Type of Seizure
Diunggah oleh
Geevine CansinoHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Type of Seizure
Diunggah oleh
Geevine CansinoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CANSINO, Gianelei Vianne F.
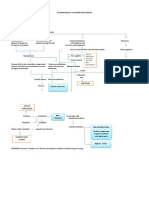
BSN III-L3 Type of Seizure Specific Type Description People may experience unusual sensations such as uncontrollable jerky motions of a body part, sight or hearing impairment, sudden sweating or flushing, nausea, and feelings of fear. Only a finger or hand may shake, or mouth may jerk uncontrollably A person may talk unintelligibly, may be dizzy May experience unusual or unpleasant sights, sounds, odors, or tastes Without loss of consciousness A.K.A. Temporal lobe epilepsy or Psychomotor seizure Lasts for only one or two minutes Person either remains motionless or moves automatically but inappropriately for time and place May experience emotions of fear, anger, elation, or irritability The person does not remember the episode when it is over. May be preceded by an aura (a warning sensation characterized by feelings of fear, abdominal discomfort, dizziness, or strange odors and sensations Usually less than 20 seconds. Muscle tone is greatly increased and the body, arms, or legs make sudden stiffening movements. Consciousness is usually preserved. Most often occur during sleep and usually involve all or most of the brain, affecting both sides of the body. If the person is standing when the seizure starts, he or she often will fall. Person feels tired after seizure. Consist of rhythmic jerking movements of the arms and legs, sometimes on both sides of the body. Not followed by a period of tiredness or confusion Nursing Management Keep the bed in a low position with side rails up, and use padded side rails as needed. Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements Safety measures should be taken if there is an indication that the person is experiencing an aura before the onset of a seizure. Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements Stay with the client Protect patient from injury Promote patent airway. Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements Stay with the client Let patient lie down on floor Do not restrain movement
1. Partial Seizures
a. Simple Partial Seizures
b. Complex Partial Seizures
2. Generalized Seizures
a. Tonic Seizures
b. Clonic Sezures
CANSINO, Gianelei Vianne F. BSN III-L3 Protect patient from injury Promote patent airway. Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements Protect patient from injury Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements Stay with the client Let patient lie down on floor Do not restrain movement Protect patient from injury Promote patent airway Loosen clothing Do not try to force inserting a tongue blade Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Presence of aura (if known) e. Movements
c. Atonic Seizures
Usually lasts less than 15 seconds Muscles suddenly lose strength The eyelids may drop, the head may nod, and the person may drop things and often falls to the ground. A.K.A. "drop attacks" or "drop seizures." The person usually remains conscious.
d. Tonic-Clonic Seizures
a.k.a. Grand mal seizure Generally lasts 1 to 3 minutes The tonic phase comes first: - All the muscles stiffen. - Air being forced past the vocal cords causes a cry or groan. - The person loses consciousness and falls to the floor. - The tongue or cheek may be bitten, so bloody saliva may come from the mouth. - The person may turn a bit blue in the face. Clonic phase: - The arms and usually the legs begin to jerk rapidly and rhythmically, bending and relaxing at the elbows, hips, and knees. - After a few minutes, the jerking slows and stops. - Bladder or bowel control sometimes is lost as the body relaxes.
CANSINO, Gianelei Vianne F. BSN III-L3 Consciousness returns slowly, and the person may be drowsy, confused, agitated, or depressed. A.K.A. Myoclonic or Petit mal seizure Characterized by a sudden, momentary loss or impairment of consciousness. Overt symptoms are often as slight as an upward staring of the eyes, a staggering gait, or a twitching of the facial muscles. No aura occurs Person often resumes activity without realizing that the seizure has occurred. -
e. Absence Seizures
Protect patient from injury Observe and document the following: a. Date, time of onset, duration b. Activity at time of onset c. Level of consciousness (confused, dazed, excited, unconscious) d. Movements
References: Smeltzer, S.(2010). Brunner and Suddarths Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing. Volume 2. http://ddsn.sc.gov/providers/manualsandguidelines/Documents/HealthCareGuidelines/NursingMgmtSeizures.pdf http://www.epilepsy.com/epilepsy/types_seizures http://www.webmd.com/epilepsy/guide/types-of-seizures-their-symptoms Microsoft Encarta 2009. 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- VT Quick Facts For NCLEX Pediatrics PDFDokumen23 halamanVT Quick Facts For NCLEX Pediatrics PDFMerlande Remy90% (10)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Kava Kava The Anti-Anxiety HerbDokumen85 halamanKava Kava The Anti-Anxiety HerbPetar Matić100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaGeevine Cansino91% (11)
- Instruments of Pharmacology LabDokumen3 halamanInstruments of Pharmacology LabOm Prakash Mishra67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure in 58 Year OldDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Heart Failure in 58 Year OldGeevine Cansino100% (2)
- Atlas of EEG, Seizure Semiology, and Management 2nd EdDokumen384 halamanAtlas of EEG, Seizure Semiology, and Management 2nd Edsolecitodelmar100% (9)
- Antiepileptic Drugs-A Clinician - S Manual, 2e (Jan 15, 2016) - (0190214961) - (Oxford University Press) PDFDokumen299 halamanAntiepileptic Drugs-A Clinician - S Manual, 2e (Jan 15, 2016) - (0190214961) - (Oxford University Press) PDFMaria Camelia SanduBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Test 1 Part A Time Limit and InstructionsDokumen9 halamanReading Test 1 Part A Time Limit and Instructionsmathews v.vBelum ada peringkat
- Labor and DeliveryDokumen218 halamanLabor and DeliveryAlmera Tan Nolasco-Quetulio100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewerDokumen8 halamanPsychiatric Nursing ReviewerDarren Mae MosadaBelum ada peringkat
- NeuroSensory ExamsDokumen26 halamanNeuroSensory Examsquidditch07100% (1)
- Journal On PainDokumen5 halamanJournal On PainGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Attack and StrokeDokumen6 halamanHeart Attack and StrokeGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- EDSA 1 After 28 Years: Assessing Philippine DemocracyDokumen3 halamanEDSA 1 After 28 Years: Assessing Philippine Democracymafuyuc100% (1)
- HeartAttackActionPlan EnglishDokumen1 halamanHeartAttackActionPlan EnglishAlan LiuBelum ada peringkat
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDokumen1 halamanNewton's Second Law of MotionGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Heart AttackDokumen2 halamanHeart AttackGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- R.A. 916Dokumen5 halamanR.A. 916Jerico Custodio100% (1)
- Directions: Check Observations in Appropriate Column and Make Necessary JustificationsDokumen2 halamanDirections: Check Observations in Appropriate Column and Make Necessary JustificationsGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Retirement in AgingDokumen7 halamanRetirement in AgingGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Journal On Sense of CoherenceDokumen13 halamanJournal On Sense of CoherenceGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Disease and Stroke StatisticsDokumen20 halamanHeart Disease and Stroke StatisticsGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen8 halamanPDFGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug StudyGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Utility of Leopold Maneuvers in Screening For. - .Dokumen3 halamanUtility of Leopold Maneuvers in Screening For. - .Geevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Depression ScaleDokumen3 halamanGeriatric Depression ScaleGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Dirty DozenDokumen23 halamanDirty DozenGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanDrug StudyGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Leopold's Maneuver JournalDokumen5 halamanLeopold's Maneuver JournalGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Journal (Pallia)Dokumen10 halamanJournal (Pallia)Geevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Abdominal TraumaDokumen77 halamanAbdominal TraumaFairuz Az ZabiedahBelum ada peringkat
- Prepared By: ALIP, Jorven CANSINO, Gianelei Vianne DIN, Myla Angela LORENZO, Joei IsabelDokumen11 halamanPrepared By: ALIP, Jorven CANSINO, Gianelei Vianne DIN, Myla Angela LORENZO, Joei IsabelGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- APA Citation StyleDokumen13 halamanAPA Citation StyleCamille FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Dash Diet For HypertensivesDokumen5 halamanDash Diet For HypertensivesGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Journal On BreastfeedingDokumen7 halamanJournal On BreastfeedingGeevine CansinoBelum ada peringkat
- Generalized SeizuresDokumen12 halamanGeneralized SeizuresyangmayangggBelum ada peringkat
- Crisis Convulsivas Focales PDFDokumen88 halamanCrisis Convulsivas Focales PDFAndrés MontalvoBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy Treatment Goals and TypesDokumen23 halamanEpilepsy Treatment Goals and TypesindyBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Guide To Treatment of Childhood Absence EpilepsyDokumen10 halamanA Practical Guide To Treatment of Childhood Absence EpilepsyLorenz BelloBelum ada peringkat
- Behaviour And/or Feelings.: Published March 2022Dokumen1 halamanBehaviour And/or Feelings.: Published March 2022Var InderBelum ada peringkat
- Neurosensory Disorders 22306Dokumen14 halamanNeurosensory Disorders 22306bekbekk cabahugBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Seizures and Epilepsy: Lucyna Zawadzki, MD Director of Pediatric Epilepsy Program UWHC MadisonDokumen42 halamanOverview of Seizures and Epilepsy: Lucyna Zawadzki, MD Director of Pediatric Epilepsy Program UWHC MadisonImraan MohaBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy Treatment and ClassificationDokumen20 halamanEpilepsy Treatment and ClassificationViktor Charles KDBelum ada peringkat
- Anticonvulsant DrugDokumen3 halamanAnticonvulsant DrugPerlieCagueteBelum ada peringkat
- R V VictorDokumen4 halamanR V VictorWandi NBelum ada peringkat
- Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures CaseDokumen7 halamanGeneralized Tonic-Clonic Seizures CaseMA 09Belum ada peringkat
- Tonic-Clonic Seizure?: SymptomsDokumen3 halamanTonic-Clonic Seizure?: SymptomsMaria Jessica DumdumBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy Support Questionnaire: ConfidentialDokumen6 halamanEpilepsy Support Questionnaire: Confidentialbilal hadiBelum ada peringkat
- Seizure: Focal/partial SeizuresDokumen7 halamanSeizure: Focal/partial SeizuresMauren DazaBelum ada peringkat
- Hep ADokumen13 halamanHep ARakesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Issue 1 BAB 2 LaporanDokumen32 halamanLearning Issue 1 BAB 2 LaporanHelmiBelum ada peringkat
- Crash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised PatientDokumen30 halamanCrash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised Patientmazen bokhari100% (1)
- 4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVDokumen391 halaman4 - Perception & Coordination Alterations RVgeng gengBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Epileptic Patients in Orthodontic CareDokumen7 halamanManaging Epileptic Patients in Orthodontic CareVineeth VTBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Epilepsy Detection Using Fractal Dimensions Segmentation and GP SVM ClassificationDokumen12 halamanAutomatic Epilepsy Detection Using Fractal Dimensions Segmentation and GP SVM ClassificationJulie Escora MontañoBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical and Hospital Pharmacy Questionnaire BLUE PACOPDokumen39 halamanClinical and Hospital Pharmacy Questionnaire BLUE PACOPSophia AndresBelum ada peringkat
- EPILEPSYDokumen5 halamanEPILEPSYIffa NooramBelum ada peringkat