current Sources & MirrorsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Pin2 - 4 08 13Dokumen1 halamanPin2 - 4 08 13Kashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- QNX Neutrino Rtos FaqsDokumen6 halamanQNX Neutrino Rtos FaqsKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Math expressions guide: superscripts, subscripts, Greek symbols & moreDokumen1 halamanMath expressions guide: superscripts, subscripts, Greek symbols & moreKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Pore Region of TRPV3 Ion Channel Specifically Required for Heat ActivationDokumen15 halamanPore Region of TRPV3 Ion Channel Specifically Required for Heat ActivationKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- Install LogDokumen6 halamanInstall LogKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- CrtlogDokumen1 halamanCrtlogKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- In 2 Science Lead RecordDokumen2 halamanIn 2 Science Lead RecordKashka IraniBelum ada peringkat
- A Steganography Intrusion Detection SystemDokumen21 halamanA Steganography Intrusion Detection SystemjamessomBelum ada peringkat
- ResumeDokumen2 halamanResumekoduruabhinavBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Spider SilkDokumen9 halamanProperties of Spider SilkArifah PujiatiBelum ada peringkat
- Special Core AnalysisDokumen21 halamanSpecial Core AnalysisMuizzuddin Shidqi As-Sa'diBelum ada peringkat
- HLP-A Series Operating ManualDokumen117 halamanHLP-A Series Operating ManualComunicaciones RogeBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Science Grade 8 Term-IDokumen48 halamanIntegrated Science Grade 8 Term-Ifredmbuvi1Belum ada peringkat
- Vernacular HungarianDokumen51 halamanVernacular HungariandeltagBelum ada peringkat
- RFQ 3894-21Dokumen9 halamanRFQ 3894-21ZewduErkyhunBelum ada peringkat
- GeForce RTX 3090 GA102 GF PG136-A03 Rev BDokumen67 halamanGeForce RTX 3090 GA102 GF PG136-A03 Rev BSe SavBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 1 - RTL Part1Dokumen2 halamanSheet 1 - RTL Part1sad birdBelum ada peringkat
- Business EnglishDokumen100 halamanBusiness Englishanonymous9196806Belum ada peringkat
- PLG Script For Prison LifeDokumen7 halamanPLG Script For Prison LifeXxcode 1Belum ada peringkat
- Metaltech-Automex-2019-Post-Show-Report CompressedDokumen9 halamanMetaltech-Automex-2019-Post-Show-Report Compressedapi-480638034Belum ada peringkat
- DS0000087 - Programmer's Manual - of X-LIB Software LibraryDokumen175 halamanDS0000087 - Programmer's Manual - of X-LIB Software LibraryAmir Nazem zadeh100% (1)
- Regal Raptor DAYTONA Euro IV Owner ManualDokumen25 halamanRegal Raptor DAYTONA Euro IV Owner ManualKrzysztof Jakiś50% (2)
- UM4730 Integration GuideDokumen0 halamanUM4730 Integration Guidenarse8488Belum ada peringkat
- Wimax For DummiesDokumen35 halamanWimax For DummiesMichael John MjattaBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar ApplicationsDokumen25 halamanStudy of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar Applicationsk rajendraBelum ada peringkat
- Removing and Installing Underground Storage TanksDokumen7 halamanRemoving and Installing Underground Storage TanksM Waqas Habib100% (1)
- Homework 5Dokumen3 halamanHomework 5Engr Ghulam MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- 432D SpecalogDokumen20 halaman432D Specalogbasurapana100% (2)
- Amines Plant PresentationDokumen22 halamanAmines Plant Presentationirsanti dewiBelum ada peringkat
- DARPA Insight Industry Day BriefingDokumen26 halamanDARPA Insight Industry Day BriefingGhislain SeburyamoBelum ada peringkat
- NDIR Type Infrared Gas Analyzer Type ZKJ-3Dokumen97 halamanNDIR Type Infrared Gas Analyzer Type ZKJ-3Yoga SanBelum ada peringkat
- Inspected by QCP Approval 1-APC 1 - APC 2 - DAR 2 - DAR Al-Handeseh 3 - Negemco 4 - Vendor 5 - Third PartyDokumen4 halamanInspected by QCP Approval 1-APC 1 - APC 2 - DAR 2 - DAR Al-Handeseh 3 - Negemco 4 - Vendor 5 - Third PartyAhmad DagamsehBelum ada peringkat
- Python TutorialDokumen12 halamanPython TutorialSazzad HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Palu Mallet KrisbowDokumen1 halamanPalu Mallet Krisbowhamidin_syarifBelum ada peringkat
- Multi-degree vibration analysisDokumen7 halamanMulti-degree vibration analysisJose Da SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Otating Ontrol Evices: T M S ADokumen11 halamanOtating Ontrol Evices: T M S ANeme VasquesBelum ada peringkat
- Age of Empires 2Dokumen1 halamanAge of Empires 2tulsiBelum ada peringkat