Trade Barrier: Trade Barriers Are Government-Induced Restrictions On
Diunggah oleh
Thanasekaran TharumanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Trade Barrier: Trade Barriers Are Government-Induced Restrictions On
Diunggah oleh
Thanasekaran TharumanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Trade barrier
Trade barriers are government-induced restrictions on [1] international trade. The barriers can take many forms, including the following:
Tariffs Non-tariff barriers to trade Import licenses Export licenses Import quotas Subsidies Voluntary Export Restraints Local content requirements Embargo Currency devaluation[2] Trade restriction
Most trade barriers work on the same principle: the imposition of some sort of cost on trade that raises the price of the traded products. If two or more nations repeatedly use trade barriers against each other, then a trade war results. Economists generally agree that trade barriers are detrimental and decrease overall economic efficiency, this can be explained by the theory of comparative advantage. In theory ,free trade involves the removal of all such barriers, except perhaps those considered necessary for health or national security. In practice, however,
even those countries promoting free trade heavily subsidize certain industries, such as agriculture and steel. Trade barriers are often criticized for the effect they have on the developing world. Because rich-country players call most of the shots and set trade policies, goods such as crops that developing countries are best at producing still face high barriers. Trade barriers such as taxes on food imports or subsidies for farmers in developed economies lead to overproduction and dumping on world markets, thus lowering prices and hurting poor-country farmers. Tariffs also tend to be anti-poor, with low rates for raw commodities and high rates for labor-intensive processed goods. The Commitment to Development Index measures the effect that rich country trade policies actually have on the developing world. Another negative aspect of trade barriers is that it would cause a limited choice of products and would therefore force customers to pay higher prices and accept inferior quality.[3]
Balance of payments
Balance of payments (BoP) accounts are an accounting record of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world.[1] These transactions include payments for the country's exports and imports of goods, services, financial capital,
and financial transfers. The BoP accounts summarize international transactions for a specific period, usually a year, and are prepared in a single currency, typically the domestic currency for the country concerned. Sources of funds for a nation, such as exports or the receipts of loans and investments, are recorded as positive or surplus items. Uses of funds, such as for imports or to invest in foreign countries, are recorded as negative or deficit items. When all components of the BOP accounts are included they must sum to zero with no overall surplus or deficit. For example, if a country is importing more than it exports, its trade balance will be in deficit, but the shortfall will have to be counterbalanced in other ways such as by funds earned from its foreign investments, by running down central bank reserves or by receiving loans from other countries.
While the overall BOP accounts will always balance when all types of payments are included, imbalances are possible on individual elements of the BOP, such as the current account, the capital account excluding the central bank's reserve account, or the sum of the two. Imbalances in the latter sum can result in surplus countries accumulating wealth, while deficit nations become increasingly indebted. The term "balance of payments" often refers to this sum: a country's balance of payments is said to be in surplus (equivalently, the balance of payments is positive) by a certain amount if sources of funds (such as export goods sold and bonds sold) exceed uses of funds (such as paying for imported goods and paying for foreign bonds purchased) by that amount. There is said to be a balance of payments deficit (the balance of payments is said to be negative) if the former are less than the latter. Under a fixed exchange rate system, the central bank
accommodates those flows by buying up any net inflow of funds into the country or by providing foreign currency funds to the foreign exchange market to match any international outflow of
funds, thus preventing the funds flows from affecting theexchange rate between the country's currency and other currencies. Then the net change per year in the central bank's foreign exchange reserves is sometimes called the balance of payments surplus or deficit. Alternatives to a fixed exchange rate system include a managed float where some changes of exchange rates are allowed, or at the other extreme a purely floating exchange rate (also known as a purely flexible exchange rate). With a pure float the central bank does not intervene at all to protect or devalue its currency, allowing the rate to be set by the market, and the central bank's foreign exchange reserves do not change. Historically there have been different approaches to the question of how or even whether to eliminate current account or trade imbalances. With record trade imbalances held up as one of the contributing factors to the financial crisis of 20072010, plans to address global imbalances have been high on the agenda of policy makers since 2009.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 4 The Interntional Flow of Funds and Exchange RatesDokumen14 halamanChapter 4 The Interntional Flow of Funds and Exchange RatesRAY NICOLE MALINGI100% (1)
- Balance of PaymentDokumen65 halamanBalance of PaymentJoshua GriffinBelum ada peringkat
- Balance of PaymentsDokumen14 halamanBalance of Paymentsনীল রহমানBelum ada peringkat
- Trade Barrier: Trade Barriers Are A General Term That Describes Any Government Policy or Regulation That RestrictsDokumen3 halamanTrade Barrier: Trade Barriers Are A General Term That Describes Any Government Policy or Regulation That RestrictsAlex LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Trade BarriersDokumen4 halamanTrade BarriersNikhl MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Trade BarriersDokumen16 halamanTrade BarriersErum MohtashimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Barriers To International TradeDokumen13 halamanChapter 6 Barriers To International TradeSayed Nayeem Azad Anik 203-11-6615Belum ada peringkat
- Trade in The Global Economy. Theories, Performance and Institutional StructuresDokumen64 halamanTrade in The Global Economy. Theories, Performance and Institutional StructuresJemaicaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Ricardian ModelDokumen9 halamanChapter 2 - Ricardian ModelFrancisca QueirozBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 International Trade TheoryDokumen40 halamanChapter 4 International Trade TheoryAtiqul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Trade BarriersDokumen3 halamanPresentation On Trade BarriersFahad SiddiqiBelum ada peringkat
- Mama's AssignmentDokumen34 halamanMama's AssignmentUche Aquilina OzegbeBelum ada peringkat
- International Economics: Modern Trade TheoriesDokumen30 halamanInternational Economics: Modern Trade Theoriessneha wazBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Trade BarriersDokumen7 halamanTypes of Trade BarriersSharma ShikhaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To International TradeDokumen56 halamanIntroduction To International TradeArldiIshmanRachmanBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Trade Liberalization On Economic Growth in TanzaniaDokumen19 halamanThe Impact of Trade Liberalization On Economic Growth in Tanzaniayaqoob008Belum ada peringkat
- Contemporary World 3Dokumen62 halamanContemporary World 3Adrian AndalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - Claasical& Non Classical TheoryDokumen35 halamanUnit 2 - Claasical& Non Classical TheoryGlendsss RjndlrBelum ada peringkat
- International TradeDokumen13 halamanInternational TradeFiona UsherBelum ada peringkat
- Post-Heckscher-Ohlin Theories of Trade and Intra - Industry TradeDokumen8 halamanPost-Heckscher-Ohlin Theories of Trade and Intra - Industry TradeTashinga wakatamaBelum ada peringkat
- International Marketing Planning and ControlDokumen8 halamanInternational Marketing Planning and ControlAkash BiradarBelum ada peringkat
- The Instruments of Trade PolicyDokumen43 halamanThe Instruments of Trade PolicyHarika HarikaBelum ada peringkat
- EconomicsDokumen31 halamanEconomicsLakshmi KruthigaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 IE NewDokumen49 halamanChapter 1 IE NewTrâm NgọcBelum ada peringkat
- International Trade and Its Importance Adam Smith and The Theory of AA Narrative ReporttolosaDokumen4 halamanInternational Trade and Its Importance Adam Smith and The Theory of AA Narrative ReporttolosaNicki Lyn Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Theory of Market-1Dokumen259 halamanTheory of Market-1Adel Taarabty100% (1)
- Week 01-The Fundamentals of EconomicsDokumen33 halamanWeek 01-The Fundamentals of EconomicsPutri WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- BOP SlideDokumen19 halamanBOP SlidePrajesh CalicutBelum ada peringkat
- Intra Industry Trade TheoryDokumen2 halamanIntra Industry Trade TheoryGalibur Rahman100% (1)
- Regional Economic Integration: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokumen34 halamanRegional Economic Integration: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinJulia NopsBelum ada peringkat
- INFLATIONDokumen17 halamanINFLATIONlillygujjarBelum ada peringkat
- Barriers To International TradeDokumen3 halamanBarriers To International TradeKanika KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring The EconomyDokumen34 halamanMeasuring The EconomyJoanaMarie CaisipBelum ada peringkat
- MarshallDokumen9 halamanMarshallSam CatlinBelum ada peringkat
- Course Overview and Introduction To International Financial ManagementDokumen41 halamanCourse Overview and Introduction To International Financial Managementbhargavi100% (1)
- Fiscal PolicyDokumen19 halamanFiscal PolicyShreya SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Classical Theories of International Trade-1Dokumen22 halamanClassical Theories of International Trade-1Mahender TewatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Terms of TradeDokumen25 halamanTerms of Tradetaufeeki1002Belum ada peringkat
- Theories of International Trade and Investment-Chapter 10 (Textbook - Chapter 5)Dokumen49 halamanTheories of International Trade and Investment-Chapter 10 (Textbook - Chapter 5)Dinesh DinnuBelum ada peringkat
- Ch02 World Trade An Overview 1Dokumen32 halamanCh02 World Trade An Overview 1XIKAMBelum ada peringkat
- TBS Midterm Exam MACRO 2016Dokumen6 halamanTBS Midterm Exam MACRO 2016OussemaBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Basis of International TradeDokumen6 halaman01 Basis of International TradeDev Prosad DBelum ada peringkat
- The Product Life Cycle TheoryDokumen6 halamanThe Product Life Cycle TheoryAyiik ToktookBelum ada peringkat
- Nilai Tukar Dan Neraca Pembayaran: Lecture: Al Muizzuddin F., Se., MeDokumen18 halamanNilai Tukar Dan Neraca Pembayaran: Lecture: Al Muizzuddin F., Se., MeReza AfrisalBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 3 - 4 - Determination of Economic ActivityDokumen61 halamanLecture - 3 - 4 - Determination of Economic ActivityAnil KingBelum ada peringkat
- ME Cycle 8 Session 7Dokumen96 halamanME Cycle 8 Session 7OttilieBelum ada peringkat
- International Production TheoryDokumen49 halamanInternational Production Theorykoodhorah0% (1)
- DPB 1023 Microeconomics: Lecturer: Suzana Binti IthnainDokumen23 halamanDPB 1023 Microeconomics: Lecturer: Suzana Binti Ithnainhxzyrxh hxzyqxh100% (1)
- Economics: Measuring The Cost of LivingDokumen21 halamanEconomics: Measuring The Cost of LivingHanBelum ada peringkat
- GATT To WTO PesentationDokumen13 halamanGATT To WTO PesentationsusanBelum ada peringkat
- Money & BankingDokumen46 halamanMoney & BankingAbdihakimBelum ada peringkat
- California Energy Commission - The Outlook For Global Trade in Liquefied Natural Gas Projections To The Year 2020Dokumen51 halamanCalifornia Energy Commission - The Outlook For Global Trade in Liquefied Natural Gas Projections To The Year 2020Maki IkedaBelum ada peringkat
- International Economics Exam-1Dokumen5 halamanInternational Economics Exam-1Barış AsaBelum ada peringkat
- Trade Policy in Developing CountriesDokumen14 halamanTrade Policy in Developing CountriesFarhan NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By: David D'Penha 33 Deepa Thakkar 34 Gayatri Das 48 Kunali Shah 69Dokumen21 halamanPresented By: David D'Penha 33 Deepa Thakkar 34 Gayatri Das 48 Kunali Shah 69David Jonathan D'PenhaBelum ada peringkat
- Import Substitution and Export PromotionDokumen6 halamanImport Substitution and Export Promotionprasanth704Belum ada peringkat
- Export Promotion: By: Rajeev Kumar Ap NitkDokumen24 halamanExport Promotion: By: Rajeev Kumar Ap NitkPriyanka AnejaBelum ada peringkat
- Origin and Development of World Trade Organisation (WTO) : By: Dr. Piyush ChaubeyDokumen8 halamanOrigin and Development of World Trade Organisation (WTO) : By: Dr. Piyush ChaubeyVirendraBelum ada peringkat
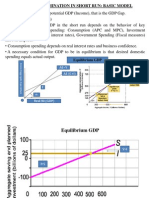
- Income Determination in Short Run: Basic Model: Ae Y AE (C+I) Ae YDokumen31 halamanIncome Determination in Short Run: Basic Model: Ae Y AE (C+I) Ae YAman Singh RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure CNDokumen2 halamanBrochure CNThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- University College of Engineering Tindivanam: Requirements Form Name of The Staff Designation: Department/HostelDokumen3 halamanUniversity College of Engineering Tindivanam: Requirements Form Name of The Staff Designation: Department/HostelThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: Finance SectionDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: Finance SectionThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Are Entrepreneurs Born or MadeDokumen5 halamanAre Entrepreneurs Born or MadeThanasekaran Tharuman100% (1)
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Finance Section: Sl. No. Particulars Bill No/Date Cheque Drawn in Favour of Amount RsDokumen1 halamanFinance Section: Sl. No. Particulars Bill No/Date Cheque Drawn in Favour of Amount RsThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamDokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: University College of Engineering, TindivanamThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University:: Chennai: (Establishment)Dokumen1 halamanAnna University:: Chennai: (Establishment)Thanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- University College of Engineering, Tindivanam (A Constituent College of Anna University Chennai) Melpakkam - 604 001Dokumen1 halamanUniversity College of Engineering, Tindivanam (A Constituent College of Anna University Chennai) Melpakkam - 604 001Thanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Ethics and Human Values (1) .PPT 1Dokumen25 halamanProfessional Ethics and Human Values (1) .PPT 1Thanasekaran Tharuman50% (2)
- EMS/ISO 14000 Need of The Hour: National Environmental Engineering Research InstituteDokumen38 halamanEMS/ISO 14000 Need of The Hour: National Environmental Engineering Research InstituteThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Total Quality Management TQMDokumen25 halamanTotal Quality Management TQMThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Indian Money Market - and Capital MarketDokumen3 halamanStructure of Indian Money Market - and Capital MarketThanasekaran Tharuman100% (1)
- 2 Marks ItfDokumen12 halaman2 Marks Itfradhasat3568Belum ada peringkat
- Working Capital Management Unit - IVDokumen54 halamanWorking Capital Management Unit - IVThanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- RM 1Dokumen260 halamanRM 1Thanasekaran TharumanBelum ada peringkat
- Notes To The Financial StatementsDokumen4 halamanNotes To The Financial StatementsROB101512Belum ada peringkat
- Business Cycles in Romania PAperDokumen10 halamanBusiness Cycles in Romania PAperElena PotoroacăBelum ada peringkat
- Novartis Case QuestionsDokumen3 halamanNovartis Case QuestionshinderBelum ada peringkat
- Nov 11 Oil and Gas Production NoteDokumen2 halamanNov 11 Oil and Gas Production NoteguardajoiasBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate Finance Case StudyDokumen26 halamanCorporate Finance Case StudyJimy ArangoBelum ada peringkat
- Class - Xii - Entrepreneurship - Sample Paper - Solved No.2 - 2018-19Dokumen9 halamanClass - Xii - Entrepreneurship - Sample Paper - Solved No.2 - 2018-19Rishav BhattBelum ada peringkat
- 211 - F - Bevcon Wayors-A Study On Financial Cost Efficiency at Bevcon WayorsDokumen70 halaman211 - F - Bevcon Wayors-A Study On Financial Cost Efficiency at Bevcon WayorsPeacock Live ProjectsBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Literacy and Financial Risk Tolerance of Individual Investors: Multinomial Logistic Regression ApproachDokumen11 halamanFinancial Literacy and Financial Risk Tolerance of Individual Investors: Multinomial Logistic Regression ApproachlaluaBelum ada peringkat
- 12 - Duty To Account For Secret Profits - JuliaDokumen6 halaman12 - Duty To Account For Secret Profits - JuliaJulia IliagouevaBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Relationship Marketing: Building Customer Relationships For Enduring Profits in A Wired EconomyDokumen36 halamanCustomer Relationship Marketing: Building Customer Relationships For Enduring Profits in A Wired Economylidia_pozoBelum ada peringkat
- Ee Announcement Presentation FinalDokumen31 halamanEe Announcement Presentation Finalkoundi_3Belum ada peringkat
- Types of Corporate RestructuringDokumen46 halamanTypes of Corporate RestructuringJebin James100% (1)
- Measures To Improve Life Insurance ProfitabilityDokumen9 halamanMeasures To Improve Life Insurance ProfitabilityTirth ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Panama Petrochem LTDDokumen7 halamanPanama Petrochem LTDflying400Belum ada peringkat
- Chap 009Dokumen51 halamanChap 009kmillatBelum ada peringkat
- Term Paper On APEX FOODS LTD. Samina Sultana-8451Dokumen45 halamanTerm Paper On APEX FOODS LTD. Samina Sultana-8451pranta senBelum ada peringkat
- SaatchiDokumen11 halamanSaatchiBólájí AkínyemíBelum ada peringkat
- HBR Customer Centered OrganizationDokumen46 halamanHBR Customer Centered Organizationtarunchat100% (2)
- Cash and Receivables: ObjectivesDokumen25 halamanCash and Receivables: ObjectivesAlex OuedraogoBelum ada peringkat
- Us Digital Gambling Halftime Report August 2023Dokumen34 halamanUs Digital Gambling Halftime Report August 2023Antonius VincentBelum ada peringkat
- BizplanbDokumen390 halamanBizplanbMuhands JoBelum ada peringkat
- Đề thi thử THPT Quốc gia năm 2020 môn Anh trường THPT Ngô Quyền, Thành Phố Hải Phòng lần 1 mã đề 242Dokumen5 halamanĐề thi thử THPT Quốc gia năm 2020 môn Anh trường THPT Ngô Quyền, Thành Phố Hải Phòng lần 1 mã đề 242Nguyễn TrinhBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 2 AnswerDokumen7 halamanQuiz 2 AnswerSri SarveentaranBelum ada peringkat
- Sikkim Co Operative Societies Act 1978Dokumen67 halamanSikkim Co Operative Societies Act 1978Latest Laws TeamBelum ada peringkat
- Crisil 5000921214Dokumen189 halamanCrisil 5000921214eepBelum ada peringkat
- State Bank of India Internship ProjectDokumen61 halamanState Bank of India Internship ProjectPrince BhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- EouDokumen12 halamanEouRuby SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 Discounted DividendDokumen5 halamanChapter 10 Discounted Dividendmahnoor javaidBelum ada peringkat
- Trade Directory 2012 KleinDokumen364 halamanTrade Directory 2012 Kleinqqlang100% (4)
- Lecture 12. Consignment AccountingDokumen1 halamanLecture 12. Consignment AccountingPalash KunduBelum ada peringkat
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingDari EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (98)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationDari EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (11)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassDari EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassBelum ada peringkat
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityDari EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailDari EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (237)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsDari EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (94)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesDari EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereDari EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always TherePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaDari EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaBelum ada peringkat
- Why the Rich Are Getting RicherDari EverandWhy the Rich Are Getting RicherPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (405)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationDari EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (46)
- Economics 101: How the World WorksDari EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (34)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDari EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (229)
- Vienna: How the City of Ideas Created the Modern WorldDari EverandVienna: How the City of Ideas Created the Modern WorldBelum ada peringkat
- Economics in America: An Immigrant Economist Explores the Land of InequalityDari EverandEconomics in America: An Immigrant Economist Explores the Land of InequalityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistDari EverandDoughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st-Century EconomistPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (37)
- Technofeudalism: What Killed CapitalismDari EverandTechnofeudalism: What Killed CapitalismPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateDari EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimatePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (349)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomDari EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomBelum ada peringkat
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenDari EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNDari Everand2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetDari EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetBelum ada peringkat
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyDari EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)